💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
文献来源:

㼿鲸鱼优化算法(whale optimization algorithm, WOA)是一种受自然启发的元启发式优化算法,由Mirjalili和Lewis于2016年提出。㼿这个算法已经显示出它解决许多问题的能力。对其他一些受自然启发的算法,如ABC和PSO进行了全面的调查。但是,没有对WOA进行调查搜索工作。㼿因此,本文对WOA进行了系统的meta分析调查,以帮助研究者将其应用于不同领域或与其他常用算法进行混合。本文从WOA的算法背景、特点、局限性、改进、杂交和应用等方面对WOA进行了深入介绍。接下来,提出WOA性能来解决不同的问题。㼿en,建立了WOA修饰和杂交的统计结果,并与最常用的优化算法和WOA进行了比较。㼿e调查结果表明,WOA在收敛速度和勘探与开采之间的平衡方面优于其他常用算法。与WOA相比,WOA修饰和杂化也表现良好。此外,我们的研究为提出一种混合WOA和BAT算法的新技术铺平了道路。㼿e BAT算法用于探索阶段,而WOA算法用于开发阶段。最后,从WOA- bata获得的统计结果在16个基准函数中非常具有竞争力,并且优于WOA。WOA-BAT在CEC2005的13个功能和CEC2019的7个功能上也表现出色。
原文摘要:
+e whale optimization algorithm (WOA) is a nature-inspired metaheuristic optimization algorithm, which was proposed by Mirjalili and Lewis in 2016. +is algorithm has shown its ability to solve many problems. Comprehensive surveys have been conducted about some other nature-inspired algorithms, such as ABC and PSO. Nonetheless, no survey search work has been
conducted on WOA. +erefore, in this paper, a systematic and meta-analysis survey of WOA is conducted to help researchers to use it in difffferent areas or hybridize it with other common algorithms. +us, WOA is presented in depth in terms of algorithmic backgrounds, its characteristics, limitations, modififications, hybridizations, and applications. Next, WOA performances are presented to solve difffferent problems. +en, the statistical results of WOA modififications and hybridizations are established and compared with the most common optimization algorithms and WOA. +e survey’s results indicate that WOA performs better than other common algorithms in terms of convergence speed and balancing between exploration and exploitation. WOA modififications and hybridizations also perform well compared to WOA. In addition, our investigation paves a way to present a new technique by hybridizing both WOA and BAT algorithms. +e BAT algorithm is used for the exploration phase, whereas the WOA algorithm is used for the exploitation phase. Finally, statistical results obtained from WOA-BAT are very competitive and better than WOA in 16 benchmarks functions. WOA-BAT also outperforms well in 13 functions from CEC2005 and 7 functions from CEC2019.
📚2 运行结果
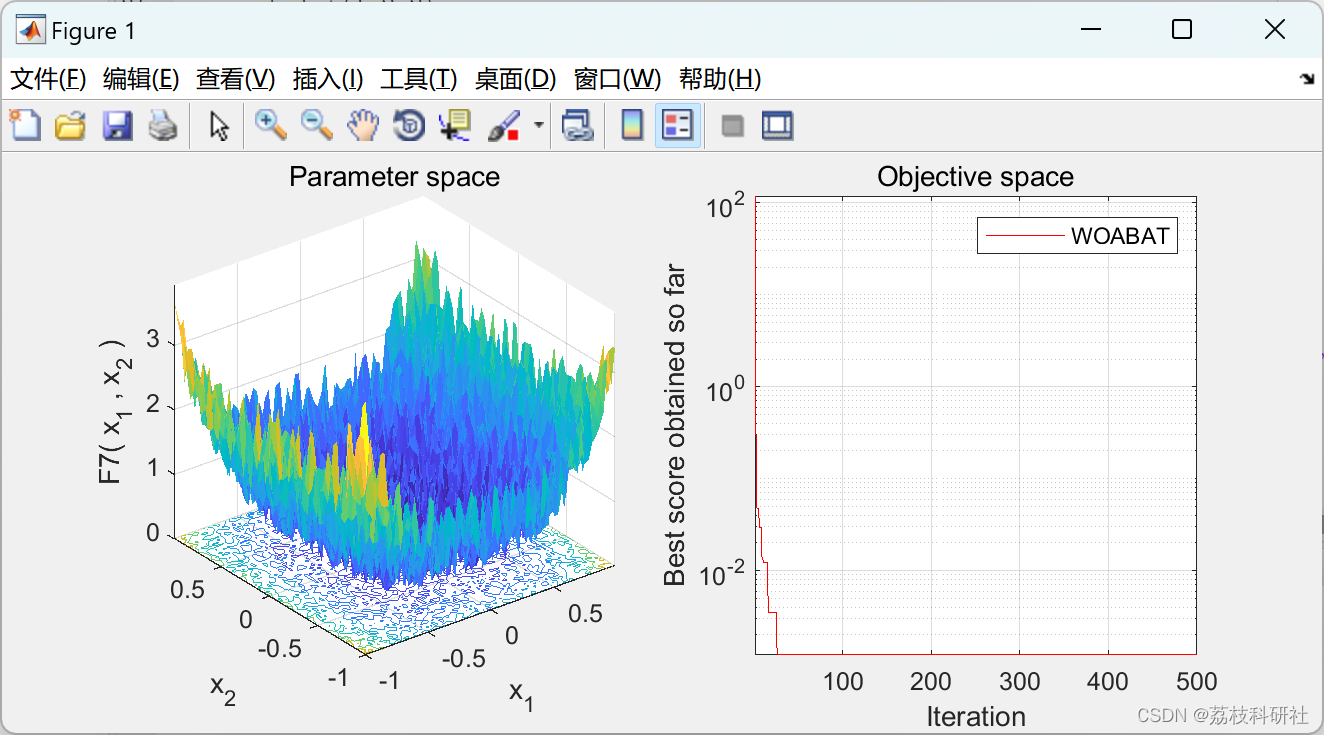
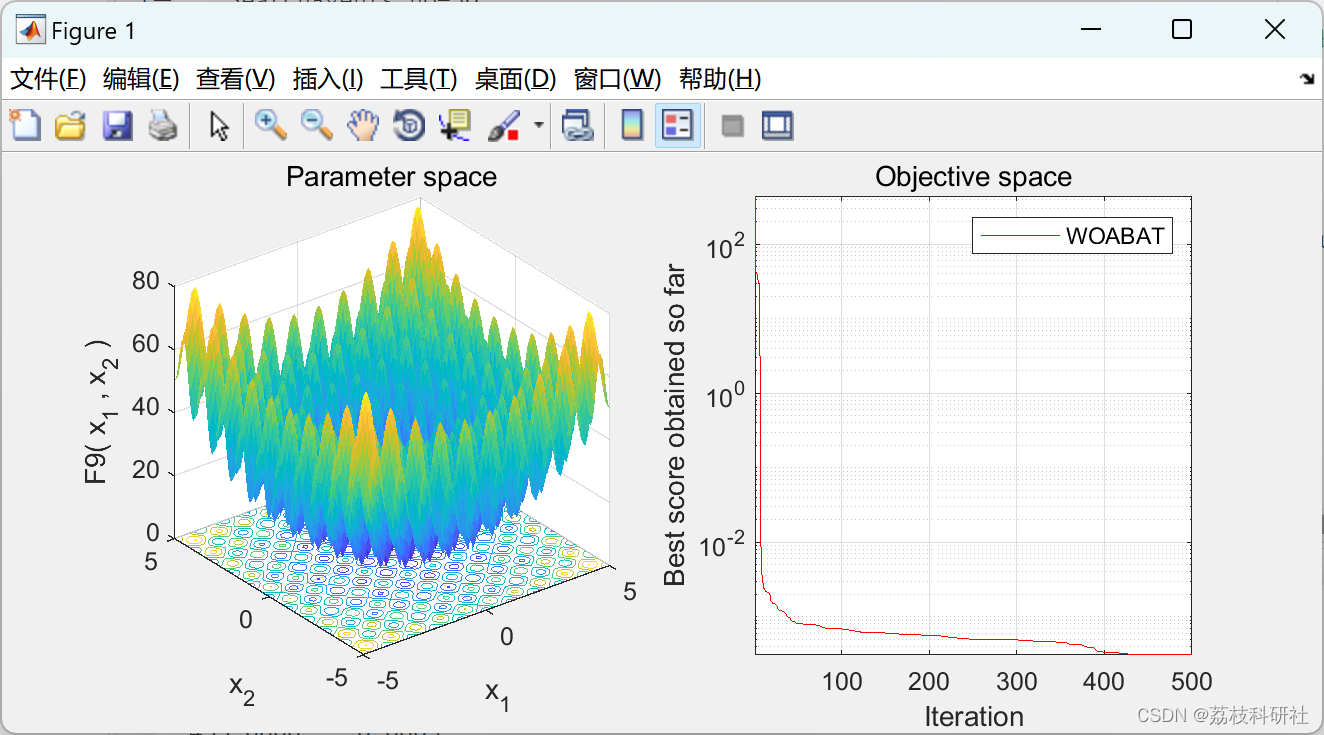 部分代码:
部分代码:
% WOABAT
function [Leader_score,Leader_pos,Convergence_curve]=WOABAT(SearchAgents_no,Max_iter,lb,ub,dim,fobj)
% initialize position vector and score for the leader
Leader_pos=zeros(1,dim);
Leader_score=inf; %change this to -inf for maximization problems
%Initialize the positions of search agents
Positions=initialization(SearchAgents_no,dim,ub,lb);
Convergence_curve=zeros(1,Max_iter);
%bat algorithm addition
Qmin=0; % Frequency minimum
Qmax=2; % Frequency maximum
Q=zeros(SearchAgents_no,1); % Frequency
v=zeros(SearchAgents_no,dim); % Velocities
r=0.5;
A1=0.5;
t=0;% Loop counter
% summ=0;
% Main loop
while t<Max_iter
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
% Return back the search agents that go beyond the boundaries of the search space
Flag4ub=Positions(i,:)>ub;
Flag4lb=Positions(i,:)<lb;
Positions(i,:)=(Positions(i,:).*(~(Flag4ub+Flag4lb)))+ub.*Flag4ub+lb.*Flag4lb;
% Calculate objective function for each search agent
fitness=fobj(Positions(i,:));
% Update the leader
if fitness<Leader_score % Change this to > for maximization problem
Leader_score=fitness; % Update alpha
Leader_pos=Positions(i,:);
end
end
a=2-t*((2)/Max_iter); % a decreases linearly fron 2 to 0 in Eq. (2.3)
% a2 linearly dicreases from -1 to -2 to calculate t in Eq. (3.12)
a2=-1+t*((-1)/Max_iter);
% Update the Position of search agents
for i=1:size(Positions,1)
r1=rand(); % r1 is a random number in [0,1]
r2=rand(); % r2 is a random number in [0,1]
A=2*a*r1-a; % Eq. (2.3) in the paper
C=2*r2; % Eq. (2.4) in the paper
b=1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
l=(a2-1)*rand+1; % parameters in Eq. (2.5)
p = rand(); % p in Eq. (2.6)
for j=1:size(Positions,2)
if p<0.5
if abs(A)>=1
rand_leader_index = floor(SearchAgents_no*rand()+1);
X_rand = Positions(rand_leader_index, :);
Q(i)=Qmin+(Qmin-Qmax)*rand;
v(i,:)=v(i,j)+(X_rand(j)-Leader_pos(j))*Q(i);
z(i,:)= Positions(i,:)+ v(i,:);
%%%% problem
if rand>r
% The factor 0.001 limits the step sizes of random walks
z (i,:)=Leader_pos(j)+0.001*randn(1,dim);
end
% Evaluate new solutions
Fnew=fobj(z(i,:));
% Update if the solution improves, or not too loud
if (Fnew<=fitness) && (rand<A1)
Positions(i,:)=z(i,:);
fitness=Fnew;
end
elseif abs(A)<1
Q(i)=Qmin+(Qmin-Qmax)*rand;
v(i,:)=v(i,j)+(Positions(i,:)-Leader_pos(j))*Q(i);
z(i,:)= Positions(i,:)+ v(i,:);
%%%% problem
if rand>r
% The factor 0.001 limits the step sizes of random walks
z (i,:)=Leader_pos(j)+0.001*randn(1,dim);
end
% Evaluate new solutions
Fnew=fobj(z(i,:));
% Update if the solution improves, or not too loud
if (Fnew<=fitness) && (rand<A1)
Positions(i,:)=z(i,:);
fitness=Fnew;
end
end
elseif p>=0.5
distance2Leader=abs(Leader_pos(j)-Positions(i,j));
% Eq. (2.5)
Positions(i,j)=distance2Leader*exp(b.*l).*cos(l.*2*pi)+Leader_pos(j);
end
end
end
t=t+1;
Convergence_curve(t)=Leader_score;
[t Leader_score]
end
🎉3 参考文献
部分理论来源于网络,如有侵权请联系删除。























 751
751











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








