本节主要聚焦liability-based mandate
immunization and indexation 都可以看成是 passive strategy
immunization, may be viewed simply as a special case of interest rate hedging
Immunization is the process of structuring and managing a fixed-income bond portfolio to minimize the variance in the realized rate of return over a known time horizon
This variance arises from the volatility of future interest rates
这里的realized rate of return应该理解为capital g/l + reinvestment return
the goal of the immunization strategy is to achieve a rate of return close to IRR(or cash flow yield), not market value-weighted average of the individual bond YTM(对于single bond是IRR,而bond portfolio则是holding period rate of return (ROR))
immunization strategy是要复刻一个或一组zero-coupond bond(本来是要在假设无违约风险的前提下通过这些零息债券来hedge future liability的)
structural risk就是设计的债券组合的cash flow yield与目标复刻的零息债券的YTM不一致 (Structural risk arises from the potential for shifts and twists to the yield curve)
降低structural risk的方法之一是将barbell portfolio转为bullet portfolio(指集中在目标债券组合的duration)
The portfolio dispersion and convexity statistics are used to assess the structural risk to the interest rate immunization strategy
An advantage to using convexity(而不是dispersion)to measure the extent of structural risk is that the portfolio statistic can be approximated by the market value-weighted average of the individual bonds’ convexities
When the yield curve is upwardly sloped, (market value weighted) average duration is less than the portfolio duration
using the average duration in building the immunizing portfolio instead of the portfolio duration would introduce model risk to the strategy
对一些经常提及的概念进行展开:
Dispersion 和 convexity 每期的计算(借用书中表格):

11.2324 = (5-12.0008)^2 * 0.2292
81.0931 = 14*(14+1)*0.3862
(rounding导致的尾差不一致)
因为是semi-annual period,所以annualized dispersion:8.2594 = 33.0378/ (2^2);
convexity in semi-annual periods:182.1437 = 189.0580 / (1+cash flow yield)^2;
annualized convexity:45.5359 = 182.1437 / (2^2),cash flow yield given as 1.8804%
portfolio convexity statistic 是指在immunizated portfolio中这几者之间的关系:


假设原来的yield curve是虚线(一般yield curve不是flat的,而是紫线的形状),
移到虚线上方的都是upward,移到虚线下方则是downward
而越走越下的就是flatten,反之越走越高的就是steepen
黑线:upward steepen,橙线:upward flatten;
紫线:downward steepen,蓝线:downward flatten
利率曲线或yield curve 上升对债券而言不是好事:upward and steepening shift (sometimes called a “bear steepener”)
1. 有了前期的知识准备,现在可以开始构建immunized portfolio,先从manage single liability开始:
macaulay duration of portfolio ≈ liability due date(即the horizon for the liability)
minimizes the portfolio convexity
但 This portfolio must be regularly rebalanced over the horizon to maintain the target duration
常见的组合有:laddered、bullet、barbell,如一开始所说,immunization本质是hedge interest rate risk,对于small parallel shift,三者可以表现比较一致(只要duration接近即可),但他们的convexity不一样,即当non-paralled shift或twist出现时,表现明显不同
An obvious advantage to the laddered portfolio is protection from shifts and twists—the cash flows are essentially “diversified” across the time spectrum
这句话应该这么理解:只有在不知将会怎么non-paralleled shift or twist时才是laddered较好,知道的话应该针对yield curve的变化构建组合
整体思路:找不到期限匹配的default-free bond做cash flow matching或由于成本等原因无法实现,转而做duration matching
使用duration matching strategy并不是一劳永逸,当yield curve shift and twist导致money duration mismatch时,the asset manager needs to rebalance the portfolio immediately(minimize portfolio convexity只能减少这个影响,必要时还是要rebalance)
实际上,the manager likely waits until the mismatch is large enough to justify the transaction costs in selling some bonds and buying others
Another method to rebalance the portfolio is to use interest rate derivatives
在duration matching strategy制定后出现yield curve shift or twist导致duration gap;A derivatives overlay strategy is then used to close the duration gap while keeping the underlying portfolio unchanged(derivative overlay当然也可以用来做active management,只是一种工具)
cash matching和duration mtching都是passive strategy,而derivative overlay是一种帮助动态调回至duration matching的方法
contingent immunization则是一种passive-active混合的方法,将超出threshold的surplus部分用active strategy
在本节主基调是liability-driven(即passive strategy)的前提下,contingent immunization主要想lower duration matching的cost
相当于整个liability-based mandate下的4种策略是如何联系的已经梳理了一次
2. manage multi-period liabilities
对于有多期liability需要应对的情况(如每年要有一定的生活花销),这种情况做cash flow matching就会用到laddered(barbell和bullet显然不合适),一般有两种构建laddered的方法:
直接买不同到期日的债券
买债券ETF
same duration (and cash flow yield)的前提下, the barbell clearly has the highest convexity and the bullet the lowest,这句话与刚刚建议采用laddered好像是冲突的,刚觉应该用barbell才对,我的理解如下:
laddered虽然不是曲度最大,但仍是have relatively high convexity
虽然在convexity上与barbell比不占优,但 Compared with the barbell, the laddered portfolio has much less cash flow reinvestment risk
实际中,laddered更适用于做 liquidity management
laddered的好处:balanced position between the two sources of interest rate risk — cash flow reinvestment and market price volatility
那么对于多期的情况,具体条件应该如何考虑:
(本质上single-period 下前两个条件的结合)
the dispersion of cash flows and the convexity of assets are greater than those of the liabilities
尝试厘清single与multi-period的差异:
BPV只是计出近似的For each 1 bp change in the cash flow yield, the market value changes,因为convexity is not included
两种常见的多期债务:accumulated benefit obligation (ABO) & projected benefit obligation (PBO)
ABO is the legal obligation to the plan sponsor, the PBO is the liability reported in financial statements and used to assess the plan’s funding status
discount rate r:high-quality corporate bonds (government regulators and the accounting authorities allow high-quality corporate bonds to be used to discount the future liabilities)
ABO与PBO的公式就是差了(1+w)^T
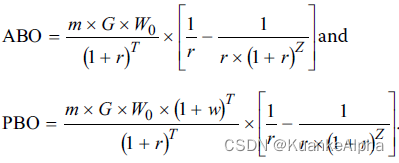
ABO represents the legal liability today of the plan sponsor if the plan were to be closed or converted to another type of plan, such as a defined contribution (DC) plan,所以:
The plan sponsor must decide which liability measure to use for risk management and asset allocation
if the corporation anticipates that it might be a target for an acquisition and that the acquirer likely would want to convert the retirement plan from defined benefit to defined contribution, the ABO measure matters more than the PBO
之前一直在讲用债券组合来hedge liability duration,而其实是可以是资产组合的:
如一个50%equity、40%fixed-income、10%alternative的组合
asset BPV = 0.5*BPV(E) + 0.4*BPV(D) + 0.1*BPV(A)
只是在学习时为了方便,直接假设 equity 和 alternative 的BPV都是0,但 Assuming zero duration does not imply that no interest rate risk
除了债券,第二种可以使用的工具是 SWAP
Swaps are typically quoted as a fixed rate against the MRR flat, meaning no spread
即 swap of 4.00% against the MRR flat is the same as a swap of 4.25% against MRR + 0.25%
一般swap的fix rate是大于floating rate的,少了不确定性那肯定要付出代价
一般而言,swap payer是have negative duration;swap receiver则是positive duration
一般 use a partial hedge rather than attempt to reduce the duration gap to zero
SWAP与future的对比:
一般不用futures来管理duration,因为 futures contracts are marked to market and settled at the end of each trading day into the margin account,那就会导致 significant daily cash inflows and outflows
用swap则有可能在签好一个swap后,swap rate的市价(指swap rate)上升了,即 If swap rates rise, the value of the receive-fixed swap becomes negative and stakeholders will need an explanation of those losses
第三种工具:option-based derivatives overlay strategy,其实就是swaption
当swap有价值时,可以行权“take delivery” of the swap,即 使swap生效;
或close out the swap to capture the gain 来 offset the loss incurred on the higher value for the pension plan liabilities
另一种 derivatives overlay:swaption collar
buys the receiver swaption, but instead of paying the premium in cash, writes a payer swaption(是write payer swap不是enter payer swap),还是为了构建零成本collar
与swaption对应,一般,对于swaption而言,市场的swap rate 升到高于有权enter的receiver swap的swap rate;或 对于swaption collar而言,市场的swap rate升到高于write的payer swap的swap rate时:会选择亏本close out(因为 potential losses on the receive-fixed swap and swaption collar are time-deferred and rate-contingent and therefore are uncertain)
有一个悖论:投资者需要hedge interest rate risk,但用derivative overlay strategy却需要对interest rate的未来走势有自己的观点才能选择具体使用的工具
但无论如何,一般这节所讲的投资者是在关注hedge liability duration gap,所以主要是怕利率下降导致liability的增多无法被覆盖
一些相关的零散小知识:
一般,yields on high-quality corporate bonds are less volatile than on more-liquid Treasuries(这是因为treasury的需求量较大,所以波动也大)
less volatility in the 'corporate/swap spread' than in the 'corporate/ Treasury spread',这是因为corporate bond和swap都认为是有credit risk的,而treasury是认为是无credit risk,所以corporate与treasury之间的差异比corporate与swap间的差异多了一项credit risk spread(未抵消),当然就波动会更大
Collateralization on derivatives used in an LDI strategy introduces a new risk factor:the risk that available collateral becomes exhausted(抵质押物大幅贬值)
credit risk if the swaption is not collateralized
“collateral exhaustion risk” if it is collateralized
前面一直讲的immunization可以理解为在liability端的角度出发,要解决未来的债务问题;其实也可以从资产端的角度,构建一种fixed-income like的组合来满足稳定收入,即indexation
bond-index是指数提供商选出来作为代表债券市场行情的指标,而投资者是想通过复刻这些指数来达到复刻债券市场的行情
一些债券市场的基本知识:
Fixed-income markets are much larger and broader than equity markets
matrix pricing or evaluated pricing:makes use of observable liquid benchmark yields to estimate the current market yield and price
rebalancing of bond market indexes usually occurs monthly rather than semi-annually or annually as it does for equity indexes,所以全复刻的话要成本高,要频繁rebalance
Another method used to address a portfolio’s sensitivity to rate changes along the yield curve is referred to as the present value of distribution of cash flows methodology
Indexation的整体逻辑:
it is neither feasible nor cost-effective for investors to pursue full replication
Enhanced Indexing 可以用 stratified sampling or cell approach
increase allocation to Treasuries over corporates when significant spread widening is anticipated, or reverse
liability-based mandate已经介绍完,接下来介绍total return mandate
total return swap(TRS)比ETF、MF好的地方:
requires less initial cash outlay than direct investment in the bond portfolio for similar performance(ETF、MF其实都属于直接投资)
TRS also carries counterparty credit risk,但 can offer exposure to assets that are difficult to access directly
smart beta主要应用于equity,finxed-income也会用到,本质是做 factor tilts(因子倾斜),因子选得好的话 can capture a significant proportion of excess returns without the significantly higher fees associated with active management
For Type II, III, and IV assets and liabilities, curve duration statistics, such as effective duration, are needed
Strategic hedging is the active management of the hedging ratio
Because asset BPVs are less than liability BPVs in typical pension funds, the derivatives overlay requires the use of receive-fixed interest rate swaps(主要是怕current swap market rates fall)
实际上,raise the hedging ratio when lower rates are anticipated;反之则reduce hedging ratio
策略应用的小结:
If rates are expected to be low, the receive-fixed swap typically is the preferred derivative
If rates are expected to go up, the swaption collar can become attractive
If rates are projected to reach a certain threshold that depends on the option costs and the strike rates, the purchased receiver swaption can become the favored choice







 文章探讨了利率免疫策略,包括immunization、durationmatching和convexity在管理固定收益债券组合中的作用,以对冲利率风险。内容涉及如何构建对利率变化敏感度较低的组合,如laddered、bullet和barbell策略,并讨论了在利率曲线变动时如何通过衍生品进行再平衡。此外,文章还提到了多期负债的管理,如累积福利义务(ABO)和预计福利义务(PBO),以及使用衍生品如互换和期权进行主动风险管理。
文章探讨了利率免疫策略,包括immunization、durationmatching和convexity在管理固定收益债券组合中的作用,以对冲利率风险。内容涉及如何构建对利率变化敏感度较低的组合,如laddered、bullet和barbell策略,并讨论了在利率曲线变动时如何通过衍生品进行再平衡。此外,文章还提到了多期负债的管理,如累积福利义务(ABO)和预计福利义务(PBO),以及使用衍生品如互换和期权进行主动风险管理。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








