创建线程
std::thread thObj(<CALLBACK>);其中的函数可以是函数指针,函数对象,lambda函数。线程创建完成即开始运行。
#include <thread>
void thread_function(){
std::cout<<"thread function Executing"<<std::endl;
}
int main() {
std::thread threadObj(thread_function);
std::cout<<"Display From MainThread"<<std::endl;
threadObj.join();
std::cout<<"Exit of Main function"<<std::endl;
return 0;
}使用std::thread::get_id()和std::this_thread::get_id()可以获取线程id,其中std::thread::id是一个对象。
等待及分离线程
std::thread th(funcPtr);
// Some Code
th.join();
std::thread th(funcPtr);
// Some Code
th.detach();使用join等待创建的线程结束,detach使线程分离。
对同一个线程连续调用join或detach会造成崩溃。因此在调用前最好先使用threadObj.joinable()判断线程当前状态。
创建一个线程后必须对其调用join或detach,因为std::thread的虚构函数会进行检查如果仍是joinable状态则终止进程。
线程传参
在创建std::thread对象时增加函数需要的参数即可。如果要传引用需要使用std::ref()。
如果要创建对象成员函数的线程:
std::thread threadObj(&Class::MemberFunction,&Class,arg);竞争条件,锁
为了避免多线程对共享数据操作产生错误,对共享数据进行更改时使用锁。
#include<iostream>
#include<thread>
#include<vector>
#include<mutex>
class Wallet{
int mMoney;
std::mutex mutex;
public:
Wallet() :mMoney(0){}
int getMoney() { return mMoney; }
void addMoney(int money){
mutex.lock();
for(int i = 0; i < money; ++i){
mMoney++;
}
mutex.unlock();
}
};为了避免忘记解锁,可以使用lock_guard。
class Wallet{
int mMoney;
std::mutex mutex;
public:
Wallet() :mMoney(0){}
int getMoney() { return mMoney; }
void addMoney(int money){
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lockGuard(mutex);
for(int i = 0; i < money; ++i){
mMoney++;
}
}
};条件变量
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <functional>
#include <mutex>
#include <condition_variable>
using namespace std::placeholders;
class Application{
std::mutex m_mutex;
std::condition_variable m_condVar;
bool m_bDataLoaded;
public:
Application(){
m_bDataLoaded = false;
}
void loadData(){
// Make This Thread sleep for 1 Second
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1000));
std::cout<<"Loading Data from XML"<<std::endl;
// Lock The Data structure
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> guard(m_mutex);
// Set the flag to true, means data is loaded
m_bDataLoaded = true;
// Notify the condition variable
m_condVar.notify_one();
}
bool isDataLoaded(){
return m_bDataLoaded;
}
void mainTask(){
std::cout<<"Do Some Handshaking"<<std::endl;
// Acquire the lock
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> mlock(m_mutex);
// Start waiting for the Condition Variable to get signaled
// Wait() will internally release the lock and make the thread to block
// As soon as condition variable get signaled, resume the thread and
// again acquire the lock. Then check if condition is met or not
// If condition is met then continue else again go in wait.
while(m_bDataLoaded!=true){
m_condVar.wait(mlock, std::bind(&Application::isDataLoaded, this));
}
std::cout<<"Do Processing On loaded Data"<<std::endl;
}
};
int main(){
Application app;
std::thread thread_1(&Application::mainTask, &app);
std::thread thread_2(&Application::loadData, &app);
thread_2.join();
thread_1.join();
return 0;
}等待条件时首先加锁,wait函数内部会解锁并阻塞进行等待,收到通知后会重新上锁。因为有可能被虚假唤醒,所以唤醒后需要重新检查条件。
std::future std::promise
如果我们想要线程返回一个结果可以用future和promise来实现。future保存一个我们将来想要获取的值,而promise与future相关联用来设置future的值。
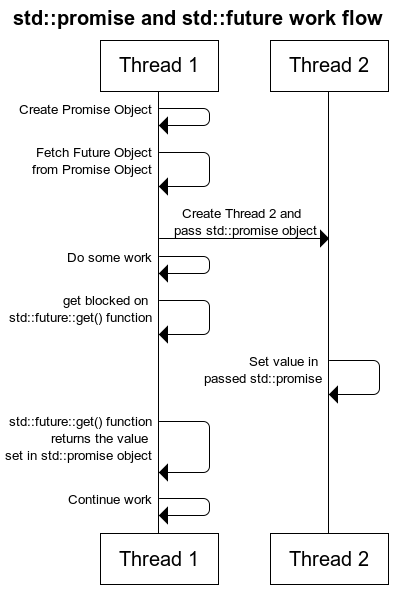
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <future>
void initiazer(std::promise<int> * promObj){
std::cout<<"Inside Thread"<<std::endl; promObj->set_value(35);
}
int main(){
std::promise<int> promiseObj;
std::future<int> futureObj = promiseObj.get_future();
std::thread th(initiazer, &promiseObj);
std::cout<<futureObj.get()<<std::endl;
th.join();
return 0;
}通过创建promise然后取得其关联的future,将promise传递给其他线程,在其他线程中调用set_value设置future的值,之后调用get取得值。
std::async
template <class Fn, class... Args>
future<typename result_of<Fn(Args...)>::type> async (launch policy, Fn&& fn, Args&&... args);async是一个函数模板,可以接收一个函数并且异步执行。它会返回一个future用来获取返回值。
launch policy有两种
std::launch::async 起一个新线程来执行,异步。
std::launch::deferred 在其他线程调用
future的get时再执行,同步。
std::future<std::string> resultFromDB = std::async(std::launch::async, fetchDataFromDB, "Data");
// Do Some Stuff
//Fetch Data from DB
// Will block till data is available in future<std::string> object.
std::string dbData = resultFromDB.get();async首先创建一个thread和promise对象,然后返回其关联的future对象。
std::packaged_task<>
packaged_task<>保存一个函数和需要返回的值。只可移动,不可拷贝。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <future>
#include <string>
// Fetch some data from DB
std::string getDataFromDB( std::string token){
// Do some stuff to fetch the data
std::string data = "Data fetched from DB by Filter :: " + token;
return data;
}
int main(){
// Create a packaged_task<> that encapsulated the callback i.e. a function
std::packaged_task<std::string (std::string)> task(getDataFromDB);
// Fetch the associated future<> from packaged_task<>
std::future<std::string> result = task.get_future();
// Pass the packaged_task to thread to run asynchronously
std::thread th(std::move(task), "Arg");
// Join the thread. Its blocking and returns when thread is finished.
th.join();
// Fetch the result of packaged_task<> i.e. value returned by getDataFromDB()
std::string data = result.get();
std::cout << data << std::endl;
return 0;
}async相当于封装了packaged_task<>,promise,future。






















 1292
1292











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








