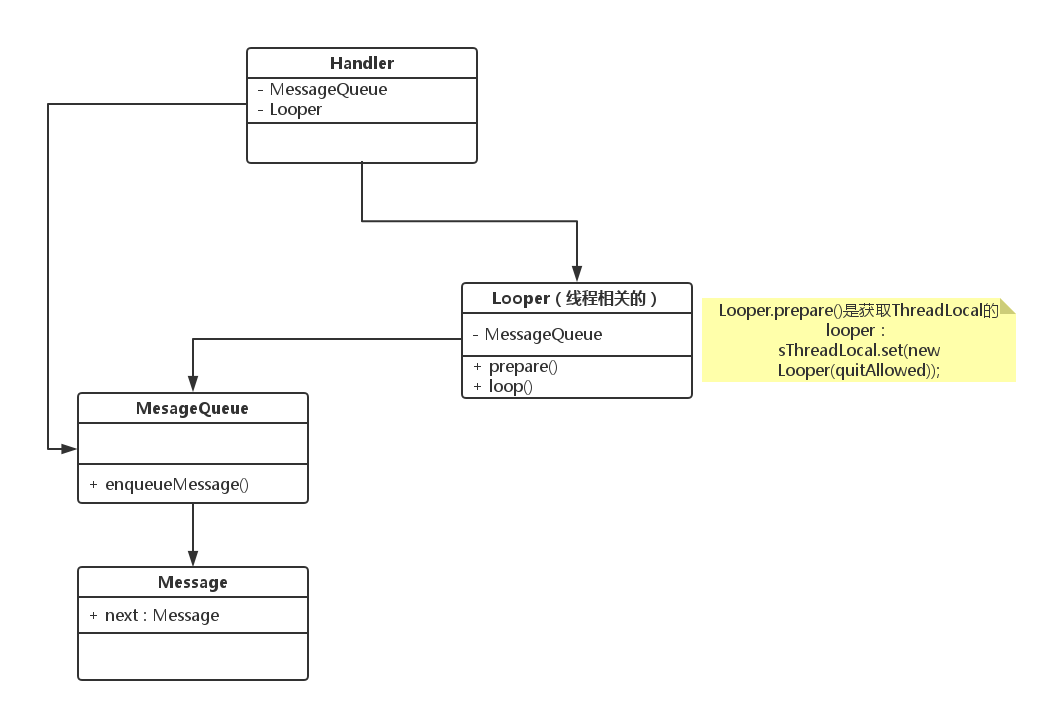
Handler、Looper、Message三者的关系并不复杂:
- Handler内部有一个Looper,Looper是存放在ThreadLocal里的,而ThreadLocal是线程里的数据,故Looper是线程相关的。
- Looper内部有MessageQueue,MessageQueue负责管理Message。loop()方法就是一直在遍历MessageQueue,然后将消息分发处理。
- Hander内部也有一个MessageQueue,这个MessageQueue是获取了Looper里的那个MessageQueue,是同一个。Handler中的postMessage或者SendMessage之类的发送消息是调用了MessageQueue.enqueueMessage方法,在loop循环中也就获取到了Message。
那么为什么handler可以进行线程中的切换工作?我们用一个在子线程中接受消息并处理的例子来分析handler的使用方法:
//子线程中接受并处理消息demo
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Looper.prepare();
mHandler = new Handler(Looper.myLooper()){
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
Log.d(TAG,"msg received");
}
};
Looper.loop();
}
}).start();步骤总结如下:
1. 首先调用Looper.prepare()初始化Looper
2. new Handler,并将looper的值传入
3. 开启loop模式
我们大体知道prepare是初始化looper,loop函数就是一个死循环,不停地从消息队列里取消息,分发处理,其中handleMessage就是在子线程中处理消息的。这是我们就会好奇prepare这个函数到底干啥了,是不是就是new了一个Looper?那么就去找源码分析:
//looper的源码
/** Initialize the current thread as a looper.
* This gives you a chance to create handlers that then reference
* this looper, before actually starting the loop. Be sure to call
* {@link #loop()} after calling this method, and end it by calling
* {@link #quit()}.
*/
public static void prepare() {
prepare(true);
}
private static void prepare(boolean quitAllowed) {
if (sThreadLocal.get() != null) {
throw new RuntimeException("Only one Looper may be created per thread");
}
sThreadLocal.set(new Looper(quitAllowed));
}如上图所示,prepare调用了prepare(true),这个参数是表明是否允许退出,一般主线程UI不允许退出,用户只能调用public的prepare,不能调用带参数的private的prepare。最终执行了sThreadLocal.set方法,并把将new出来的Looper传入。果然,这个prepare就是在内部new了一个Looper,那么这个ThreadLocal是做什么的呢?后面的myLooper函数是怎么获取到这个looper的呢?
首先sThreadLocal的定义如下:
//Looper源码
// sThreadLocal.get() will return null unless you've called prepare().
static final ThreadLocal<Looper> sThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Looper>();这个就是简单的new了一下,没啥好看的,主要看set函数,找到ThreadLocal的set函数:
//ThreadLocal源码
/**
* Sets the current thread's copy of this thread-local variable
* to the specified value. Most subclasses will have no need to
* override this method, relying solely on the {@link #initialValue}
* method to set the values of thread-locals.
*
* @param value the value to be stored in the current thread's copy of
* this thread-local.
*/
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
/**
* Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in
* InheritableThreadLocal.
*
* @param t the current thread
* @return the map
*/
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}这个set函数就是将value设置到ThreadLocalMap的一个对象中,而这个对象是通过getMap函数获得的,也就是从当前Thread获取的,查看Thread的源码:
public
class Thread implements Runnable {
//省略
/* ThreadLocal values pertaining to this thread. This map is maintained
* by the ThreadLocal class. */
ThreadLocal.ThreadLocalMap threadLocals = null;
//省略
}在每个Thread的对象中,都有一个成员变量threadLocals,类型是ThreadLocalMap。
现在整个流程我们大体能够通一下,prepare函数主要是生成一个Looper对象,通过ThreadLocal的set函数存储在当前线程中的ThreadLocalMap里。这样,每个线程都有自己的ThreadLocalMap,也就对应着有自己的Looper。那么这个ThreadLocalMap是如何定义的呢?
//ThreadLocal源码
static class ThreadLocalMap {
static class Entry extends WeakReference<ThreadLocal<?>> {
/** The value associated with this ThreadLocal. */
Object value;
Entry(ThreadLocal<?> k, Object v) {
super(k);
value = v;
}
}
private Entry[] table;
/**
* Set the value associated with key.
*
* @param key the thread local object
* @param value the value to be set
*/
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
// We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at
// least as common to use set() to create new entries as
// it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast
// path would fail more often than not.
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold)
rehash();
}
/**
* Get the entry associated with key. This method
* itself handles only the fast path: a direct hit of existing
* key. It otherwise relays to getEntryAfterMiss. This is
* designed to maximize performance for direct hits, in part
* by making this method readily inlinable.
*
* @param key the thread local object
* @return the entry associated with key, or null if no such
*/
private Entry getEntry(ThreadLocal<?> key) {
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (table.length - 1);
Entry e = table[i];
if (e != null && e.get() == key)
return e;
else
return getEntryAfterMiss(key, i, e);
}可以看到ThreadLocalMap就是一个用数组实现的简单的map,存储不同ThreadLocal的数值。其中以ThreadLocal变量作为key,具体细节就不再分析了。
整个过程可以总结如下图:
























 6982
6982











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








