1.Sensor相关的类:Sensor,SensorManager
- Sensor(点击可查看官方文档,需要梯子)
常用传感器类型
- TYPE_ALL——A constant describing all sensor types.
- TYPE_ACCELEROMETE
- TYPE_LINEAR_ACCELERATION
- TYPE_GRAVITY
- TYPE_GYROSCOPE
- TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD
- TYPE_ORIENTATION——已弃用
- TYPE_MOTION_DETECT——Requires API level 24 (Android 7.0, Nougat)
- TYPE_SIGNIFICANT_MOTION
- TYPE_STATIONARY_DETECT
- TYPE_STEP_COUNTER
- TYPE_STEP_DETECTOR
- TYPE_HEART_BEAT——A constant describing a motion detect sensor.Requires API level 24 (Android 7.0, Nougat)
- TYPE_HEART_RATE
- TYPE_PRESSURE
- TYPE_PROXIMITY
- TYPE_TEMPERATURE——已弃用
- TYPE_AMBIENT_TEMPERATURE
- TYPE_RELATIVE_HUMIDITY
- TYPE_LIGHT
常用传感器方法:
- getVendor()——传感器生产商
- getName()——传感器名称
- getId()——传感器ID,Requires API level 24 (Android 7.0, Nougat)
- getType()——传感器类型
- getStringType()——传感器类型
- getVersion()——传感器版本号
- getResolution()——传感器精度
- isWakeUpSensor()——Returns true if the sensor is a wake-up sensor.
Always make sure to disable sensors you don't need, especially when your activity is paused. Failing to do so can drain the battery in just a few hours.
Note that the system will not disable sensors automatically when the screen turns off.
- SensorManager (点击可查看官方文档,需要梯子)
常量值
- GRAVITY_EARTH Value——9.80665f
- STANDARD_GRAVITY——9.80665f
- PRESSURE_STANDARD_ATMOSPHERE——1013.25f(hPa)
- SENSOR_ALL——A constant that includes all sensors
- SENSOR_ACCELEROMETER
- SENSOR_MAGNETIC_FIELD——All values are in micro-Tesla (uT) and measure the ambient magnetic field in the X, Y and -Z axis.
- SENSOR_ORIENTATION
- SENSOR_ORIENTATION_RAW
- SENSOR_PROXIMITY
- SENSOR_TEMPERATURE
- SENSOR_LIGHT
- SENSOR_DELAY_FASTEST——get sensor data as fast as possible(费电!)
- SENSOR_DELAY_GAME——rate suitable for games(实时性要求)
- SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL——rate (default) suitable for screen orientation changes(默认)
- SENSOR_DELAY_UI——rate suitable for the user interface(延迟较大)
常用方法:
- int getSensors()——return available sensors
- getSensorList(type: Int)——return a list of sensors matching the asked type:MutableList<Sensor>.
- getDefaultSensor(type: Int)——return default sensor
- getDefaultSensor(type: Int, wakeUp: Boolean)
- registerListener(listener: SensorListener, sensors: Int)——Registers a SensorListener for given sensors.
- registerListener(listener: SensorListener, sensors: Int, rate: Int)——Registers a SensorListener for given sensors.
- registerListener(listener: SensorEventListener, sensor: Sensor, samplingPeriodUs: Int)——Registers a SensorEventListener for the given sensor at the given sampling frequency.
- unregisterListener(listener: SensorListener)——Unregisters a listener for all sensors.
- unregisterListener(listener: SensorListener, sensors: Int)——Unregisters a listener for the sensors with which it is registered.
- unregisterListener(listener: SensorEventListener)——Unregisters a listener for all sensors.
- unregisterListener(listener: SensorEventListener, sensor: Sensor)——Unregisters a listener for the sensors with which it is registered.
2.传感器数据处理:SensorEvent属性
- accuracy——The accuracy of this event.
- sensor——The sensor that generated this event.
- timestamp——The time in nanosecond at which the event happened.
- values——The length and contents of the values array depends on which sensor type is being monitored
Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER: All values are in SI units (m/s^2)
- values[0]: Acceleration minus Gx on the x-axis
- values[1]: Acceleration minus Gy on the y-axis
- values[2]: Acceleration minus Gz on the z-axis
3.接口:SensorListener,SensorEventListener (点击可查看官方文档,需要梯子)
以下两个方法在SensorListener中已弃用,可以在SensorEvenListener中使用
- int onAccuracyChanged(sensor: Int, accuracy: Int) This class was deprecated in API level 21.
- int onSensorChanged(sensor: Int, values: FloatArray) This class was deprecated in API level 21.
4.使用传感器
1)调用Context的getSystemService(Context.SENSOR_SERVICE)方法获取SensorManager对象
2)调用SensorManager的getDefaultSensor(int type)方法来获取指定类型的传感器
3)在Activity的onResume()方法中调用registerListener(SensorEventListener listener,Sensor sensor,int rate)为指定的传感器注册监听器,Android系统会通过传感器获取外界环境的数据,并将数据传给监听器的监听方法
5.列出手机所有传感器信息代码
package com.lee.sensor;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.List;
public class ListAllSensorsActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_list_all_sensors);
// 从系统服务中获得传感器管理器
SensorManager sensorManager = (SensorManager) getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE);
// 从传感器管理器中获得全部的传感器列表
List<Sensor> allSensors = sensorManager.getSensorList(Sensor.TYPE_ALL);
// 保存每个传感器的信息
StringBuilder sensorsInfo = new StringBuilder("手机有"+allSensors.size()+"个传感器,分别是:\n\n");
for(Sensor s:allSensors){
switch(s.getType()){
case Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER:
sensorsInfo.append("加速度传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_LINEAR_ACCELERATION:
sensorsInfo.append("线性加速度传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_GRAVITY:
sensorsInfo.append("重力传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_GYROSCOPE:
sensorsInfo.append("陀螺仪传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_ORIENTATION:
sensorsInfo.append("方向传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_MOTION_DETECT:
sensorsInfo.append("运动状态检测传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_SIGNIFICANT_MOTION:
sensorsInfo.append("剧烈运动检测传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_STATIONARY_DETECT:
sensorsInfo.append("静止状态检测传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_STEP_COUNTER:
sensorsInfo.append("步数计数器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_STEP_DETECTOR:
sensorsInfo.append("步伐检测器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD:
sensorsInfo.append("电磁场传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_LIGHT:
sensorsInfo.append("环境光线传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_PRESSURE:
sensorsInfo.append("压力传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_PROXIMITY:
sensorsInfo.append("距离传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_AMBIENT_TEMPERATURE:
sensorsInfo.append("温度传感器");
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_RELATIVE_HUMIDITY:
sensorsInfo.append("相对湿度传感器");
break;
default:
sensorsInfo.append("未知传感器");
break;
}
sensorsInfo.append("\n设备类型码:").append(s.getType())
.append("\n设备名称:").append(s.getName())
.append("\n设备版本:").append(s.getVersion())
.append("\n供应商:").append(s.getVendor())
.append("\n\n");
}
// 显示所有传感器的信息
TextView textView = findViewById(R.id.sensors_list_tv);
textView.setText(sensorsInfo);
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<ScrollView
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
tools:context=".ListAllSensorsActivity"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/sensors_list_tv"
android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
</ScrollView>
6.测试加速度,线性加速度,重力加速度,陀螺仪,电磁场传感器代码
package com.lee.sensor;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import android.hardware.SensorEvent;
import android.hardware.SensorEventListener;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class TestSensorActivity extends Activity implements SensorEventListener {
private SensorManager mSensorManager;
private TextView mTextViewAcceleration;
private TextView mTextViewLinearAcceleration;
private TextView mTextViewGravity;
private TextView mTextViewGyroscope;
private TextView mTextViewMagneticField;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_test_sensor);
mTextViewAcceleration = findViewById(R.id.accelerometer_tv);
mTextViewLinearAcceleration = findViewById(R.id.linear_accelerometer_tv);
mTextViewGravity = findViewById(R.id.gravity_tv);
mTextViewGyroscope = findViewById(R.id.gyroscope_tv);
mTextViewMagneticField = findViewById(R.id.magnetic_field_tv);
mSensorManager = (SensorManager) getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE); // 获取SensorManager服务
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
// 为加速度传感器注册监听器
mSensorManager.registerListener(TestSensorActivity.this,
mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER),
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_UI);
// 为线性加速度传感器注册监听器
mSensorManager.registerListener(TestSensorActivity.this,
mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_LINEAR_ACCELERATION),
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_UI);
// 为重力加速度传感器注册监听器
mSensorManager.registerListener(TestSensorActivity.this,
mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_GRAVITY),
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_UI);
// 为陀螺仪传感器注册监听器
mSensorManager.registerListener(TestSensorActivity.this,
mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_GYROSCOPE),
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_UI);
// 为电磁场传感器注册监听器
mSensorManager.registerListener(TestSensorActivity.this,
mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD),
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_UI);
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
// 取消注册所有传感器
mSensorManager.unregisterListener(TestSensorActivity.this);
}
// 当传感器的值改变时回调此方法
@Override
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
switch (event.sensor.getType()) {
case Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER:
str.append("X方向上的加速度:");
str.append(event.values[0]);
str.append("\nY方向上的加速度:");
str.append(event.values[1]);
str.append("\nZ方向上的加速度:");
str.append(event.values[2]);
mTextViewAcceleration.setText(str);
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_LINEAR_ACCELERATION:
str.append("X方向上的线性加速度:");
str.append(event.values[0]);
str.append("\nY方向上的线性加速度:");
str.append(event.values[1]);
str.append("\nZ方向上的线性加速度:");
str.append(event.values[2]);
mTextViewLinearAcceleration.setText(str);
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_GRAVITY:
str.append("X方向上的重力加速度:");
str.append(event.values[0]);
str.append("\nY方向上的重力加速度:");
str.append(event.values[1]);
str.append("\nZ方向上的重力加速度:");
str.append(event.values[2]);
mTextViewGravity.setText(str);
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_GYROSCOPE:
str.append("绕X轴旋转的角速度:");
str.append(event.values[0]);
str.append("\n绕Y轴旋转的角速度:");
str.append(event.values[1]);
str.append("\n绕Z轴旋转的角速度:");
str.append(event.values[2]);
mTextViewGyroscope.setText(str);
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD:
str.append("X方向上的磁感应强度:");
str.append(event.values[0]);
str.append("\nY方向上的磁感应强度:");
str.append(event.values[1]);
str.append("\nZ方向上的磁感应强度:");
str.append(event.values[2]);
mTextViewMagneticField.setText(str);
break;
}
}
// 当传感器精度改变时回调此方法
@Override
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor sensor, int accuracy) {
}
}<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<ScrollView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
tools:context=".TestSensorActivity">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical">
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/acceleration_sensor"
android:textSize="15dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/accelerometer_tv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="15dp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="@string/linear_acceleration_sensor"
android:textSize="15dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/linear_accelerometer_tv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="15dp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="@string/gravity_sensor"
android:textSize="15dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/gravity_tv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="15dp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="@string/gyroscope_sensor"
android:textSize="15dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/gyroscope_tv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="15dp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="@string/magnetic_field_sensor"
android:textSize="15dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/magnetic_field_tv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="15dp" />
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
android:text="@string/orientation_sensor"
android:textSize="15dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/orientation_tv"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textSize="15dp" />
</LinearLayout>
</ScrollView>7.方向传感器
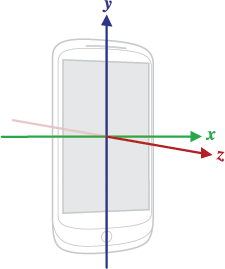
先看下地理坐标系和设备坐标系的区别:


TYPE_ORIENTATION并非真实的传感器,而是由其他传感器模拟而来。
Sensor.TYPE_ORIENTATION: All values are angles in degrees.
- values[0]: Azimuth, angle between the magnetic north direction and the y-axis, around the z-axis (0 to 359). 0=North, 90=East, 180=South, 270=West
- values[1]: Pitch, rotation around x-axis (-180 to 180), with positive values when the z-axis moves toward the y-axis.
- values[2]: Roll, rotation around the y-axis (-90 to 90) increasing as the device moves clockwise.
- Note: This definition is different from yaw, pitch and roll used in aviation where the X axis is along the long side of the plane (tail to nose).
- Note: This sensor type exists for legacy reasons, please use rotation vector sensor type and getRotationMatrix() in conjunction with remapCoordinateSystem() and getOrientation() to compute these values instead.
- Important note: For historical reasons the roll angle is positive in the clockwise direction (mathematically speaking, it should be positive in the counter-clockwise direction).
package com.lee.sensor;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import android.hardware.SensorEvent;
import android.hardware.SensorEventListener;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class OrientationActivity extends Activity {
private SensorManager mSensorManager;
private MySensorEventListener mListener;
private TextView mTextViewOrientation;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_orientation);
mTextViewOrientation = findViewById(R.id.orientation_tv);
mSensorManager = (SensorManager) getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE); // 获取SensorManager服务
mListener = new MySensorEventListener();
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mSensorManager.registerListener(mListener, mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_ORIENTATION),
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL);
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
// 取消注册所有传感器
mSensorManager.unregisterListener(mListener);
}
class MySensorEventListener implements SensorEventListener {
@Override
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
str.append("绕Z轴旋转的角度/方位角:");
str.append(event.values[0]);
str.append("\n绕X轴旋转的角度/倾斜角:");
str.append(event.values[1]);
str.append("\n绕Y轴旋转的角度/滚动角:");
str.append(event.values[2]);
mTextViewOrientation.setText(str);
}
@Override
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor sensor, int accuracy) {
}
}
}不过,TYPE_ORIENTATAION 已被标记为过时,Android推荐使用SensorManager的方法 getOrientation() 来获取方向数据。
public static float[] getOrientation (float[] R, float[] values)
- R is a rotation matrix
- values holds the results
- values[0]: Azimuth(方位角), angle of rotation about the -z axis. This value represents the angle between the device's y axis and the magnetic north pole. When facing north, this angle is 0, when facing south, this angle is π. Likewise, when facing east, this angle is π/2, and when facing west, this angle is -π/2. The range of values is -π to π.
- values[1]: Pitch(倾斜角), angle of rotation about the x axis. This value represents the angle between a plane parallel to the device's screen and a plane parallel to the ground. Assuming that the bottom edge of the device faces the user and that the screen is face-up, tilting the top edge of the device toward the ground creates a positive pitch angle. The range of values is -π to π.
- values[2]: Roll(滚动角), angle of rotation about the y axis. This value represents the angle between a plane perpendicular to the device's screen and a plane perpendicular to the ground. Assuming that the bottom edge of the device faces the user and that the screen is face-up, tilting the left edge of the device toward the ground creates a positive roll angle. The range of values is -π/2 to π/2.
该方法的第一个参数R为旋转矩阵,可通过SensorManager的 getRotationMatrix() 获得,第二个参数保存函数计算所得的方向数据。
public static boolean getRotationMatrix (float[] R, float[] I, float[] gravity, float[] geomagnetic)
- This method computes the inclination matrix I as well as the rotation matrix R transforming a vector from the device coordinate system to the world's coordinate system which is defined as a direct orthonormal basis.R is the identity matrix when the device is aligned with the world's coordinate system, that is, when the device's X axis points toward East, the Y axis points to the North Pole and the device is facing the sky.
- R is an array of 9 floats holding the rotation matrix R when this function returns. R can be null.
- I is an array of 9 floats holding the rotation matrix I when this function returns. I can be null.
- gravity is an array of 3 floats containing the gravity vector expressed in the device's coordinate.You can simply use the
valuesreturned by aSensorEventof aSensorof typeTYPE_ACCELEROMETER.- geomagnetic is an array of 3 floats containing the geomagnetic vector expressed in the device's coordinate.You can simply use the
valuesreturned by aSensorEventof aSensorof typeTYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD.
getRotationMatrix()源码
public static boolean getRotationMatrix(float[] R, float[] I,
float[] gravity, float[] geomagnetic) {
// TODO: move this to native code for efficiency
float Ax = gravity[0];
float Ay = gravity[1];
float Az = gravity[2];
final float normsqA = (Ax * Ax + Ay * Ay + Az * Az);
final float g = 9.81f;
final float freeFallGravitySquared = 0.01f * g * g;
if (normsqA < freeFallGravitySquared) {
// gravity less than 10% of normal value
return false;
}
final float Ex = geomagnetic[0];
final float Ey = geomagnetic[1];
final float Ez = geomagnetic[2];
float Hx = Ey * Az - Ez * Ay;
float Hy = Ez * Ax - Ex * Az;
float Hz = Ex * Ay - Ey * Ax;
final float normH = (float) Math.sqrt(Hx * Hx + Hy * Hy + Hz * Hz);
if (normH < 0.1f) {
// device is close to free fall (or in space?), or close to
// magnetic north pole. Typical values are > 100.
return false;
}
final float invH = 1.0f / normH;
Hx *= invH;
Hy *= invH;
Hz *= invH;
final float invA = 1.0f / (float) Math.sqrt(Ax * Ax + Ay * Ay + Az * Az);
Ax *= invA;
Ay *= invA;
Az *= invA;
final float Mx = Ay * Hz - Az * Hy;
final float My = Az * Hx - Ax * Hz;
final float Mz = Ax * Hy - Ay * Hx;
if (R != null) {
if (R.length == 9) {
R[0] = Hx; R[1] = Hy; R[2] = Hz;
R[3] = Mx; R[4] = My; R[5] = Mz;
R[6] = Ax; R[7] = Ay; R[8] = Az;
} else if (R.length == 16) {
...
}
}
if (I != null) {
...
}
return true;
}代码中首先对加速度g和磁力计m数据做了一个差乘,得出一个水平东西方向we的向量(差乘的定义)。经过这个运算,本来只有一个平面的向量,变成了三个三维立体平面的向量,从而可以用来计算设备的方向。源码中后面又做了一次差乘,是用计算出的水平东西方向we的向量和重力向量g做的差乘,这次运算重新得出一个水平南北sn方向的向量,最后旋转矩阵中用这三个向量(两个计算出的水平向量、一个重力向量)构成。详细推导参考文章
getOrientation()源码:
public static float[] getOrientation(float[] R, float[] values) {
/*
* 4x4 (length=16) case:
* / R[ 0] R[ 1] R[ 2] 0 \
* | R[ 4] R[ 5] R[ 6] 0 |
* | R[ 8] R[ 9] R[10] 0 |
* \ 0 0 0 1 /
*
* 3x3 (length=9) case:
* / R[ 0] R[ 1] R[ 2] \
* | R[ 3] R[ 4] R[ 5] |
* \ R[ 6] R[ 7] R[ 8] /
*
*/
if (R.length == 9) {
values[0] = (float) Math.atan2(R[1], R[4]);
values[1] = (float) Math.asin(-R[7]);
values[2] = (float) Math.atan2(-R[6], R[8]);
} else {
...
}
return values;
}实现代码:
package com.lee.sensor;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import android.hardware.SensorEvent;
import android.hardware.SensorEventListener;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class OrientationActivity extends Activity {
private SensorManager mSensorManager;
private MySensorEventListener mListener;
private TextView mTextViewOrientation;
private float[] accelerometerValues = new float[3];
private float[] magneticFieldValues = new float[3];
private float[] orientationValues = new float[3];
private float[] rotationMatrix = new float[9];
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_orientation);
mTextViewOrientation = findViewById(R.id.orientation_tv);
mSensorManager = (SensorManager) getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE); // 获取SensorManager服务
mListener = new MySensorEventListener();
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mSensorManager.registerListener(mListener, mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_GRAVITY),
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL);
mSensorManager.registerListener(mListener, mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD),
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL);
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
// 取消注册所有传感器
mSensorManager.unregisterListener(mListener);
}
class MySensorEventListener implements SensorEventListener {
@Override
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
switch (event.sensor.getType()) {
case Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER:
accelerometerValues = event.values;
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD:
magneticFieldValues = event.values;
break;
}
SensorManager.getRotationMatrix(rotationMatrix, null,
accelerometerValues, magneticFieldValues);
SensorManager.getOrientation(rotationMatrix, orientationValues);
orientationValues[0] = (float) Math.toDegrees(orientationValues[0]);
orientationValues[1] = (float) Math.toDegrees(orientationValues[1]);
orientationValues[2] = (float) Math.toDegrees(orientationValues[2]);
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
str.append("绕Z轴旋转的角度/方位角:");
str.append(orientationValues[0]);
str.append("\n绕X轴旋转的角度/倾斜角:");
str.append(orientationValues[1]);
str.append("\n绕Y轴旋转的角度/滚动角:");
str.append(orientationValues[2]);
mTextViewOrientation.setText(str);
}
@Override
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor sensor, int accuracy) {
}
}
}
一个小坑:实现代码中getRotationMatrix()的第三个参数是传入一个加速度传感器的数据,内部计算时需要的是重力传感器,在手机保持静止的状态下,加速度传感器可以当作重力传感器使用。但是当人手持手机行走时,加速度的数值就不等于重力传感器的数值,所计算出来的方向波动较大。解决方法是,第三个参数传入重力传感器的数据。
package com.lee.sensor;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.hardware.Sensor;
import android.hardware.SensorEvent;
import android.hardware.SensorEventListener;
import android.hardware.SensorManager;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class OrientationActivity extends Activity {
private SensorManager mSensorManager;
private MySensorEventListener mListener;
private TextView mTextViewOrientation;
private float[] gravityValues = new float[3];
private float[] magneticFieldValues = new float[3];
private float[] orientationValues = new float[3];
private float[] rotationMatrix = new float[9];
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_orientation);
mTextViewOrientation = findViewById(R.id.orientation_tv);
mSensorManager = (SensorManager) getSystemService(SENSOR_SERVICE); // 获取SensorManager服务
mListener = new MySensorEventListener();
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
mSensorManager.registerListener(mListener, mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_GRAVITY),
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL);
mSensorManager.registerListener(mListener, mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD),
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_NORMAL);
}
@Override
protected void onPause() {
super.onPause();
// 取消注册所有传感器
mSensorManager.unregisterListener(mListener);
}
class MySensorEventListener implements SensorEventListener {
@Override
public void onSensorChanged(SensorEvent event) {
switch (event.sensor.getType()) {
case Sensor.TYPE_GRAVITY:
gravityValues = event.values;
break;
case Sensor.TYPE_MAGNETIC_FIELD:
magneticFieldValues = event.values;
break;
}
SensorManager.getRotationMatrix(rotationMatrix, null,
gravityValues, magneticFieldValues);
SensorManager.getOrientation(rotationMatrix, orientationValues);
orientationValues[0] = (float) Math.toDegrees(orientationValues[0]);
orientationValues[1] = (float) Math.toDegrees(orientationValues[1]);
orientationValues[2] = (float) Math.toDegrees(orientationValues[2]);
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
str.append("绕Z轴旋转的角度/方位角:");
str.append(orientationValues[0]);
str.append("\n绕X轴旋转的角度/倾斜角:");
str.append(orientationValues[1]);
str.append("\n绕Y轴旋转的角度/滚动角:");
str.append(orientationValues[2]);
mTextViewOrientation.setText(str);
}
@Override
public void onAccuracyChanged(Sensor sensor, int accuracy) {
}
}
}






















 1276
1276











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








