产品需求:1、app通过蓝牙连接到板子设备
2、以发报文的形式与板子设备通讯
3、当设备接受到正确的报文指令后,会将检测的数据返回
4、将返回的数据解析设置到界面显示即可
板子介绍:
准备工作:
1:、与嵌入式工程师交互(将驱动这里指串口,装在电脑上)
2、将对应线路接好
3、报文的协议文档等可先看看了解一下(这里用的是MODBUS RTU协议)
其实也就差不多这些准备(有问题可以直接问相关嵌入式人员),废话少说,下面就直接进行主题吧。。。
第一步:首先我们可以整理一下思路:
1、实现搜索功能,针对蓝牙周围设备的发现
2、对目标 设备进行连接
3、开发期间是多与串口交互(可以先实现app将数据传递串口,协议先不做考虑)
4、在实现串口向app的数据的传递(协议先不做考虑)
5、实现对数据的解析(根据协议去实现解析即可),在将数据显示即可
以上为整体的实现步骤,开发的时候在具体到细节!
第二步:防止一头雾水,我们先来简单复习一下BlueTooth相关的api
1:BuletoothAdapter
这个类的对象代表了本地的蓝牙适配器,相当于蓝牙工作流程图中的手机里的蓝牙适配器,也就是说比如这个应用程序是运行在手机上,那么手机上的蓝牙适配器就是本地蓝牙适配器。
cancelDiscovery() 根据字面意思,是取消发现,也就是说当我们正在搜索设备的时候调用这个方法将不再继续搜索
disable() 关闭蓝牙
enable() 打开蓝牙,这个方法打开蓝牙不会弹出提示,更多的时候我们需要问下用户是否打开,一下这两行代码同样是打开蓝牙,不过会提示用户:
Intemtenabler=new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE);
startActivityForResult(enabler,reCode); 同startActivity(enabler);
getAddress() 获取本地蓝牙地址
getDefaultAdapter() 获取默认BluetoothAdapter,实际上,也只有这一种方法获取BluetoothAdapter
getName() 获取本地蓝牙名称
getRemoteDevice(String address) 根据蓝牙地址获取远程蓝牙设备
getState() 获取本地蓝牙适配器当前状态(感觉可能调试的时候更需要)
isDiscovering() 判断当前是否正在查找设备,是返回true
isEnabled() 判断蓝牙是否打开,已打开返回true,否则,返回false
listenUsingRfcommWithServiceRecord(String name,UUID uuid)根据名称,UUID创建并返回BluetoothServerSocket,这是创建BluetoothSocket服务器端的第一步
startDiscovery() 开始搜索,这是搜索的第一步
2:BuletoothDevice
这个类的对象代表了远程的蓝牙设备,相当于蓝牙工作流程图中的计算机里的蓝牙适配器,也就是说比如这个应用程序是运行在手机上,那么BuletoothDevice代表了你要连接的远程的那个设备上面的蓝牙适配器。
createRfcommSocketToServiceRecord(UUIDuuid)根据UUID创建并返回一个BluetoothSocket 这个方法也是我们获取BluetoothDevice的目的——创建BluetoothSocket
3.BluetoothSocket,跟BluetoothServerSocket相对,是客户端一共5个方法,不出意外,都会用到
close(), 关闭
connect() 连接
getInptuStream() 获取输入流
getOutputStream() 获取输出流
getRemoteDevice() 获取远程设备,这里指的是获取bluetoothSocket指定连接的那个远程蓝牙设备
第三步:实现功能
3.1:开启蓝牙,判断手机是否支持蓝牙
BluetoothAdapter mBluetoothAdapter = BluetoothAdapter.getDefaultAdapter();
if(mBluetoothAdapter == null){ //不支持
return;
}
if(!mBluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()){ //蓝牙未开启,则开启蓝牙
Intent enableIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE);
startActivityForResult(enableIntent, REQUEST_ENABLE_BT);
}
//......
public void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data){
if(requestCode == REQUEST_ENABLE_BT){
if(requestCode == RESULT_OK){ //蓝牙开启
}
}
} if (!getPackageManager().hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_BLUETOOTH_LE)) { //针对设备不支持ble,可以进行操作
Toast.makeText(this, R.string.ble_not_supported, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
finish();
}if (mBluetoothAdapter == null || !mBluetoothAdapter.isEnabled()) {
Intent enableBtIntent = new Intent(BluetoothAdapter.ACTION_REQUEST_ENABLE);
startActivityForResult(enableBtIntent, REQUEST_ENABLE_BT);
}
@Override
protected void onActivityResult(int requestCode, int resultCode, Intent data) {
switch (requestCode) {
case REQUEST_ENABLE:
if (resultCode == Activity.REQUEST_ENABLE_BT) { //蓝牙启用
} else { //蓝牙没有启用
}
break;
}
} private void scanLeDevice(final boolean enable) {
if (enable) {
// Stops scanning after a pre-defined scan period.
mHandler.postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
mScanning = false;
mBluetoothAdapter.stopLeScan(mLeScanCallback);
}
}, SCAN_PERIOD); //在这里可以自己进行时间的设置,比如搜索10秒
mScanning = true;
mBluetoothAdapter.startLeScan(mLeScanCallback); //开始搜索
} else {
mScanning = false;
mBluetoothAdapter.stopLeScan(mLeScanCallback);//停止搜索
}
} private BluetoothAdapter.LeScanCallback mLeScanCallback = new BluetoothAdapter.LeScanCallback() {
@Override
public void onLeScan(final BluetoothDevice device, int rssi, byte[] scanRecord) {
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
//device.getName();获取蓝牙设备名字
//device.getAddress();获取蓝牙设备mac地址 可以将数据使用EventBus进行需要传递
}
});
}
};public boolean connect(final String address) {
if (mBluetoothAdapter == null || address == null) {
Log.w(TAG,"BluetoothAdapter not initialized or unspecified address.");
return false;
}
// Previously connected device. Try to reconnect. (先前连接的设备。 尝试重新连接)
if (mBluetoothDeviceAddress != null&& address.equals(mBluetoothDeviceAddress)&& mBluetoothGatt != null) {
Log.d(TAG,"Trying to use an existing mBluetoothGatt for connection.");
if (mBluetoothGatt.connect()) {
mConnectionState = STATE_CONNECTING;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
final BluetoothDevice device = mBluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(address);
if (device == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Device not found. Unable to connect.");
return false;
}
// We want to directly connect to the device, so we are setting the
// autoConnect
// parameter to false.
mBluetoothGatt = device.connectGatt(this, false, mGattCallback); //这里才是真正连接
Log.d(TAG, "Trying to create a new connection.");
mBluetoothDeviceAddress = address;
mConnectionState = STATE_CONNECTING;
return true;
}private final BluetoothGattCallback mGattCallback = new BluetoothGattCallback() {
@Override //当连接上设备或者失去连接时会回调该函数
public void onConnectionStateChange(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status,int newState) {
if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_CONNECTED) { //连接成功
mBluetoothGatt.discoverServices(); //连接成功后就去找出该设备中的服务 private BluetoothGatt mBluetoothGatt;
} else if (newState == BluetoothProfile.STATE_DISCONNECTED) { //连接失败
}
}
@Override //当设备是否找到服务时,会回调该函数
public void onServicesDiscovered(BluetoothGatt gatt, int status) {
if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) { //找到服务了
//在这里可以对服务进行解析,寻找到你需要的服务
} else {
Log.w(TAG, "onServicesDiscovered received: " + status);
}
}
@Override //当读取设备时会回调该函数
public void onCharacteristicRead(BluetoothGatt gatt,BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) {
System.out.println("onCharacteristicRead");
if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) {
//读取到的数据存在characteristic当中,可以通过characteristic.getValue();函数取出。然后再进行解析操作。
//int charaProp = characteristic.getProperties();if ((charaProp | BluetoothGattCharacteristic.PROPERTY_NOTIFY) > 0)表示可发出通知。 判断该Characteristic属性
}
}
@Override //当向设备Descriptor中写数据时,会回调该函数
public void onDescriptorWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt,BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor, int status) {
System.out.println("onDescriptorWriteonDescriptorWrite = " + status + ", descriptor =" + descriptor.getUuid().toString());
}
@Override //设备发出通知时会调用到该接口
public void onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt,BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) {
if (characteristic.getValue() != null) {
System.out.println(characteristic.getStringValue(0));
}
System.out.println("--------onCharacteristicChanged-----");
}
@Override
public void onReadRemoteRssi(BluetoothGatt gatt, int rssi, int status) {
System.out.println("rssi = " + rssi);
}
@Override //当向Characteristic写数据时会回调该函数
public void onCharacteristicWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt,BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) {
System.out.println("--------write success----- status:" + status);
};
}public List<BluetoothGattService> getSupportedGattServices() {
if (mBluetoothGatt == null)
return null;
return mBluetoothGatt.getServices(); //此处返回获取到的服务列表
} 注意:这里你就可以和相关的嵌入式工程师交互,使用哪些服务以及使用哪些UUID即可
private void displayGattServices(List<BluetoothGattService> gattServices) {
if (gattServices == null)
return;
for (BluetoothGattService gattService : gattServices) { // 遍历出gattServices里面的所有服务
List<BluetoothGattCharacteristic> gattCharacteristics = gattServices.getCharacteristics();
for (BluetoothGattCharacteristic gattCharacteristic : gattCharacteristics) { // 遍历每条服务里的所有Characteristic
if (gattCharacteristic.getUuid().toString().equalsIgnoreCase(需要通信的UUID)) {
// 有哪些UUID,每个UUID有什么属性及作用,一般硬件工程师都会给相应的文档。我们程序也可以读取其属性判断其属性。
// 此处可以可根据UUID的类型对设备进行读操作,写操作,设置notification等操作
// BluetoothGattCharacteristic gattNoticCharacteristic 假设是可设置通知的Characteristic
// BluetoothGattCharacteristic gattWriteCharacteristic 假设是可读的Characteristic
// BluetoothGattCharacteristic gattReadCharacteristic 假设是可写的Characteristic
}
}
}
}public void setCharacteristicNotification(BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, boolean enabled) {
if (mBluetoothAdapter == null || mBluetoothGatt == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "BluetoothAdapter not initialized");
return;
}
mBluetoothGatt.setCharacteristicNotification(characteristic, enabled);
BluetoothGattDescriptor descriptor = characteristic.getDescriptor(UUID
.fromString(SampleGattAttributes.CLIENT_CHARACTERISTIC_CONFIG));
if (descriptor != null) {
System.out.println("write descriptor");
descriptor.setValue(BluetoothGattDescriptor.ENABLE_NOTIFICATION_VALUE);
mBluetoothGatt.writeDescriptor(descriptor);
}
}public void readCharacteristic(BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) { //可读的UUID
if (mBluetoothAdapter == null || mBluetoothGatt == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "BluetoothAdapter not initialized");
return;
}
mBluetoothGatt.readCharacteristic(characteristic);
}public void wirteCharacteristic(BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic) { //可写的UUID
if (mBluetoothAdapter == null || mBluetoothGatt == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "BluetoothAdapter not initialized");
return;
}
mBluetoothGatt.writeCharacteristic(characteristic);
}4.3:针对读的操作在加深一下理解:请看
/***读操作***/ void readBatrery(){ //如上面所说,想要和一个学生通信,先知道他的班级(ServiceUUID)和学号(CharacUUID)BluetoothGattService batteryService=mBluetoothGatt.getService(UUID.fromString("0000180f-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb")); if(batteryService!=null){//此处的0000180f...是举例,实际开发需要询问硬件那边
BluetoothGattCharacteristic batteryCharacteristic=batteryService.getCharacteristic(UUID.fromString("00002a19-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb")); if(batteryCharacteristic!=null){//此处的00002a19...是举例,实际开发需要询问硬件那边
mBluetoothGatt.readCharacteristic(batteryCharacteristic); } } }//如果读取电量(或者读取其他值)成功之后 ,会来到 回调: @Override public void onCharacteristicRead(BluetoothGatt gatt,BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) { super.onCharacteristicRead(gatt, characteristic, status); //读取到值,根据UUID来判断读到的是什么值 if (characteristic.getUuid().toString() .equals("00002a19-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb")) {// 获取到电量 int battery = characteristic.getValue()[0]; } } /***写操作***/ void sendSetting(){//读取电量, 这是读取batteryCharacteristic值的方法,读取其他的值也是如此,只是它们的ServiceUUID 和CharacUUID不一样BluetoothGattService sendService=mBluetoothGatt.getService(UUID.fromString("00001805-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb")); if(sendService!=null){//此处的00001805...是举例,实际开发需要询问硬件那边
BluetoothGattCharacteristic sendCharacteristic=sendService.getCharacteristic(UUID.fromString("00002a08-0000-1000-8000-00805f9b34fb")); if(sendCharacteristic!=null){ sendCharacteristic.setValue(new byte[] { 0x01,0x20,0x03 });//随便举个数据 mBluetoothGatt.writeCharacteristic(sendCharacteristic);//写命令到设备, } } } //如果下发配置成功之后,会来到回调: @Override public void onCharacteristicWrite(BluetoothGatt gatt,BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic, int status) { super.onCharacteristicWrite(gatt, characteristic, status); if (status == BluetoothGatt.GATT_SUCCESS) {//write成功(发送值成功),可以根据 characteristic.getValue()来判断是哪个值发送成功了,比如 连接上设备之后你有一大串命令需要下发,你调用多次写命令,//此处的00002a08...是举例,实际开发需要询问硬件那边
这样你需要判断是不是所有命令都成功了,因为android不太稳定,有必要来check命令是否成功,否则你会发现你明明调用 写命令,但是设备那边不响应 } } 第四步:主要的相关的代码如上,具体的实现就没有直接展示了。敬请原谅!谢谢!
本人也是第一次操作蓝牙这一块,期间看了很多的博客,很有帮助,推荐给大家(链接),也可以自己去查资料。
MODBUS协议 一种问答方式的通信协议
Android BLE开发之Android手机与BLE终端通信
串口:使用的demo,app和蓝牙交互与串口交互:(有需要可以找我接收)









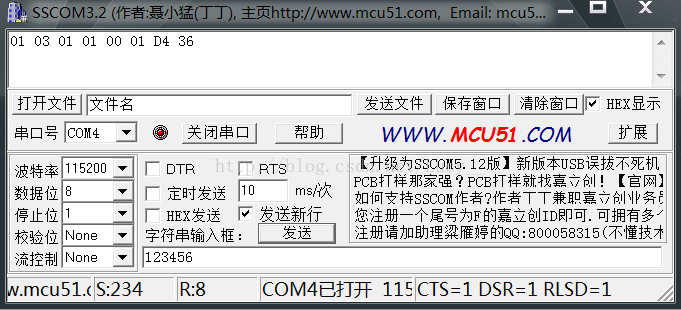
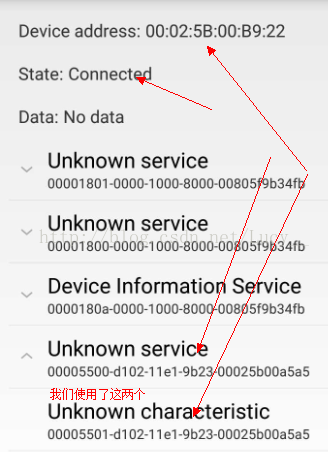














 2736
2736

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








