一个简易版支付路由实现
By 马冬亮(凝霜 Loki)
一个人的战争(http://blog.csdn.net/MDL13412)
缘起
今天跟小伙伴晚上出去吃饭,聊到:假如用户选着工行支付,总共有1000单,其中300单给财付通,100 单给百付宝,600给支付宝(支付渠道)
算法设计
我们先看一种简单的情况:取一个大小为1000的数组,其中[0-300)分配给财富通,[300,400)分配给百付宝,[400,1000)分配给支付宝(当然可以约分后再计算,这里为了清晰,不进行约分),如下图所示:
对于这个数组,我们将对应区间内的内容填充为相应支付渠道的引用,使用一个计数器,每次有支付请求到来时,就将计数器加1并对1000取余,并用这个计数器去引用数组中的支付渠道,就可以按比例分配的目的。
这个算法的一些弊端:
- 支付渠道分配不均匀,一段时间内的请求,都会是某个支付渠道;
- 动态添加、删除支付渠道困难;
- 动态改变支付渠道所占比例困难;
- 在支付路由集群中,会造成比例不稳定;
下面我们对这一算法进行改进:
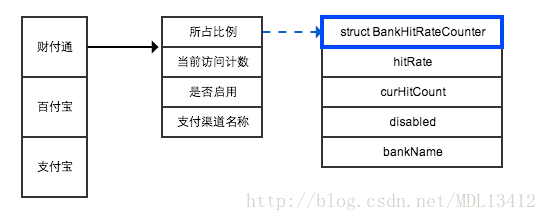
按照支付渠道的数量开一个数组,里面维护一些计算比例的基本信息,如下图所示:
这次,计数器在支付渠道之间自增、取余,而对应的支付渠道,利用hitRate和curHitCount两个变量来模拟上一个算法中区间的比例;
例如,当前有1001次支付请求:
第1次,选择财付通渠道,对应的财付通渠道curHitCount加1,其值小于对应的hitRate,因此可以选择;
第2次,选择百付宝渠道,符合条件,选取;
第3次,选择支付宝渠道,符合条件,选取;
第4次,选择财付通渠道,符合条件,选取;
第5次,选择百付宝渠道,符合条件,选取;
......
第300次,选择支付宝渠道,符合条件,选取;
第301次,选择百付宝渠道,因为此时其curHitCount = 100,大于等于其hitRate,按照其权重,其不再进行分配,选择下一渠道支付宝,符合条件,选取;
第302次,因为上次百付宝选取失败,选择了支付宝,因此这次计数器取余后的结果为0,因此选取财付通渠道,符合条件,选取;
第303次,选择百付宝渠道,同样因为权重问题,跳过,选择下一渠道支付宝,符合条件,选取;
....
在700次请求后,财付通渠道的权重用完,因此后续的300次支付全部使用支付宝渠道;
第1001次,因为所有支付渠道权重全部用完,因此需要重置个系统的curHitCount,开始新一轮的分配。
实现
为了让算法更清晰,去掉了各种校验以及多线程的处理,让读者更容易理解。
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
#include <utility>
#include <list>
#include <vector>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
class BankRouter
{
typedef map<string, int> BankHistRateIndexMapping_t;
struct BankHitRateCounter
{
BankHitRateCounter(const string name, const unsigned int rate) :
hitRate(rate),
curHitCount(0),
disabled(false),
bankName(name)
{
}
unsigned int hitRate;
unsigned int curHitCount;
bool disabled;
const string bankName;
};
typedef vector<BankHitRateCounter> BankRateArray_t;
public:
typedef pair<string, unsigned int> BankHitRate_t;
public:
BankRouter(list<BankHitRate_t> bankHitRate)
{
int index = 0;
for (list<BankHitRate_t>::const_iterator iter = bankHitRate.begin();
bankHitRate.end() != iter; ++iter) {
// 去重、校验等逻辑省略...
bankRateArray_.push_back(
BankHitRateCounter(iter->first, iter->second));
bankRateMapping_[iter->first] = index++;
}
bankRateLength_ = bankRateArray_.size();
}
virtual ~BankRouter()
{
}
string nextBank()
{
if (curBankPtr_ >= bankRateLength_) {
curBankPtr_ = 0;
}
int curBankPtrBk = curBankPtr_;
bool flag = false;
while (true) {
if (curBankPtr_ >= bankRateLength_) {
curBankPtr_ = 0;
flag = true;
}
// 如果遍历一遍还没有合适的银行可供选择,则说明所有银行均不可用
// 或者计数器已满,需要重置
if (curBankPtrBk == curBankPtr_ && flag) {
// 检测是否全部为disabled,防止死循环,略...
resetBankRateArray();
curBankPtr_ = 0;
curBankPtrBk = 0;
flag = false;
}
if (bankRateArray_[curBankPtr_].disabled) {
++curBankPtr_;
} else {
if (++bankRateArray_[curBankPtr_].curHitCount <=
bankRateArray_[curBankPtr_].hitRate) {
return bankRateArray_[curBankPtr_++].bankName;
} else {
++curBankPtr_;
}
}
}
}
void enableBank(string bankName)
{
bankRateArray_[bankRateMapping_[bankName]].disabled = false;
}
void dienableBank(string bankName)
{
bankRateArray_[bankRateMapping_[bankName]].disabled = true;
}
private:
void resetBankRateArray()
{
for (BankRateArray_t::iterator iter = bankRateArray_.begin();
bankRateArray_.end() != iter; ++iter) {
iter->curHitCount = 0;
}
}
private:
BankRouter(const BankRouter &);
BankRouter &operator =(const BankRouter &);
private:
BankRateArray_t bankRateArray_;
int curBankPtr_;
int bankRateLength_;
BankHistRateIndexMapping_t bankRateMapping_;
};
void test(BankRouter &br, const int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cout << br.nextBank() << endl;
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
list<BankRouter::BankHitRate_t> l;
l.push_back(make_pair("cft", 3));
l.push_back(make_pair("bfb", 1));
l.push_back(make_pair("zfb", 6));
BankRouter br(l);
test(br, 20);
cout << "--------------------" << endl;
br.dienableBank("cft");
test(br, 14);
cout << "--------------------" << endl;
br.enableBank("cft");
test(br, 20);
return 0;
}运行结果(大家可以观察支付渠道的切换):
cft
bfb
zfb
cft
zfb
cft
zfb
zfb
zfb
zfb
cft
bfb
zfb
cft
zfb
cft
zfb
zfb
zfb
zfb
--------------------
bfb
zfb
zfb
zfb
zfb
zfb
zfb
bfb
zfb
zfb
zfb
zfb
zfb
zfb
--------------------
cft
cft
cft
cft
bfb
zfb
cft
zfb
cft
zfb
zfb
zfb
zfb
cft
bfb
zfb
cft
zfb
cft
zfb
























 1004
1004

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








