项目要点
- 图片读取 : img = cv2.imread('./images/test_01.png')
- 灰度图: gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
- 高斯模糊: blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0) # 去噪点
- 边缘检测: edged = cv2.Canny(blurred, 75, 200)
- 检测轮廓: cnts = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[-2] # 两个返回值 contours, hierarchy
- 描绘轮廓: cv2.drawContours(contours_img, cnts, -1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
- 轮廓面积排序: cnts = sorted(cnts, key = cv2.contourArea, reverse = True)
- 计算轮廓周长: perimeter = cv2.arcLength(c, True)
- 得到近似轮廓: approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.15 * perimeter, True)
- 计算变换矩阵: M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect, dst) # dst 为目标值
- 通过坐标透视变换转换: warped = cv2.warpPerspective(image,M,(max_width, max_height)) # 注意传参
- ret, thresh1 = cv2.threshold(img,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU) 二值化处理图片
- 计算非零个数, 先做与运算: mask = cv2.bitwise_and(thresh, thresh, mask = mask)
- 计算非零个数,选中的选项, 非零个数比较多: total = cv2.countNonZero(mask)
- 画出正确选项: cv2.drawContours(warped, [cnts[k]], -1, color, 3)
- cv2.putText(warped, f'{score:.2f}',(210,36), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,0.9, (0,0,255), 2) # 在图片上体现分数
- 显示图片: cv2.imshow(name, img)
1 提取答题卡部分图像内容
1.1 读取图片
- 定义显示函数
def cv_show(name, img):
cv2.imshow(name, img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()import cv2
import numpy as np
# 读图片,预处理
img = cv2.imread('./images/test_01.png')
# 转变为黑白图
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv_show('img', img)
1.2 边缘检测
- 定义显示函数
# 高斯模糊去噪点
blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
# 边缘检测
edged = cv2.Canny(blurred, 75, 200)
cv_show('img', edged)
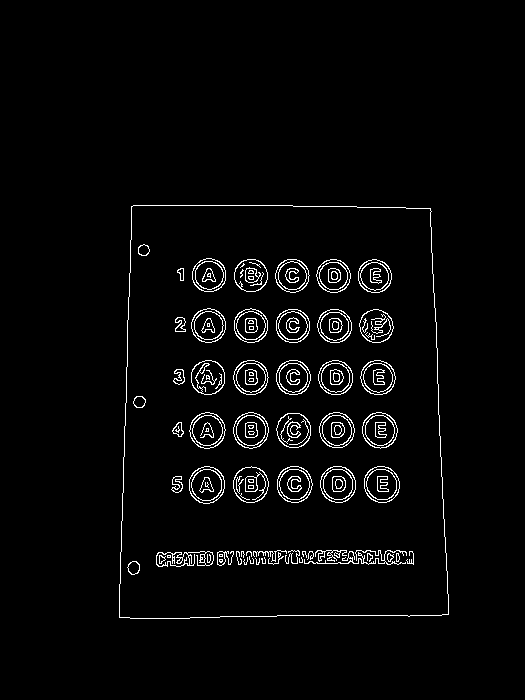
1.3 检测轮廓
# 检测轮廓
cnts = cv2.findContours(edged.copy(), cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[-2]
# 画轮廓会修改原图
contours_img = img.copy()
cv2.drawContours(contours_img, cnts, -1, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv_show('contours_img', contours_img)
1.4 找出答题卡轮廓
-
本次其实原本也只检测到了一个轮廓.
# 确保拿到的轮廓是答题卡的轮廓
if cnts:
# 对轮廓面积排序
cnts = sorted(cnts, key = cv2.contourArea, reverse = True)
# 遍历每一个轮廓
for c in cnts:
# 计算周长
perimeter = cv2.arcLength(c, True)
# 得到近似轮廓
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.15 * perimeter, True)
# 应该只剩下四个角的坐标
print(len(c))
print(len(approx))
if len(approx) == 4:
# 保存approx
docCnt = approx
# 找到后直接退出
break
print(docCnt)
contours_img = img.copy()
cv2.drawContours(contours_img, docCnt, -1, (0, 0, 255), 10)
cv_show('contours_img', contours_img)

1.5 透视变换
# 找到进行透视变换的点
# 要求变换矩形的四个坐标
# 先对获取到的4个角点坐标排序
# 排序功能封装为一个函数
def order_points(pts):
# 创建全为0 的矩阵, 来接收找到的坐标
rect = np.zeros((4, 2), dtype = 'float32')
s = pts.sum(axis = 1)
# 左上角的坐标一定是X,Y相加最小的,右下为最大的
rect[0] = pts[np.argmin(s)]
rect[2] = pts[np.argmax(s)]
# 右上角的x,y 相减的差值一定是最小的
# 左下角的x,y 相减,差值一定是最大的
diff = np.diff(pts, axis = 1)
rect[1] = pts[np.argmin(diff)]
rect[3] = pts[np.argmax(diff)]
return rect# 把透视变换功能封装为一个函数
def four_point_transform(image, pts):
# 对输入的四个坐标排序
rect = order_points(pts) # 调取函数: order_points
(tl, tr, br, bl) = rect
# 空间中两点的距离
widthA = np.sqrt((br[0] - bl[0])** 2 + (br[1] - bl[1]) ** 2)
widthB = np.sqrt((tr[0] - tl[0])** 2 + (tr[1] - tl[1]) ** 2)
max_width = max(int(widthA), int(widthB))
heightA = np.sqrt((tr[0] - br[0])** 2 + (tr[1] - br[1]) ** 2)
heightB = np.sqrt((tl[0] - bl[0])** 2 + (tl[1] - bl[1]) ** 2)
max_wdith = (int(widthA), int(widthB))
max_height =max(int(heightA), int(heightB))
# 构造变换后的空间坐标
dst = np.array([
[0, 0],
[max_width - 1, 0],
[max_width - 1, max_height -1],
[0, max_height - 1]], dtype = 'float32')
# 计算变换矩阵
M = cv2.getPerspectiveTransform(rect, dst) # dst 为目标值
# 透视变换
warped = cv2.warpPerspective(image, M, (max_width, max_height)) # 注意传参
return warped
# 进行透视变换
warped = four_point_transform(gray, docCnt.reshape(4, 2))
cv_show('warped', warped)
2 处理答题卡
2.1 二值化图像 (两个返回值)
# 二值化 # +inv 黑白颠倒
# ret, thresh1 = cv2.threshold(img,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)
thresh = cv2.threshold(warped, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV | cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
cv_show('thresh', thresh)
2.2 找每一个圆圈的轮廓
# 找每一个圆圈的轮廓
cnts = cv2.findContours(thresh, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)[0]
thresh_contours = thresh.copy()
cv2.drawContours(thresh_contours, cnts, -1, 255, 3) # 255表示填充白色,填充为0时为后图
cv_show('thresh_contours', thresh_contours)

2.3 找出特定轮廓 (选项)
# 遍历所有轮廓, 找到特点宽高和特定比例的轮廓, 及圆圈的轮廓
question_cnts = []
for c in cnts:
# 找到轮廓的外接矩形
(x, y, w, h) = cv2.boundingRect(c)
# 计算高宽比
ar = w / float(h)
# 根据实际情况制定标准
if w >= 20 and h >= 20 and ar >= 0.9 and ar <= 1.1:
question_cnts.append(c)
print(len(question_cnts)) # 253 分数判定
3.1 轮廓排序封装函数
# 设计做法看轮廓,找出选择的答案
# 轮廓排序封装函数
def sort_contours(cnts, method = 'left-to-right'):
reverse = False
# 排序的时候取x轴数据, i= 0, 取y轴数据 i=1
i = 0
if method == 'right-to-left' or method == 'bottom-to-top':
reverse = True
if method == 'top-to-bottom' or method == 'bottom-to-top':
i = 1
# 计算每个轮廓的外接矩形
bounding_boxes = [cv2.boundingRect(c) for c in cnts]
# 计算轮廓的垂直边界最小矩形,矩形是与图像上下边界平行的
(cnts, bounding_boxes) = zip(*sorted(zip(cnts, bounding_boxes),
key = lambda a: a[1][i], reverse = reverse))
# a 表示zip(cnt, bounding_boxes)
# rint(bounding_boxes[1])
return cnts, bounding_boxes
# 按照从上到下的排序 :question_cnts
question_cnts = sort_contours(question_cnts, method = 'top-to-bottom')[0]
print(len(question_cnts)) # 253.2 找出选择答案, 然后评分
# 正确答案
ANSWER_KEY = {0:1, 1:2, 2:1, 3:2, 4:1} # 1,4,0,2,1
correct = 0
# enumerate,遍历了所有元素,并从零开始的计为每个元素生成索引, q为index
for (q, i) in enumerate(np.arange(0, 25, 5)):
first_num = True
# 每次取出5个,再按x大小排序
# 每5个一组进行排序, 0表示cnts 原轮廓, 默认排序'left-to-right'
cnts = sort_contours(question_cnts[i: i+ 5])[0]
print('-------------------', len(cnts)) # 5个选项
bubbled = None # 冒泡
# 遍历每一个结果
for (j, c) in enumerate(cnts):
#使用掩膜,即mask
mask = np.zeros(thresh.shape, dtype = 'uint8')
cv2.drawContours(mask, [c], -1, 255, -1) # 255表示填充白色
# 计算非零个数, 先做与运算
mask = cv2.bitwise_and(thresh, thresh, mask = mask)
# cv_show('mask', mask)
# 计算非零个数,选中的选项, 非零个数比较多, 没选中的非零个数小一些
total = cv2.countNonZero(mask)
# print('******', total,j)
if bubbled is None or total > bubbled[0]:
bubbled = (total, j) # 正确选项的 total 值较高
color = (0, 0 ,255)
k = ANSWER_KEY[q] # enumerate 的序列值
# print(len(cnts))
# 判断是否正确
if k == bubbled[1] and first_num == True:
correct += 1
first_num = False
print('正确选项: ',k)
cv2.drawContours(warped, [cnts[k]], -1, color, 3) # 画出正确选项
# 计算得分
score = int((correct / 5)* 100)
print(f'score:{score:.2f} 分')
warped_copy = warped.copy()
cv2.putText(warped_copy, f'{score:.2f}', (210, 36), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
0.9, (0, 0, 255), 2)
cv_show('result', warped_copy)





















 6902
6902











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








