信号量值是一个计数器,用于控制多进程对共享资源的访问;进程获取共享资源需要以下步骤:
1.检查资源的信号量值
2.如果信号量值是正,进程可以访问资源;进程将信号量值减1,表示进程已经使用了一个资源
3.如果信号量值是0,进程被阻塞直到信号量值大于0;被阻塞进程被唤醒时重复执行步骤1
注:检查信号量值和减1必须为原子操作
SysV信号量有以下特征:
1.信号量是一个信号量值集合,在创建信号量时指定信号量值个数;由于存在多个信号量值,所以操作信号量时必须是原子操作;
2.SysV IPC在没有进程使用时依然存在,所以要考虑在进程退出时归还进程获得的信号量值;
3.当信号量值不满足要求时,必须阻塞进程;当信号量满足要求时,唤醒被阻塞的进程
I.数据结构
i.信号量(信号量值集合)
include/linux/sem.h
85 /* One semaphore structure for each semaphore in the system. */
86 struct sem {
87 int semval; /* current value */
88 int sempid; /* pid of last operation */
89 };
90
91 /* One sem_array data structure for each set of semaphores in the system. */
92 struct sem_array {
93 struct kern_ipc_perm sem_perm; /* permissions .. see ipc.h */
94 time_t sem_otime; /* last semop time */
95 time_t sem_ctime; /* last change time */
96 struct sem *sem_base; /* ptr to first semaphore in array */
97 struct list_head sem_pending; /* pending operations to be processed */
98 struct list_head list_id; /* undo requests on this array */
99 unsigned long sem_nsems; /* no. of semaphores in array */
100 };
ii.信号量阻塞进程队列
/* semop system calls takes an array of these. */
struct sembuf {
unsigned short sem_num; /* semaphore index in array */
short sem_op; /* semaphore operation */
short sem_flg; /* operation flags */
};
102 /* One queue for each sleeping process in the system. */
103 struct sem_queue {
104 struct list_head list; /* queue of pending operations */
105 struct task_struct *sleeper; /* this process */
106 struct sem_undo *undo; /* undo structure */
107 int pid; /* process id of requesting process */
108 int status; /* completion status of operation */
109 struct sembuf *sops; /* array of pending operations */
110 int nsops; /* number of operations */
111 int alter; /* does the operation alter the array? */
112 };
iii.进程信号量UNDO队列(用于进程退出时归还获取的信号量值)
114 /* Each task has a list of undo requests. They are executed automatically
115 * when the process exits.
116 */
117 struct sem_undo {
118 struct list_head list_proc; /* per-process list: all undos from one process. */
119 /* rcu protected */
120 struct rcu_head rcu; /* rcu struct for sem_undo() */
121 struct sem_undo_list *ulp; /* sem_undo_list for the process */
122 struct list_head list_id; /* per semaphore array list: all undos for one array */
123 int semid; /* semaphore set identifier */
124 short * semadj; /* array of adjustments, one per semaphore */
125 };
126
127 /* sem_undo_list controls shared access to the list of sem_undo structures
128 * that may be shared among all a CLONE_SYSVSEM task group.
129 */
130 struct sem_undo_list {
131 atomic_t refcnt;
132 spinlock_t lock;
133 struct list_head list_proc;
134 };
135
136 struct sysv_sem {
137 struct sem_undo_list *undo_list;
138 };
include/linux/sched.h
1217 struct task_struct {
1364 struct sysv_sem sysvsem;
1543 };
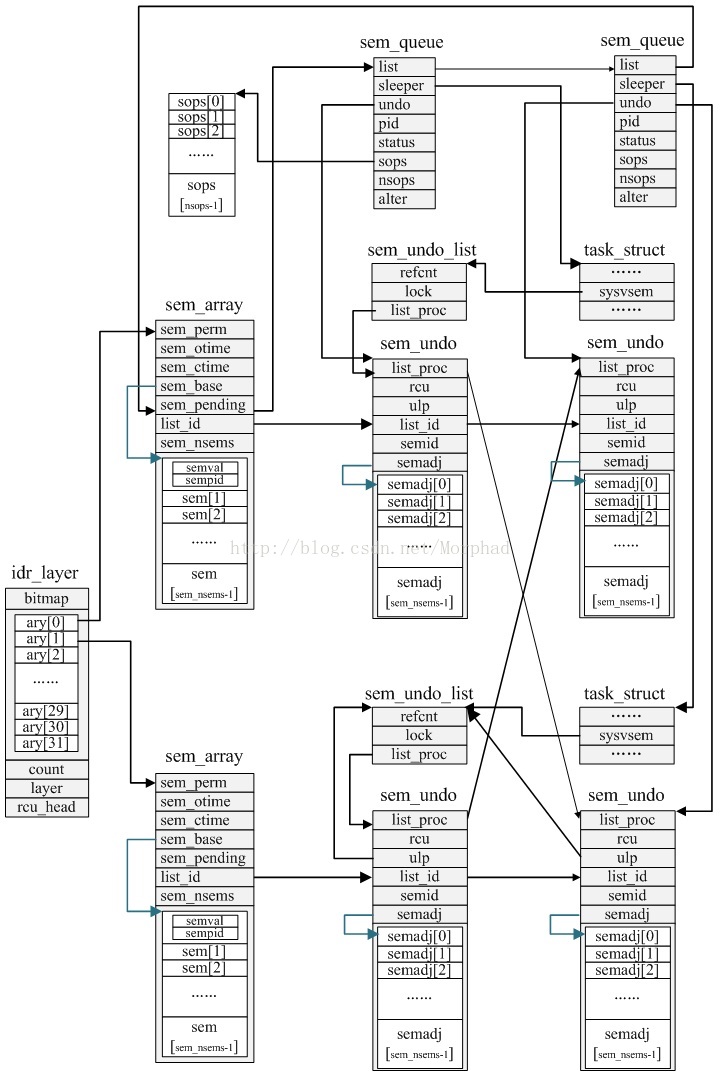
iv.结构之间关系
上述结构之间关系如下图:
II.信号量创建
信号量由newary来创建:
227 /**
228 * newary - Create a new semaphore set
229 * @ns: namespace
230 * @params: ptr to the structure that contains key, semflg and nsems
231 *
232 * Called with sem_ids.rw_mutex held (as a writer)
233 */
234
235 static int newary(struct ipc_namespace *ns, struct ipc_params *params)
236 {
237 int id;
238 int retval;
239 struct sem_array *sma;
240 int size;
241 key_t key = params->key;
242 int nsems = params->u.nsems;
243 int semflg = params->flg;
244
245 if (!nsems)
246 return -EINVAL;
247 if (ns->used_sems + nsems > ns->sc_semmns)
248 return -ENOSPC;
249
250 size = sizeof (*sma) + nsems * sizeof (struct sem);
251 sma = ipc_rcu_alloc(size);
252 if (!sma) {
253 return -ENOMEM;
254 }
255 memset (sma, 0, size);
256
257 sma->sem_perm.mode = (semflg & S_IRWXUGO);
258 sma->sem_perm.key = key;
259
260 sma->sem_perm.security = NULL;
261 retval = security_sem_alloc(sma);
262 if (retval) {
263 ipc_rcu_putref(sma);
264 return retval;
265 }
266
267 id = ipc_addid(&sem_ids(ns), &sma->sem_perm, ns->sc_semmni);
268 if (id < 0) {
269 security_sem_free(sma);
270 ipc_rcu_putref(sma);
271 return id;
272 }
273 ns->used_sems += nsems;
274
275 sma->sem_base = (struct sem *) &sma[1];
276 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&sma->sem_pending);
277 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&sma->list_id);
278 sma->sem_nsems = nsems;
279 sma->sem_ctime = get_seconds();
280 sem_unlock(sma);
281
282 return sma->sem_perm.id;
283 }1.参数“信号量值个数”合法性校验,及系统允许信号量值个数检验
2.分配信号量结构(包括信号量值集合),并初始化(信号量等待队列、undo队列置空,信号量创建时间等)
3.将信号量添加到信号量基数树中,并返回基数树id
III.信号量操作
i.原子操作try_atomic_semop
334 /*
335 * Determine whether a sequence of semaphore operations would succeed
336 * all at once. Return 0 if yes, 







 本文详细介绍了Linux SysV IPC中的信号量机制,包括信号量的用途、操作步骤、特征,以及信号量创建、操作、撤销的过程。重点讨论了信号量的原子操作、阻塞与唤醒机制,以及进程退出时的信号量值归还策略。
本文详细介绍了Linux SysV IPC中的信号量机制,包括信号量的用途、操作步骤、特征,以及信号量创建、操作、撤销的过程。重点讨论了信号量的原子操作、阻塞与唤醒机制,以及进程退出时的信号量值归还策略。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章















 786
786

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








