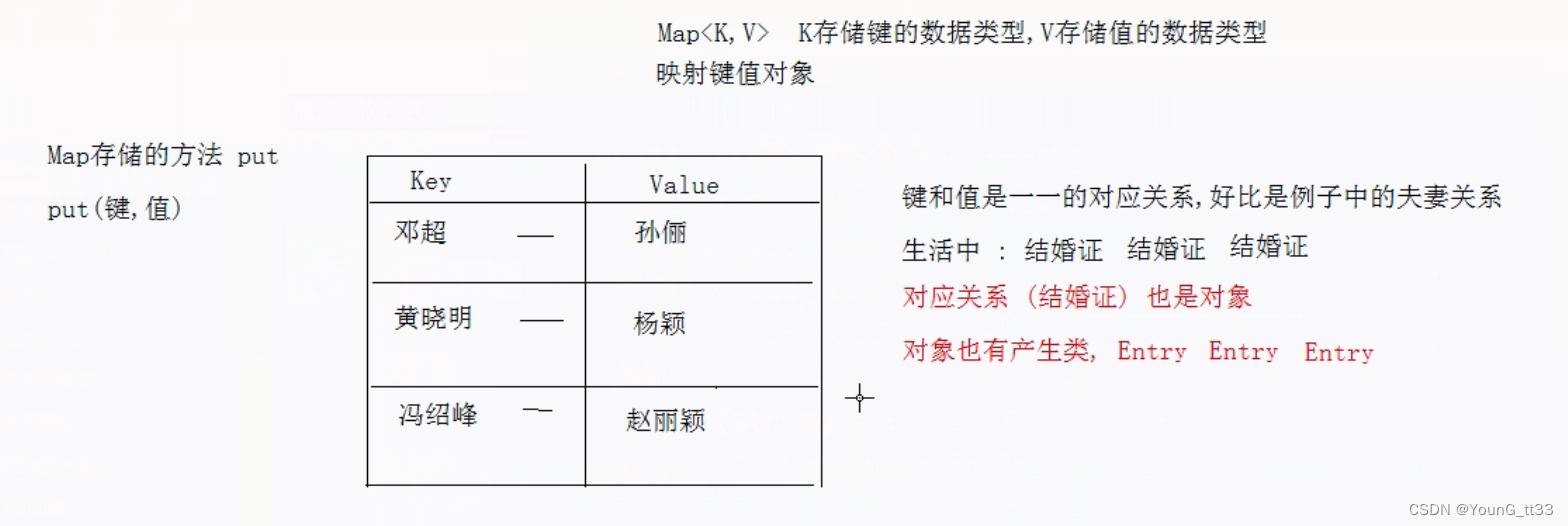
java.util.Map接口,是双列集合的顶级接口. Map与Collection<E>没关系
Map集合容器每次存储2个对象,一个对象称为键(Key),一个对象称为值(Value)
在一个Map的集合容器中,键保证唯一性,不包含重复键,每个键只能对应一个值
1 Map接口方法
-
V put(K,V)存储键值对,存储重复键,返回被覆盖之前的值,若没被覆盖返回null
/**
* put方法,存储键值对
* Map接口的实现类HashMap
*/
public static void mapPut(){
//创建对象,指定键的数据类型,值的数据
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("a",1);
map.put("b",2);
map.put("c",3);
map.put("d",4);
Integer value = map.put("c",5);
System.out.println("map = " + map);
System.out.println("value = " + value);
}-
V get(K)通过键获取值,参数传递键,找这个键对应的值,没有这个键返回null
/**
* V get(K)通过键获取值,参数传递键,找这个键对应的值,没有这个键返回null
*/
public static void mapGet(){
//创建对象,指定键的数据类型,值的数据
Map<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("a",1);
map.put("b",2);
map.put("c",3);
map.put("d",4);
//键找值
Integer value = map.get("f");
System.out.println(value);
}-
boolean containsKey(K)判断集合是否包含这个键,包含返回true
-
boolean containsValue(V)判断集合是否包含这个值,包含返回true
-
int size() 返回集合长度,Map集合中键值对的个数
-
V remove(K)移除指定的键值对,返回被移除之前的值
-
Collection<V> values() Map集合中的所有的值拿出,存储到Collection集合
/*boolean containsKey(K)判断集合是否包含这个键,包含返回true
- boolean containsValue(V)判断集合是否包含这个值,包含返回true
- int size() 返回集合长度,Map集合中键值对的个数
- V remove(K)移除指定的键值对,返回被移除之前的值
- Collection<V> values() Map集合中的所有的值拿出,存储到Collection集合
*/
public static void mapMethod(){
//创建集合,键是整数,值是String
Map<Integer,String> map = new HashMap<Integer, String>();
map.put(1,"a");
map.put(2,"b");
map.put(3,"c");
map.put(4,"d");
map.put(5,"e");
//boolean containsKey(K)判断集合是否包含这个键,包含返回true
boolean b = map.containsKey(1);
System.out.println("集合中包含键:"+b);
//boolean containsValue(V)判断集合是否包含这个值,包含返回true
b = map.containsValue("c");
System.out.println("集合中包含值:"+b);
//size()返回集合的长度
int size = map.size();
System.out.println("集合长度:"+size);
//V remove(K)移除指定的键值对,返回被移除之前的值
String value = map.remove(1);
System.out.println("被删除之前的:"+value);
System.out.println(map);
//Collection<V> values() Map集合中的所有的值拿出,存储到Collection集合
Collection<String> coll = map.values();
for(String s : coll){
System.out.println(s);
}
}2 Map集合的遍历-键找值
-
实现思想 :
-
Map接口定义了方法 keySet() 所有的键,存储到Set集合
-
遍历Set集合
-
取出Set集合元素 Set集合的元素是Map集合的键
-
Map集合方法get()传递键获取值
-
/**
* - Map接口定义了方法 keySet() 所有的键,存储到Set集合
* - 遍历Set集合
* - 取出Set集合元素 **Set集合的元素是Map集合的键**
* - Map集合方法get()传递键获取值
*/
public static void mapKeySet(){
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("a","java");
map.put("b","c++");
map.put("c","php");
map.put("d","python");
map.put("e","erlang");
//Map接口定义了方法 keySet() 所有的键,存储到Set集合
Set<String> set = map.keySet();
//遍历Set集合
Iterator<String> it = set.iterator();
//取出Set集合元素 **Set集合的元素是Map集合的键**
while (it.hasNext()){
String key = it.next();
//Map集合方法get()传递键获取值
String value = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"==="+value);
}
}
3 Map集合的遍历-键值对映射关系
-
实现思想 :
-
Map接口的方法 Set< Map.Entry<Key,Value> > entrySet()
-
方法返回Set集合,集合中存储的元素,比较特别
-
存储的是Map集合中,键值对映射关系的对象 , 内部接口 Map.Entry
-
-
遍历Set集合
-
取出Set集合的元素
-
是Map.Entry接口对象(实现类)
-
接口的对象方法: getKey() ,getValue()
-
-
public static void mapEntrySet(){
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String, String>();
map.put("a","java");
map.put("b","c++");
map.put("c","php");
map.put("d","python");
map.put("e","erlang");
//Map接口的方法 Set< Map.Entry<Key,Value> > entrySet()
Set<Map.Entry<String,String>> set = map.entrySet();
//- 遍历Set集合
Iterator<Map.Entry<String,String>> it = set.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
//取出Set集合的元素
Map.Entry<String,String> entry = it.next();
//- 接口的对象方法: getKey() ,getValue()
String key = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key +"==="+ value);
}
}4 HashMap
-
HashMap集合特点
-
是哈希表结构
-
保证键唯一性,用于键的对象,必须重写hashCode,equals方法
-
线程不安全集合,运行速度快
-
集合运行使用null,作为键或者值
-
/**
* HashMap集合
* 键是Person,值是String
*/
public static void hashMap2(){
Map<Person,String> map = new HashMap<Person, String>();
map.put(new Person("a",20),"广东");
map.put(new Person("b",22),"香港");
map.put(new Person("b",22),"贵港");
map.put(new Person("c",24),"澳门");
map.put(new Person("d",26),"深圳");
System.out.println("map = " + map);
}
/**
* HashMap集合
* 键是字符串,值是Person
*/
public static void hashMap1(){
Map<String, Person> map = new HashMap<String, Person>();
map.put("a",new Person("张三",20));
map.put("b",new Person("张三",20));
map.put("c",new Person("张三",20));
map.put(null,null);
//Set<String> set = map.keySet();
for(String key : map.keySet()){
//Person person = map.get(key);
System.out.println(key+"==="+map.get(key));
}
System.out.println("==============");
//Set<Map.Entry<String,Person>> set = map.entrySet();
for(Map.Entry<String,Person> entry : map.entrySet()){
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+"==="+entry.getValue());
}5 LinkedHashMap
LinkedHashMap继承HashMap实现Map接口,LinkedHashMap底层实现原理是哈希表,双向链,存取有序. 其它的特性和父类HashMap一样.
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map<String,String> map = new LinkedHashMap<String, String>();
map.put("aa","qq");
map.put("123","qq");
map.put("bbb","qq");
System.out.println(map);
}//怎么存怎么取6 Hashtable集合类
Map接口的实现类Hashtable, Hashtable类诞生于JDK1.0版本, Map接口诞生于JDK1.2版本. Hashtable类从JDK1.2开始,改进为实现Map接口
-
Hashtable类的特点
-
底层数据结构是哈希表
-
线程安全的,运行速度慢,被更加先进的HashMap取代
-
不允许null值,null键, 存储null直接抛出空指针异常
-
7 Vector集合类
List接口的实现Vector,命运和Hashtable一样.
-
Vector类的特点
-
底层实现结构是数组
-
数组的默认容量是10,每次扩容是原来的长度*2
-
线程安全,运行速度慢,被ArrayList取代
-
8. TreeMap集合
-
TreeMap集合的特点
-
底层实现是红黑树结构 (添加查询速度比较快)
-
存储到TreeMap中元素,对键进行排序
-
排序依据 :
-
对象的自然顺序,作为键的对象,实现了接口Comparable
-
自己提供比较器,实现接口Comparator,优先级高
-
-
线程不安全的,运行速度快
-
/**
* TreeMap集合存储对象
* Student作为键,字符串是值
* 自定义的比较器排序
*/
public static void treeMap2(){
Map<Student,String> map = new TreeMap<Student, String>( new MyCom() );
map.put(new Student("a",20),"广东");
map.put(new Student("b",19),"广西");
System.out.println("map = " + map);
}
/**
* TreeMap集合存储对象
* Person作为键,字符串是值
*/
public static void treeMap1(){
Map<Person,String> map = new TreeMap<Person, String>();
map.put(new Person("a",20),"广东");
map.put(new Person("b",19),"广西");
System.out.println("map = " + map);
}/**
* 自定义的比较器,实现接口 Comparator
*/
class MyCom implements Comparator<Student>{
/**
* 方法compare 是TreeMap调用
* 传递参数,后来的对象传递到s1, 已经有的对象传递到s2
*/
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2){
return s1.getAge() - s2.getAge();
}
} /**
* 进行比较:
* compareTo方法由,集合TreeMap调用
* 传递相关的参数 集合中后来的对象是this,先来的对象是参数 p
*/
public int compareTo(Person p){
return this.age - p.age;
}9. Properties
-
Properties集合特点
-
继承Hashtable,实现Map接口
-
底层是哈希表结构
-
线程是安全的,运行速度慢
-
集合没有泛型的写法,键和值的数据类型锁定为String类型
-
集合有自己的特有方法
-
此集合可以和IO流对象结合使用,实现数据的持久存储
-
方法和IO相关 : load(输入流)
-
/**
* 集合遍历
* Properties类的方法 stringPropertyNames() [等效于map.keySet()] 返回Set集合
* Set集合存储的是 Properties集合的所有键
*/
public static void prop3(){
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty("a","1");
prop.setProperty("b","2");
prop.setProperty("c","3");
Set<String> set = prop.stringPropertyNames();
for(String key : set){
System.out.println(key +"=="+ prop.getProperty(key));
}
}
/**
* 集合取出元素
* Properties集合取出方法 getProperty(String key)
*/
public static void prop2(){
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty("a","1");
prop.setProperty("b","2");
prop.setProperty("c","3");
System.out.println(prop);
String value = prop.getProperty("a");
System.out.println(value);
}
/**
* 集合存储键值对
* Map接口,存储方法put
* Properties集合存储方法 setProperty(String key,String value)
*/
public static void prop1(){
Properties prop = new Properties();
prop.setProperty("a","1");
prop.setProperty("b","2");
prop.setProperty("c","3");
System.out.println(prop);
}





















 584
584











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








