文章目录
Spring的事务传播行为
事务发生传播的前提是,至少有两个或两个以上的事务发生关联.
事务传播行为(propagation behavior) 指的就是当一个事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,这个事务方法应该如何进行。
事务传播行为是 Spring 框架独有的事务增强特性,是spring提供的事务增强功能;不属于数据库的行为.
比如说,开启了事务的方法A里面调用了具有事务的方法B;这时,方法B是直接在方法A内开启的事务执行;或者是方法B单独开启自己的单独事务执行,这个的话需要决定于方法B,要考虑到方法B使用了什么传播类型的事务.
| 事务传播行为类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|
PROPAGATION_REQUIRED | 如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务,如果已经存在一个事务中,加入到这个事务中。这是默认的事务传播行为。 |
PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS | 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。 |
PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW | 新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。 |
| PROPAGATION_MANDATORY | 使用当前的事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。 |
| PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED | 以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。 |
| PROPAGATION_NEVER | 以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。 |
| PROPAGATION_NESTED | 如果当前存在事务,则在嵌套事务内执行。如果当前没有事务,则执行与 PROPAGATION_REQUIRED 类似的操作。 |
这里案例的话,主要看看前三种事务传播行为;
案例搭建
这边的话,案例首先通用,这个案例的话就是在一个方法A中调用方法B
xml配置文件通用模板
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
</beans>
还有一点,上篇笔记中忘记补充了,实际的使用时,事务一般加在服务层的代码部分;
这里也就不整数据多的表了;就简简单单的两个数据表;一个字段名是namea,一个字段名是nameb
#测试使用的数据表1;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS t_testa(
`namea` VARCHAR(20)
);
#测试使用的数据表2;
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS t_testb(
`nameb` VARCHAR(20)
);
使用的maven包
<dependencies>
<!-- spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--junit测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.13</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- spring-jdbc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 阿里数据源 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql-context-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.22</version>
</dependency>
<!--aspectj-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId>
<version>5.2.2.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
database.properties
数据库连接池需要的属性参数
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/day20211024_study_mybatis_db?characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai
user=root
pwd=123456
initialSize = 5
maxActive = 10
spring-jdbc.xml
这里配置开启事务注解识别
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--标记开启注解扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.xiaozhi.spring">
</context:component-scan>
<!--配置引入数据源配置-->
<context:property-placeholder location="database.properties"/>
<!--创建连接池配置-->
<bean id="druidDataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${driver}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${pwd}"/>
<property name="initialSize" value="${initialSize}"/>
<property name="maxActive" value="${maxActive}"/>
</bean>
<!--配置JdbcTemplate 引用数据源-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务-->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="druidDataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!--开启事务自动配置-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>
</beans>
用于整合配置文件的spring.xml,这里案例暂时就引入一个spring-jdbc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--引入使用jdbc-->
<import resource="spring-jdbc.xml"></import>
</beans>
测试类1的数据访问层TestOneDao
/**
* @author by CSDN@小智RE0
* @date 2021-11-21 09:18
* 测试使用的数据访问类1;
*/
@Repository
public class TestOneDao {
//自动装配注入spring提供的jdbc;
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//这里定义一个方法A;
public void methodA(){
System.out.println("这是方法A的底层实现");
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into t_testa(namea) values ('阿杰')");
}
}
测试类2的数据访问层TestTwoDao
/**
* @author by CSDN@小智RE0
* @date 2021-11-21 09:19
* 测试使用的数据访问2
*/
@Repository
public class TestTwoDao {
//自动装配注入spring提供的jdbc;
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
//这里定义方法B;
public void methodB(){
System.out.println("这是方法B的底层实现");
jdbcTemplate.update("insert into t_testb(nameb) values ('小智')");
}
}
测试类2的服务层TestTwoService
/**
* @author by CSDN@小智RE0
* @date 2021-11-21 09:23
*测试使用的服务类2
*/
@Service(value = "testTwoService")
public class TestTwoService {
//自动装配测试类2的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestTwoDao testTwoDao;
//事务注解加载服务类的方法上;
@Transactional
public void methodB(){
testTwoDao.methodB();
}
}
测试类1的服务类TestOneService
在这里会用方法A调用测试类2的服务类方法B;
/**
* @author by CSDN@小智RE0
* @date 2021-11-21 09:23
* 测试使用的服务类1
*/
@Service(value = "testOneService")
public class TestOneService {
//自动装配测试1的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestOneDao testOneDao;
//自动装配测试2的服务类;
@Autowired
TestTwoService testTwoService;
@Transactional
public void methodA(){
testOneDao.methodA();
//调用服务类2的方法B;
testTwoService.methodB();
}
}
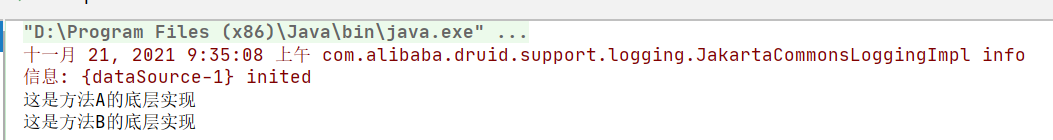
这次初步搭建案例的话,我就简单地在方法上加了事务注解@Transactional
测试一下
public class TestDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
TestOneService oneService = app.getBean("testOneService", TestOneService.class);
//调用执行测试;
oneService.methodA();
}
}
搭建基本完成
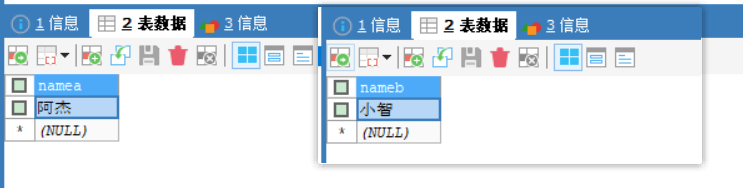
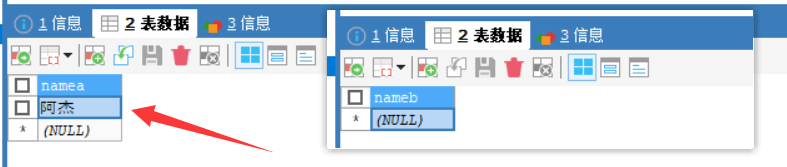
已经存入数据
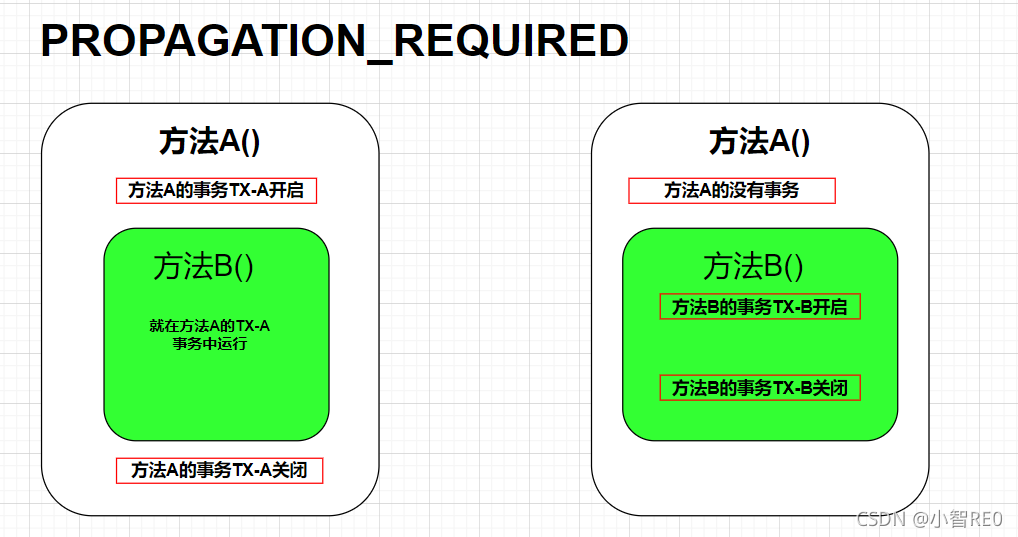
(1)PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
指定的方法必须在事务内执行,若当前存在事务,加入到当前事务中,若当前没有事务,则创建一个新事务,这种传播行为是最常见的,也是 spring 默认的传播行为;
这个通俗一点,就是说现在有两个方法,方法A和方法B; 我在方法A内调用方法B;方法B底层是开启了PROPAGATION_REQUIRED这个类传播型的事务,
- 要是方法A已经开启了事务,那么方法B就会加入到方法A开启的事务中运行;
- 要是方法A没有事务,那么方法B就创建单独属于自己的新事务,在自己的事务中运行;
简单图解看一下
Ok,用案例来看看效果,具体怎么看到效果呢;
我先把数据库中之前测试的两个姓名数据删除掉;
📢先试试方法A有事务,方法B有事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,方法A调用方法B;
这里先给方法A直接用事务;
TestOneService
@Service(value = "testOneService")
public class TestOneService {
//自动装配测试1的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestOneDao testOneDao;
//自动装配测试2的服务类;
@Autowired
TestTwoService testTwoService;
//默认的事务
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodA(){
testOneDao.methodA();
//调用服务类2的方法B;
testTwoService.methodB();
}
}
方法B中也是使用事务Propagation.REQUIRED
方法B中写个异常方法,不要在这里捕获它;
TestTwoService
@Service(value = "testTwoService")
public class TestTwoService {
//自动装配测试类2的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestTwoDao testTwoDao;
//方法B这里就用这个默认的事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodB(){
testTwoDao.methodB();
//这里手动写个算术异常;
int num =10/0;
}
}
OK,我再执行测试一下
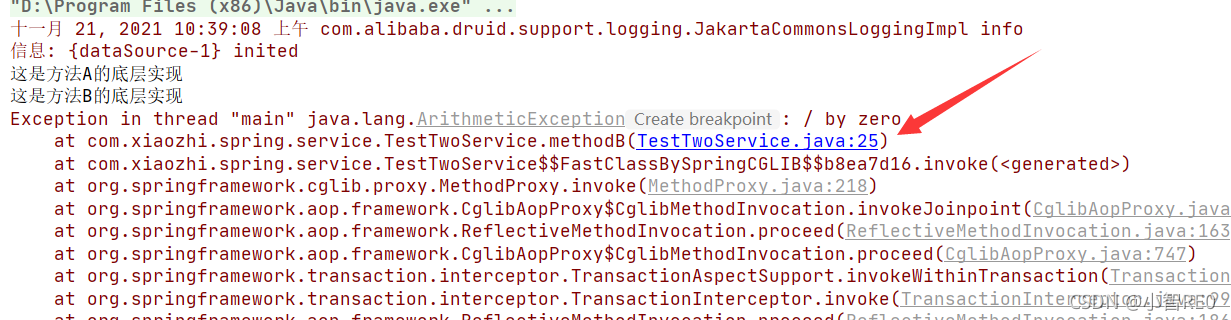
由于方法B与方法A的在同一个事务中运行;这里方法B中出错,就连数据表A的数据都没有添加进去;
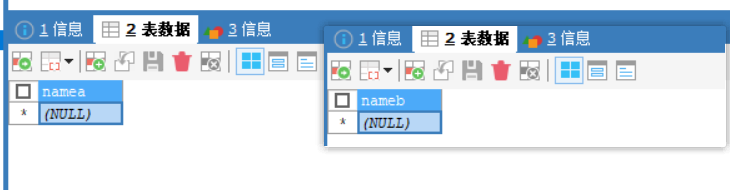
📢现在试试方法A没有事务,方法B使用事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,方法A调用方法B
TestOneService
@Service(value = "testOneService")
public class TestOneService {
//自动装配测试1的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestOneDao testOneDao;
//自动装配测试2的服务类;
@Autowired
TestTwoService testTwoService;
//方法A这里现在不加事务注解
public void methodA(){
testOneDao.methodA();
//调用服务类2的方法B;
testTwoService.methodB();
}
}
方法B使用事务Propagation.REQUIRED;
在方法B中手动写异常;
TestTwoService
@Service(value = "testTwoService")
public class TestTwoService {
//自动装配测试类2的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestTwoDao testTwoDao;
//方法B这里就用这个默认的事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodB(){
testTwoDao.methodB();
//这里手动写个算术异常;
int num =10/0;
}
}
测试执行
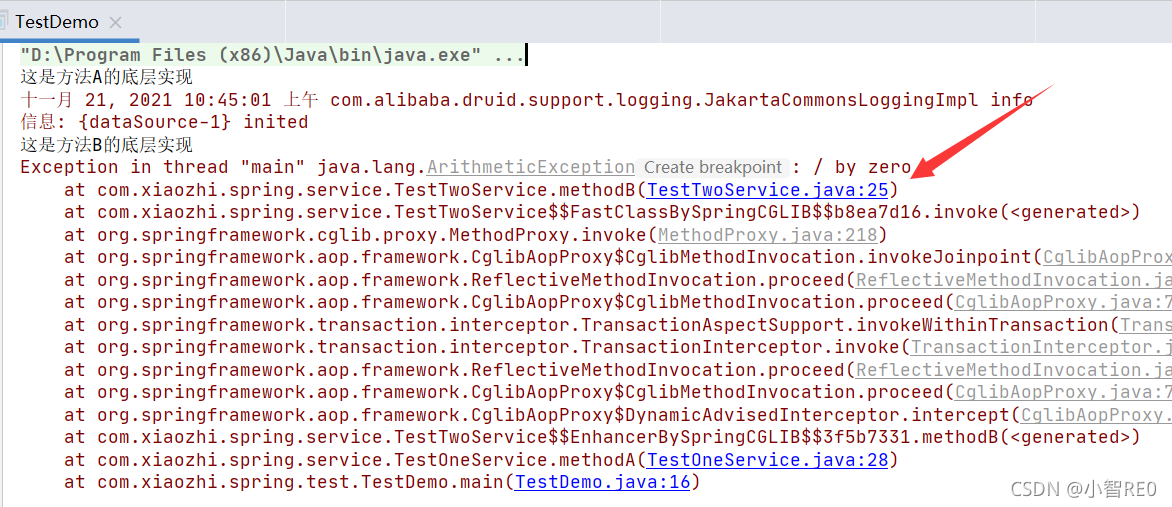
这里的话,注意到,由于方法A没有事务;方法B中使用了事务Propagation.REQUIRED;然后方法A调用方法B,时,方法B自己单独自己开启注解,和方法A没关系;方法A底层的添加数据实现了;但是方法B由于有异常,事务检测到了异常,拒绝执行添加数据;
(2)PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS
支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行
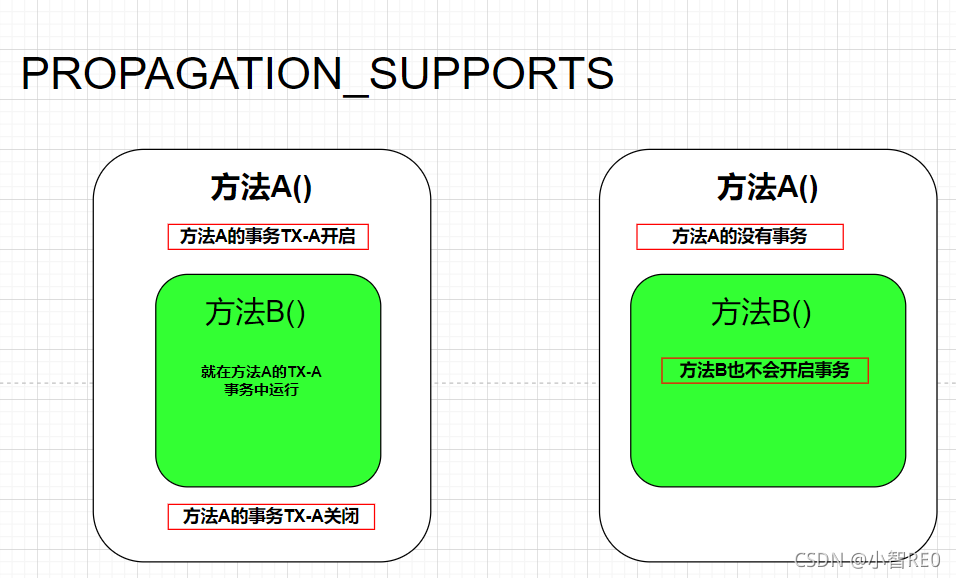
通俗说一下,现在有两个方法,方法A和方法B; 我在方法A内调用方法B;方法B底层是开启了PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS这个类传播型的事务,
- 要是方法A开启了事务,那么方法B就会加入到方法A开启的事务中运行;
- 要是方法A没有开启事务,那么方法B也不开启事务;
简图
同样,写案例之前,我这里也把之前数据库添加的数据删除掉;
这里演示同样的,分为两种;
📢 方法A中开启了事务,方法B开启事务Propagation.SUPPORTS;方法A调用方法B
方法A就用默认的事务;
TestOneService
@Service(value = "testOneService")
public class TestOneService {
//自动装配测试1的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestOneDao testOneDao;
//自动装配测试2的服务类;
@Autowired
TestTwoService testTwoService;
//方法A使用默认的事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodA(){
testOneDao.methodA();
//调用服务类2的方法B;
testTwoService.methodB();
}
}
方法B使用事务Propagation.SUPPORTS;
同样地;方法B中有异常;
TestTwoService
@Service(value = "testTwoService")
public class TestTwoService {
//自动装配测试类2的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestTwoDao testTwoDao;
//方法B这里使用事务Propagation.SUPPORTS
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS)
public void methodB(){
testTwoDao.methodB();
//这里手动写个算术异常;
int num =10/0;
}
}
测试执行
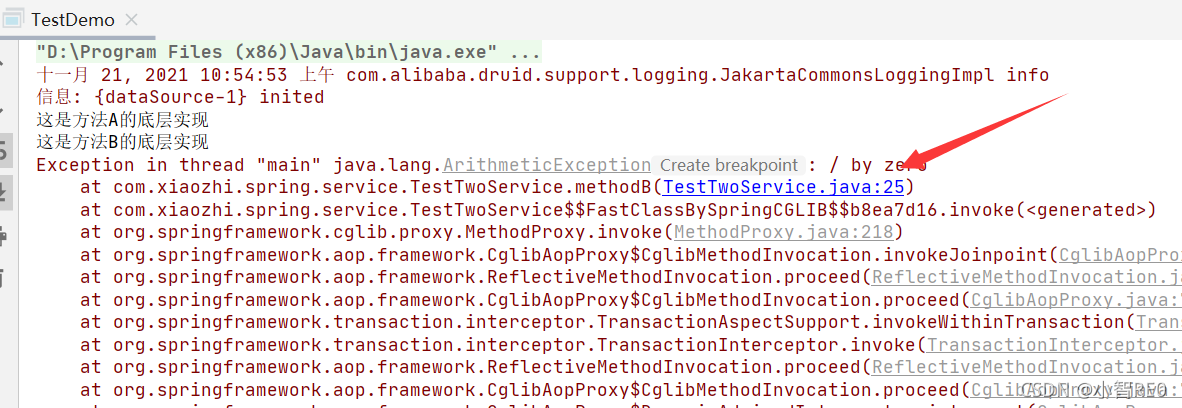
数据库这边,两张表都没有数据添加情况;
由于方法1开启了事务,方法B开启事务Propagation.SUPPORTS;方法A调用方法B;那么方法B就加入到方法A的事务当中;
📢 试试方法A不开启事务,方法B开启事务Propagation.SUPPORTS;方法A调用方法B
方法A不使用事务
TestOneService
@Service(value = "testOneService")
public class TestOneService {
//自动装配测试1的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestOneDao testOneDao;
//自动装配测试2的服务类;
@Autowired
TestTwoService testTwoService;
//方法A不使用事务
public void methodA(){
testOneDao.methodA();
//调用服务类2的方法B;
testTwoService.methodB();
}
}
方法B使用事务Propagation.SUPPORTS;
这里同样地方法B中手动添加异常;
@Service(value = "testTwoService")
public class TestTwoService {
//自动装配测试类2的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestTwoDao testTwoDao;
//方法B这里使用事务Propagation.SUPPORTS
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS)
public void methodB(){
testTwoDao.methodB();
//这里手动写个算术异常;
int num =10/0;
}
}
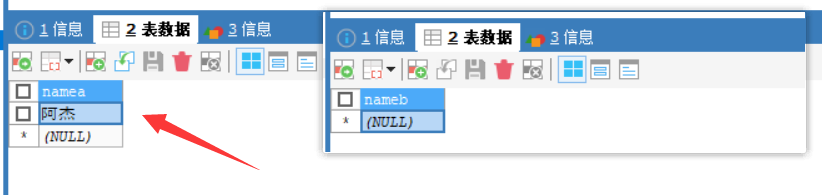
测试执行一下
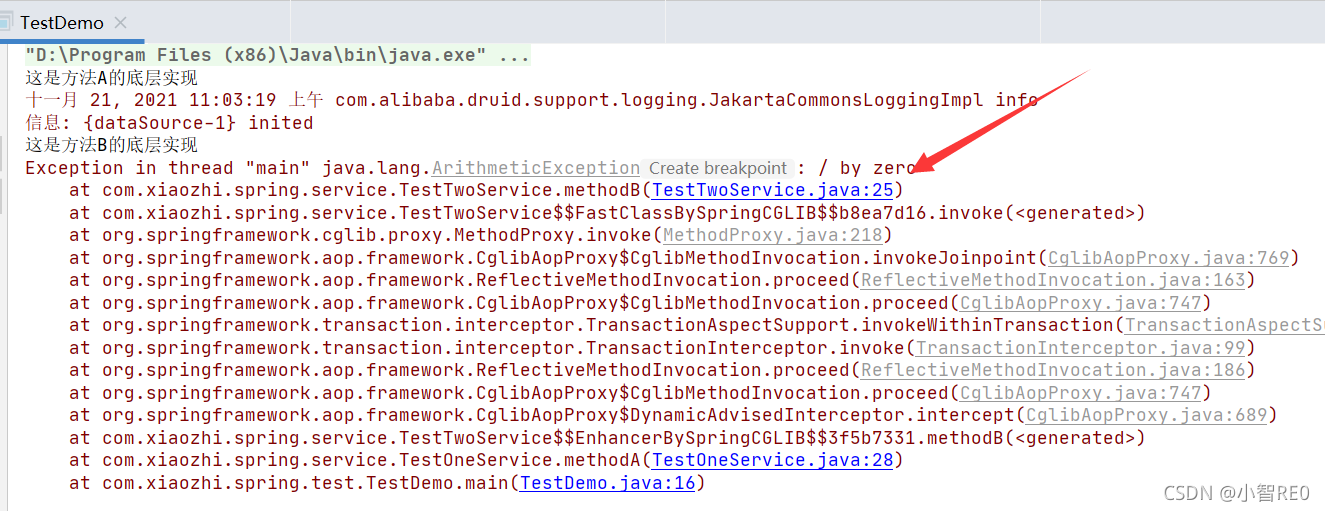
OK,注意到数据表A和B都已经添加了数据,也就是方法A和方法B都没有事务;
方法A不开启事务,方法B开启事务Propagation.SUPPORTS;方法A调用方法B;那么方法B也不开启事务;
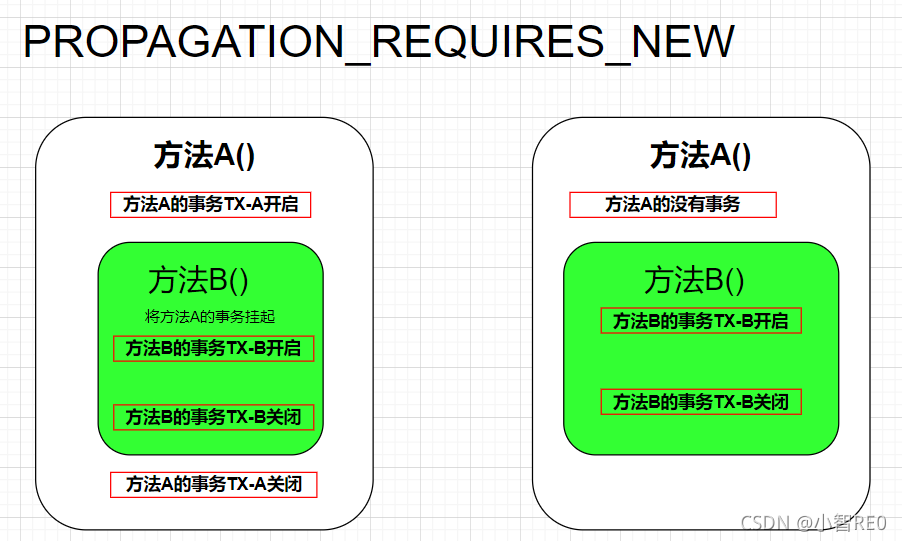
(3)PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW
总是新建一个事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起,直到新建的事务结束.
通俗地说,现在有两个方法,方法A和方法B; 我在方法A内调用方法B;方法B底层是开启了PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW这个类传播型的事务;
- 要是方法A开启了事务,那么方法B会把方法A的事务挂起;转而新建属于自己的事务,在自己的事务内运行;
- 要是方法A没有开启事务,那么方法B就去创建属于自己的事务,在自己的事务中运行;
简易图解看一下
写案例之前,我这里也把之前数据库添加的数据删除掉;
这次案例有一点特别;
📢 方法A中开启事务;方法B开启事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW,用方法A调用方法B;
方法A使用默认的事务;在调用方法B之后,再手动写个异常;
TestOneService
@Service(value = "testOneService")
public class TestOneService {
//自动装配测试1的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestOneDao testOneDao;
//自动装配测试2的服务类;
@Autowired
TestTwoService testTwoService;
//方法A使用默认的事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRED
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodA(){
testOneDao.methodA();
//调用服务类2的方法B;
testTwoService.methodB();
//这里手动写个算术异常;
int num =10/0;
}
}
方法B使用事务Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW;
TestTwoService
@Service(value = "testTwoService")
public class TestTwoService {
//自动装配测试类2的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestTwoDao testTwoDao;
//方法B使用事务Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void methodB(){
testTwoDao.methodB();
}
}
测试执行一下
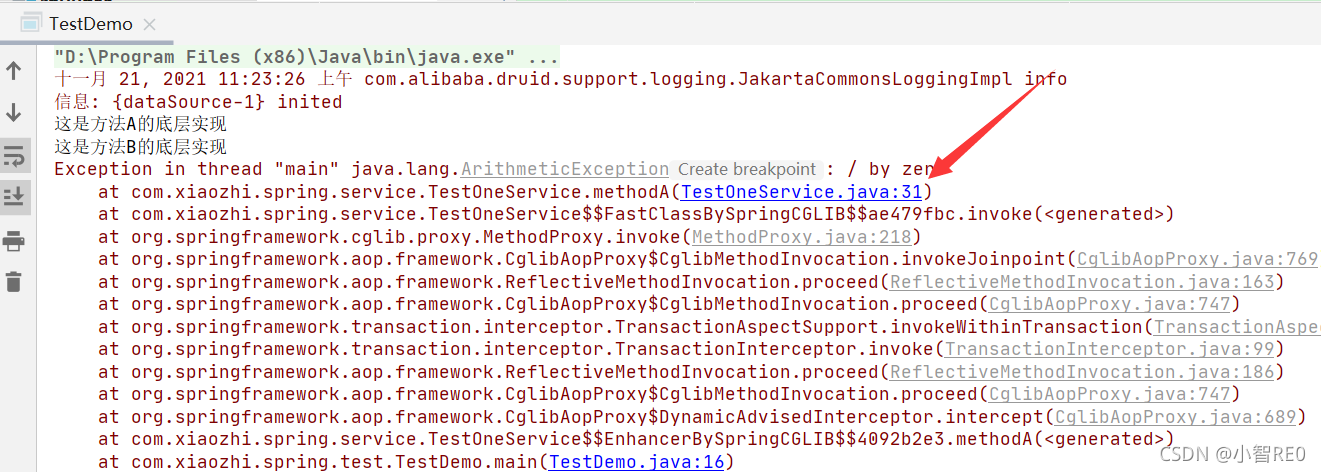
注意到,数据表B添加了数据;即方法B执行了;
刚才方法A中开启事务;方法B开启事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW,用方法A调用方法B;
发现方法A中出现异常,并不会影响方法B的执行;因为方法B把方法A的事务挂起;转而自己单独开了事务;
📢 试试方法A不开启事务,方法B开启事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW,方法A调用方法B
首先把之前数据表填入的数据删除掉;
这个案例的话,在方法A处不开启事务;
这里也不写异常
TestOneService
@Service(value = "testOneService")
public class TestOneService {
//自动装配测试1的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestOneDao testOneDao;
//自动装配测试2的服务类;
@Autowired
TestTwoService testTwoService;
//方法A处不开启事务
public void methodA(){
testOneDao.methodA();
//调用服务类2的方法B;
testTwoService.methodB();
}
}
方法B中使用事务Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW;
且在方法B中添加异常;
TestTwoService
@Service(value = "testTwoService")
public class TestTwoService {
//自动装配测试类2的数据访问类;
@Autowired
TestTwoDao testTwoDao;
//方法B使用事务Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void methodB(){
testTwoDao.methodB();
//这里写个异常;
int num =10/0;
}
}
测试执行
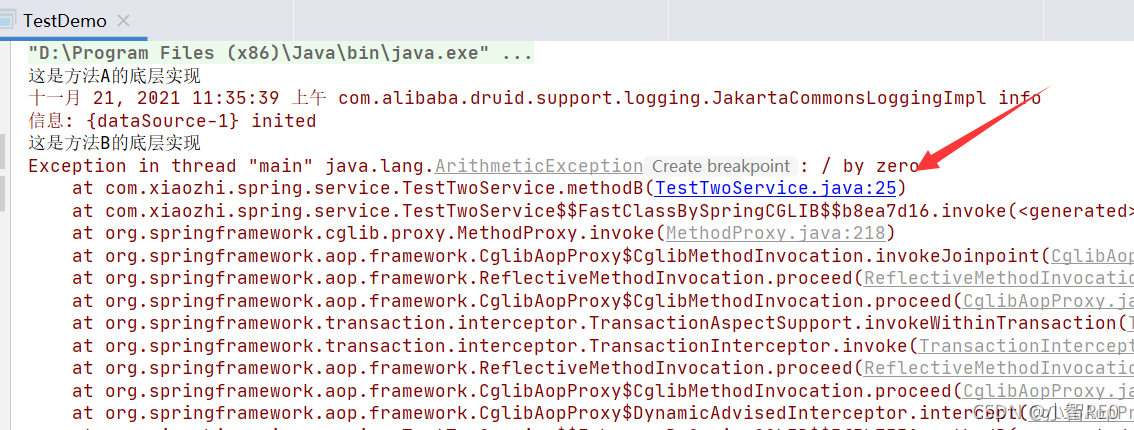
可看到数据表A添加了数据;数据表B并没有添加的数据;
方法A不开启事务,方法B开启事务PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW,方法A调用方法B;
这里方法B自己创建了事务,和调用它的方法A没有关系;
由于方法B中的异常被事务检测到了;所以方法B没有去执行添加数据到数据库;方法B的异常并不会影响到没开事务的方法A;所以方法A正常地添加了数据;
声明式事务失效的几种情况
- @Transactional注解 应用在非 public 修饰的方法上;
- @Transactional注解 的属性 propagation 设置错误时;
- 在同一个类中方法进行调用,导致@Transactional 失效;
- 异常在出现时就被 catch 捕获了;导致@Transactional 失效
- 数据库引擎不支持事务;比如
MyIsam和memory引擎则不支持事务;最近使用的数据库默认是Innodb引擎,它支持事务








 本文详细解析了Spring框架中的事务传播行为,包括REQUIRED、SUPPORTS及REQUIRES_NEW三种常见类型的使用场景,并通过实例展示了不同传播行为的效果。
本文详细解析了Spring框架中的事务传播行为,包括REQUIRED、SUPPORTS及REQUIRES_NEW三种常见类型的使用场景,并通过实例展示了不同传播行为的效果。

















 3449
3449

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










