目录
一,标准库中的list类模板
list类模板
- list是可在常数范围内,在任意位置插入和删除的序列式容器,且该容器可前后双向迭代;
- list底层是双向非循环链表结构,每个元素存储在互不相关的独立节点中,在节点中通过指针指向前后元素;
- list和forward_list非常相似,最主要不同在于forward_list 是单向链表,只能朝前迭代,让其更简单高效;
- 与其他序列式容器相比(array/vector/deque),list通常在任意位置进行插入、移除元素的执行效率更好;
- list和forward_list最大缺陷,是不支持任意位置的随机访问,必须从开头迭代到指定位置,需要线性的时间开销,list还需要一些额外空间,以保存每个节点的相关信息(对存储类型较小元素的大list来说这可能是一个重要因素);

二,string类的常用接口
构造函数
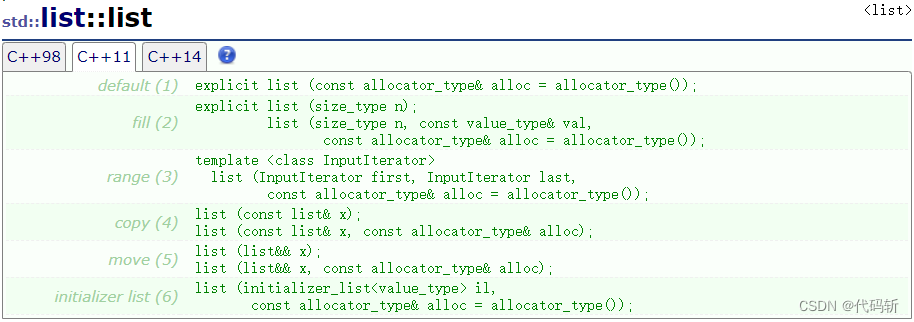
- list(),构造空list;
- list(size_type n, const value_type& val=value_type()),构造n个元素值为val的list;
- list(const list& x),拷贝构造;
- list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last),用区间中的元素构造list;
int main()
{
list<int> L1; //空list
list<int> L2(5, 2); //5个值为2的list
list<int> L3(L2); //拷贝L2
string s("abcd");
list<int> L4(s.begin(), s.end()); //使用迭代器区间构建
return 0;
}list iterator的使用
- begin+end,返回第一个元素的迭代器+返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器;
- rbegin+rend,返回第一个元素的reverse_iterator,即end位置,返回最后一个元素下一个位置的reverse_iterator,即begin位置;
int main()
{
string s("abcd");
list<int> L(s.begin(), s.end());
list<int>::iterator it = L.begin();
while(it != L.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
list<int>::reverse_iterator rit = L.rbegin();
while (rit != L.rend())
{
cout << *rit << " ";
++rit;
}
return 0;
}list容量函数
- empty,检测list是否为空;
- size,返回有效节点个数;
int main()
{
string s("abcd");
list<int> L(s.begin(), s.end());
cout << L.size() << endl;
cout << L.empty() << endl;
return 0;
}list元素访问函数
- front
- back
int main()
{
string s("abcd");
list<char> L(s.begin(), s.end());
cout << L.front() << endl;
cout << L.back() << endl;
return 0;
}list修改函数
- push_front,头插;
- pop_front,头删;
- push_back,尾插;
- pop_back,尾删;
- insert,pos位置插入;
- erase,pos位置删除;
- swap,交换;
- clear,清空有效元素;
int main()
{
list<int>L, L1;
L.push_back(2);
L.push_back(3);
L.push_front(1);
L.insert(L.begin(), 0);
L.erase(--L.end());
L.pop_back();
L.pop_front();
L1.push_back(10);
L.swap(L1);
L.clear();
return 0;
}list迭代器失效
- 迭代器失效即迭代器所指向的节点无效,即该节点被删除了;
- list插入不会导致list失效,删除时会失效,其他操作迭代器不受影响;
int main()
{
list<int> L;
L.push_back(1);
L.push_back(2);
L.push_back(3);
L.push_back(4);
auto pos = ++L.begin();
L.erase(pos);
//pos位置节点已删除释放,即失效,不可在操作
++pos;
*pos;
return 0;
}三,list模拟实现
namespace mylist
{
//节点类模板
template<class T>
struct __list_node
{
__list_node(const T& data = T())
:_prev(nullptr)
, _next(nullptr)
, _data(data)
{}
__list_node<T>* _prev;
__list_node<T>* _next;
T _data;
};
//迭代器类模板,模仿指针
//template<class T>
//struct __list_iterator
//{
// typedef __list_iterator<T> self;
// typedef __list_node<T> Node;
// Node* _node;
//
// __list_iterator(Node* node)
// :_node(node)
// {}
//
// //拷贝构造、赋值重载,默认浅拷贝即可
// //析构函数,指针指向的节点不属于迭代器的,无需自己销毁
//
// //解引用,*it = it.operator*()
// T& operator* ()
// {
// return _node->_data;
// }
// //前置++
// __list_iterator<T>& operator++()
// {
// _node = _node->_next;
// return *this;
// }
// //后置++
// __list_iterator<T> operator++(int)
// {
// self tmp = *this;
// _node = _node->_next;
// return tmp;
// }
// //前置--
// __list_iterator<T>& operator--()
// {
// _node = _node->_prev;
// return *this;
// }
// //后置--
// __list_iterator<T> operator--(int)
// {
// self tmp = *this;
// _node = _node->_prev;
// return *this;
// }
//
// //比较
// bool operator != (const __list_iterator<T>& it) const
// {
// return _node != it._node;
// }
// bool operator == (const __list_iterator<T>& it) const
// {
// return _node == it._node;
// }
//};
template<class T, class Ref, class ptr>
struct __list_iterator
{
typedef __list_iterator<T, Ref, ptr> self;
typedef __list_node<T> Node;
Node* _node;
__list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
//拷贝构造、赋值重载,默认浅拷贝即可
//析构函数,指针指向的节点不属于迭代器的,无需自己销毁
//解引用,*it = it.operator*()
Ref& operator* ()
{
return _node->_data;
}
ptr operator-> () //本来调用为it->->_vale,编译器通过处理省略了一个->
{
return &(_node->_data);
}
//前置++
self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;
}
//后置++
self operator++(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
//前置--
self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
//后置--
self operator--(int)
{
self tmp = *this;
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;
}
//比较
bool operator != (const self& it) const
{
return _node != it._node;
}
bool operator == (const self& it) const
{
return _node == it._node;
}
};
//list类模板
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef __list_node<T> Node;
public:
typedef __list_iterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef __list_iterator<T, const T&, const T*> const_iterator; //typedef const __list_iterator<T> const_iterator; //调用的是迭代器的const函数
iterator begin() { return iterator(_head->_next); }
iterator end() { return iterator(_head); }
const_iterator begin()const { return const_iterator(_head->_next); }
const_iterator end()const { return const_iterator(_head); }
public:
list()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
}
list(const list<T>& L)
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
for (const auto& i : L)
{
push_back(i);
}
}
//现代写法,还不如传统写法
//list(const list<T>& L)
//{
// _head = new Node;
// _head->_prev = _head;
// _head->_next = _head;
// list<T> tmp(L.begin(), L.end());
// std::swap(_head, tmp._head);
//}
template<class InputIterator>
list(InputIterator first, InputIterator last)
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_prev = _head;
_head->_next = _head;
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
++first;
}
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> L)
{
std::swap(_head, L._head);
return *this;
}
~list()
{
clear();
delete _head;
_head = nullptr;
}
void clear()
{
auto it = begin();
//while (it != end())
//{
// Node* cur = it._node;
// ++it;
// delete cur;
//}
//_head->_prev = _head;
//_head->_next = _head;
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}
void push_back(const T& x)
{
//Node* trail = _head->_prev;
//Node* newnode = new Node(x);
//trail->_next = newnode;
//_head->_prev = newnode;
//newnode->_prev = trail;
//newnode->_next = _head;
insert(end(), x);
}
void push_front(const T& x)
{
insert(begin(), x);
}
void pop_back()
{
erase(--end());
}
void pop_front()
{
erase(begin());
}
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& x)
{
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* newnode = new Node(x);
newnode->_prev = prev;
newnode->_next = cur;
prev->_next = newnode;
cur->_prev = newnode;
//return iterator(newnode); //匿名对象
return newnode; //单参数构造函数,支持隐式类型转换
}
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
Node* next= cur->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete cur;
return next;
}
size_t size()
{
size_t sz = 0;
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
++it;
++sz;
}
return sz;
}
bool empty()
{
return begin() == end();
}
private:
Node* _head;
};
}
























 552
552











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








