接口的实现类
动态代理
/**
* retrofit.create()
*/
public <T> T create(final Class<T> service){
validateServiceInterface(service);
return (T)
Proxy.newProxyInstance(
service.getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[]{service},
new InvocationHandler(){
private final Object[] emptyArgs = new Object[0];
@Override
public @Nullable Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, @Nullable object args)
throw Throwable{
if(method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class){ //如果这个方法的作用域是一个类
return method.invoke(this, args); //直接调用
}
args = atgs != null ? args : emptyArgs;
Platform platform = Platform.get();
return platform.isDefaultMethod(method) //判断是否有默认方法
? platform.invokeDefaultMethod(method, service, proxy, args) //直接调用
: loadServiceMethod(method).invoke(args); //去加载
}
}
)
}
这里使用了Proxy.newProxyInstance来生成了实现类,这种技术称之为动态代理
所有的方法调用最终会使用newProxyMethod中传入的InvocationHandler
//Proxy.newProxyInstance
@CallerSensitive
public static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
throws IllegalArgumentException
{
Objects.requireNonNull(h);
final Class<?>[] intfs = interfaces.clone();
final SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
checkProxyAccess(Reflection.getCallerClass(), loader, intfs);
}
/*
* Look up or generate the designated proxy class.
*/
Class<?> cl = getProxyClass0(loader, intfs);//得到了class对象。
/*
* Invoke its constructor with the designated invocation handler.
*/
try {
if (sm != null) {
checkNewProxyPermission(Reflection.getCallerClass(), cl);
}
final Constructor<?> cons = cl.getConstructor(constructorParams);
final InvocationHandler ih = h;
if (!Modifier.isPublic(cl.getModifiers())) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Void>() {
public Void run() {
cons.setAccessible(true);
return null;
}
});
}
return cons.newInstance(new Object[]{h});
} catch (IllegalAccessException|InstantiationException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
Throwable t = e.getCause();
if (t instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) t;
} else {
throw new InternalError(t.toString(), t);
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException e) {
throw new InternalError(e.toString(), e);
}
}
这里通过Proxy.getProxyClass0得到class对象,然后下面对这个class进行构造:
//Proxy.getProxyClass0
private static Class<?> getProxyClass0(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>... interfaces) {
if (interfaces.length > 65535) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("interface limit exceeded");
}
// If the proxy class defined by the given loader implementing
// the given interfaces exists, this will simply return the cached copy;
// otherwise, it will create the proxy class via the ProxyClassFactory
return proxyClassCache.get(loader, interfaces);
}
而这个proxyClassCache是一个weakCache
private static final WeakCache<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>> proxyClassCache = new WeakCache<>(new KeyFactory(), new ProxyClassFactory());
对于这个cache的get方法:
public V get(K key, P parameter){
Object.requireNonNull(parameter);
epungeStaleEntries(); //删除过时条目
Object cacheKey = Cachekey.valueOf(key, refQueue);
ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> valuesMap = map.get(cacheKey);
if(valueMap == null){
ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> oldValuesMap
= map.putIfAbsent(cacheKey, valuesMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>());
if(oldValuesMap != null){
valuesMap = oldValuesMap;
}
}
Object subKey = Objects.requireNonNull(subKeyFactory.apply(key, parameter));
Supplier<V> supplier = valuesMap.get(subKey);
Factory factory = null;
while(true){
if(supplier != null){
V value = supplier.get();
if(value != null){
return value;
}
}
if(factory == null){
factory = new Factory(key, parameter, subKey, valuesMap);
}
if(supplier == null){
supplier = valuesMap.putIfAbsent(subKey, factory);
if(supplier == null){
supplier = factory;
}
}else{
if(valuesMap.replace(subKey, supplier, factory)){
supplier = factory;
}else{
supplier = valuesMap.get(subKey);
}
}
}
}
当第一次创建的时候,factory肯定为null,不存在cache中,所以去看Factory
//WeakCache.Factory
private final class Factory implements Supplier<V>{
private final K key;
private final P parameter;
private final Object subKey;
private final ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> valuesMap;
Factory(K key, P parameter, Object subKey, ConcurrentMap<Object, Supplier<V>> valuesMap){
this.key = key;
this.parameter = parameter;
this.subKey = subKey;
this.valuesMap = valuesMap;
}
@Override
public synchronized V get() { // serialize access
// re-check
Supplier<V> supplier = valuesMap.get(subKey);
if (supplier != this) {
// something changed while we were waiting:
// might be that we were replaced by a CacheValue
// or were removed because of failure ->
// return null to signal WeakCache.get() to retry
// the loop
return null;
}
// else still us (supplier == this)
// create new value
V value = null;
try {
value = Objects.requireNonNull(valueFactory.apply(key, parameter)); //这里拿value
} finally {
if (value == null) { // remove us on failure
valuesMap.remove(subKey, this);
}
}
// the only path to reach here is with non-null value
assert value != null;
// wrap value with CacheValue (WeakReference)
CacheValue<V> cacheValue = new CacheValue<>(value);
// put into reverseMap
reverseMap.put(cacheValue, Boolean.TRUE);
// try replacing us with CacheValue (this should always succeed)
if (!valuesMap.replace(subKey, this, cacheValue)) {
throw new AssertionError("Should not reach here");
}
// successfully replaced us with new CacheValue -> return the value
// wrapped by it
return value;
}
}
value由valueFactory创建。
private final BiFunction<K, P, V> valueFactory;
在Factory中的构造器中被构造。
private static final WeakCache<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>>
proxyClassCache = new WeakCache<>(new KeyFactory(), new ProxyClassFactory());
再去看ProxyFactory:
private static final class ProxyClassFactory
implements BiFunction<ClassLoader, Class<?>[], Class<?>>
{
// prefix for all proxy class names
private static final String proxyClassNamePrefix = "$Proxy";
// next number to use for generation of unique proxy class names
private static final AtomicLong nextUniqueNumber = new AtomicLong();
@Override
public Class<?> apply(ClassLoader loader, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
Map<Class<?>, Boolean> interfaceSet = new IdentityHashMap<>(interfaces.length);
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
/*
* Verify that the class loader resolves the name of this
* interface to the same Class object.
*/
Class<?> interfaceClass = null;
try {
interfaceClass = Class.forName(intf.getName(), false, loader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
}
if (interfaceClass != intf) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
intf + " is not visible from class loader");
}
//检测Interface
if (!interfaceClass.isInterface()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
interfaceClass.getName() + " is not an interface");
}
/*
* Verify that this interface is not a duplicate.
*/
//同时load接口
if (interfaceSet.put(interfaceClass, Boolean.TRUE) != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"repeated interface: " + interfaceClass.getName());
}
}
String proxyPkg = null; // package to define proxy class in
int accessFlags = Modifier.PUBLIC | Modifier.FINAL;
/*
* Record the package of a non-public proxy interface so that the
* proxy class will be defined in the same package. Verify that
* all non-public proxy interfaces are in the same package.
检查接口的Modifier
*/
for (Class<?> intf : interfaces) {
int flags = intf.getModifiers();
if (!Modifier.isPublic(flags)) {
accessFlags = Modifier.FINAL;
String name = intf.getName();
int n = name.lastIndexOf('.');
String pkg = ((n == -1) ? "" : name.substring(0, n + 1));
if (proxyPkg == null) {
proxyPkg = pkg;
} else if (!pkg.equals(proxyPkg)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"non-public interfaces from different packages");
}
}
}
if (proxyPkg == null) {
// if no non-public proxy interfaces, use com.sun.proxy package
proxyPkg = ReflectUtil.PROXY_PACKAGE + ".";
}
/*
* Choose a name for the proxy class to generate.
*/
long num = nextUniqueNumber.getAndIncrement();
String proxyName = proxyPkg + proxyClassNamePrefix + num;
/*
* Generate the specified proxy class.
*/
//生成proxy的类。
byte[] proxyClassFile = ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass(
proxyName, interfaces, accessFlags);
try {
return defineClass0(loader, proxyName,
proxyClassFile, 0, proxyClassFile.length);
} catch (ClassFormatError e) {
/*
* A ClassFormatError here means that (barring bugs in the
* proxy class generation code) there was some other
* invalid aspect of the arguments supplied to the proxy
* class creation (such as virtual machine limitations
* exceeded).
*/
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e.toString());
}
}
}
这里就生成了class, 由ProxyGenerator.generateProxyClass生成。
不过java自带的Proxy是基于接口的,无法设置父类。
Cglib 动态代理
Cglib在SpringBoot中也有使用,支持了父类构造
public class CglibTest{
public static void main(String...args){
var enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(SuperClass.class);
enhancer.setInterfaces(new Class[]{GitHub.class, Runnable.class});
enhancer.setCallback(new FixedValue(){
public Object loadObject() throws Exception{
return "Hello";
}
});
Object object = enhancer.create();
System.out.println(object.toString());
}
}
对于需要各种函数的应用场景:
public class CglibTest{
public static void main(String...args){
var enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(SuperClass.class);
enhancer.setInterfaces(new Class[]{GitHub.class, Runnable.class});
enhancer.setCallback(new FixedValue(){
public Object loadObject() throws Exception{
return "Hello";
}
});
Object object = enhancer.create();
System.out.println(object.toString());
System.out.println(object.equals(null));
if(object instanceof GitHub github){
github.contributors("", "");
}
}
}
这种操作会直接抛出异常:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ClassCastException: class java.lang.String cannot be cast to class java.lang.Boolean (java.lang.String and java.lang.Boolean are in module java.base of loader 'bootstrap')
at com.bennyhuo.retrofit.tutorials.sample.proxy.SuperClass$$EnhancerByCGLIB$$512d0ac6.equals(<generated>)
at com.bennyhuo.retrofit.tutorials.sample.proxy.CglibTest.main(CglibTest.java:38)
cglib实现原理
private Object createHelper() {
preValidate();
Object key = KEY_FACTORY.newInstance((superclass != null) ? superclass.getName() : null,
ReflectUtils.getNames(interfaces),
filter == ALL_ZERO ? null : new WeakCacheKey<CallbackFilter>(filter),
callbackTypes,
useFactory,
interceptDuringConstruction,
serialVersionUID);
this.currentKey = key;
Object result = super.create(key);
return result;
}
通过KEY_FACTORY进行创建,而KEY_FACTORY的创建:
private static final EnhancerKey KEY_FACTORY =
(EnhancerKey)KeyFactory.create(EnhancerKey.class, KeyFactory.HASH_ASM_TYPE, null);
//KeyFactory.create
public static KeyFactory create(ClassLoader loader, Class keyInterface, KeyFactoryCustomizer customizer,
List<KeyFactoryCustomizer> next) {
Generator gen = new Generator();
gen.setInterface(keyInterface);
if (customizer != null) {
gen.addCustomizer(customizer);
}
if (next != null && !next.isEmpty()) {
for (KeyFactoryCustomizer keyFactoryCustomizer : next) {
gen.addCustomizer(keyFactoryCustomizer);
}
}
gen.setClassLoader(loader);
return gen.create();
}
public KeyFactory create() {
setNamePrefix(keyInterface.getName());
return (KeyFactory)super.create(keyInterface.getName());
}
而这个super.create:
protected Object create(Object key) {
try {
ClassLoader loader = getClassLoader();
Map<ClassLoader, ClassLoaderData> cache = CACHE;
ClassLoaderData data = cache.get(loader);
if (data == null) {
synchronized (AbstractClassGenerator.class) {
cache = CACHE;
data = cache.get(loader);
if (data == null) {
Map<ClassLoader, ClassLoaderData> newCache = new WeakHashMap<ClassLoader, ClassLoaderData>(cache);
data = new ClassLoaderData(loader);
newCache.put(loader, data);
CACHE = newCache;
}
}
}
this.key = key;
Object obj = data.get(this, getUseCache()); //在这里创建类
if (obj instanceof Class) {
return firstInstance((Class) obj);
}
return nextInstance(obj);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Error e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CodeGenerationException(e);
}
}
对于这个生成的data.get:
//AbstractClassGenerator
public Object get(AbstractClassGenerator gen, boolean useCache) {
if (!useCache) {
return gen.generate(ClassLoaderData.this);
} else {
Object cachedValue = generatedClasses.get(gen);
return gen.unwrapCachedValue(cachedValue);
}
}
又由gen.generate方法创建:
protected Class generate(ClassLoaderData data) {
Class gen;
Object save = CURRENT.get();
CURRENT.set(this);
try {
ClassLoader classLoader = data.getClassLoader();
if (classLoader == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("ClassLoader is null while trying to define class " +
getClassName() + ". It seems that the loader has been expired from a weak reference somehow. " +
"Please file an issue at cglib's issue tracker.");
}
synchronized (classLoader) {
String name = generateClassName(data.getUniqueNamePredicate());
data.reserveName(name);
this.setClassName(name);
}
if (attemptLoad) {
try {
//试图从类加载器直接加载
gen = classLoader.loadClass(getClassName());
return gen;
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// ignore
}
}
//这里才是真正生成的地方:
byte[] b = strategy.generate(this);
String className = ClassNameReader.getClassName(new ClassReader(b));
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain = getProtectionDomain();
synchronized (classLoader) { // just in case
if (protectionDomain == null) {
gen = ReflectUtils.defineClass(className, b, classLoader);
} else {
gen = ReflectUtils.defineClass(className, b, classLoader, protectionDomain);
}
}
return gen;
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Error e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new CodeGenerationException(e);
} finally {
CURRENT.set(save);
}
}
其策略先是用ClassLoaderData生成ClassLoader,从类加载器里通过ClassName进行加载, 如果没有加载出来,则使用strategy.generate生成字节码。
生成类名的方法:
private String generateClassName(Pridicate nameTestPredicate){
return namingPolicy.getClassName(namePrefix, source.name, key, nameTestPredicate);
}
那么借用NamingPolicy和GeneratorStrategy就能获取字节码了。
class MyStrategyNamingPolicy implements NamingPolicy, GeneratorStrategy{
private GeneratorStrategy strategy = new DefaultGeneratorStrategy();
private NamingPolicy policy = new DefaultNamingPolicy();
private String className;
@Override
public byte[] generate(ClassGenerator cg) throws Exception {
byte[] code = strategy.generate(cg);
FilesKt.writeBytes(new File(className + ".class"), code);
return code;
}
@Override
public String getClassName(String prefix, String source, Object key, Predicate names) {
className = policy.getClassName(prefix, source, key, names);
return className;
}
}
MyStrategyNamingPolicy strategyNamingPolicy = new MyStrategyNamingPolicy();
enhancer.setStrategy(strategyNamingPolicy);
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(strategyNamingPolicy);
可以看到,生成的类返回的东西都是什么var10000
...
public final int hashCode() {
FixedValue var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
Object var1 = var10000.loadObject();
return var1 == null ? 0 : ((Number)var1).intValue();
}
protected final Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException {
FixedValue var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
return var10000.loadObject();
}
...
Invocation Handler
cglib支持使用InvocationHandler进行处理
enhancer.setCallback(new InvocationHandler() {
private SuperClass superClass = new SuperClass("test");
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("before");
try{
Method method1 = SuperClass.class.getMethod(method.getName(), method.getParameterTypes());
return method1.invoke(superClass, args);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}finally {
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
});
......
((SuperClass)obj).Hello();
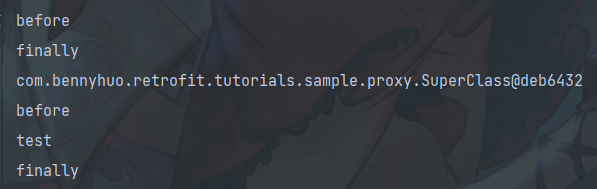
再看生成的字节码:
public final void Hello() {
try {
InvocationHandler var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
if (var10000 == null) {
CGLIB$BIND_CALLBACKS(this);
var10000 = this.CGLIB$CALLBACK_0;
}
var10000.invoke(this, CGLIB$Hello$0, new Object[0]);
} catch (Error | RuntimeException var1) {
throw var1;
} catch (Throwable var2) {
throw new UndeclaredThrowableException(var2);
}
}
MethodInterceptor
enhancer.setCallback(new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object intercept(Object obj, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy proxy) throws Throwable {
return proxy.invokeSuper(obj, args);
}
});
MethodInterceptor支持父类调用与自身调用, api分别是invokeSuper和invoke
生成的字节码一共有三个文件,其中有一个叫FastClass, 用索引定义好的各种方法调用
public Object invoke(int var1, Object var2, Object[] var3) throws InvocationTargetException {
SuperClass var10000 = (SuperClass)var2;
int var10001 = var1;
try {
switch (var10001) {
case 0:
var10000.Hello();
return null;
case 1:
return new Boolean(var10000.equals(var3[0]));
case 2:
return var10000.toString();
case 3:
return new Integer(var10000.hashCode());
}
} catch (Throwable var4) {
throw new InvocationTargetException(var4);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot find matching method/constructor");
}
又用了getIndex通过方法签名返回索引
public int getIndex(Signature var1) {
String var10000 = var1.toString();
switch (var10000.hashCode()) {
case -728081021:
if (var10000.equals("Hello()V")) {
return 0;
}
break;
case 1826985398:
if (var10000.equals("equals(Ljava/lang/Object;)Z")) {
return 1;
}
break;
case 1913648695:
if (var10000.equals("toString()Ljava/lang/String;")) {
return 2;
}
break;
case 1984935277:
if (var10000.equals("hashCode()I")) {
return 3;
}
}
return -1;
}
加载Service Method
ServiceMethod<?> loadServiceMethod(Method method){
ServiceMethod<?> result = serviceMethodCache.get(method);
if(result != null) return result; //缓存获取
synchronized(serviceMethodCache){
result = serviceMethodCache.get(method);
if(result == null){
result = ServiceMethod.parseAnnotations(this, method);
serviceMethodCache.put(method, result);
}
}
return result;
}
这里可以看到,加载ServiceMethod使用了缓冲机制, 并且加锁, 实现了线程安全。
private final Map<Method, ServiceMethod<?>> serviceMethodCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
再看```ServiceMethod`中的代码:
abstract class ServiceMethod<T>{
static <T> ServiceMethod<T> parseAnnotations(Retrofit, Method method){
Requestfactory requestFactory = RequestFactory.parseAnnotations(retrofit, method);
Type returnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
if(Utils.hasUnresolvableType(returnType)){
throw methodError(method, "Method return type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s", returnType);
}
if(returnType == void.class){
throw methodError(method, "Service methods cannot return void.");
}
return HttpServiceMethod.parseAnnotations(retrofit, method, requestFactory);
}
abstract @Nullable T invoke(Object[] args);
}
这里Service的静态方法parseAnnotations负责创建ServiceMethod对象,invoke抽象方法就是要实现的方法调用。
Service.invoke在**HttpServiceMethod**中有唯一实现,也就是Service.parseAnnotations中最后返回的那个调用方法的作用域。
//HttpServiceMethod.invoke
@Override
final @Nullable ReturnT invoke(Object[] args){
Call<ResponseT> call = new OkHttpCall<>(requestFactory, args, callFactory, responseConverter);
return adapt(call, args);
}
这里调用的adapt实际上是HttpServiceMethod类中的一个抽象方法,其具体实现有以下三个,很明显,这里调用的就是retrofit的内置的adapter。破案了。
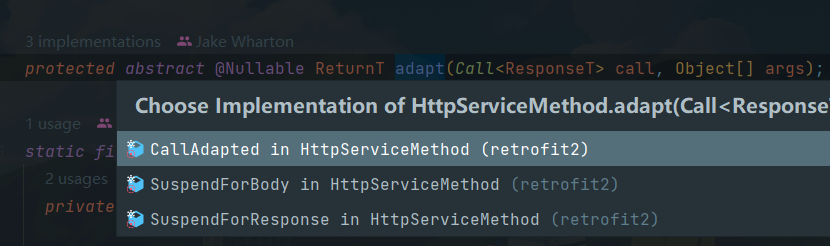
请求处理
public interface GitHub {
@GET("/repos/{owner}/{repo}/contributors")
Call<List<Contributor>> contributors(
@Path("owner") String owner,
@Path("repo") String repo);
default void hello(){
System.out.println("Hello");
}
class Contributor {
public final String login;
public final int contributions;
public Contributor(String login, int contributions) {
this.login = login;
this.contributions = contributions;
}
}
在之前的加载ServiceMethod过程中, ServiceMethod由parseAnnotation方法解析并放入缓存中,缓存是一个ConcurrentHashMap
abstract class ServiceMethod<T> {
static <T> ServiceMethod<T> parseAnnotations(Retrofit retrofit, Method method) {
RequestFactory requestFactory = RequestFactory.parseAnnotations(retrofit, method);
Type returnType = method.getGenericReturnType();
if (Utils.hasUnresolvableType(returnType)) {
throw methodError(
method,
"Method return type must not include a type variable or wildcard: %s",
returnType);
}
if (returnType == void.class) {
throw methodError(method, "Service methods cannot return void.");
}
return HttpServiceMethod.parseAnnotations(retrofit, method, requestFactory);
}
abstract @Nullable T invoke(Object[] args);
}
上来就先RequestFactory.parseAnnotation进行了一个解析,并且拿到了一个*RequestFactory *
static RequestFactory parseAnnotations(Retrofit retrofit, Method method) {
return new Builder(retrofit, method).build();
}
Builder(Retrofit retrofit, Method method) {
this.retrofit = retrofit;
this.method = method;
this.methodAnnotations = method.getAnnotations();
this.parameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
this.parameterAnnotationsArray = method.getParameterAnnotations();
}
这里分别用反射拿到了方法注解,参数类型,参数注解
RequestFactory build() {
for (Annotation annotation : methodAnnotations) {
parseMethodAnnotation(annotation);
}
if (httpMethod == null) {
throw methodError(method, "HTTP method annotation is required (e.g., @GET, @POST, etc.).");
}
if (!hasBody) {
if (isMultipart) {
throw methodError(
method,
"Multipart can only be specified on HTTP methods with request body (e.g., @POST).");
}
if (isFormEncoded) {
throw methodError(
method,
"FormUrlEncoded can only be specified on HTTP methods with "
+ "request body (e.g., @POST).");
}
}
int parameterCount = parameterAnnotationsArray.length;
parameterHandlers = new ParameterHandler<?>[parameterCount];
for (int p = 0, lastParameter = parameterCount - 1; p < parameterCount; p++) {
parameterHandlers[p] =
parseParameter(p, parameterTypes[p], parameterAnnotationsArray[p], p == lastParameter);
}
if (relativeUrl == null && !gotUrl) {
throw methodError(method, "Missing either @%s URL or @Url parameter.", httpMethod);
}
if (!isFormEncoded && !isMultipart && !hasBody && gotBody) {
throw methodError(method, "Non-body HTTP method cannot contain @Body.");
}
if (isFormEncoded && !gotField) {
throw methodError(method, "Form-encoded method must contain at least one @Field.");
}
if (isMultipart && !gotPart) {
throw methodError(method, "Multipart method must contain at least one @Part.");
}
return new RequestFactory(this);
}
build方法就直接进行解析建立了。
private void parseMethodAnnotation(Annotation annotation) {
if (annotation instanceof DELETE) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("DELETE", ((DELETE) annotation).value(), false);
} else if (annotation instanceof GET) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("GET", ((GET) annotation).value(), false);
} else if (annotation instanceof HEAD) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("HEAD", ((HEAD) annotation).value(), false);
} else if (annotation instanceof PATCH) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("PATCH", ((PATCH) annotation).value(), true);
} else if (annotation instanceof POST) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("POST", ((POST) annotation).value(), true);
} else if (annotation instanceof PUT) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("PUT", ((PUT) annotation).value(), true);
} else if (annotation instanceof OPTIONS) {
parseHttpMethodAndPath("OPTIONS", ((OPTIONS) annotation).value(), false);
} else if (annotation instanceof HTTP) {
HTTP http = (HTTP) annotation;
parseHttpMethodAndPath(http.method(), http.path(), http.hasBody());
} else if (annotation instanceof retrofit2.http.Headers) {
String[] headersToParse = ((retrofit2.http.Headers) annotation).value();
if (headersToParse.length == 0) {
throw methodError(method, "@Headers annotation is empty.");
}
headers = parseHeaders(headersToParse);
} else if (annotation instanceof Multipart) {
if (isFormEncoded) {
throw methodError(method, "Only one encoding annotation is allowed.");
}
isMultipart = true;
} else if (annotation instanceof FormUrlEncoded) {
if (isMultipart) {
throw methodError(method, "Only one encoding annotation is allowed.");
}
isFormEncoded = true;
}
}
假设用的方法注解是Get吧, 那么他就拿到了这个Get注解里面的值,然后进行解析
private void parseHttpMethodAndPath(String httpMethod, String value, boolean hasBody) {
if (this.httpMethod != null) {
throw methodError(
method,
"Only one HTTP method is allowed. Found: %s and %s.",
this.httpMethod,
httpMethod);
}
this.httpMethod = httpMethod;
this.hasBody = hasBody;
if (value.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// Get the relative URL path and existing query string, if present.
int question = value.indexOf('?');
if (question != -1 && question < value.length() - 1) {
// Ensure the query string does not have any named parameters.
String queryParams = value.substring(question + 1);
Matcher queryParamMatcher = PARAM_URL_REGEX.matcher(queryParams);
if (queryParamMatcher.find()) {
throw methodError(
method,
"URL query string \"%s\" must not have replace block. "
+ "For dynamic query parameters use @Query.",
queryParams);
}
}
this.relativeUrl = value;
this.relativeUrlParamNames = parsePathParameters(value);
}
通过对方法注解进行解析以后, 就直接返回了。
随后RequestFactory.build方法就走到解析参数部分。
int parameterCount = parameterAnnotationsArray.length;
parameterHandlers = new ParameterHandler<?>[parameterCount];
for (int p = 0, lastParameter = parameterCount - 1; p < parameterCount; p++) {
parameterHandlers[p] =
parseParameter(p, parameterTypes[p], parameterAnnotationsArray[p], p == lastParameter);
}
这里new了一个ParameterHandler
abstract class ParameterHandler<T> {
abstract void apply(RequestBuilder builder, @Nullable T value) throws IOException;
....
这里有个方法叫apply, 抽象类里面还有一堆子类, 这么看的话,是负责把参数装配到RequestBuilder里的一个作用。
private @Nullable ParameterHandler<?> parseParameter(
int p, Type parameterType, @Nullable Annotation[] annotations, boolean allowContinuation) {
ParameterHandler<?> result = null;
if (annotations != null) {
for (Annotation annotation : annotations) {
ParameterHandler<?> annotationAction =
parseParameterAnnotation(p, parameterType, annotations, annotation);
if (annotationAction == null) {
continue;
}
if (result != null) {
throw parameterError(
method, p, "Multiple Retrofit annotations found, only one allowed.");
}
result = annotationAction;
}
}
if (result == null) {
if (allowContinuation) {
try {
if (Utils.getRawType(parameterType) == Continuation.class) {
isKotlinSuspendFunction = true;
return null;
}
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError ignored) {
// Ignored
}
}
throw parameterError(method, p, "No Retrofit annotation found.");
}
return result;
}
这个里面的parseParameterAnnotation方法负责了参数注解的解析
@Nullable
private ParameterHandler<?> parseParameterAnnotation(
int p, Type type, Annotation[] annotations, Annotation annotation) {
if (annotation instanceof Url) {
validateResolvableType(p, type);
if (gotUrl) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "Multiple @Url method annotations found.");
}
if (gotPath) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "@Path parameters may not be used with @Url.");
}
if (gotQuery) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "A @Url parameter must not come after a @Query.");
}
if (gotQueryName) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "A @Url parameter must not come after a @QueryName.");
}
if (gotQueryMap) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "A @Url parameter must not come after a @QueryMap.");
}
if (relativeUrl != null) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "@Url cannot be used with @%s URL", httpMethod);
}
gotUrl = true;
if (type == HttpUrl.class
|| type == String.class
|| type == URI.class
|| (type instanceof Class && "android.net.Uri".equals(((Class<?>) type).getName()))) {
return new ParameterHandler.RelativeUrl(method, p);
} else {
throw parameterError(
method,
p,
"@Url must be okhttp3.HttpUrl, String, java.net.URI, or android.net.Uri type.");
}
} else if (annotation instanceof Path) {
...
这里其实就是进行了一堆的解析,校验。不过值得一提的是, 在Path中, 有一个Converter, 对值进行了一个转换,虽然内置的这个toStringConverter是直接toString了, 不过我们也可以装配自己的Converter什么的进去。
......
else if (annotation instanceof Path) {
validateResolvableType(p, type);
if (gotQuery) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "A @Path parameter must not come after a @Query.");
}
if (gotQueryName) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "A @Path parameter must not come after a @QueryName.");
}
if (gotQueryMap) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "A @Path parameter must not come after a @QueryMap.");
}
if (gotUrl) {
throw parameterError(method, p, "@Path parameters may not be used with @Url.");
}
if (relativeUrl == null) {
throw parameterError(
method, p, "@Path can only be used with relative url on @%s", httpMethod);
}
gotPath = true;
Path path = (Path) annotation;
String name = path.value();
validatePathName(p, name);
Converter<?, String> converter = retrofit.stringConverter(type, annotations);
return new ParameterHandler.Path<>(method, p, name, converter, path.encoded());
}
Converter
public final class SimpleService2 {
public static final String API_URL = "https://api.github.com";
public static void main(String... args) throws IOException {
// Create a very simple REST adapter which points the GitHub API.
Retrofit retrofit =
new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(API_URL)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.client(new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addInterceptor(new HttpLoggingInterceptor(System.out::println).setLevel(HttpLoggingInterceptor.Level.BODY))
.build())
.build();
// Create an instance of our GitHub API interface.
GitHub2 github = retrofit.create(GitHub2.class);
// github.hello();
System.out.println(github.getClass());
Call<List<GitHub2.Contributor>> call = github.contributors(new Date(), "square", "retrofit");
List<GitHub2.Contributor> body = call.execute().body();
for (GitHub2.Contributor contributor : body) {
System.out.println(contributor.login + "(" + contributor.contributions + ")");
}
System.out.println(contributor.login + " (" + contributor.contributions + ")");
}
}
这种情况下,去观察生成的URL为https://api.github.com/repositories/892275/contributors?current=Mon+Sep+26+23%3A26%3A25+CST+2022&page=2, 看来是直接调用了ToStringConverter, 其内部的实现为:
public String convert(Object value){return value.toString()};
其实我们也可以自己实现一个Converter
public class DateConverter implements Converter<Date, String> {
private static final SimpleDateFormat SIMPLE_DATE_FORMAT = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyyMMdd_HH:mm:ss");
@Nullable
@Override
public String convert(Date value) throws IOException {
return SIMPLE_DATE_FORMAT.format(value);
}
public static class DateConverterFactory extends Converter.Factory{
@Nullable
@Override
public Converter<?, String> stringConverter(Type type, Annotation[] annotations, Retrofit retrofit) {
if(type == Date.class)
return new DateConverter();
return super.stringConverter(type, annotations, retrofit);
}
public static Factory create(){
return new DateConverterFactory();
}
}
}
Retrofit retrofit =
new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(API_URL)
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.client(new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addInterceptor(new HttpLoggingInterceptor(System.out::println).setLevel(HttpLoggingInterceptor.Level.BODY))
.build())
.addConverterFactory(DateConverter.DateConverterFactory.create())
.build();
添加Converter之后生成的URL为https://api.github.com/repositories/892275/contributors?current=20220926_23%3A41%3A02&page=2
%3A是冒号:的转义字符
动态更换baseUrl
public Builder baseUrl(String baseUrl) {
Objects.requireNonNull(baseUrl, "baseUrl == null");
return baseUrl(HttpUrl.get(baseUrl));
}
public Builder baseUrl(HttpUrl baseUrl) {
Objects.requireNonNull(baseUrl, "baseUrl == null");
List<String> pathSegments = baseUrl.pathSegments();
if (!"".equals(pathSegments.get(pathSegments.size() - 1))) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("baseUrl must end in /: " + baseUrl);
}
this.baseUrl = baseUrl;
return this;
}
通常我们使用第一个·baseUrl方法, 第二个baseUrl在最后很明显,直接将Retrofit类中一个叫baseUrl的字段进行了赋值操作。
//RequestFactory.Builder
Builder(Retrofit retrofit, Method method) {
this.retrofit = retrofit;
this.method = method;
this.methodAnnotations = method.getAnnotations();
this.parameterTypes = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
this.parameterAnnotationsArray = method.getParameterAnnotations();
}
//RequestFactory
RequestFactory(Builder builder) {
method = builder.method;
baseUrl = builder.retrofit.baseUrl;
httpMethod = builder.httpMethod;
relativeUrl = builder.relativeUrl;
headers = builder.headers;
contentType = builder.contentType;
hasBody = builder.hasBody;
isFormEncoded = builder.isFormEncoded;
isMultipart = builder.isMultipart;
parameterHandlers = builder.parameterHandlers;
isKotlinSuspendFunction = builder.isKotlinSuspendFunction;
}
这里给Builder传入了retrofit对象,并作为retrofit字段的值, 而随后在RequestFactory中,baseUrl又直接来自builder.retrofit.baseUrl, 期间并没有进行任何copy行为, 再看对于Request的生成:
//RequestFactory.create
okhttp3.Request create(Object[] args) throws IOException {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") // It is an error to invoke a method with the wrong arg types.
ParameterHandler<Object>[] handlers = (ParameterHandler<Object>[]) parameterHandlers;
int argumentCount = args.length;
if (argumentCount != handlers.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Argument count ("
+ argumentCount
+ ") doesn't match expected count ("
+ handlers.length
+ ")");
}
RequestBuilder requestBuilder =
new RequestBuilder(
httpMethod,
baseUrl,
relativeUrl,
headers,
contentType,
hasBody,
isFormEncoded,
isMultipart);
if (isKotlinSuspendFunction) {
// The Continuation is the last parameter and the handlers array contains null at that index.
argumentCount--;
}
List<Object> argumentList = new ArrayList<>(argumentCount);
for (int p = 0; p < argumentCount; p++) {
argumentList.add(args[p]);
handlers[p].apply(requestBuilder, args[p]);
}
return requestBuilder.get().tag(Invocation.class, new Invocation(method, argumentList)).build();
}
这里上面进行了一堆校验, 生成交给了requestBuilder.get
//RequestBuilder.get
Request.Builder get() {
HttpUrl url;
HttpUrl.Builder urlBuilder = this.urlBuilder;
//retrofit对RequestBuilder的构造并没有给urlBuilder赋非空值, 这里跳过
if (urlBuilder != null) {
url = urlBuilder.build();
} else {
// No query parameters triggered builder creation, just combine the relative URL and base URL.
//noinspection ConstantConditions Non-null if urlBuilder is null.
url = baseUrl.resolve(relativeUrl);
if (url == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Malformed URL. Base: " + baseUrl + ", Relative: " + relativeUrl);
}
}
RequestBody body = this.body;
if (body == null) {
// Try to pull from one of the builders.
if (formBuilder != null) {
body = formBuilder.build();
} else if (multipartBuilder != null) {
body = multipartBuilder.build();
} else if (hasBody) {
// Body is absent, make an empty body.
body = RequestBody.create(null, new byte[0]);
}
}
//Request.url
public Builder url(HttpUrl url) {
if (url == null) throw new NullPointerException("url == null");
this.url = url;
return this;
}
//Request
Request(Builder builder) {
this.url = builder.url;
this.method = builder.method;
this.headers = builder.headers.build();
this.body = builder.body;
this.tags = Util.immutableMap(builder.tags);
}
这里url的构造生成调用的是baseUrl.resolve方法,从头到尾,生成使用的始终都是retrofit对象中的**baseUrl字段**, 也就是说,可以用Reflect直接修改retrofit的baseUrl字段, 那么, 一切都会变的好了起来。
//HttpUrl
final String scheme;
/** Decoded username. */
private final String username;
/** Decoded password. */
private final String password;
/** Canonical hostname. */
final String host;
/** Either 80, 443 or a user-specified port. In range [1..65535]. */
final int port;
/**
* A list of canonical path segments. This list always contains at least one element, which may be
* the empty string. Each segment is formatted with a leading '/', so if path segments were ["a",
* "b", ""], then the encoded path would be "/a/b/".
*/
private final List<String> pathSegments;
/**
* Alternating, decoded query names and values, or null for no query. Names may be empty or
* non-empty, but never null. Values are null if the name has no corresponding '=' separator, or
* empty, or non-empty.
*/
private final @Nullable List<String> queryNamesAndValues;
/** Decoded fragment. */
private final @Nullable String fragment;
/** Canonical URL. */
private final String url;
首先, 生成一个帮助类
public class HttpUrlHelper {
private static final Field hostField;
private final HttpUrl httpUrl;
static {
try {
hostField = HttpUrl.class.getDeclaredField("host");
hostField.setAccessible(true);
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public HttpUrlHelper(HttpUrl httpUrl){
this.httpUrl = httpUrl;
}
public HttpUrl getHttpUrl(){
return httpUrl;
}
public void setBaseUrl(String host)throws Exception{
hostField.set(httpUrl, host);
}
}
运行以下代码:
public static void main(String... args) throws Exception {
// Create a very simple REST adapter which points the GitHub API.
HttpUrlHelper httpUrlHelper = new HttpUrlHelper(HttpUrl.get(API_URL));
Retrofit retrofit =
new Retrofit.Builder()
.baseUrl(httpUrlHelper.getHttpUrl())
.addConverterFactory(GsonConverterFactory.create())
.client(new OkHttpClient.Builder()
.addInterceptor(new HttpLoggingInterceptor(System.out::println).setLevel(HttpLoggingInterceptor.Level.BODY))
.build())
.build();
// Create an instance of our GitHub API interface.
GitHub github = retrofit.create(GitHub.class);
getContributors(github);
httpUrlHelper.setBaseUrl(FALSE_URL);
getContributors(github);
}
private static void getContributors(GitHub github) throws Exception {
Call<List<GitHub.Contributor>> call = github.contributors("square", "retrofit");
List<GitHub.Contributor> contributors = call.execute().body();
for (GitHub.Contributor contributor : contributors) {
System.out.println(contributor.login + " (" + contributor.contributions + ")");
}
}
两次请求分别为:
https://api.github.com/repos/square/retrofit/contributors
https://false.api.github.com/repos/square/retrofit/contributors
啊, 顺带一提,final的基本类型是无法用反射修改的,如果碰见final的基本类型,就别想着反射修改了。
处理响应
返回结果类型:
- returnType:
Call<List<Contributor>> - responseType:
Call<List<Contributor>>
适配返回结果
在传入的create方法中生成的InvocationHandler中
return platform.isDefaultMethod(method)
? platform.invokeDefaultMethod(method, service, proxy, args)
: loadServiceMethod(method).invoke(args);
invoke方法是接口ServiceMethod的一个声明,具体实现在HttpServiceMethod中
//HttpServiceMethod.invoke
@Override
final @Nullable ReturnT invoke(Object[] args){
Call<ResponseT> call = new OkHttpCall<>(requestFactory, args, callFactory, responseConverter);
return adapt(call, args);
}
adapt方法有三个默认实现

这里打开CallAdapted
//CallAdapted.adapt
@Override
protected ReturnT adapt(Call<ResponseT> call, Object[] args){
return callAdapter.adapt(call);
}
而callAdapter是一个适配器模式
public interface CallAdapter<R, T>{
Type responseType();
T adapt(Call<R> call);
}
在DefaultCallAdapterFactory中
public @Nullable CallAdapter<?, ?> get(
Type returnType, Annotation[] annotations, Retrofit retrofit) {
if (getRawType(returnType) != Call.class) {
return null;
}
//检测是否是泛型
if (!(returnType instanceof ParameterizedType)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Call return type must be parameterized as Call<Foo> or Call<? extends Foo>");
}
//得到第一个泛型实参
final Type responseType = Utils.getParameterUpperBound(0, (ParameterizedType) returnType);
final Executor executor =
Utils.isAnnotationPresent(annotations, SkipCallbackExecutor.class)
? null
: callbackExecutor;
return new CallAdapter<Object, Call<?>>() {
@Override
public Type responseType() {
return responseType;
}
@Override
public Call<Object> adapt(Call<Object> call) {
//如果有线程, 那就切换一下
return executor == null ? call : new ExecutorCallbackCall<>(executor, call);
}
};
}
getRawType获得泛型参数的最外层类型, Call类型在创建时传入的时OkHttpCall
//HttpServiceMethod.invoke
final ReturnT invoke(Object[] args){
Call<ResponseT> call = new OkHttpCall<>(requestFactory, args, callFactory, responseConverter);
return adapt(call, args);
}
支持RxJava
//RxJavaCallAdapterFactory.get
public @Nullable CallAdapter<?, ?> get(
Type returnType, Annotation[] annotations, Retrofit retrofit) {
Class<?> rawType = getRawType(returnType);
boolean isSingle = rawType == Single.class;
boolean isCompletable = rawType == Completable.class;
if (rawType != Observable.class && !isSingle && !isCompletable) {
return null;
}
if (isCompletable) {
return new RxJavaCallAdapter(Void.class, scheduler, isAsync, false, true, false, true);
}
boolean isResult = false;
boolean isBody = false;
Type responseType;
if (!(returnType instanceof ParameterizedType)) {
String name = isSingle ? "Single" : "Observable";
throw new IllegalStateException(
name
+ " return type must be parameterized"
+ " as "
+ name
+ "<Foo> or "
+ name
+ "<? extends Foo>");
}
Type observableType = getParameterUpperBound(0, (ParameterizedType) returnType);
Class<?> rawObservableType = getRawType(observableType);
if (rawObservableType == Response.class) {
if (!(observableType instanceof ParameterizedType)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Response must be parameterized" + " as Response<Foo> or Response<? extends Foo>");
}
responseType = getParameterUpperBound(0, (ParameterizedType) observableType);
} else if (rawObservableType == Result.class) {
if (!(observableType instanceof ParameterizedType)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Result must be parameterized" + " as Result<Foo> or Result<? extends Foo>");
}
responseType = getParameterUpperBound(0, (ParameterizedType) observableType);
isResult = true;
} else {
responseType = observableType;
isBody = true;
}
return new RxJavaCallAdapter(
responseType, scheduler, isAsync, isResult, isBody, isSingle, false);
}
从代码中可以看到,RxJava不只支持Observable还支持Completable的ReturnType, 还支持
Response和Result的ResponseType, 如果ReturnType是Result,那么isResult为true, 不然的话若也不是Response, 那么isBody为true。
public Object adapt(Call<R> call) {
OnSubscribe<Response<R>> callFunc =
isAsync ? new CallEnqueueOnSubscribe<>(call) : new CallExecuteOnSubscribe<>(call);
OnSubscribe<?> func;
if (isResult) {
func = new ResultOnSubscribe<>(callFunc);
} else if (isBody) {
func = new BodyOnSubscribe<>(callFunc);
} else {
func = callFunc;
}
Observable<?> observable = Observable.create(func);
if (scheduler != null) {
observable = observable.subscribeOn(scheduler);
}
if (isSingle) {
return observable.toSingle();
}
if (isCompletable) {
return observable.toCompletable();
}
return observable;
}
通常拿到的是一个BodyOnSubscibe的类
//Observable.create
public static <T> Observable<T> create(OnSubscribe<T> f) {
return new Observable<T>(RxJavaHooks.onCreate(f));
}
static void initCreate() {
onObservableCreate = new Func1<Observable.OnSubscribe, Observable.OnSubscribe>() {
@Override
public Observable.OnSubscribe call(Observable.OnSubscribe f) {
return RxJavaPlugins.getInstance().getObservableExecutionHook().onCreate(f);
}
};
...
}
//RxJavaHooks.onCreate.
public static <T> Observable.OnSubscribe<T> onCreate(Observable.OnSubscribe<T> onSubscribe) {
Func1<Observable.OnSubscribe, Observable.OnSubscribe> f = onObservableCreate;
if (f != null) {
return f.call(onSubscribe);
}
return onSubscribe;
}
这里没得看, 反正就是RxJava的一个思路,最终会调用到onNext就是了,subcribe最终会调用RxJavaHooks.onObservableStart进行订阅
//Observable.subsribe
ublic final Subscription subscribe(final Action1<? super T> onNext) {
if (onNext == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("onNext can not be null");
}
Action1<Throwable> onError = InternalObservableUtils.ERROR_NOT_IMPLEMENTED;
Action0 onCompleted = Actions.empty();
return subscribe(new ActionSubscriber<T>(onNext, onError, onCompleted));
}
public void onNext(Response<R> response) {
if (response.isSuccessful()) {
subscriber.onNext(response.body());
} else {
subscriberTerminated = true;
Throwable t = new HttpException(response);
try {
subscriber.onError(t);
} catch (OnCompletedFailedException
| OnErrorFailedException
| OnErrorNotImplementedException e) {
RxJavaPlugins.getInstance().getErrorHandler().handleError(e);
} catch (Throwable inner) {
Exceptions.throwIfFatal(inner);
CompositeException composite = new CompositeException(t, inner);
RxJavaPlugins.getInstance().getErrorHandler().handleError(composite);
}
}
}
response的body的类型就是ResponseType
//CallExecuteObservable.onsubscribeActual
protected void subscribeActual(Observer<? super Response<T>> observer) {
// Since Call is a one-shot type, clone it for each new observer.
Call<T> call = originalCall.clone();
CallDisposable disposable = new CallDisposable(call);
observer.onSubscribe(disposable);
if (disposable.isDisposed()) {
return;
}
boolean terminated = false;
try {
Response<T> response = call.execute();
if (!disposable.isDisposed()) {
observer.onNext(response);
}
if (!disposable.isDisposed()) {
terminated = true;
observer.onComplete();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
Exceptions.throwIfFatal(t);
if (terminated) {
RxJavaPlugins.onError(t);
} else if (!disposable.isDisposed()) {
try {
observer.onError(t);
} catch (Throwable inner) {
Exceptions.throwIfFatal(inner);
RxJavaPlugins.onError(new CompositeException(t, inner));
}
}
}
其实就是直接拿Response, 然后调用onNext.
{
subscriberTerminated = true;
Throwable t = new HttpException(response);
try {
subscriber.onError(t);
} catch (OnCompletedFailedException
| OnErrorFailedException
| OnErrorNotImplementedException e) {
RxJavaPlugins.getInstance().getErrorHandler().handleError(e);
} catch (Throwable inner) {
Exceptions.throwIfFatal(inner);
CompositeException composite = new CompositeException(t, inner);
RxJavaPlugins.getInstance().getErrorHandler().handleError(composite);
}
}
}
response的body的类型就是`ResponseType`
```java
//CallExecuteObservable.onsubscribeActual
protected void subscribeActual(Observer<? super Response<T>> observer) {
// Since Call is a one-shot type, clone it for each new observer.
Call<T> call = originalCall.clone();
CallDisposable disposable = new CallDisposable(call);
observer.onSubscribe(disposable);
if (disposable.isDisposed()) {
return;
}
boolean terminated = false;
try {
Response<T> response = call.execute();
if (!disposable.isDisposed()) {
observer.onNext(response);
}
if (!disposable.isDisposed()) {
terminated = true;
observer.onComplete();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
Exceptions.throwIfFatal(t);
if (terminated) {
RxJavaPlugins.onError(t);
} else if (!disposable.isDisposed()) {
try {
observer.onError(t);
} catch (Throwable inner) {
Exceptions.throwIfFatal(inner);
RxJavaPlugins.onError(new CompositeException(t, inner));
}
}
}
其实就是直接拿Response, 然后调用onNext.






















 7万+
7万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








