1.大体思路
队列内使用最大堆排序,将最大值放在根节点,出队操即每次取出堆顶值,并将队列长度减1;入队操作则是在队列末尾加入待入队的数字,并使用之前函数BuildMaxHeap(Arr, Len)重新建立最大堆;获得队首值则直接返回Arr[0]即可,每次操作前检查队列是否为空。
2.代码如下
#include <iostream>
#include <ctime>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace std;
int Len;
int Arr[100];
//struct HeapStruct {
// int Capacity;
// int Size;
// int *Element;
//};
//HeapStruct* Initialize(int MaxNum) {
//}
void Swape(int *p, int *q) {
int tmp = *p;
*p = *q;
*q = tmp;
}
void RandomSort(int *nArr, int nLen) {
srand(time(NULL));
for(int i = 0; i < nLen; ++i) {
int nIndex = rand() % nLen;
Swape(&nArr[i], &nArr[nIndex]);
//Sleep(2000); //等待2s,更新随机种子
}
}
void InitArr(int *nArr, int nLen) { //初始化数组
srand(time(NULL));
for(int i = 0; i < nLen; ++i) {
//nArr[i] = rand() % 100;
nArr[i] = i;
}
}
void PrintArr(int *nArr, int nLen) { //打印数组
for(int i = 0; i < nLen; ++i) {
cout << nArr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
//返回父节点下标
int Parent(int i) {
return (i - 1) / 2;
}
//返回i左节点下标
int LeftChild(int i) {
return 2 * i + 1;
}
//返回i右节点下标
int RightChild(int i) {
return 2 * i + 2;
}
//最大堆化,保证每个父节点都比子节点大
void MaxHeapify(int *nArr, int nLen, int i) {
int LC = LeftChild(i);
int RC = RightChild(i);
int nMaxPos;
if(LC < nLen && nArr[LC] > nArr[i]) {
nMaxPos = LC;
} else {
nMaxPos = i;
}
if(RC < nLen && nArr[RC] > nArr[nMaxPos]) {
nMaxPos = RC;
}
if(nMaxPos != i) {
Swape(&nArr[nMaxPos], &nArr[i]);
MaxHeapify(nArr, nLen, nMaxPos);
}
}
//将最大值移动到树的根节点,即数组头
void BuildMaxHeap(int *nArr, int nLen) {
for(int i = Parent(nLen - 1); i >= 0; --i) {
MaxHeapify(nArr, nLen, i);
}
}
//最大堆排序
void HeapSort(int *nArr, int nLen) {
BuildMaxHeap(nArr, nLen); //将最大值移动至堆顶
for(int i = nLen - 1; i > 0; --i) {
Swape(&nArr[i], &nArr[0]); //将堆顶的最大值放在数组最末尾nArr[nLen - 1]处
--nLen; //在堆中去除末尾元素(因为已经排好序,最后一位是最大值)
MaxHeapify(nArr, nLen, 0); //从堆顶开始,将刚刚交换上来的nArr[i]往下移动,直至满足其父节点大于其本身的值
}
}
int HeadQueue() { //取队头元素
if(Arr == nullptr || Len == 0) {
cout << "queue empty" << endl;
return -1;
}
return Arr[0];
}
int PopQueue() { //出队
if(Arr == nullptr || Len == 0) {
cout << "queue empty" << endl;
return -1;
}
int res = Arr[0];
Swape(&Arr[Len - 1], &Arr[0]);
--Len;
BuildMaxHeap(Arr, Len);
return res;
}
void PushQueue(int element) { //入队
++Len;
Arr[Len - 1] = element;
BuildMaxHeap(Arr, Len);
}
int main() {
Len = 0;
// InitArr(nArr, Len);
// RandomSort(nArr, Len);
// PrintArr(Arr, Len);
// cout << endl;
//HeapSort(nArr, Len);
cout << "push 5" << endl;
PushQueue(5);
cout << "push 9" << endl;
PushQueue(9);
cout << "push 3" << endl;
PushQueue(3);
cout << "push 15" << endl;
PushQueue(15);
cout << "push -4" << endl;
PushQueue(-4);
cout << "HeadQueue is " << HeadQueue() << endl;
cout << "now queue is " << endl;
PrintArr(Arr, Len);
cout << "pop " << PopQueue() << endl;
cout << "pop " << PopQueue() << endl;
cout << "pop " << PopQueue() << endl;
cout << "push 20" << endl;
PushQueue(20);
cout << "push 6" << endl;
PushQueue(6);
cout << "now queue is " << endl;
PrintArr(Arr, Len);
cout << "pop " << PopQueue() << endl;
cout << "pop " << PopQueue() << endl;
cout << "HeadQueue is " << HeadQueue() << endl;
cout << "now queue is " << endl;
PrintArr(Arr, Len);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
3.运行结果
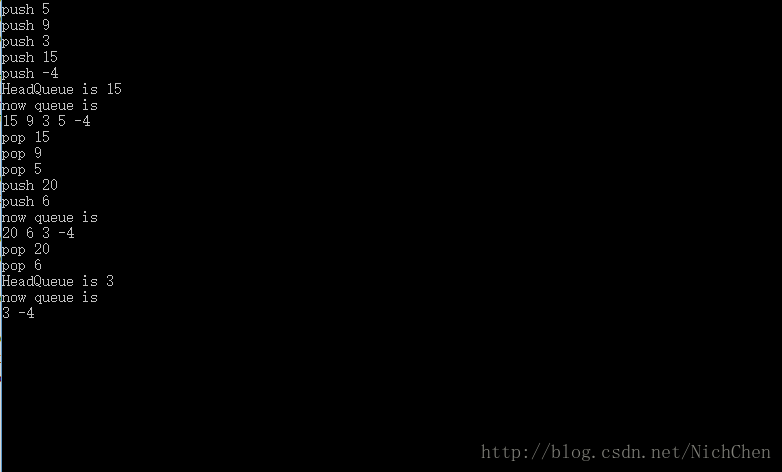
4.总结
需要注意的是,堆排序与二叉搜索树不同,二叉堆只保证了父节点大于子节点,因此在上面输出结果中,Arr数组并不能保证是降序排列的,但可以确保堆顶元素为队内最大值,即可以实现优先队列。出于性能考虑,优先队列用堆来实现,具有O(log n)时间复杂度的插入和提取元素性能,O(n)的初始化构造的时间复杂度。如果使用自平衡二叉查找树,插入与删除的时间复杂度为O(log n),构造二叉树的时间复杂度为O(n log n)。






















 564
564

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








