【0】README
0.1)本文旨在总结出表达式树的构建步骤, 其中还涉及到中缀转后缀表达式,以及如何计算 表达式树中的值;
0.2)本文源代码均为原创;
0.3) 其实, 实现一个简单的计算器, 也即求出中缀表达式的值,我们也可以用栈来实现, 参见 http://blog.csdn.net/pacosonswjtu/article/details/49225529 ; 此处给出 表达式树的实现 仅在于加深对表达式树的理解及它的应用;
【1】表达式树的相关概念
1.1)定义:表达式树的树叶是 操作数operand,比如常量或变量,而其他节点是操作符 operator;
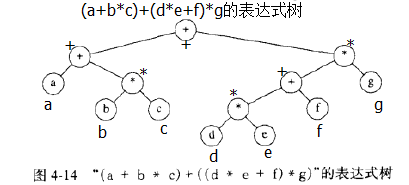
1.2)对上图中的表达式进行遍历(先序+中序+后序)
- 先序遍历: + + a * b c * + * d e f g
- 中序遍历: a + b * c + ( d * c + f ) * g (这里要加上括号, 这也是我们为什么要采用 后缀或逆波兰记法 来表示 用户输入的运算表达式 以计算结果, 一句话,方便可靠)
- 后序遍历: a b c * + d e * f + g * +
- Attention)这里,我们没有给出源代码,因为这个先序,后序 or 中序 的源代码和二叉树遍历的源代码相差无几,这里只是了解下 表达式树的概念,并了解下用 树的遍历计算 表达式的值;
【2】如何构造一颗表达式树(表达式树的定义很关键,对于写我们的递归程序而言)
我们给出一种算法将后缀表达式转变为 表达式树:
- step1)用户输入中缀表达式, 我们首先将其转为后缀表达式;
- step2)我们将后缀表达式转为 表达式树的形式;
- step3)我们来计算该表达式树的计算结果是多少?
2.1 ) download source code: https://github.com/pacosonTang/dataStructure-algorithmAnalysis/tree/master/chapter4/p71_compute_expr_tree
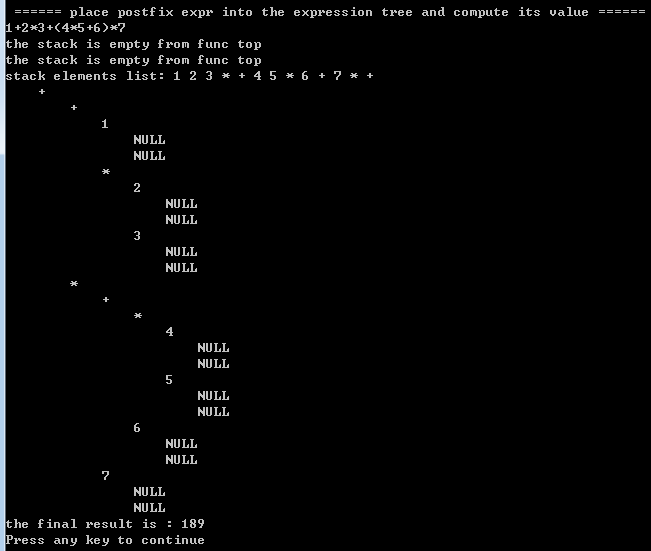
2.2 ) source code at a glance:
2.2.1)expr_tree.c source code :
#include "stack.h"
#include "binary_tree.h"
extern void infir_to_postfix();
extern int computeResult(int operand1, int operand2, int operator_);
extern ElementType compute_postfix();
extern Stack operand;
extern int isOperator(char ch);
extern int computeResult(int operand1, int operand2, int operator_);
// building an expr tree for storing postfix expr
BinaryTree postfixToExprTree()
{
int value;
BinaryTree* treeArray;
int size;
int index;
ElementType *p;
int i ;
size = getTopOfStack(operand) + 1; //get the top of stack, and add 1 to compute size of the stack
treeArray = (BinaryTree*)malloc(size * sizeof(BinaryTree)); // alloc memory for treeArray
index = 0; // set the index of treeArray 0
p = getArray(operand);
i = 0;
while(i < getTopOfStack(operand))
{
value = *(p+i++);
if(value == ' ') // if the value equals ' ', continue
continue;
treeArray[index++] = createBinaryTree(value);// for every element need to build tree node
if(isOperator(value)) // if the value belongs to operator,
{
index--;
insertNode(treeArray[index-1], treeArray[index], 0);
insertNode(treeArray[index-2], treeArray[index], 1);
treeArray[index-2] = treeArray[index];
index --;
}
// (treeArray+index++) = createBinaryTree(value);// if the value belongs to operand, push the element into the treeArray
}
return *treeArray;
}
// preorder the tree
void printPreorder(int depth, BinaryTree root)
{
int i;
if(root) {
for(i = 0; i < depth; i++)
printf(" ");
printf("%c\n", root->value);
printPreorder(depth + 1, root->left);
printPreorder(depth + 1, root->right); // Attention: there's difference between traversing binary tree and common tree
}
else {
for(i = 0; i < depth; i++)
printf(" ");
printf("NULL\n");
}
}
// postordering expression tree with operantors and operands to compute the result of these nodes
int postorder_compute_postfix_expr_tree(BinaryTree root)
{
int temp1;
int temp2;
if(isOperator(root->value)) {
temp1 = postorder_compute_postfix_expr_tree(root->left);
temp2 = postorder_compute_postfix_expr_tree(root->right); // Attention: there's difference between traversing binary tree and common tree
return computeResult(temp1, temp2, root->value);
}
else
return root->value - 48;
}
int main()
{
BinaryTree bt;
// 1.convert infix into postfix expr
printf("\n ====== convert infix into postfix expr ====== \n");
infir_to_postfix(); // after this func is called over, we get the postfix of the expr
// 2.convert postfix into the expression tree
bt = postfixToExprTree();
printPreorder(1, bt);
//3.compute postfix expr stored in the expression tree
printf("the final result is : %2d \n", postorder_compute_postfix_expr_tree(bt));
return 0;
}2.2.2)binary_tree.c source code :
#include "binary_tree.h"
// create a BinaryTree with root node
BinaryTree createBinaryTree(TreeElementType value)
{
BinaryTree t;
t = (BinaryTree)malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree));
if(!t) {
Error("out of space, from func createBinaryTree");
return NULL;
}
t->left = NULL;
t->right = NULL;
t->value = value;
return t;
}
// make the BinaryTree empty
BinaryTree makeTreeEmpty(BinaryTree t)
{
if(t){
makeTreeEmpty(t->left);
makeTreeEmpty(t->right);
free(t);
}
return NULL;
}
//insert a Tree node with value e into left child or right child of the parent
BinaryTree insert(TreeElementType e, BinaryTree parent, int isLeft)
{
BinaryTree node;
if(!parent){
Error("for parent BinaryTree node is empty , you cannot insert one into the parent node, from func insert");
return NULL;
}
node = (BinaryTree)malloc(sizeof(struct BinaryTree));
if(!node) {
Error("out of space, from func insert");
return NULL;
}
node->value = e;
node->right = NULL;
node->left = NULL;// building the node with value e over
if(isLeft) { // the tree node inserting into left child of the parent
if(parent->left) {
Error("for parent has already had a left child , you cannot insert one into the left child, from func insert");
return NULL;
}
parent->left = node;
}
else { // the tree node inserting into right child of the parent
if(parent->right) {
Error("for parent has already had a right child , you cannot insert one into the right child, from func insert");
return NULL;
}
parent->right = node;
}
return node;
}
//insert a Tree node into left child or right child of the parent
BinaryTree insertNode(BinaryTree node, BinaryTree parent, int isLeft)
{
if(!parent){
Error("for parent BinaryTree node is empty , you cannot insert one into the parent node, from func insert");
return NULL;
}
if(!node) {
Error("for the node inserted is NULL , so you cannot insert a NULL node, from func insert");
return NULL;
}
if(isLeft) // the tree node inserting into left child of the parent
parent->left = node;
else // the tree node inserting into right child of the parent
parent->right = node;
return node;
}
// find the BinaryTree root node with value equaling to e
BinaryTree find(TreeElementType e, BinaryTree root)
{
BinaryTree temp;
if(root == NULL)
return NULL;
if(root->value == e)
return root;
temp = find(e, root->left);
if(temp)
return temp;
else
return find(e, root->right);
}
// analog print directories and files name in the BinaryTree, which involves postorder traversal.
void printPostorder(int depth, BinaryTree root)
{
int i;
if(root) {
printPostorder(depth + 1, root->left);
printPostorder(depth + 1, root->right); // Attention: there's difference between traversing binary tree and common tree
for(i = 0; i < depth; i++)
printf(" ");
printf("%c\n", root->value);
}
else {
for(i = 0; i < depth; i++)
printf(" ");
printf("NULL\n");
}
}2.2.3)stack.h source code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define ElementType int
#define EmptyStack -1
#define Error(str) printf("%s",str)
#define FatalError(str) printf("%s",str)
#define minStackSize 5
struct Stack;
typedef struct Stack *Stack;
int isFull(Stack s);
int isEmpty(Stack s);
Stack createStack(int);
void disposeStack(Stack s);
void makeEmpty(Stack s);
void push(ElementType e, Stack s);
ElementType top(Stack s);
void pop(Stack s);
ElementType top(Stack s);
int getTopOfStack(Stack s);
ElementType *getArray(Stack s);
void printStack(Stack s);
void printStack_postfix(Stack s);
struct Stack {
int capacity;
int topOfStack;
ElementType *array;
} ;2.2.4)binary_tree.h source code :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#define TreeElementType char
#define Error(str) printf("%s",str)
struct BinaryTree;
typedef struct BinaryTree *BinaryTree;
BinaryTree createBinaryTree(TreeElementType); // this func is different from that in p70_preorder_binary_tree.c
BinaryTree makeTreeEmpty(BinaryTree);
BinaryTree insert(TreeElementType, BinaryTree, int);
BinaryTree insertNode(BinaryTree, BinaryTree, int);
BinaryTree find(TreeElementType, BinaryTree);
void printPostorder(int depth, BinaryTree root);
// we adopt child-sibling notation
struct BinaryTree
{
TreeElementType value;
BinaryTree left;
BinaryTree right;
};2.2.5)stack.c source code :
#include "stack.h"
int getTopOfStack(Stack s)
{
return s->topOfStack;
}
//return stack's array
ElementType *getArray(Stack s)
{
return s->array;
}
//judge whether the stack is empty or not
int isFull(Stack s)
{
return s->capacity - 1 == s->topOfStack ? 1 : 0;
}
//judge whether the stack is empty or not
int isEmpty(Stack s)
{
return s->topOfStack == -1;
}
//create stack with the head node
Stack createStack(int size)
{
Stack s;
s = (Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct Stack));
if(size < minStackSize) {
Error("stack size is too small, and creating stack with defualt size 5");
size = minStackSize;
}
if(s == NULL) {
FatalError("out of space when allocting memory for stack s");
return NULL;
}
s->array = (ElementType *)malloc(size * sizeof(ElementType));
if(s->array == NULL) {
FatalError("out of space when allocting memory for stack's array ");
return NULL;
}
s->topOfStack = -1;
s->capacity = size;
return s;
}
//dispose stack
void disposeStack(Stack s)
{
free(s->array);
free(s);
}
//pop all elements in the stack
void makeEmpty(Stack s)
{
if(s->topOfStack == -1)
Error("must create the stack first");
while(!isEmpty(s))
pop(s);
}
//push the node with value e into the stack s
//attend that first moving ptr ,then executing push operation
void push(ElementType e, Stack s)
{
ElementType *temp = s->array;
if(isFull(s))
Error("the Stack is full, push failure! ");
else{
s->topOfStack ++;
s->array[s->topOfStack] = e;
}
}
// pop the node or element on the top of stack
//attend that first executing pop operation,then moving ptr
void pop(Stack s)
{
if(isEmpty(s))
Error("empty stack");
else
s->topOfStack --;
}
// return the value of the top node in the stack
ElementType top(Stack s)
{
if(!isEmpty(s))
return s->array[s->topOfStack];
Error("the stack is empty from func top\n");
return -1;
}
//print value of element in the stack s
void printStack(Stack s)
{
int i;
if(isEmpty(s)){
Error("empty stack");
return ;
}
for(i=0; i<= s->topOfStack; i++)
printf("%4d", s->array[i]);
printf("\n");
}
//print value of element in the stack s with postfix
void printStack_postfix(Stack s)
{
int i;
if(isEmpty(s)){
Error("empty stack");
return ;
}
printf("stack elements list: ");
for(i=0; i<= s->topOfStack; i++)
printf("%c", s->array[i]);
printf("\n");
}2.2.6)compute_postfix.c source code :
#include "stack.h"
#define Size 100
// refer to p50.c and put it into the same project
extern struct Stack;
typedef struct Stack *Stack;
extern Stack operand; // operand is an extern variable defined in infixToPostfix
extern int isOperator(char ch);
extern void infir_to_postfix();
int computeResult(int operand1, int operand2, int operator_);
int computeResult(int operand1, int operand2, int operator_)
{
switch(operator_)
{
case '+': return operand1 + operand2;
case '*': return operand1 * operand2;
default: return 0; break;
}
}
// compute final result of responding postfix
ElementType compute_postfix()
{
Stack output;
int i;
ElementType *p;
int value;
int operand1;
int operand2;
output = createStack(Size); // create stack with length Size
i = 0;
p = getArray(operand); // get operand->array
while(i < getTopOfStack(operand))
{
value = *(p+i++);
if(value == ' ')
continue;
if(isOperator(value))
{
operand1 = top(output);
pop(output);
operand2 = top(output);
pop(output);
value = computeResult(operand1, operand2, value);
push(value, output);
continue;
}
push(value - 48, output);
}
return getArray(output)[0];
}2.2.7)infixToPostfix.c source code :
#include "stack.h"
#define Size 100
// refer to p50.c and put it into the same project
extern struct Stack;
typedef struct Stack *Stack;
Stack operand; // declaration of Stack operand
int isOperator(char ch);
void infir_to_postfix();
//compare operator's priority between ch1 and ch2, return -1, 0 or 1
int priorityBigger(char ch1, char ch2)
{
int size = 8;
char operator_[]={ '(', ')', ' ', '+', '-', ' ', '*', '/'};
int index1, index2;
int i;
if(ch1 - ch2 == 0)
return 0;
for(i = 0; i< size; i++)
if(operator_[i] == ch1)
index1 = i;
else if(operator_[i] == ch2)
index2 = i;
index1 -= index2;
if(index1 == 1 || index1 == -1)
return 0;
else if(index1 > 1)
return 1;
else if(index1 < -1)
return -1;
}
//judge whether the ch is operator or not ,also 1 or 0
int isOperator(char ch)
{
int size;
char operator_[]={'(', '+', '-', '*', '/', ')'};
int i;
size = 6;
for(i = 0; i < size; i++)
if(ch == operator_[i])
break;
return i == size ? 0 : 1;
}
//convert a part of str with length len into responding element value
ElementType strToElement(int *str, int len)
{
int i;
int value;
i = value = 0;
while(i < len)
{
value += *(str+i) - 48;
if(++i == len)
break;
value *= 10;
}
return value;
}
// convert infix expr into postfix expr
//for operand and operator cannot be in the same type ,we treat them as char and split them with space
void infixToPostfix(Stack s1, Stack s2,char *expr)
{
char ch;
int i;
char top_t;
int flag;
i = 0;
flag = 0;
while((ch = *(expr+i++)) != '\0')
{
if(ch == ')'){// if ch equals ')', pop elements in stack s2 between '(' and ')' into stack s1
while((top_t = top(s2)) != '(' )
{
push(top_t, s1);
push(' ', s1);
pop(s2);
}
pop(s2); // pop '(' in stack s2
continue;
}
if(isOperator(ch)) // isOperator is true
{
if(ch == '(')
{
push(ch, s2); // push '(' into operator stack s2
flag = 1;
continue;
}
while((top_t = top(s2)) != -1 && priorityBigger(top_t, ch) >= 0 && flag ==0)
{
pop(s2);
push(top_t, s1);
push(' ', s1);
}
push(ch, s2); // push operator into operator stack s2
flag = 0;
}
else
{
push(ch, s1);
push(' ', s1); // we treat them as char and split them with space
}
}
// pop element in s2 and push it into s1
while(!isEmpty(s2))
{
push(top(s2), s1);
push(' ', s1);
pop(s2);
}
}
// read expr from console till '\n' and we just only focus on '+' and '*';
// postfix expression like 6 5 2 3 + 8 * + 3 + *
char *read()
{
char *temp;
int len;
char ch;
temp = (char*)malloc(Size * sizeof(char));
len = 0;
while((ch = getchar()) != '\n')
{
if(ch == ' ')
continue;
temp[len++] = ch;
}
temp[len] = '\0';
return temp;
}
// there are 2 stacks, that's operand and operator;
//works list
//1.read expr, 2.convert the expr from infix to postfix, 3.
/*
int main()
{
Stack operand;
Stack operator_;
operand = createStack(Size);
operator_ = createStack(Size);
// convert infix into postfix expr
infixToPostfix(operand, operator_, read());
printStack_postfix(operand);
// compute postfix expr
return 0;
}
*/
void infir_to_postfix()
{
Stack operator_;
//create stack operand and operator_
operand = createStack(Size);
operator_ = createStack(Size);
// convert infix into postfix expr
infixToPostfix(operand, operator_, read());
printStack_postfix(operand);
}





















 3611
3611

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








