【0】README
0)本文部分文字描述转自 “how tomcat works”,旨在学习 “tomcat(12)StandardContext源码剖析” 的基础知识;
1)Context实例表示一个具体的web 应用程序,其中包含一个或多个Wrapper实例,每个Wrapper 表示一个具体的servlet定义;
2)Context容器还需要其他组件的支持,如载入器和Session 管理器。本章要intro 的 StandardContext是 catalina中Context接口的标准实现;
3)本文首先会回顾StandardContext类的实例化和配置,然后讨论与其相关的StandardMapper类 和 ContextConfig类。接下来,学习对于引入的每个HTTP 请求的方法调用序列;
【1】StardardContext 配置
1)intro:创建了StandardContext实例后,必须调用其start() 方法来为引入的每个http 请求提供服务;
1.1)StandardContext对象可能启动失败:这时available 设置为false,该属性表明StandardContext 对象是否可用;1.2)若启动成功:available=true,则表明StandardContext 对象配置正确;
2)正确配置StandardContext后,StandardContext才能读入并解析默认的 web.xml文件,该文件位于 %CATALINA_HOME%/conf 目录下,该文件的内容会应用到所有部署到tomcat 中的应用程序中。这也保证了StandardContext 实例可以处理应用程序级的web.xml 文件;
3)StandardContext.configured属性:表明StandardContext 实例是否正确配置
3.1)StandardContext使用了一个事件监听器作为其配置器;(干货——StandardContext使用了一个事件监听器作为其配置器,参见下图中StandardContext.start()方法中lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(BEFORE_START_EVENT, null) 调用)3.2)当调用StandardContext.start()方法时,其中要做的一件事情是,触发一个生命周期事件。该事件调用监听器,对StandardContext实例进行配置;3.3)若配置成功,则监听器将 configured设置为true,否则StandardContext 实例拒绝启动,也就无法为http 请求提供服务了;
Attention)下面的图片借用了 “tomcat(10)安全性中章节【6.4】中Supplement-补充模块”的第1张图;
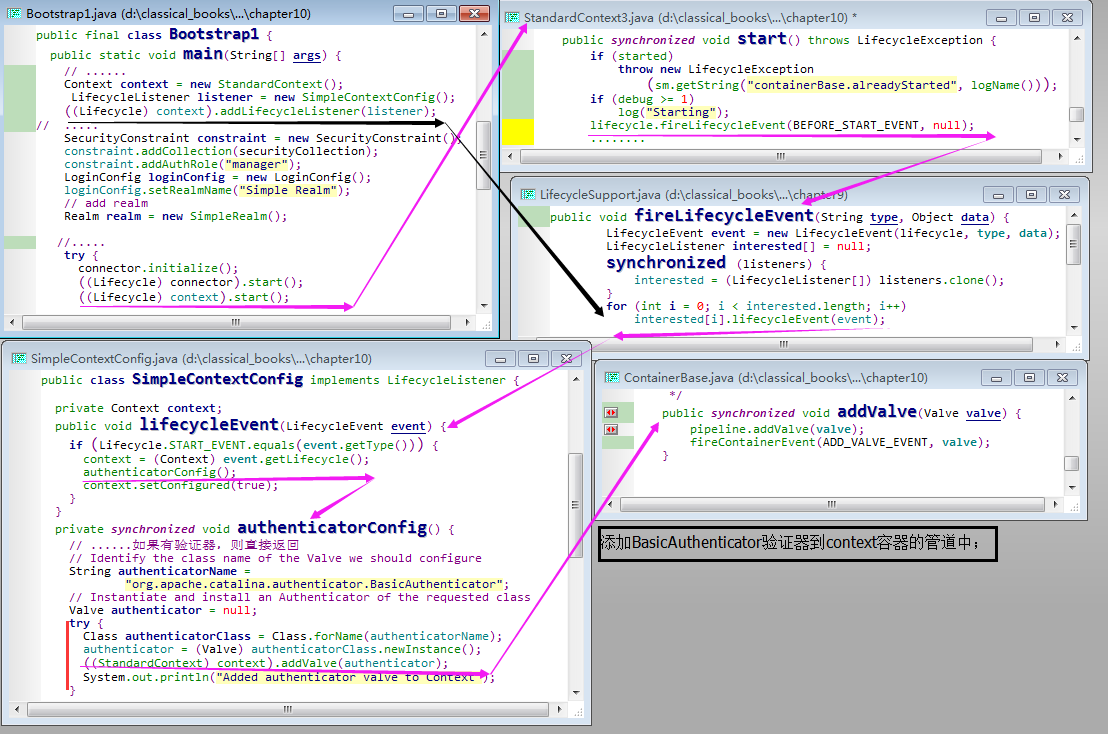
【1.1】StandardContext 类的构造函数
1)源代码如下:
public StandardContext() { // org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext.StandardContext().
super();
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardContextValve());
namingResources.setContainer(this);
}
2)构造函数最重要的事情:是为 StandardContext 实例的管道对象设置基础阀;
【1.2】启动StandardContext 实例
1)start()方法会初始化 StandardContext对象,用生命周期监听器配置 StandardContext实例;
1.1)StandardContext 对象可能启动失败:这时available 设置为false,该属性表明StandardContext 对象是否可用;1.2)若启动成功:available=true,则表明StandardContext 对象配置正确,与其关联的子容器和组件都正确启动;
2)正确配置后,StandardContext实例可以准备为引入的 http 请求提供服务了。若期间发生了错误,则available设置为false;
3)StandardContext.configured属性:表明StandardContext 实例是否正确配置
3.1)在start()方法的末尾, StandardContext实例会检查 configured变量的值,若configured设置为 true,则StandardContext 启动成功;
3.2)否则,调用stop() 方法,关闭在start() 方法已经启动的所有组件;
public synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException { //org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext.start()方法
if (started)
throw new LifecycleException
(sm.getString("containerBase.alreadyStarted", logName()));
if (debug >= 1)
log("Starting");
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(BEFORE_START_EVENT, null);
if (debug >= 1)
log("Processing start(), current available=" + getAvailable());
setAvailable(false);
setConfigured(false);
boolean ok = true;
// Add missing components as necessary
if (webappResources == null) { // (1) Required by Loader
if (debug >= 1)
log("Configuring default Resources");
try {
if ((docBase != null) && (docBase.endsWith(".war")))
setResources(new WARDirContext());
else
setResources(new FileDirContext());
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
log("Error initializing resources: " + e.getMessage());
ok = false;
}
}
if (ok) {
if (!resourcesStart())
ok = false;
}
// Install DefaultContext configuration
if (!getOverride()) {
Container host = getParent();
if (host instanceof StandardHost) {
((StandardHost)host).installDefaultContext(this);
Container engine = host.getParent();
if( engine instanceof StandardEngine ) {
((StandardEngine)engine).installDefaultContext(this);
}
}
}
if (getLoader() == null) { // (2) Required by Manager
if (getPrivileged()) {
if (debug >= 1)
log("Configuring privileged default Loader");
setLoader(new WebappLoader(this.getClass().getClassLoader()));
} else {
if (debug >= 1)
log("Configuring non-privileged default Loader");
setLoader(new WebappLoader(getParentClassLoader()));
}
}
if (getManager() == null) { // (3) After prerequisites
if (debug >= 1)
log("Configuring default Manager");
setManager(new StandardManager());
}
// Initialize character set mapper
getCharsetMapper();
// Post work directory
postWorkDirectory();
// Reading the "catalina.useNaming" environment variable
String useNamingProperty = System.getProperty("catalina.useNaming");
if ((useNamingProperty != null)
&& (useNamingProperty.equals("false"))) {
useNaming = false;
}
if (ok && isUseNaming()) {
if (namingContextListener == null) {
namingContextListener = new NamingContextListener();
namingContextListener.setDebug(getDebug());
namingContextListener.setName(getNamingContextName());
addLifecycleListener(namingContextListener);
}
}
// Binding thread
ClassLoader oldCCL = bindThread();
// Standard container startup
if (debug >= 1)
log("Processing standard container startup");
if (ok) {
try {
addDefaultMapper(this.mapperClass);
started = true;
// Start our subordinate components, if any
if ((loader != null) && (loader instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) loader).start();
if ((logger != null) && (logger instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) logger).start();
// Unbinding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
// Binding thread
oldCCL = bindThread();
if ((cluster != null) && (cluster instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
if ((realm != null) && (realm instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
if ((resources != null) && (resources instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) resources).start();
// Start our Mappers, if any
Mapper mappers[] = findMappers();
for (int i = 0; i < mappers.length; i++) {
if (mappers[i] instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) mappers[i]).start();
}
// Start our child containers, if any
Container children[] = findChildren();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
if (children[i] instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) children[i]).start();
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic),
// if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(START_EVENT, null);
if ((manager != null) && (manager instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) manager).start();
} finally {
// Unbinding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
}
}
if (!getConfigured())
ok = false;
// We put the resources into the servlet context
if (ok)
getServletContext().setAttribute
(Globals.RESOURCES_ATTR, getResources());
// Binding thread
oldCCL = bindThread();
// Create context attributes that will be required
if (ok) {
if (debug >= 1)
log("Posting standard context attributes");
postWelcomeFiles();
}
// Configure and call application event listeners and filters
if (ok) {
if (!listenerStart())
ok = false;
}
if (ok) {
if (!filterStart())
ok = false;
}
// Unbinding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
// Set available status depending upon startup success
if (ok) {
if (debug >= 1)
log("Starting completed");
setAvailable(true);
} else {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.startFailed"));
try {
stop();
} catch (Throwable t) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.startCleanup"), t);
}
setAvailable(false);
throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("standardContext.startFailed"));
}
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(AFTER_START_EVENT, null);
// Load and initialize all "load on startup" servlets
oldCCL = bindThread();
loadOnStartup(findChildren());
unbindThread(oldCCL);
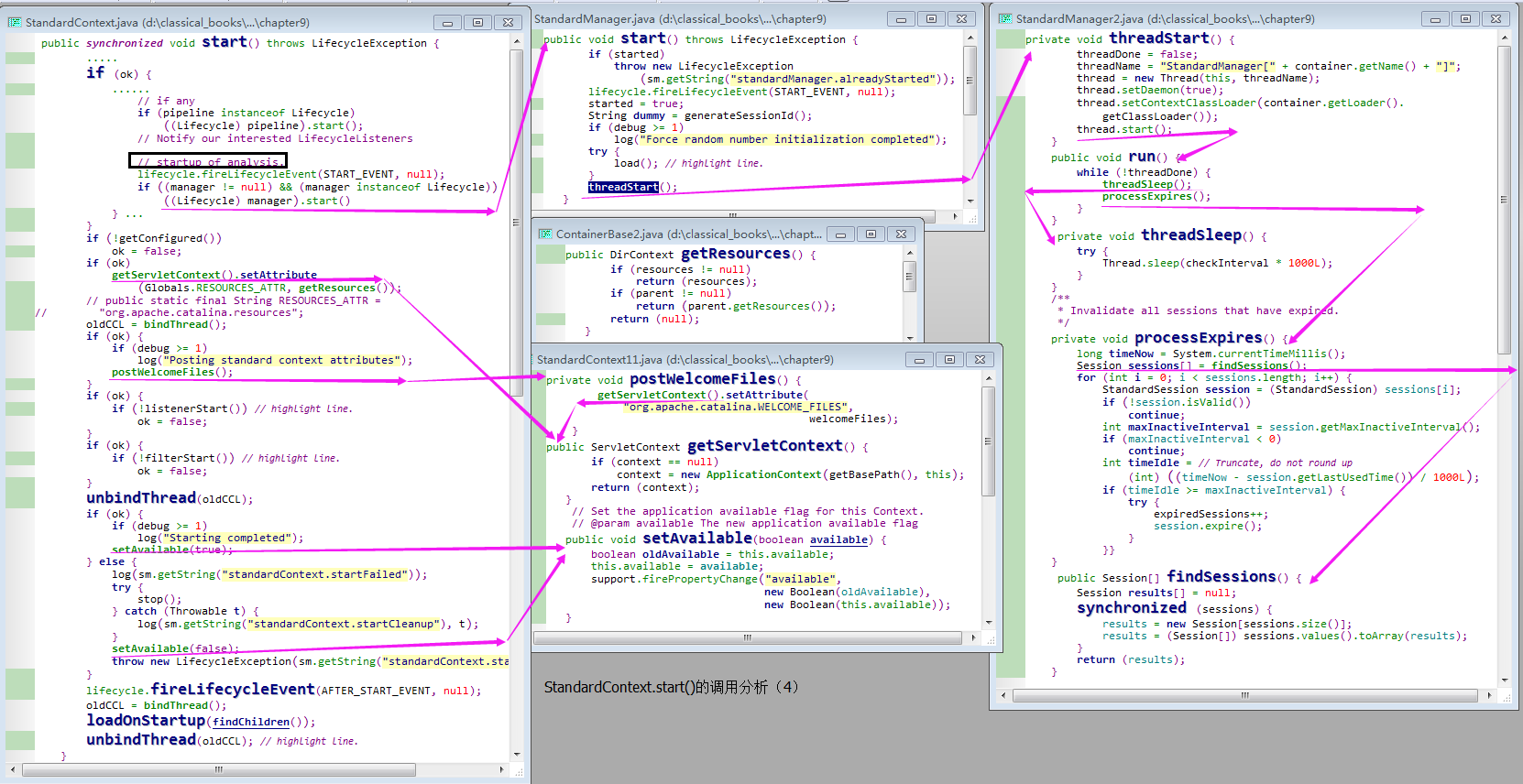
}work1)触发 BEFORE_START 事件;public synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException { //org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext.start()方法。 if (started) throw new LifecycleException (sm.getString("containerBase.alreadyStarted", logName())); if (debug >= 1) log("Starting"); // Notify our interested LifecycleListeners lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(BEFORE_START_EVENT, null);work2)将 availability 属性设置为false;work3)将 configured 属性设置为 false;if (debug >= 1) log("Processing start(), current available=" + getAvailable()); setAvailable(false); setConfigured(false); boolean ok = true;work4)配置资源;// Add missing components as necessary if (webappResources == null) { // (1) Required by Loader if (debug >= 1) log("Configuring default Resources"); try { if ((docBase != null) && (docBase.endsWith(".war"))) setResources(new WARDirContext()); else setResources(new FileDirContext()); } catch (IllegalArgumentException e) { log("Error initializing resources: " + e.getMessage()); ok = false; } } if (ok) { if (!resourcesStart()) ok = false; } // Install DefaultContext configuration if (!getOverride()) { Container host = getParent(); if (host instanceof StandardHost) { ((StandardHost)host).installDefaultContext(this); Container engine = host.getParent(); if( engine instanceof StandardEngine ) { ((StandardEngine)engine).installDefaultContext(this); } } }work5)设置载入器;if (getLoader() == null) { // (2) Required by Manager if (getPrivileged()) { if (debug >= 1) log("Configuring privileged default Loader"); setLoader(new WebappLoader(this.getClass().getClassLoader())); } else { if (debug >= 1) log("Configuring non-privileged default Loader"); setLoader(new WebappLoader(getParentClassLoader())); } }work6)设置Session 管理器;if (getManager() == null) { // (3) After prerequisites if (debug >= 1) log("Configuring default Manager"); setManager(new StandardManager()); }work7)初始化字符集映射器;// Initialize character set mapper getCharsetMapper(); // defined in start(). public CharsetMapper getCharsetMapper() { // Create a mapper the first time it is requested if (this.charsetMapper == null) { try { Class clazz = Class.forName(charsetMapperClass); this.charsetMapper = (CharsetMapper) clazz.newInstance(); } catch (Throwable t) { this.charsetMapper = new CharsetMapper(); } } return (this.charsetMapper); }work8)启动与该Context 容器相关联的组件;// Post work directory postWorkDirectory(); // Reading the "catalina.useNaming" environment variable String useNamingProperty = System.getProperty("catalina.useNaming"); if ((useNamingProperty != null) && (useNamingProperty.equals("false"))) { useNaming = false; } if (ok && isUseNaming()) { if (namingContextListener == null) { namingContextListener = new NamingContextListener(); namingContextListener.setDebug(getDebug()); namingContextListener.setName(getNamingContextName()); addLifecycleListener(namingContextListener); } } // Binding thread ClassLoader oldCCL = bindThread();work9)启动子容器;work10)启动管道对象;work11)启动Session 管理器;
work12)触发 START 事件,在这里监听器(ContextConfig 实例)会执行一些配置操作,若配置成功,ContextConfig 实例会将 StandardContext.configured 变量设置为 true;// Set available status depending upon startup success if (ok) { if (debug >= 1) log("Starting completed"); setAvailable(true); } else { log(sm.getString("standardContext.startFailed")); try { stop(); } catch (Throwable t) { log(sm.getString("standardContext.startCleanup"), t); } setAvailable(false); throw new LifecycleException(sm.getString("standardContext.startFailed")); }work13)检查 configured 属性的值,若为true,则调用 postWelcomePages()方法,载入那些需要在启动时就载入的子容器,即 Wrapper实例,将 availability属性设置为 true。若 configured 变量为false, 则调用stop() 方法;// Create context attributes that will be required if (ok) { // defined in start() method. if (debug >= 1) log("Posting standard context attributes"); postWelcomeFiles(); } private void postWelcomeFiles() { getServletContext().setAttribute("org.apache.catalina.WELCOME_FILES", welcomeFiles); }work14)触发 AFTER_START 事件;
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(AFTER_START_EVENT, null); // highlight line.
// Load and initialize all "load on startup" servlets
oldCCL = bindThread();
loadOnStartup(findChildren());
unbindThread(oldCCL);
【1.3】 org.apahce.catalina.core.StandardContext.invoke() 方法
1)该方法首先会检查应用程序是否正在重载过程中,若是,则等待应用程序重载完成。然后,它调用其父类的 ContainerBase.invoke() 方法;
public void invoke(Request request, Response response) throws IOException, ServletException {
// Wait if we are reloading
while (getPaused()) { // 返回 paused属性的值,当paused为true时,表明应用程序正在重载;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
;
}
}
// Normal request processing
if (swallowOutput) {
try {
SystemLogHandler.startCapture();
super.invoke(request, response);
} finally {
String log = SystemLogHandler.stopCapture();
if (log != null && log.length() > 0) {
log(log);
}
}
} else {
super.invoke(request, response);
}
}Attention)上述的StandardContext.invoke() 方法是tomcat 4中的实现,而在 tomcat5中,StandardContext 并没有提供 invoke()方法的实现,所以会执行 ContainerBase.invoke() 方法;而检查应用程序是否正在重载的工作移到了 StandardContextValve.invoke() 方法中;
【2】StandardContextMapper 类
1)对于每个引入的http 请求,都会调用 StandardContext实例的管道对象的基础阀的invoke() 方法来处理;
1.1)StandardContext 实例的基础阀:是 org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextValve 类的实例;1.2)StandardContextValve.invoke()方法要做的第一件事:是获取一个要处理 http 请求 的Wrapper 实例;
2)在tomcat4中,StandardContextValve实例在它包含的 StandardContext中查找。StandardContextValve实例使用 StandardContext实例的映射器找到一个合适的 Wrapper实例。获得Wrapper实例后,它就会调用 Wrapper.invoke()方法;
3)我们谈谈映射器: ContainerBase类是 StandardContext类的父类,前者定义 addDefaultMapper()方法用来添加一个默认的映射器,如下所示:
protected void addDefaultMapper(String mapperClass) { // org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.addDefaultMapper() method.
// Do we need a default Mapper?
if (mapperClass == null)
return;
if (mappers.size() >= 1)
return;
// Instantiate and add a default Mapper
try {
Class clazz = Class.forName(mapperClass);
Mapper mapper = (Mapper) clazz.newInstance();
mapper.setProtocol("http");
addMapper(mapper);
} catch (Exception e) {
log(sm.getString("containerBase.addDefaultMapper", mapperClass),
e);
}
}
3.2)StandardContext.start()方法中会调用 addDefaultMapper()方法,并传入变量mapperClass的值:
public synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException {
// ......
if (ok) {
try {
addDefaultMapper(this.mapperClass);
started = true;
} //......
// private String mapperClass = "org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextMapper";
3.3)必须要调用映射器的setContainer()方法,通过传入一个容器的实例,将映射器和容器相关联。在Catalina中,org.apache.catalina.Mapper 接口的实现类是 org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextMapper类 。StandardContextMapper实例只能与 Context级容器相关联,setContainer()方法如下所示:
public void setContainer(Container container) { // org.apche.catalina.core.StandardContextMapper.setContainer().
if (!(container instanceof StandardContext))
throw new IllegalArgumentException
(sm.getString("httpContextMapper.container"));
context = (StandardContext) container;
}
public StandardContext() { // 而在StandardContext构造中调用setContainer().
super();
pipeline.setBasic(new StandardContextValve());
namingResources.setContainer(this);
}
3.4)映射器最重要的方法是map()方法,该方法会返回用来处理http 请求的子容器,该方法签名如下:
public Container map(Request request, boolean update) { // org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextMapper.map().
int debug = context.getDebug();
// Has this request already been mapped?
if (update && (request.getWrapper() != null))
return (request.getWrapper());
// Identify the context-relative URI to be mapped
String contextPath =
((HttpServletRequest) request.getRequest()).getContextPath();
String requestURI = ((HttpRequest) request).getDecodedRequestURI();
String relativeURI = requestURI.substring(contextPath.length());
// Apply the standard request URI mapping rules from the specification
Wrapper wrapper = null;
String servletPath = relativeURI;
String pathInfo = null;
String name = null;
// Rule 1 -- Exact Match
// Rule 2 -- Prefix Match
// Rule 3 -- Extension Match
// Rule 4 -- Default Match
// Update the Request (if requested) and return this Wrapper
if ((debug >= 1) && (wrapper != null))
context.log(" Mapped to servlet '" + wrapper.getName() +
"' with servlet path '" + servletPath +
"' and path info '" + pathInfo +
"' and update=" + update);
if (update) {
request.setWrapper(wrapper);
((HttpRequest) request).setServletPath(servletPath);
((HttpRequest) request).setPathInfo(pathInfo);
}
return (wrapper);
}
}
4)现在,我们回到org.apche.catalina.core.StandardContextValve:其invoke()方法对于引入的每个http 请求,都会调用Context容器的map()方法,并传入一个 org.apache.catalina.Request 对象。
public void invoke(Request request, Response response, ValveContext valveContext)
throws IOException, ServletException { <span style="font-family: Arial, Helvetica, sans-serif;">//org.apche.catalina.core.StandardContextValve.invoke().</span>
// .....
// Disallow any direct access to resources under WEB-INF or META-INF
HttpServletRequest hreq = (HttpServletRequest) request.getRequest();
String contextPath = hreq.getContextPath();
String requestURI = ((HttpRequest) request).getDecodedRequestURI();
String relativeURI =
requestURI.substring(contextPath.length()).toUpperCase();
//......
Context context = (Context) getContainer();
Wrapper wrapper = null;
try {
wrapper = (Wrapper) context.map(request, true); // highlight line.->ContainerBase.map().
} //......
// Ask this Wrapper to process this Request
response.setContext(context);
wrapper.invoke(request, response);
}
4.1)map() 方法会针对某个特定的协议调用 findMapper()方法返回一个映射器对象,然后调用映射器对象的map() 方法获取 Wrapper实例;
public Container map(Request request, boolean update) {
// Select the Mapper we will use
Mapper mapper = findMapper(request.getRequest().getProtocol());
if (mapper == null)
return (null);
// Use this Mapper to perform this mapping
return (mapper.map(request, update));
}
public Mapper findMapper(String protocol) {
if (mapper != null)
return (mapper); // mapper == StandardContextMapper
else
synchronized (mappers) {
return ((Mapper) mappers.get(protocol));
}
}
4.2)下面对org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextMapper.map()方法的调用过程进行分析:
step1)会先标识出相对于Context的URL:step2)然后,它试图应用匹配规则找到一个适合的Wrapper实例;
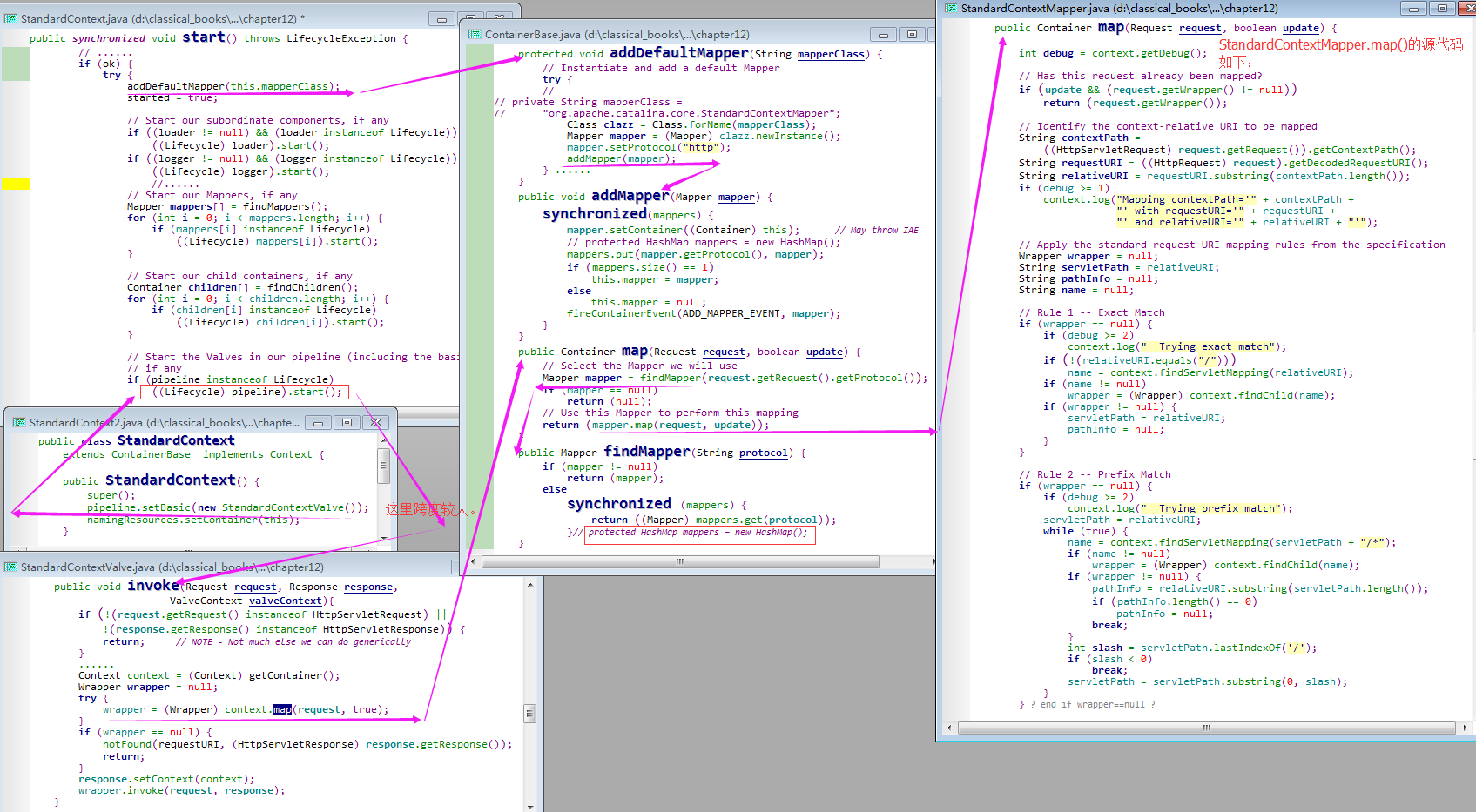
Attention)以上代码的都是基于tomcat4在做分析,而在tomcat5中,Mapper接口及其相关类已经被移除了。事实上,StandardContextValve.invoke()方法会从 request对象中获取 适合的 Wrapper实例: Wrapper wrapper = reqeust.getWrapper(); (该Wrapper实例指明了封装在 request对象中的映射信息)
// step1 begins.
public Container map(Request request, boolean update) { // org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContextMapper.map().
int debug = context.getDebug();
// Has this request already been mapped?
if (update && (request.getWrapper() != null))
return (request.getWrapper());
// Identify the context-relative URI to be mapped
String contextPath =
((HttpServletRequest) request.getRequest()).getContextPath();
String requestURI = ((HttpRequest) request).getDecodedRequestURI();
String relativeURI = requestURI.substring(contextPath.length());
if (debug >= 1)
context.log("Mapping contextPath='" + contextPath +
"' with requestURI='" + requestURI +
"' and relativeURI='" + relativeURI + "'");
// step1 ends.
// step2 begins.
// Apply the standard request URI mapping rules from the specification
Wrapper wrapper = null;
String servletPath = relativeURI;
String pathInfo = null;
String name = null;
// Rule 1 -- Exact Match
if (wrapper == null) {
if (debug >= 2)
context.log(" Trying exact match");
if (!(relativeURI.equals("/")))
name = context.findServletMapping(relativeURI);
if (name != null)
wrapper = (Wrapper) context.findChild(name); //highlight line.
if (wrapper != null) {
servletPath = relativeURI;
pathInfo = null;
}
}
// Rule 2 -- Prefix Match
if (wrapper == null) {
if (debug >= 2)
context.log(" Trying prefix match");
servletPath = relativeURI;
while (true) {
name = context.findServletMapping(servletPath + "/*");
if (name != null)
wrapper = (Wrapper) context.findChild(name); // highlight line.
if (wrapper != null) {
pathInfo = relativeURI.substring(servletPath.length());
if (pathInfo.length() == 0)
pathInfo = null;
break;
}
int slash = servletPath.lastIndexOf('/');
if (slash < 0)
break;
servletPath = servletPath.substring(0, slash);
}
}
// Rule 3 -- Extension Match
if (wrapper == null) {
if (debug >= 2)
context.log(" Trying extension match");
int slash = relativeURI.lastIndexOf('/');
if (slash >= 0) {
String last = relativeURI.substring(slash);
int period = last.lastIndexOf('.');
if (period >= 0) {
String pattern = "*" + last.substring(period);
name = context.findServletMapping(pattern); // highlight line.
if (name != null)
wrapper = (Wrapper) context.findChild(name);
if (wrapper != null) {
servletPath = relativeURI;
pathInfo = null;
}
}
}
}
// Rule 4 -- Default Match
if (wrapper == null) {
if (debug >= 2)
context.log(" Trying default match");
name = context.findServletMapping("/");
if (name != null)
wrapper = (Wrapper) context.findChild(name); //highlight line.
if (wrapper != null) {
servletPath = relativeURI;
pathInfo = null;
}
}
// step2 ends.
// step3 begins.
// Update the Request (if requested) and return this Wrapper
if ((debug >= 1) && (wrapper != null))
context.log(" Mapped to servlet '" + wrapper.getName() +
"' with servlet path '" + servletPath +
"' and path info '" + pathInfo +
"' and update=" + update);
if (update) {
request.setWrapper(wrapper);
((HttpRequest) request).setServletPath(servletPath);
((HttpRequest) request).setPathInfo(pathInfo);
}
return (wrapper);
}
对以上代码的分析(Analysis):
以上代码演示了通过 StandardContext.start()方法如何找到映射器和利用 URI 等信息来找到相应的Wrapper容器的;(Bootstrap.main() 设置了相应的child)
【3】对重载的支持
1)启用重载功能:StandardContext.reloadable 属性指明该应用程序是否 启用了重载功能。当启用了之后,当 web.xml 文件发生变化或 WEB-INF/classes 目录下的其中一个文件被重新编译后,应用程序会重载;
2)StandardContext是通过其载入器实现应用程序重载的: 在 tomcat4中,StandardContext对象中的 WebappLoader类实现了 Loader接口,并使用另一个线程检查 WEB-INF 目录中的所有类和JAR 文件的时间戳。只需要调用其 setContainer()方法将 WebappLoader 对象与 StandardContext 对象相关联就可以启动该检查线程。
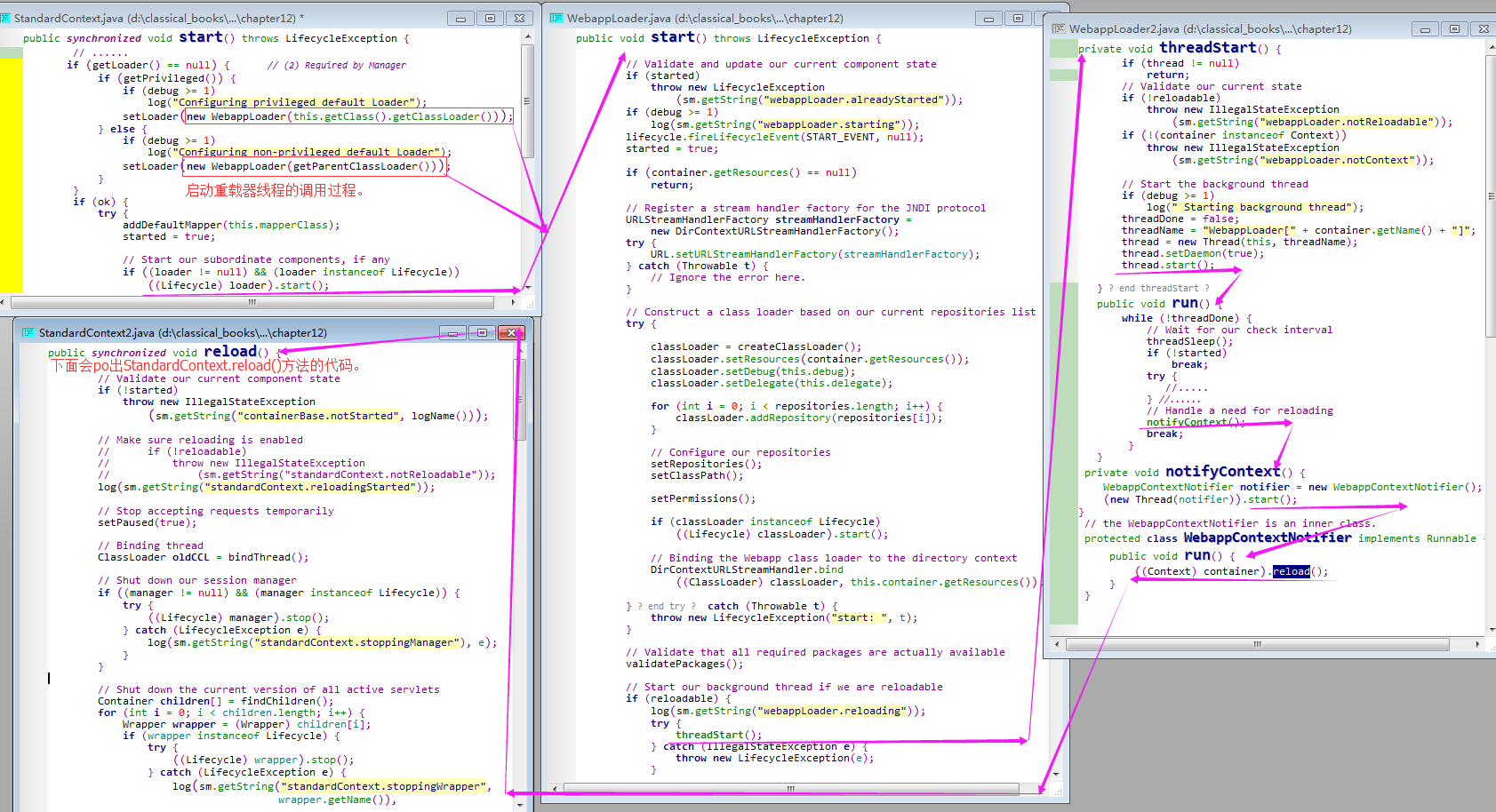
public synchronized void reload() { //org.apache.catalina.core.StandardContext.reload().
// Validate our current component state
if (!started)
throw new IllegalStateException
(sm.getString("containerBase.notStarted", logName()));
// Make sure reloading is enabled
// if (!reloadable)
// throw new IllegalStateException
// (sm.getString("standardContext.notReloadable"));
log(sm.getString("standardContext.reloadingStarted"));
// Stop accepting requests temporarily
setPaused(true);
// Binding thread
ClassLoader oldCCL = bindThread();
// Shut down our session manager
if ((manager != null) && (manager instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) manager).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.stoppingManager"), e);
}
}
// Shut down the current version of all active servlets
Container children[] = findChildren();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) children[i];
if (wrapper instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
((Lifecycle) wrapper).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.stoppingWrapper",
wrapper.getName()),
e);
}
}
}
// Shut down application event listeners
listenerStop();
// Clear all application-originated servlet context attributes
if (context != null)
context.clearAttributes();
// Shut down filters
filterStop();
if (isUseNaming()) {
// Start
namingContextListener.lifecycleEvent
(new LifecycleEvent(this, Lifecycle.STOP_EVENT));
}
// Binding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
// Shut down our application class loader
if ((loader != null) && (loader instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) loader).stop();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.stoppingLoader"), e);
}
}
// Binding thread
oldCCL = bindThread();
// Restart our application class loader
if ((loader != null) && (loader instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) loader).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.startingLoader"), e);
}
}
// Binding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
// Create and register the associated naming context, if internal
// naming is used
boolean ok = true;
if (isUseNaming()) {
// Start
namingContextListener.lifecycleEvent
(new LifecycleEvent(this, Lifecycle.START_EVENT));
}
// Binding thread
oldCCL = bindThread();
// Restart our application event listeners and filters
if (ok) {
if (!listenerStart()) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.listenerStartFailed"));
ok = false;
}
}
if (ok) {
if (!filterStart()) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.filterStartFailed"));
ok = false;
}
}
// Restore the "Welcome Files" and "Resources" context attributes
postResources();
postWelcomeFiles();
// Restart our currently defined servlets
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
if (!ok)
break;
Wrapper wrapper = (Wrapper) children[i];
if (wrapper instanceof Lifecycle) {
try {
((Lifecycle) wrapper).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.startingWrapper",
wrapper.getName()),
e);
ok = false;
}
}
}
// Reinitialize all load on startup servlets
loadOnStartup(children);
// Restart our session manager (AFTER naming context recreated/bound)
if ((manager != null) && (manager instanceof Lifecycle)) {
try {
((Lifecycle) manager).start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.startingManager"), e);
}
}
// Unbinding thread
unbindThread(oldCCL);
// Start accepting requests again
if (ok) {
log(sm.getString("standardContext.reloadingCompleted"));
} else {
setAvailable(false);
log(sm.getString("standardContext.reloadingFailed"));
}
setPaused(false);
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(Context.RELOAD_EVENT, null);
}
3)WebappLoader.setContainer()方法的实现代码如下:
public void setContainer(Container container) { // org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappLoader.setContainer().
// Deregister from the old Container (if any)
if ((this.container != null) && (this.container instanceof Context))
((Context) this.container).removePropertyChangeListener(this);
// Process this property change
Container oldContainer = this.container;
this.container = container;
support.firePropertyChange("container", oldContainer, this.container);
// Register with the new Container (if any)
if ((this.container != null) && (this.container instanceof Context)) {
setReloadable( ((Context) this.container).getReloadable() );
((Context) this.container).addPropertyChangeListener(this);
}
}
对上述代码的分析(Analysis):看上述代码的 最后一个if语句块:如果当前容器是 Context容器,则调用 setRealoadable()方法。这说明,WebappLoader.reloadable 属性的值与 StandardContext.reloadable 属性的值相同;
4)下面是 WebappLoader.setReloadable() 方法的实现代码:
public void setReloadable(boolean reloadable) { // org.apache.catalina.loader.WebappLoader.setContainer(). setReloadable()
// Process this property change
boolean oldReloadable = this.reloadable;
this.reloadable = reloadable;
support.firePropertyChange("reloadable",
new Boolean(oldReloadable),
new Boolean(this.reloadable));
// Start or stop our background thread if required
if (!started)
return;
if (!oldReloadable && this.reloadable)
threadStart();
else if (oldReloadable && !this.reloadable)
threadStop();
}
对上述代码的分析(Analysis):
A1)若 reloadable 从false 修改为true:则会调用 threadStart()方法;而threadStart()方法会启动一个专用的线程来不断地检查 WEB-INF 目录下的类和 JAR 文件的时间戳;A2)若reloadable 从 true 修改为false:则调用调用 threadStop() 方法;而threadStop() 方法则会终止该线程;
Attention)在tomcat5中,为支持重载功能而进行的检查类的时间戳的工作改由 backgroundProcess()方法执行;
【4】backgroundProcess()方法
1)Context容器的运行需要其他组件的支持,例如载入器和Session 管理器。通常来说,这些组件需要使用各自的线程执行一些后台处理程序;
2)为了节省资源,在tomcat5中, 使用了不同的方法。所有的后台处理共享同一个线程。若某个组件 或 servlet容器需要周期性地执行一个操作,只需要将代码写到其 backgroundProcess()方法中即可;(干货——tomcat5中,所有的后台处理共享同一个线程。)
3)这个共享线程在 ContainerBase对象中创建。ContainerBase.start()方法调用其 threadStart()方法启动该后台线程;(Attention-这是tomcat5中的 ContainerBase.start())
public synchronized void start() throws LifecycleException { //org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.start() in tomcat5.
// Validate and update our current component state
if (started) {
log.info(sm.getString("containerBase.alreadyStarted", logName()));
return;
}
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(BEFORE_START_EVENT, null);
started = true;
// Start our subordinate components, if any
if ((loader != null) && (loader instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) loader).start();
getLogger();
if ((logger != null) && (logger instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) logger).start();
if ((manager != null) && (manager instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) manager).start();
if ((cluster != null) && (cluster instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) cluster).start();
if ((realm != null) && (realm instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) realm).start();
if ((resources != null) && (resources instanceof Lifecycle))
((Lifecycle) resources).start();
// Start our child containers, if any
Container children[] = findChildren();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
if (children[i] instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) children[i]).start();
}
// Start the Valves in our pipeline (including the basic), if any
if (pipeline instanceof Lifecycle)
((Lifecycle) pipeline).start();
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(START_EVENT, null);
// Start our thread
threadStart(); //highlight line.
// Notify our interested LifecycleListeners
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(AFTER_START_EVENT, null);
}protected void threadStart() { //org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.threadStart() in tomcat5.
if (thread != null)
return;
if (backgroundProcessorDelay <= 0)
return;
threadDone = false;
String threadName = "ContainerBackgroundProcessor[" + toString() + "]";
thread = new Thread(new ContainerBackgroundProcessor(), threadName); //highlight line.
thread.setDaemon(true);
thread.start();
}
4)threadStart()方法:通过传入一个实现了 java.lang.Runnable接口的 ContainerBackgroundProcessor 类的实例构造一个新线程。其ContainerBackgroundProcessor定义如下:
protected class ContainerBackgroundProcessor implements Runnable { //org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.ContainerBackroundProcessor class defined in tomcat 5, which is a inner class in ContainerBase
public void run() {
while (!threadDone) {
try {
Thread.sleep(backgroundProcessorDelay * 1000L);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
;
}
if (!threadDone) {
Container parent = (Container) getMappingObject();
ClassLoader cl =
Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (parent.getLoader() != null) {
cl = parent.getLoader().getClassLoader();
}
processChildren(parent, cl); // highlight line.
}
}
}
protected void processChildren(Container container, ClassLoader cl) {
try {
if (container.getLoader() != null) {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader
(container.getLoader().getClassLoader());
}
container.backgroundProcess(); // highlight line.
} catch (Throwable t) {
log.error("Exception invoking periodic operation: ", t);
} finally {
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
Container[] children = container.findChildren();
for (int i = 0; i < children.length; i++) {
if (children[i].getBackgroundProcessorDelay() <= 0) {
processChildren(children[i], cl);
}
}
}
}
对以上代码的分析(Analysis):
A1)ContainerBackgroundProcessor 类:实际上是 ContainerBase类的内部类;A2)在其run()方法中是一个while 循环,周期性地调用其 processChildren()方法:而processChildren()方法会调用其自身对象的 backgroundProcess()方法 和其 每个子容器的 processChildren()方法;A3)通过实现backgroundProcess()方法,ContainerBase类的子类可以使用一个专用线程来执行周期性任务;
5)tomcat5 中 StandardContext.backgroundProcess()方法的实现如下:
public void backgroundProcess() { //org.apache.catalina.core.ContainerBase.backgroundProcess() in tomcat 5.
if (!started)
return;
if (cluster != null) {
try {
cluster.backgroundProcess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("containerBase.backgroundProcess.cluster", cluster), e);
}
}
if (loader != null) {
try {
loader.backgroundProcess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("containerBase.backgroundProcess.loader", loader), e);
}
}
if (manager != null) {
try {
manager.backgroundProcess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("containerBase.backgroundProcess.manager", manager), e);
}
}
if (realm != null) {
try {
realm.backgroundProcess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("containerBase.backgroundProcess.realm", realm), e);
}
}
Valve current = pipeline.getFirst();
while (current != null) {
try {
current.backgroundProcess();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.warn(sm.getString("containerBase.backgroundProcess.valve", current), e);
}
current = current.getNext();
}
lifecycle.fireLifecycleEvent(Lifecycle.PERIODIC_EVENT, null);
}
























 837
837

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








