6-3 装载问题(分支限界)
一、问题描述
有一批共个集装箱要装上2艘载重量分别为C1和C2的轮船,其中集装箱i的重量为Wi,且
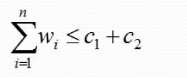
采用下面的策略可得到最优装载方案:
(1)将第一艘轮船尽可能装满;
(2)将剩余集装箱装上第二艘轮船;
二、问题分析
1、队列式分支限界法
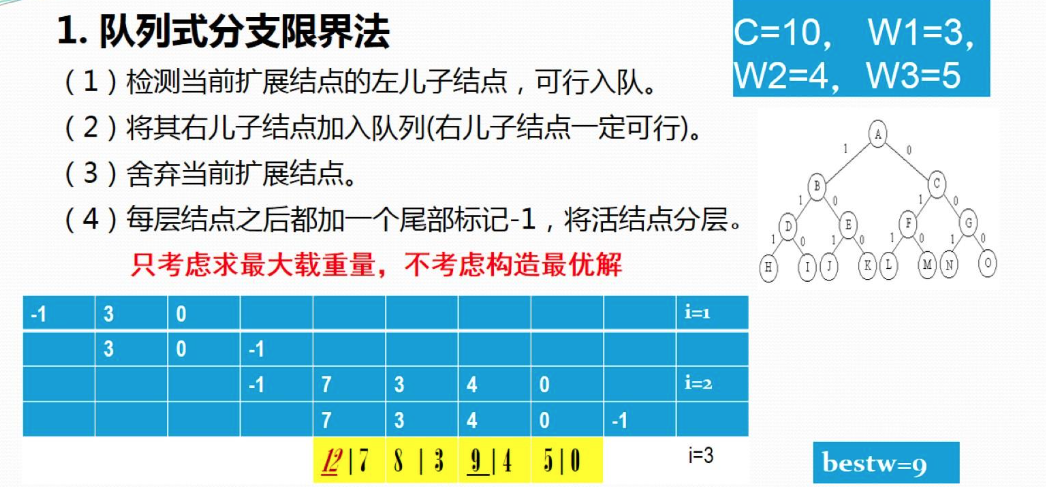
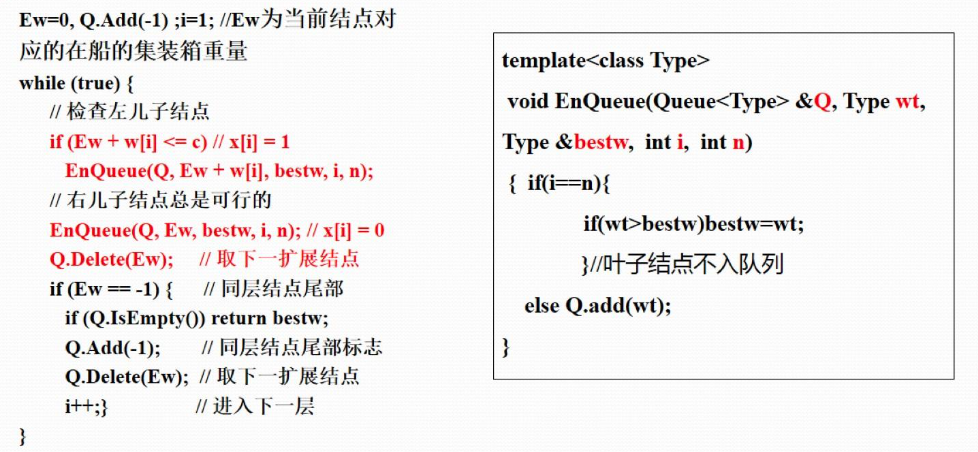
⒉.算法的改进(右子树加入剪枝条件)
上述算法中右子没有剪枝,效率较差。
策略:设bestw是当前最优解;ew是当前扩展结点所相应的重量;r是剩余集装箱的重量。
则当ew+rsbestw时,可将其右子树剪去。
为确保右子树成功剪枝,算法每一次进入左子树的时候更新bestw的值。不要等待i=n时才去更新。


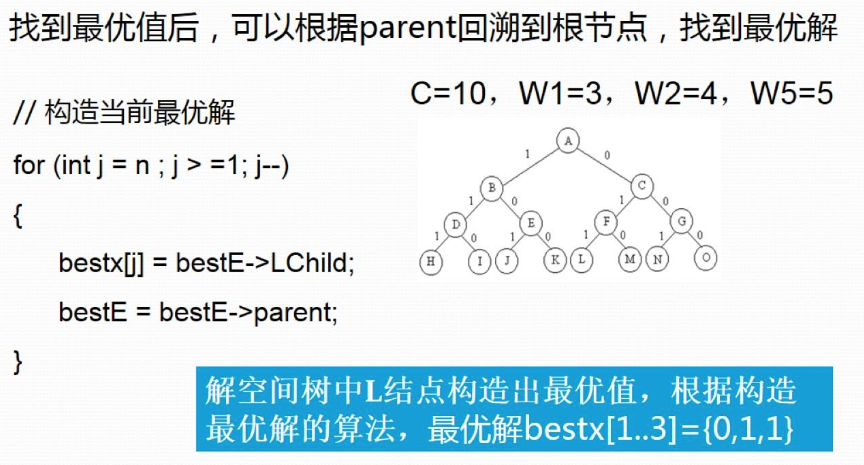
三、代码
//队列式分支限界法
/*没有构造最优解
10 3
3 4 5
10 4
3 4 5 6
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
queue<int>q;
int w[100]; //集装箱的重量
int c;
int r;//r剩余没装的总重量 ,r的初值为全部集装箱重量之和
int n;//n个集装箱
int bestw=0;//当前最优载重量
void MaxLoading(){
int top=0;
int left=r;
q.push(-1);
int i=1;//第i层
r=r-w[1];
while(i<=n&& !q.empty()){
if(i==1){
if(top+w[i]<=c){
q.push(top+w[i]);
cout<<top+w[i]<<" ";
}
q.push(top);
cout<<top<<" ";
}
top=q.front();
q.pop();
if(top==-1&&!q.empty()){
q.push(-1);
cout<<"-1\n";
i++;
top=q.front();
q.pop();
r=r-w[i];
}
int wt=top+w[i];
if(wt<=c){
if(wt>bestw) bestw=wt;
if(i<n){
q.push(wt);
cout<<wt<<" ";
}
}
if(top+r>bestw){
if(i<n){
q.push(top);
cout<<top<<" ";
}
}
}
}
int main(){
cin>>c;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>w[i];
r=r+w[i];
}
cout<<"----------\n";
MaxLoading();
cout<<"bestw="<<bestw<<endl;
return 0;
}
四、优先队列分支限界法

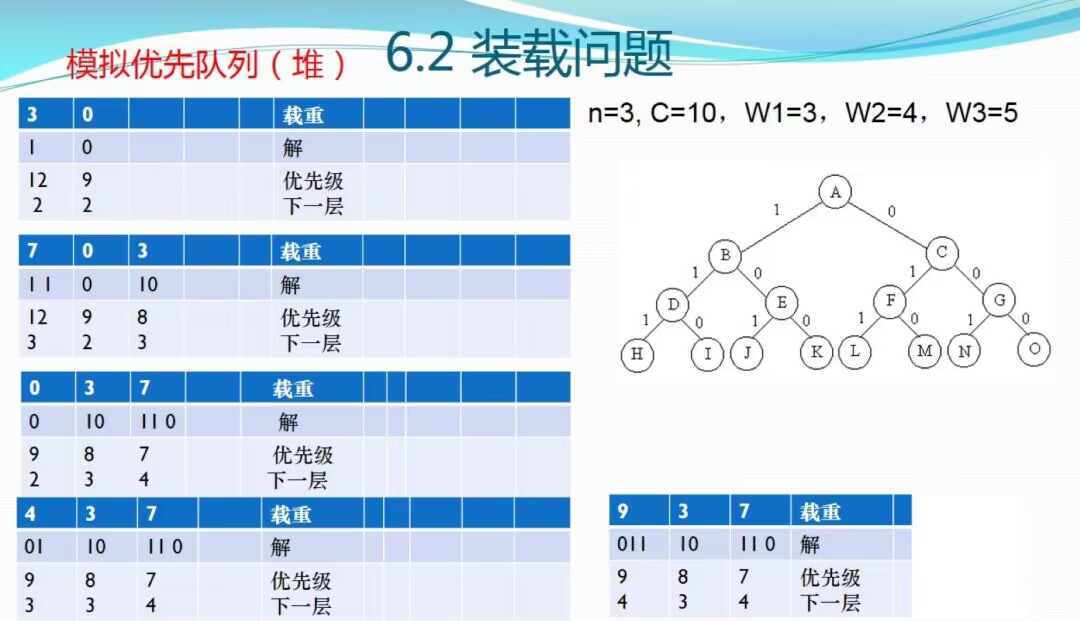
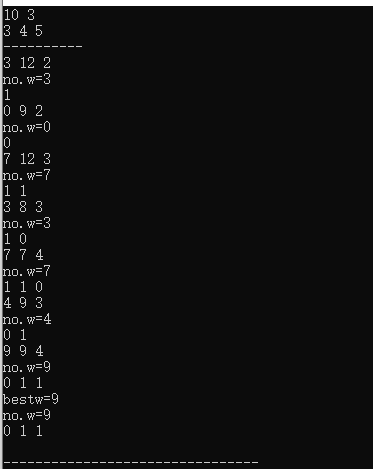
//6-3装载问题 优先队列分支限界
//优先队列分支限界法
/*
10 3
3 4 5
*/
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef struct QNode{
int w;
int priority;
int nexti;
int x[100];
}node;
bool operator < (node a, node b){
return a.priority < b.priority;
}
priority_queue<node, vector<node>, less<node> > q;
int w[100]; //集装箱的重量
int c;
int r;//r剩余没装的总重量 ,r的初值为全部集装箱重量之和
int n;//n个集装箱
int bestw=0;//当前最优载重量
int leftr[100];
void Print(node no,int n){
cout<<"no.w="<<no.w<<endl;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cout<<no.x[i]<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
}
void CalculateR(){
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
leftr[i]=r-w[i];
r-=w[i];
}
}
void MaxLoading(){
node no;
node top;
top.w=0;
int i=1;//第i层
while(i<=n){
r=leftr[i];
int wt=top.w+w[i];
if(wt<=c){
if(wt>bestw){
bestw=wt;
}
no.w=wt;
no.priority = wt+r;
no.nexti=i+1;
memcpy(no.x,top.x,sizeof(top.x));//把top.x数组复制到no.x数组
no.x[i]=1;
cout<<no.w<<" "<<no.priority<<" "<<no.nexti<<endl;
Print(no,i);
q.push(no);
}
if(top.w+r>=bestw){
no.w=top.w;
no.priority=top.w+r;
no.nexti=i+1;
memcpy(no.x,top.x,sizeof(top.x));
no.x[i]=0;
cout<<no.w<<" "<<no.priority<<" "<<no.nexti<<endl;
Print(no,i);
q.push(no);
}
top=q.top();
q.pop();
i=top.nexti;
}
cout<<"bestw="<<bestw<<endl;
Print(no,n);
}
int main(){
cin>>c;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>w[i];
r=r+w[i];
}
cout<<"----------\n";
CalculateR();
MaxLoading();
return 0;
}























 3206
3206











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










