算法基础——图论(一)
目录:
- 基础知识
- 邻接矩阵
- 邻接表
- 并查集
- 最小生成树
- 应用实例
- 畅通工程【浙江大学】
- 连通图【吉林大学】
- Is It A Tree?【北京大学】
- 找出直系亲属【浙江大学】
- 统计图的连通分支数【上海交通大学】
- Head of a Gang【浙江大学】
- 还是畅通工程【浙江大学】
- 继续畅通工程【浙江大学】
- Freckles【北京大学】
- Jungle Roads【北京大学】
一、基础知识
1、邻接矩阵(adjacency matrix)
- 定义:用一个二维矩阵来表示图的信息,二维矩阵中的每个单元表述一对顶点之间的邻接关系。
- 带权图:matrix[u][v]的值来表示u和v之间边的权值,对不存在的边一般取值为∞。
- 无权图:matrix[u][v]为1或0来表示u和v之间是否有边。
- 缺点:遍历与某顶点相邻的所有顶点,则需要依次遍历二维数组中某行的所有元素,通过其值判断是否相邻。
- 适用场景:稠密图,且需要频繁判断某特定顶点对是否相邻时。
2、邻接表(adjacency list)
- 定义:为图中的每个顶点建立一个单链表,单链表中保存与该顶点相邻的所有顶点及其相关信息。
- 缺点:当邻接表需要判断顶点u和v之间是否存在关系时,需要遍历u和v的所有邻接顶点,才能判定它们之间是否存在关系。
- 适用场景:存在大量遍历邻接顶点操作而较少判断两个特定顶点的关系时。
3、并查集(Union Find)
- 定义:用于处理一些不交集的合并和查询问题的数据结构。
- 判断任意两个元素是否属于同一个集合:
- 将集合在逻辑上表示为树结构,每个结点都指向其父结点,而树中的元素并无顺序之分,只要在同一棵树上,便说明在同一个集合中。
- 查找与合并:
- 查找:不断向上查找,直到找到它的根结点,之后根据根结点是否相同来判断两个元素是否属于同一集合。
- 合并:将两个子集合并成同一个集合。将一棵树作为另一棵树的子树,从而使得两棵树编程一棵更大的树。
- 优化方案:
- 路径压缩:在查找某个特定结点的根结点的同时,将其与根结点之间的所有结点都直接指向根结点。
- 合并时,将高度较低的树作为高度较高的树子树。
4、最小生成树(Minimum Spanning Tree,MST)
- 定义:
- 连通图:在一个无向图G中,若顶点u到顶点v有路径相连,则称u和v是连通的。若图中任意两点都是连通的,则图被称为连通图。
- 连通分量:无向图G中的一个极大连通子图称为G的一个连通分量。
- 连通图只有一个连通分量,即其自身;非连通的无向图有多个连通分量。
- 生成树:在一个无向连通图G(V, E)中,如果存在一个连通子图,它包含所有顶点和部分边,且这个子图不存在回路,那么就称这个子图为原图的一棵生成树。
- 最小生成树:在带权无向连通图中,所有生成树中边权的和最小的那一棵(或几棵)被称为该无向图的最小生成树。
- 常见算法:
- Kruskal算法 + 并查集
- 步骤:
- 初试时所有顶点属于孤立的集合。
- 按照边权递增顺序遍历所有边,若遍历到的边的两个顶点仍分属不同的集合(该边即为连通这两个集合的边中权值最小的那条),则确定该边为最小生成树上的一条边,并将该边两个顶点分属的集合合并。
- 遍历完所有边后,若原图连通,则被选取的边和所有顶点构成最小生成树;若原图不连通,最小生成树不存在。
- 步骤:
- Prim算法
- Kruskal算法 + 并查集
二、应用实例
1、题目描述:某省调查城镇交通状况,得到现有城镇道路统计表,表中列出了每条道路直接连通的城镇。省政府“畅通工程”的目标是使全省任何两个城镇间都可以实现交通(但不一定有直接的道路相连,只要互相间接通过道路可达即可)。问最少还需要建设多少条道路?【浙江大学】
- 输入格式:测试输入包含若干测试用例。每个测试用例的第1行给出两个正整数,分别是城镇数目N ( < 1000 )和道路数目M;随后的M行对应M条道路,每行给出一对正整数,分别是该条道路直接连通的两个城镇的编号。为简单起见,城镇从1到N编号。
注意:两个城市之间可以有多条道路相通,也就是说
3 3
1 2
1 2
2 1
这种输入也是合法的
当N为0时,输入结束,该用例不被处理。 - 输出格式:对每个测试用例,在1行里输出最少还需要建设的道路数目。
- 样例输入:
- 4 2
- 1 3
- 4 3
- 3 3
- 1 2
- 1 3
- 2 3
- 5 2
- 1 2
- 3 5
- 999 0
- 0
- 样例输出:
- 1
- 0
- 2
- 998
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 1000;
int father[MAX_N];
int height[MAX_N];
void Initial(int n){
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
father[i] = i;
height[i] = 0;
}
}
int Find(int x){
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
return father[x];
}
void Union(int x, int y){
x = Find(x);
y = Find(y);
if(x != y){
if(height[x] < height[y]){
father[x] = y;
}else if(height[x] > height[y]){
father[y] = x;
}else{
father[y] = x;
height[x]++;
}
}
}
int main(){
int n, m;
while(cin >> n && n != 0){
cin >> m;
Initial(n);
int x, y;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin >> x >> y;
Union(x, y);
}
int count = -1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(Find(i) == i){
count++;
}
}
cout << count << endl;
}
return 0;
}2、题目描述:给定一个无向图和其中的所有边,判断这个图是否所有顶点都是连通的。【吉林大学】
- 输入格式:每组数据的第一行是两个整数 n 和 m(0<=n<=1000)。n 表示图的顶点数目,m 表示图中边的数目。随后有 m 行数据,每行有两个值 x 和 y(0<x, y <=n),表示顶点 x 和 y 相连,顶点的编号从 1 开始计算。输入不保证这些边是否重复。
- 输出格式:对于每组输入数据,如果所有顶点都是连通的,输出"YES",否则输出"NO"。
- 样例输入:
- 4 3
- 1 2
- 2 3
- 3 2
- 3 2
- 1 2
- 2 3
- 0 0
- 样例输出:
- NO
- YES
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 1001;
int height[MAX_N];
int father[MAX_N];
void Initial(int n){
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
height[i] = 0;
father[i] = i;
}
}
int Find(int x){
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
return father[x];
}
void Union(int x, int y){
x = Find(x);
y = Find(y);
if(x != y){
if(height[x] < height[y]){
father[x] = y;
}else if(height[x] > height[y]){
father[y] = x;
}else{
father[y] = x;
height[x]++;
}
}
}
int main(){
int n, m;
while(cin >> n >> m && n != 0){
Initial(n);
int x, y;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin >> x >> y;
Union(x, y);
}
int result = -1;
bool flag = true;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(i == father[i]){
result++;
if(result > 0){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
}
if(flag){
cout << "YES" << endl;
}else{
cout << "NO" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}3、题目描述:A tree is a well-known data structure that is either empty (null, void, nothing) or is a set of one or more nodes connected by directed edges between nodes satisfying the following properties. There is exactly one node, called the root, to which no directed edges point. Every node except the root has exactly one edge pointing to it. There is a unique sequence of directed edges from the root to each node. For example, consider the illustrations below, in which nodes are represented by circles and edges are represented by lines with arrowheads. The first two of these are trees, but the last is not.
In this problem you will be given several descriptions of collections of nodes connected by directed edges. For each of these you are to determine if the collection satisfies the definition of a tree or not.【北京大学】
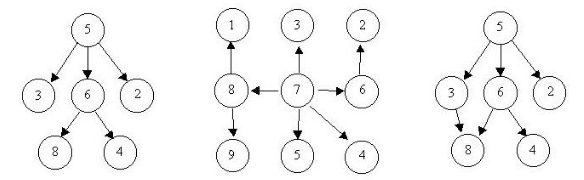
- 输入格式:The input will consist of a sequence of descriptions (test cases) followed by a pair of negative integers. Each test case will consist of a sequence of edge descriptions followed by a pair of zeroes Each edge description will consist of a pair of integers; the first integer identifies the node from which the edge begins, and the second integer identifies the node to which the edge is directed. Node numbers will always be greater than zero and less than 10000.
- 输出格式:For each test case display the line "Case k is a tree." or the line "Case k is not a tree.", where k corresponds to the test case number (they are sequentially numbered starting with 1).
- 样例输入:
- 6 8 5 3 5 2 6 4 5 6 0 0
- 8 1 7 3 6 2 8 9 7 5 7 4 7 8 7 6 0 0
- 3 8 6 8 6 4 5 3 5 6 5 2 0 0
- -1 -1
- 样例输出:
- Case 1 is a tree.
- Case 2 is a tree.
- Case 3 is not a tree.
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 10001;
int father[MAX_N];
int indegree[MAX_N];
int use[MAX_N];
void Initial(){
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
father[i] = i;
indegree[i] = 0;
use[i] = 0;
}
}
int Find(int x){
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
return father[x];
}
void Union(int x, int y){
indegree[y]++;
use[x] = 1;
use[y] = 1;
x = Find(x);
y = Find(y);
if(x != y){
father[x] = y;
}
}
bool IsTree(){
bool flag = true;
int count = 0; //连通分量数目
int root = 0; //根结点数目
for(int i = 0; i <= MAX_N; i++){
if(use[i] == 0){
continue;
}
if(i == father[i]){
count++;
}
if(indegree[i] == 0){
root++;
}else if(indegree[i] > 1){
flag = false;
}
}
if(root != 1 || count > 1){
flag = false;
}
if(count == 0 && root == 0){ //空集也是树
flag = true;
}
return flag;
}
int main(){
int x, y;
int i = 1;
Initial();
while(cin >> x >> y){
if(x == 0 && y == 0){
if(IsTree()){
cout << "Case " << i++ <<" is a tree." << endl;
}else{
cout << "Case " << i++ <<" is not a tree." << endl;
}
Initial();
}else if(x == -1 && y == -1){
break;
}else{
Union(x, y);
}
}
return 0;
}4、题目描述:如果A,B是C的父母亲,则A,B是C的parent,C是A,B的child,如果A,B是C的(外)祖父,祖母,则A,B是C的grandparent,C是A,B的grandchild,如果A,B是C的(外)曾祖父,曾祖母,则A,B是C的great-grandparent,C是A,B的great-grandchild,之后再多一辈,则在关系上加一个great-。【浙江大学】
- 输入格式:输入包含多组测试用例,每组用例首先包含2个整数n(0<=n<=26)和m(0<m<50), 分别表示有n个亲属关系和m个问题, 然后接下来是n行的形式如ABC的字符串,表示A的父母亲分别是B和C,如果A的父母亲信息不全,则用-代替,例如A-C,再然后是m行形式如FA的字符串,表示询问F和A的关系。
- 输出格式:如果询问的2个人是直系亲属,请按题目描述输出2者的关系,如果没有直系关系,请输出-。具体含义和输出格式参见样例.
- 样例输入:
- 3 2
- ABC
- CDE
- EFG
- FA
- BE
- 样例输出:
- great-grandparent
- -
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 26;
const int CHILD_CHOICE = 1;
const int PARENT_CHOICE = 2;
int father[MAX_N][2];
int result;
int CharToInt(char c){
if(c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z'){
return c - 'A';
}else{
return -1;
}
}
bool FindDad(int x, int y, int count){
if(x == y){
result = count;
return true;
}
for(int i = 0; i < 2; i++){
if(father[x][i] != -1){
if(FindDad(father[x][i], y, count + 1)){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void Union(int x, int y){
if(father[x][0] == -1){
father[x][0] = y;
}else{
father[x][1] = y;
}
}
void Print(int count, int choice){
string s = (choice == CHILD_CHOICE) ? "child" : "parent";
if(count == 1){
cout << s << endl;
}else if(count >= 2){
for(int i = 3; i <= count; i++){
cout << "great-";
}
cout << "grand" << s << endl;
}
}
int main(){
int n, m;
while(cin >> n >> m){
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
father[i][0] = -1;
father[i][1] = -1;
}
string s;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> s;
for(int i = 1; i < s.size(); i++){
Union(CharToInt(s[0]), CharToInt(s[i]));
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++){
cin >> s;
int s0 = CharToInt(s[0]), s1 = CharToInt(s[1]);
if(FindDad(s0, s1, 0) && result != 0){
Print(result, CHILD_CHOICE);
}else if(FindDad(s1, s0, 0) && result != 0){
Print(result, PARENT_CHOICE);
}else{
cout << "-" << endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}5、题目描述:该题的目的是要你统计图的连通分支数。【上海交通大学】
- 输入格式:每个输入文件包含若干行,每行两个整数i,j,表示节点i和j之间存在一条边。
- 输出格式:输出每个图的联通分支数。
- 样例输入:
- 1 4
- 4 3
- 5 5
- 样例输出:
- 2
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 1000010;
int use[MAX_N];
int father[MAX_N];
int height[MAX_N];
int Find(int x){
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
return father[x];
}
void Union(int x, int y){
use[x] = 1;
use[y] = 1;
x = Find(x);
y = Find(y);
if(x != y){
if(height[x] < height[y]){
father[x] = y;
}else if(height[x] > height[y]){
father[y] = x;
}else{
father[x] = y;
height[y]++;
}
}
}
int main(){
int x, y;
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
use[i] = 0;
father[i] = i;
height[i] = 0;
}
while(cin >> x >> y){
Union(x, y);
}
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
if(use[i] == 0){
continue;
}
if(father[i] == i){
count++;
}
}
cout << count << endl;
return 0;
}6、题目描述:One way that the police finds the head of a gang is to check people's phone calls. If there is a phone call between A and B, we say that A and B is related. The weight of a relation is defined to be the total time length of all the phone calls made between the two persons. A "Gang" is a cluster of more than 2 persons who are related to each other with total relation weight being greater than a given threthold K. In each gang, the one with maximum total weight is the head. Now given a list of phone calls, you are supposed to find the gangs and the heads.【浙江大学】
- 输入格式:For each case, the first line contains two positive numbers N and K (both less than or equal to 1000), the number of phone calls and the weight threthold, respectively. Then N lines follow, each in the following format:
Name1 Name2 Time where Name1 and Name2 are the names of people at the two ends of the call, and Time is the length of the call. A name is a string of three capital letters chosen from A-Z. A time length is a positive integer which is no more than 1000 minutes. - 输出格式:For each test case, first print in a line the total number of gangs. Then for each gang, print in a line the name of the head and the total number of the members. It is guaranteed that the head is unique for each gang. The output must be sorted according to the alphabetical order of the names of the heads.
- 样例输入:
- 8 59
- AAA BBB 10
- BBB AAA 20
- AAA CCC 40
- DDD EEE 5
- EEE DDD 70
- FFF GGG 30
- GGG HHH 20
- HHH FFF 10
- 8 70
- AAA BBB 10
- BBB AAA 20
- AAA CCC 40
- DDD EEE 5
- EEE DDD 70
- FFF GGG 30
- GGG HHH 20
- HHH FFF 10
- 样例输出:
- 2
- AAA 3
- GGG 3
- 0
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 26;
struct GangNode{
string name;
int member;
GangNode(string n, int m):name(n), member(m){};
};
int phoneTime[MAX_N];
int father[MAX_N];
int height[MAX_N];
int use[MAX_N];
vector<int> gangList;
vector<GangNode> resultList;
int CompareAsc(const GangNode &g1, const GangNode &g2){
return g1.name < g2.name;
}
void Init(){
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
height[i] = 0;
father[i] = i;
phoneTime[i] = 0;
use[i] = 0;
}
gangList.clear();
resultList.clear();
}
int StringToInt(string s){
return s[0] - 'A';
}
string IntToString(int x, int repeat){
string s = "";
char c = 'A' + x;
if(repeat == 1){
return s + c;
}else if(repeat == 2){
return s + c + c;
}else{
return s + c + c + c;
}
}
int FindFather(int x){
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
return father[x];
}
void Union(int x, int y, int time){
use[x] = 1;
use[y] = 1;
phoneTime[x] += time;
phoneTime[y] += time;
x = FindFather(x);
y = FindFather(y);
if(x != y){
if(height[x] > height[y]){
father[y] = x;
}else if(height[y] > height[x]){
father[x] = y;
}else{
father[x] = y;
height[y]++;
}
}
}
int main(){
int n, threshold;
while(cin >> n >> threshold){
Init();
string s1, s2;
int t;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> s1 >> s2 >> t;
Union(StringToInt(s1), StringToInt(s2), t);
}
//找到爸爸
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
if(use[i] == 0){
continue;
}
if(father[i] == i){
gangList.push_back(i);
}
}
int topIndex, topValue, memberCount, memberTotalValue;
for(int i = 0; i < gangList.size(); i++){
topValue = 0;
memberCount = 0;
memberTotalValue = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < MAX_N; j++){
if(use[j] == 0){
continue;
}
if(FindFather(j) == gangList[i]){
memberTotalValue += phoneTime[j];
if(phoneTime[j] > topValue){
topValue = phoneTime[j];
topIndex = j;
}
memberCount++;
use[j] = 0;
}
}
if(memberTotalValue > threshold * 2 && memberCount > 2){
resultList.push_back(GangNode(IntToString(topIndex, s1.size()), memberCount));
}
}
cout << resultList.size() << endl;
sort(resultList.begin(), resultList.end(), CompareAsc);
for(int i = 0; i < resultList.size(); i++){
cout << resultList[i].name << " " << resultList[i].member << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}7、题目描述:某省调查乡村交通状况,得到的统计表中列出了任意两村庄间的距离。省政府“畅通工程”的目标是使全省任何两个村庄间都可以实现公路交通(但不一定有直接的公路相连,只要能间接通过公路可达即可),并要求铺设的公路总长度为最小。请计算最小的公路总长度。【浙江大学】
- 输入格式:测试输入包含若干测试用例。每个测试用例的第1行给出村庄数目N ( < 100 );随后的N(N-1)/2行对应村庄间的距离,每行给出一对正整数,分别是两个村庄的编号,以及此两村庄间的距离。为简单起见,村庄从1到N编号。当N为0时,输入结束,该用例不被处理。
- 输出格式:对每个测试用例,在1行里输出最小的公路总长度。
- 样例输入:
- 3
- 1 2 1
- 1 3 2
- 2 3 4
- 4
- 1 2 1
- 1 3 4
- 1 4 1
- 2 3 3
- 2 4 2
- 3 4 5
- 0
- 样例输出:
- 3
- 5
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 101;
struct Node{
int from;
int to;
int distance;
Node(int f, int t, int d):from(f), to(t), distance(d){};
};
vector<Node> nodeList;
int height[MAX_N];
int father[MAX_N];
void Init(){
nodeList.clear();
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
height[i] = 0;
father[i] = i;
}
}
int FindFather(int x){
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
return father[x];
}
bool Union(int x, int y){
x = FindFather(x);
y = FindFather(y);
if(x != y){
if(height[x] > height[y]){
father[y] = x;
}else if(height[y] > height[x]){
father[x] = y;
}else{
father[x] = y;
height[y]++;
}
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
int CompareAsc(const Node &n1, const Node &n2){
return n1.distance < n2.distance;
}
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n && n != 0){
Init();
int f, t, d;
int threshold = n * (n - 1) / 2;
for(int i = 0; i < threshold; i++){
cin >> f >> t >> d;
nodeList.push_back(Node(f, t, d));
}
sort(nodeList.begin(), nodeList.end(), CompareAsc);
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nodeList.size(); i++){
if(Union(nodeList[i].from, nodeList[i].to)){
result += nodeList[i].distance;
}
}
cout << result << endl;
}
return 0;
}8、题目描述:省政府“畅通工程”的目标是使全省任何两个村庄间都可以实现公路交通(但不一定有直接的公路相连,只要能间接通过公路可达即可)。现得到城镇道路统计表,表中列出了任意两城镇间修建道路的费用,以及该道路是否已经修通的状态。现请你编写程序,计算出全省畅通需要的最低成本。【浙江大学】
- 输入格式:测试输入包含若干测试用例。每个测试用例的第1行给出村庄数目N ( 1< N < 100 );随后的 N(N-1)/2 行对应村庄间道路的成本及修建状态,每行给4个正整数,分别是两个村庄的编号(从1编号到N),此两村庄间道路的成本,以及修建状态:1表示已建,0表示未建。当N为0时输入结束。
- 输出格式:每个测试用例的输出占一行,输出全省畅通需要的最低成本。
- 样例输入:
- 3
- 1 2 1 0
- 1 3 2 0
- 2 3 4 0
- 3
- 1 2 1 0
- 1 3 2 0
- 2 3 4 1
- 3
- 1 2 1 0
- 1 3 2 1
- 2 3 4 1
- 0
- 样例输出:
- 3
- 1
- 0
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 101;
struct Node{
int from;
int to;
int distance;
int state; //1表示已建,0表示未建
Node(int f, int t, int d, int s):from(f), to(t), distance(d), state(s){};
};
int height[MAX_N];
int father[MAX_N];
vector<Node> nodeList;
bool CompareAsc(const Node &n1, const Node &n2){
if(n1.state == n2.state){
return n1.distance < n2.distance;
}else{
return n1.state > n2.state;
}
}
void Init(){
nodeList.clear();
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
height[i] = 0;
father[i] = i;
}
}
int Find(int x){
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
return father[x];
}
bool Union(int x, int y, int state){
x = Find(x);
y = Find(y);
if(x != y || state == 1){
if(height[x] > height[y]){
father[y] = x;
}else if(height[x] < height[y]){
father[x] = y;
}else{
father[y] = x;
height[x]++;
}
if(state == 1){
return false;
}else{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n && n != 0){
Init();
int edge = n * (n - 1) / 2;
int f, t, d, s;
for(int i = 0; i < edge; i++){
cin >> f >> t >> d >> s;
nodeList.push_back(Node(f, t, d, s));
}
sort(nodeList.begin(), nodeList.end(), CompareAsc);
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nodeList.size(); i++){
if(Union(nodeList[i].from, nodeList[i].to, nodeList[i].state)){
result += nodeList[i].distance;
}
}
cout << result << endl;
}
return 0;
}9、题目描述:In an episode of the Dick Van Dyke show, little Richie connects the freckles on his Dad's back to form a picture of the Liberty Bell. Alas, one of the freckles turns out to be a scar, so his Ripley's engagement falls through. Consider Dick's back to be a plane with freckles at various (x,y) locations. Your job is to tell Richie how to connect the dots so as to minimize the amount of ink used. Richie connects the dots by drawing straight lines between pairs, possibly lifting the pen between lines. When Richie is done there must be a sequence of connected lines from any freckle to any other freckle.【北京大学】
- 输入格式:The first line contains 0 < n <= 100, the number of freckles on Dick's back. For each freckle, a line follows; each following line contains two real numbers indicating the (x,y) coordinates of the freckle.
- 输出格式:Your program prints a single real number to two decimal places: the minimum total length of ink lines that can connect all the freckles.
- 样例输入:
- 3
- 1.0 1.0
- 2.0 2.0
- 2.0 4.0
- 样例输出:
- 3.41
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
struct Point{
double x;
double y;
Point(double x, double y):x(x), y(y){};
};
struct Node{
int p1;
int p2;
double distance;
Node(int p1, int p2, double d):p1(p1), p2(p2), distance(d){};
bool operator<(const Node &n){
return distance < n.distance;
}
};
vector<set<int> > pointSetList;
vector<Point> pointList;
vector<Node> nodeList;
double result;
void Init(){
pointSetList.clear();
pointList.clear();
nodeList.clear();
result = 0;
}
void Union(Node node){
int p1Loc = -1, p2Loc = -1;
for(int i = 0; i < pointSetList.size(); i++){
if(pointSetList[i].find(node.p1) != pointSetList[i].end()){
p1Loc = i;
}
if(pointSetList[i].find(node.p2) != pointSetList[i].end()){
p2Loc = i;
}
}
if(p1Loc == -1 && p2Loc == -1){//两点均不在已有集合
set<int> pSet;
pSet.insert(node.p1);
pSet.insert(node.p2);
pointSetList.push_back(pSet);
result += node.distance;
}else if(p2Loc == -1){//p1点在集合,p2点不在集合,将p2点加入p1所在集合
pointSetList[p1Loc].insert(node.p2);
result += node.distance;
}else if(p1Loc == -1){
pointSetList[p2Loc].insert(node.p1);
result += node.distance;
}else if(p1Loc != p2Loc){ //两点在不同集合,合并
for(set<int>::iterator iter = pointSetList[p2Loc].begin();
iter != pointSetList[p2Loc].end(); iter++){
pointSetList[p1Loc].insert(*iter);
}
pointSetList.erase(pointSetList.begin() + p2Loc);
result += node.distance;
}
}
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n){
Init();
double x, y;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> x >> y;
pointList.push_back(Point(x, y));
}
for(int i = 0; i < pointList.size(); i++){
for(int j = i + 1; j < pointList.size(); j++){
double distance = sqrt(pow(pointList[i].x - pointList[j].x, 2)
+ pow(pointList[i].y - pointList[j].y, 2));
nodeList.push_back(Node(i, j, distance));
}
}
sort(nodeList.begin(), nodeList.end());
for(int i = 0; i < nodeList.size(); i++){
Union(nodeList[i]);
}
cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << result << endl;
}
return 0;
}10、题目描述: The Head Elder of the tropical island of Lagrishan has a problem. A burst of foreign aid money was spent on extra roads between villages some years ago. But the jungle overtakes roads relentlessly, so the large road network is too expensive to maintain. The Council of Elders must choose to stop maintaining some roads. The map above on the left shows all the roads in use now and the cost in aacms per month to maintain them. Of course there needs to be some way to get between all the villages on maintained roads, even if the route is not as short as before. The Chief Elder would like to tell the Council of Elders what would be the smallest amount they could spend in aacms per month to maintain roads that would connect all the villages. The villages are labeled A through I in the maps above. The map on the right shows the roads that could be maintained most cheaply, for 216 aacms per month. Your task is to write a program that will solve such problems.(ps:如果不是连通图的话,最后的结果输出不用包含不在连通图里的那些点)【北京大学】

- 输入格式:The input consists of one to 100 data sets, followed by a final line containing only 0. Each data set starts with a line containing only a number n, which is the number of villages, 1 < n < 27, and the villages are labeled with the first n letters of the alphabet, capitalized. Each data set is completed with n-1 lines that start with village labels in alphabetical order. There is no line for the last village. Each line for a village starts with the village label followed by a number, k, of roads from this village to villages with labels later in the alphabet. If k is greater than 0, the line continues with data for each of the k roads. The data for each road is the village label for the other end of the road followed by the monthly maintenance cost in aacms for the road. Maintenance costs will be positive integers less than 100. All data fields in the row are separated by single blanks. The road network will always allow travel between all the villages. The network will never have more than 75 roads. No village will have more than 15 roads going to other villages (before or after in the alphabet). In the sample input below, the first data set goes with the map above.
- 输出格式:The output is one integer per line for each data set: the minimum cost in aacms per month to maintain a road system that connect all the villages. Caution: A brute force solution that examines every possible set of roads will not finish within the one minute time limit.
- 样例输入:
- 9
- A 2 B 12 I 25
- B 3 C 10 H 40 I 8
- C 2 D 18 G 55
- D 1 E 44
- E 2 F 60 G 38
- F 0
- G 1 H 35
- H 1 I 35
- 3
- A 2 B 10 C 40
- B 1 C 20
- 0
- 样例输出:
- 216
- 30
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_N = 26;
struct Node{
int from;
int to;
int cost;
Node(int f, int t, int c):from(f), to(t), cost(c){};
bool operator<(const Node &n){
return cost < n.cost;
};
};
vector<Node> nodeList;
int father[MAX_N];
void Init(){
nodeList.clear();
for(int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
father[i] = i;
}
}
int CharToInt(char c){
return c - 'A';
}
int Find(int x){
while(x != father[x]){
x = father[x];
}
return father[x];
}
bool Union(int x, int y){
x = Find(x);
y = Find(y);
if(x != y){
father[x] = y;
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main(){
int n;
while(cin >> n && n != 0){
Init();
char from, to;
int number, cost;
for(int i = 1; i <= n - 1; i++){
cin >> from >> number;
int f = CharToInt(from);
for(int j = 0; j < number; j++){
cin >> to >> cost;
nodeList.push_back(Node(f, CharToInt(to), cost));
}
}
sort(nodeList.begin(), nodeList.end());
int result = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nodeList.size(); i++){
if(Union(nodeList[i].from, nodeList[i].to)){
result += nodeList[i].cost;
}
}
cout << result << endl;
}
return 0;
}参考文献:
[1]杨泽邦、赵霖. 计算机考研——机试指南(第2版). [M]北京:电子工业出版社,2019.11;






















 448
448











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








