源码地址:https://github.com/Rtoax/test/blob/master/c/cpu/cpu_occupy-proc-stat.c
首先看一下文件"/proc/stat"
//"/proc/stat"
//---------------------------------
// user, nice, system, idle, iowait, irq, softirq, steal, guest, guest_nice.
//cpu 195044598 6619 410450970 967314001 64039 0 85058 394458 0 0
//cpu0 48705507 1701 102480874 241499274 14130 0 82302 103069 0 0
//cpu1 48866063 1895 102699462 241657644 15853 0 1245 97930 0 0
//cpu2 48782413 1260 102714102 242031473 18001 0 790 96743 0 0
//cpu3 48690614 1762 102556531 242125609 16054 0 720 96715 0 0上面的数值依次为:user, nice, system, idle, iowait, irq, softirq, steal, guest, guest_nice.
根据计算公式
(user + nice + system)/(user + nice + system + idle + iowait + irq + softirq)*100%或者省去一些项
(user + nice + system)/(user + nice + system + idle)*100%需要注意的是,我们需要统计一段时间的值来计算瞬时CPU利用率。那我们修改公式为:
[(user1 + nice1 + system1) - (user0 + nice0 + system0)]
/[(user1 + nice1 + system1 + idle1) - (user0 + nice0 + system0 + idle0)]*100%是不是很简单。下面给出完整的程序:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#define NR_CPU_CORES sysconf(_SC_NPROCESSORS_ONLN) //CPU核心总数
struct __cpu_core_stat {
//"/proc/stat"
//---------------------------------
// user, nice, system, idle, iowait, irq, softirq, steal, guest, guest_nice.
//cpu 195044598 6619 410450970 967314001 64039 0 85058 394458 0 0
//cpu0 48705507 1701 102480874 241499274 14130 0 82302 103069 0 0
//cpu1 48866063 1895 102699462 241657644 15853 0 1245 97930 0 0
//cpu2 48782413 1260 102714102 242031473 18001 0 790 96743 0 0
//cpu3 48690614 1762 102556531 242125609 16054 0 720 96715 0 0
long double user, nice, system, idle, iowait, irq, softirq, steal, guest, guest_nice;
};
struct __cpu_core_stat_pair {
struct __cpu_core_stat stat[2]; //0-start, 1-end
struct {
int integer, decimal;
}occupy;
// long double occupy;
};
struct cpu_cores_occupy {
int nr_cpu_core;
struct __cpu_core_stat_pair *cpus_stat;
};
static int cpu_cores_occupy_init(struct cpu_cores_occupy *cco)
{
if(!cco)
return -1;
cco->nr_cpu_core = NR_CPU_CORES;
cco->cpus_stat = malloc(sizeof(struct __cpu_core_stat_pair)*(NR_CPU_CORES+1));
return 0;
}
static int __cpu_cores_occupy_get(struct cpu_cores_occupy *cco, int stat_idx/*0-start, 1-end*/)
{
int icore = 0;
FILE *fp;
struct __cpu_core_stat_pair *cpus_stat = cco->cpus_stat;
fp = fopen("/proc/stat","r");
for(icore=0;icore<=cco->nr_cpu_core;icore++) {
fscanf(fp,"%*s %Lf %Lf %Lf %Lf %Lf %Lf %Lf %Lf %Lf %Lf",
&cpus_stat[icore].stat[stat_idx].user,
&cpus_stat[icore].stat[stat_idx].nice,
&cpus_stat[icore].stat[stat_idx].system,
&cpus_stat[icore].stat[stat_idx].idle,
&cpus_stat[icore].stat[stat_idx].iowait,
&cpus_stat[icore].stat[stat_idx].irq,
&cpus_stat[icore].stat[stat_idx].softirq,
&cpus_stat[icore].stat[stat_idx].steal,
&cpus_stat[icore].stat[stat_idx].guest,
&cpus_stat[icore].stat[stat_idx].guest_nice);
}
fclose(fp);
}
static int cpu_cores_occupy_getstart(struct cpu_cores_occupy *cco)
{
return __cpu_cores_occupy_get(cco, 0);
}
static int cpu_cores_occupy_getend(struct cpu_cores_occupy *cco)
{
return __cpu_cores_occupy_get(cco, 1);
}
static int cpu_cores_occupy_call(struct cpu_cores_occupy *cco)
{
int icore = 0, idx;
struct __cpu_core_stat_pair *cpus_stat = cco->cpus_stat;
for(icore=0;icore<=cco->nr_cpu_core;icore++) {
struct __cpu_core_stat *s0 = &cpus_stat[icore].stat[0];
struct __cpu_core_stat *s1 = &cpus_stat[icore].stat[1];
long double s0_0 = (s0->user+s0->nice+s0->system);
long double s1_0 = (s1->user+s1->nice+s1->system);
long double s0_1 = (s0->user+s0->nice+s0->system+s0->idle);
long double s1_1 = (s1->user+s1->nice+s1->system+s1->idle);
long double occupy = (s1_0 - s0_0) / (s1_1 - s0_1);
cpus_stat[icore].occupy.integer = (int)(occupy*100);
cpus_stat[icore].occupy.decimal = (int)(occupy*10000);
// printf("cpu%d %Lf = (%Lf - %Lf) / (%Lf - %Lf)\n", icore-1, cpus_stat[icore].occupy, s1_0, s0_0, s1_1, s0_1);
}
}
static int cpu_cores_occupy_display(struct cpu_cores_occupy *cco)
{
int icore = 0;
struct __cpu_core_stat_pair *cpus_stat = cco->cpus_stat;
system("clear");
for(icore=0;icore<=cco->nr_cpu_core;icore++) {
printf("cpu%d \t%3d.%-4d %%\n", icore-1,cpus_stat[icore].occupy.integer, cpus_stat[icore].occupy.decimal);
}
}
int main()
{
struct cpu_cores_occupy cco;
cpu_cores_occupy_init(&cco);
for(;;)
{
cpu_cores_occupy_getstart(&cco);
sleep(1);
cpu_cores_occupy_getend(&cco);
cpu_cores_occupy_call(&cco);
cpu_cores_occupy_display(&cco);
}
}
开始运行
[root@localhost cpu]# ./a.out
cpu-1 0.25 %
cpu0 0.0 %
cpu1 1.101 %
cpu2 0.0 %
cpu3 0.0 %
我们写一个有自旋锁死锁的程序,或者干脆一个while(1);并绑定核心运行,如下:
[root@localhost c]# taskset -c 1 ./a.out &
[1] 182556
[root@localhost c]# taskset -c 3 ./a.out &
[2] 182569
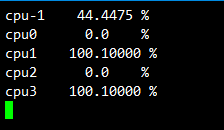
结果如下:
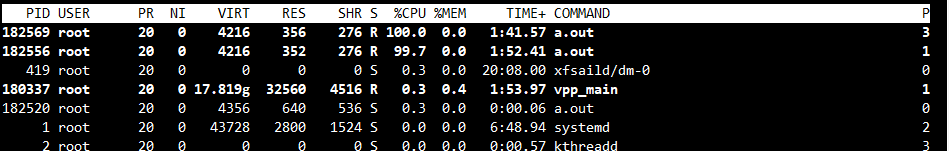
即可看见CPU利用率100%的情况,然后我们用top指令验证一下:
确认无误,下班。





















 4808
4808











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








