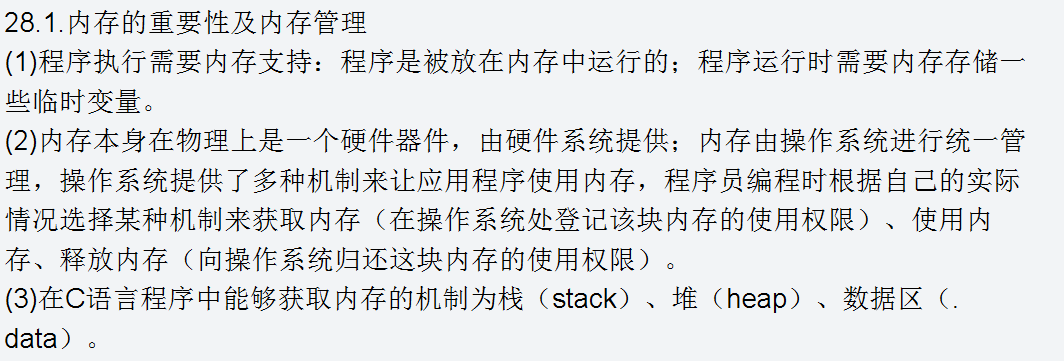
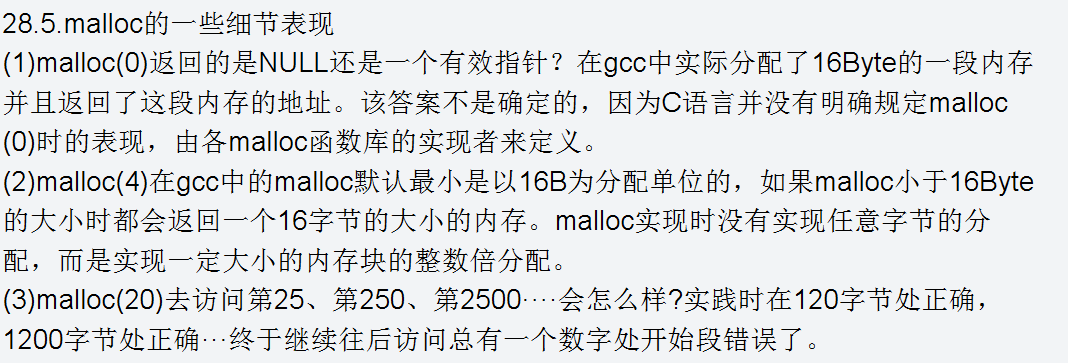
因格式问题,截图上传。
28.stack
/*
* 公司:XXXX
* 作者:Rston
* 博客:http://blog.csdn.net/rston
* GitHub:https://github.com/rston
* 项目:C语言内存管理机制
* 功能:演示栈内存是脏的和爆栈。
*/
#include <stdio.h>
int *func1(void)
{
int a = 10;
printf("in func1 &a = %p.\n", &a); // in func1 &a = 0xbfa45b2c.
return &a; // warning: function returns address of local variable [enabled by default]
} // 函数试图返回临时变量即栈变量的地址,编译报警
void func2(void)
{
int array[3] = {44, 44, 44};
printf("in func2 &array[2] = %p.\n", &array[2]); // int func2 &array[2] = 0xbfa45b2c.
}
// 使用递归爆栈
void func3(void)
{
int a = 4;
func3();
}
// 定义数组爆栈
void func4(void)
{
int array[10000000] = {0};
array[10000000 - 1] = 44;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// 演示栈内存是脏的
int *p = func1();
printf("*p = %d.\n", *p); // *p = 10.
func2();
printf("*p = %d.\n", *p); // *p = 44. 说明栈内存是脏的,函数不应该返回栈变量的指针。
// 演示爆栈
printf("即将爆栈\n"); // 即将爆栈
//func3(); // Segmentation fault (core dumped)栈被爆了,程序访问到不该访问的内存空间
func4(); // Segmentation fault (core dumped)
return 0;
}28.heap
/*
* 公司:XXXX
* 作者:Rston
* 博客:http://blog.csdn.net/rston
* GitHub:https://github.com/rston
* 项目:C语言内存管理机制
* 功能:演示堆内存使用范例。
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// 第1步:申请和绑定内存
int *p = (int *)malloc(100*sizeof(int));
// 第2步:检验申请释放成功
if (NULL == p)
{
printf("malloc error.\n");
return -1;
}
// 第3步:使用申请到的内存
*(p+10) = 123;
*(p+11) = 456;
printf("*(p+10) = %d.\n", *(p+10)); // *(p+10) = 123.
printf("*(p+11) = %d.\n", *(p+11)); // *(p+11) = 456.
// 第4步:释放申请到的内存
free(p);
// free后堆内存还是可被使用,但风险非常大,会造成不可预知的结果
*(p+20) = 123;
*(p+30) = 456;
printf("*(p+20) = %d.\n", *(p+20)); // *(p+20) = 123.
printf("*(p+30) = %d.\n", *(p+30)); // *(p+30) = 456.
// malloc(0)的表现,连续调用两次malloc(0),然后将返回的地址相减即可
int *p1 = (int *)malloc(0);
if (NULL == p1)
{
printf("malloc error.\n");
return -1;
}
if (NULL != p1)
{
printf("p1 = %p.\n", p1); // p1 = 0x9a85008.
}
int *p2 = (int *)malloc(0);
if (NULL == p2)
{
printf("malloc error.\n");
return -1;
}
if (NULL != p2)
{
printf("p2 = %p.\n", p2); // p2 = 0x9a85018.
}
printf("(p2-p1)*sizeof(int) = %d.\n", (p2-p1)*sizeof(int)); // (p2-p1)*sizeof(int) = 16. 分配16个字节的堆内存
free(p1);
free(p2);
// 测试malloc(4)实际的分配效果
int *p3 = (int *)malloc(4);
if (NULL == p3)
{
printf("malloc error.\n");
return -1;
}
if (NULL != p3)
{
printf("p3 = %p.\n", p3); // p3 = 0x9a85028.
}
int *p4 = (int *)malloc(4);
if (NULL == p4)
{
printf("malloc error.\n");
return -1;
}
if (NULL != p4)
{
printf("p4 = %p.\n", p4); // p4 = 0x9a85038.
}
printf("(p4-p3)*sizeof(int) = %d.\n", (p4-p3)*sizeof(int)); // (p4-p3)*sizeof(int) = 16. 分配16个字节的堆内存
free(p3);
free(p4);
// 测试malloc堆内存的越界访问
int *p5 = (int *)malloc(10*sizeof(int));
if (NULL == p5)
{
printf("malloc error.\n");
return -1;
}
*(p5+5) = 123;
printf("*(p5+5) = %d.\n", *(p5+5)); // *(p5+5) = 123.
*(p5+100000) = 456;
printf("*(p5+100000) = %d.\n", *(p5+10000)); // Segmentation fault (core dumped) 访问到了不该访问的内存空间
free(p5);
return 0;
}28.data_section
/*
* 公司:XXXX
* 作者:Rston
* 博客:http://blog.csdn.net/rston
* GitHub:https://github.com/rston
* 项目:C语言内存管理机制
* 功能:演示三种机制(栈、堆、数据段)申请内存空间。
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// 使用堆机制申请内存空间,定义全局变量
char str[] = "linux";
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
// const的两种实现方式
// 单片机将const修饰的变量放置代码段中实现只读
// gcc通过编译器检查实现只读,变量实际存放在数据段中
const int a = 8;
int *p1 = (int *)(&a); // 编译无警告无报错
*p1 = 10;
printf("a = %d.\n", *p1); // a = 10.
// 使用栈机制申请内存空间,定义局部变量
char b[] = "linux";
// 使用堆机制申请内存空间,手动申请内存和释放内存
char *p = (char *)malloc(10*sizeof(char));
if (NULL == p)
{
printf("malloc error.\n");
return -1;
}
memset(p, 0, 10*sizeof(char));
strcpy(p, "linux");
printf("str = %s. b = %s. p = %s.\n", str, b, p); // str = linux. b = linux. p = linux.
printf("str = %p. b = %p. p = %p.\n", str, b, p); // str = 0x804a024. b = 0xbff8cc86. p = 0x8ddc008.
free(p);
return 0;
}


























 8143
8143

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








