介绍
堆排序在 top K 问题中使用比较频繁。堆排序是采用二叉堆的数据结构来实现的,虽然实质上还是一维数组。二叉堆是一个近似完全二叉树 。
二叉堆具有以下性质:
- 父节点的键值总是大于或等于(小于或等于)任何一个子节点的键值。
- 每个节点的左右子树都是一个二叉堆(都是最大堆或最小堆)。
步骤
- 构造最大堆(Build_Max_Heap):若数组下标范围为0~n,考虑到单独一个元素是大根堆,则从下标n/2开始的元素均为大根堆。于是只要从n/2-1开始,向前依次构造大根堆,这样就能保证,构造到某个节点时,它的左右子树都已经是大根堆。
- 堆排序(HeapSort):由于堆是用数组模拟的。得到一个大根堆后,数组内部并不是有序的。因此需要将堆化数组有序化。思想是移除根节点,并做最大堆调整的递归运算。第一次将heap[0]与heap[n-1]交换,再对heap[0…n-2]做最大堆调整。第二次将heap[0]与heap[n-2]交换,再对heap[0…n-3]做最大堆调整。重复该操作直至heap[0]和heap[1]交换。由于每次都是将最大的数并入到后面的有序区间,故操作完后整个数组就是有序的了。
- 最大堆调整(Max_Heapify):该方法是提供给上述两个过程调用的。目的是将堆的末端子节点作调整,使得子节点永远小于父节点 。
代码
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Wed Apr 27 11:53:24 2016
@author: zang
"""
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import random
def heapSort(ary) :
n = len(ary)
first = int(n/2-1) #最后一个非叶子节点
for start in range(first,-1,-1) : #构造大根堆
max_heapify(ary,start,n-1)
for end in range(n-1,0,-1): #堆排,将大根堆转换成有序数组
ary[end],ary[0] = ary[0],ary[end]
max_heapify(ary,0,end-1)
return ary
#最大堆调整:将堆的末端子节点作调整,使得子节点永远小于父节点
#start为当前需要调整最大堆的位置,end为调整边界
def max_heapify(ary,start,end):
root = start
while True :
child = root*2 +1 #调整节点的子节点
if child > end : break
if child+1 <= end and ary[child] < ary[child+1] :
child = child+1 #取较大的子节点
if ary[root] < ary[child] : #较大的子节点成为父节点
ary[root],ary[child] = ary[child],ary[root] #交换
root = child
else :
break
def plotScatter(inputList):
plt.scatter(range(len(inputList)),inputList)
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
num_list = range(1000)
unsortedList = random.sample(num_list, 30)
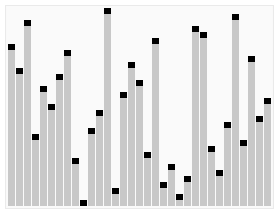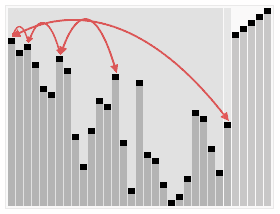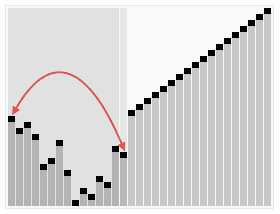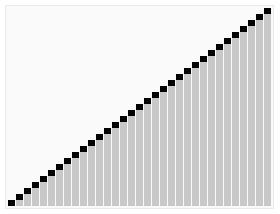
print "unsortedList:"
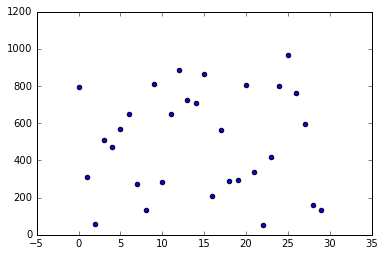
plotScatter(unsortedList)
print unsortedList
sortedList = heapSort(unsortedList)
print "sortedList:"
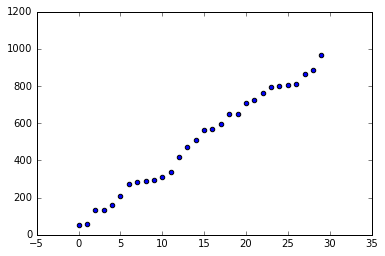
plotScatter(sortedList)
print sortedList测试
输入
[796, 311, 58, 512, 470, 568, 648, 272, 132, 813, 284, 652, 887, 727, 709, 867, 206, 562, 287, 295, 805, 336, 51, 416, 799, 967, 760, 596, 161, 131]输出
[51, 58, 131, 132, 161, 206, 272, 284, 287, 295, 311, 336, 416, 470, 512, 562, 568, 596, 648, 652, 709, 727, 760, 796, 799, 805, 813, 867, 887, 967]分析
| 情况 | 性能 |
|---|---|
| Worst case performance: | O(nlogn) |
| Best case performance: | O(nlogn) |
| Average case performance: | O(nlogn) |
| Worst case space complexity: | O(1) |























 24万+
24万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








