目录
Rockchip系列之深度分析CAN接口系列(1)_一歲抬頭的博客-CSDN博客
Rockchip系列之CAN 新增framework系统jni接口访问(2)-CSDN博客
Rockchip系列之CAN 新增framework封装service+manager访问(3)-CSDN博客
Rockchip系列之CAN APP测试应用实现(4)_一歲抬頭的博客-CSDN博客
Rockchip CAN 部分波特率收发不正常解决思路_一歲抬頭的博客-CSDN博客
Android JNI与CAN通信遇到的问题总结_android can通信-CSDN博客
Android 内核关闭CAN 串口设备回显功能_一歲抬頭的博客-CSDN博客
在上一篇博客中,介绍了如何在framework层编写一个服务类CanService,用于提供CAN通信的接口给其他应用程序或模块。还介绍了如何使用CanService类的封装类SystemCan,用于简化CAN通信的操作和配置。
在这篇博客中,将介绍如何在Android平台上开发一个App,用于测试和演示CAN通信的功能。将分别介绍App的界面设计,逻辑实现和使用方法。
这个App比较简单 只要核心接口写完了 应用端写成花都可以 目前实现了以下的功能:
- 可以选择不同的CAN设备和波特率,打开和关闭CAN总线
- 可以输入要发送的CAN数据,向CAN设备发送一帧数据
- 可以接收来自CAN设备的数据,并显示在列表中
- 可以清除已经接收到的数据
App的界面设计
使用Android Studio来开发的App,首先创建一个新的项目,命名为CanApp,并选择Empty Activity作为模板。然后,在res/layout/activity_main.xml文件中,定义了App的界面布局,如下所示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="16dp">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/canTextView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="CAN Interface:"
android:textSize="18sp" />
<Spinner
android:id="@+id/canSpinner"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/baudrateTextView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Baudrate:"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp" />
<Spinner
android:id="@+id/baudrateSpinner"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/dataTextView"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Data:"
android:textSize="18sp"
android:layout_marginTop="16dp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/dataEditText"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:hint="Enter data"
android:text="1122334455667788"
android:inputType="text" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button
android:id="@+id/sendButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Send"
android:layout_margin="8dp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/openCanButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Open CAN"
android:layout_margin="8dp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/closeCanButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Close CAN"
android:layout_margin="8dp" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/clearButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/openCanButton"
android:layout_alignStart="@id/openCanButton"
android:layout_margin="8dp"
android:text="Clear Received Data" />
</LinearLayout>
<ScrollView
android:id="@+id/scrollView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:fillViewport="true">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/receivedDataListView"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:divider="@android:color/darker_gray"
android:dividerHeight="0.5dp"
android:padding="8dp"
android:scrollbarStyle="outsideOverlay"
android:scrollbars="vertical" />
</ScrollView>
</LinearLayout>这个布局文件定义了一个垂直方向的线性布局。
APP运行效果,如下图所示:
(我写这篇博客的时候 运行环境不在身边 截图以前的视频吧)
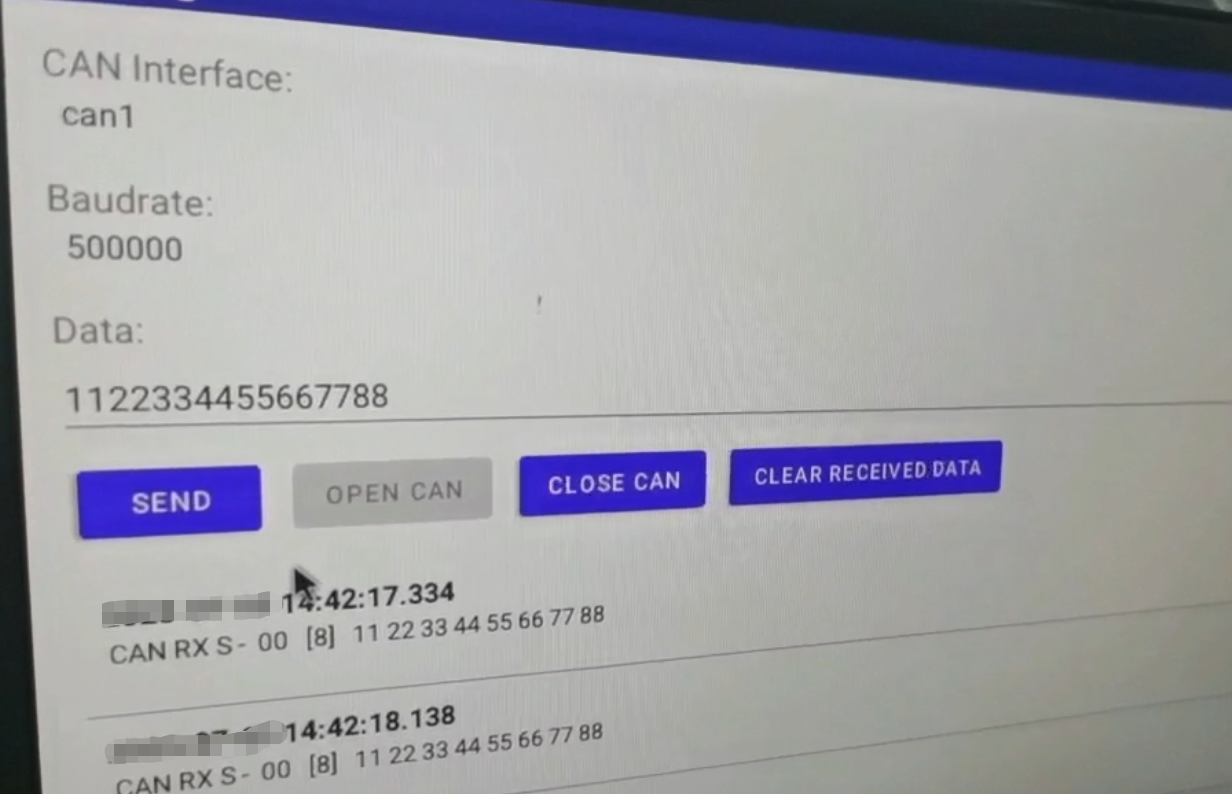
App的逻辑实现
在src/main/java/com/example/canapp/MainActivity.java文件中实现了App的逻辑功能,如下所示:
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener, View.OnClickListener {
private static final String TAG = "MainActivity";
private static final int RECEIVE_CAN_DATA = 1;
private Spinner canSpinner;
private Spinner baudrateSpinner;
private EditText dataEditText;
private Button sendButton;
private Button openCanButton;
private Button closeCanButton;
private Button clearButton;
private ListView receivedDataListView;
private ReceivedDataAdapter receivedDataAdapter;
private ScrollView scrollView;
private List<String> canList;
private List<String> baudrateList;
private String selectedCan;
private int selectedBaudrate;
private boolean isCanOpen = false;
private SystemCan systemCan;
private List<String> receivedDataList;
private Handler handler = new Handler() {
@Override
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
if (msg.what == RECEIVE_CAN_DATA) {
Bundle bundle = msg.getData();
String data = bundle.getString("data");
String timestamp = getCurrentTimestamp();
String message = timestamp + " 收到数据: " + data;
receivedDataList.add(message);
receivedDataAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
scrollToBottom();
}
}
};
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
canSpinner = findViewById(R.id.canSpinner);
baudrateSpinner = findViewById(R.id.baudrateSpinner);
dataEditText = findViewById(R.id.dataEditText);
sendButton = findViewById(R.id.sendButton);
openCanButton = findViewById(R.id.openCanButton);
closeCanButton = findViewById(R.id.closeCanButton);
clearButton = findViewById(R.id.clearButton);
receivedDataListView = findViewById(R.id.receivedDataListView);
scrollView = findViewById(R.id.scrollView);
canList = new ArrayList<>();
canList.add("can1");
canList.add("can0");
ArrayAdapter<String> canAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this, android.R.layout.simple_spinner_item, canList);
canAdapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item);
canSpinner.setAdapter(canAdapter);
canSpinner.setOnItemSelectedListener(this);
baudrateList = new ArrayList<>();
baudrateList.add("10000");
baudrateList.add("20000");
baudrateList.add("40000");
baudrateList.add("50000");
baudrateList.add("100000");
baudrateList.add("125000");
baudrateList.add("250000");
baudrateList.add("500000");
baudrateList.add("666000");
baudrateList.add("800000");
baudrateList.add("1000000");
ArrayAdapter<String> baudrateAdapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this, android.R.layout.simple_spinner_item, baudrateList);
baudrateAdapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item);
baudrateSpinner.setAdapter(baudrateAdapter);
baudrateSpinner.setOnItemSelectedListener(this);
sendButton.setOnClickListener(this);
openCanButton.setOnClickListener(this);
closeCanButton.setOnClickListener(this);
clearButton.setOnClickListener(this);
receivedDataList = new ArrayList<>();
receivedDataAdapter = new ReceivedDataAdapter(this, receivedDataList);
receivedDataListView.setAdapter(receivedDataAdapter);
//
startCanReceiverThread();
}
private void startCanReceiverThread() {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
new Thread() {
long[] ret = new long[12];
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (isCanOpen) {
try {
ret = systemCan.dev_receiveCan(systemCan.fd);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
long canId = ret[0];
long canEff = ret[1];
long canRtr = ret[2];
long canLen = ret[3];
long[] canData = Arrays.copyOfRange(ret, 4, (int) (4 + canLen));
String str = "can RX ";
str += (canEff == 0) ? "S " : "E ";
str += (canRtr == 0) ? "- " : "R ";
String canIdStr = Long.toHexString(canId);
if (canEff == 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3 - canIdStr.length(); i++) {
canIdStr = '0' + canIdStr;
}
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < 8 - canIdStr.length(); i++) {
canIdStr = '0' + canIdStr;
}
}
str = str + canIdStr + " [" + Long.toString(canLen) + "] ";
for (int i = 0; i < canLen; i++) {
String hex = Long.toHexString(canData[i]);
hex = (hex.length() == 1) ? ('0' + hex) : hex;
str = str + ' ' + hex;
}
str = str.toUpperCase();
str += '\n';
String finalStr = str;
Log.d(TAG, "Received CAN data: " + finalStr);
Message message = handler.obtainMessage(RECEIVE_CAN_DATA);
Bundle bundle = new Bundle();
bundle.putString("data", finalStr);
message.setData(bundle);
handler.sendMessage(message);
}
}
}
}.start();
}
});
thread.start();
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
closeCan();
}
@Override
public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) {
int viewId = parent.getId();
if (viewId == R.id.canSpinner) {
selectedCan = canList.get(position);
} else if (viewId == R.id.baudrateSpinner) {
String selectedBaudrateStr = baudrateList.get(position);
selectedBaudrate = Integer.parseInt(selectedBaudrateStr);
}
}
@Override
public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> parent) {
// Do nothing
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
int viewId = v.getId();
if (viewId == R.id.sendButton) {
sendCanData();
} else if (viewId == R.id.openCanButton) {
openCan();
} else if (viewId == R.id.closeCanButton) {
closeCan();
} else if (viewId == R.id.clearButton) {
clearReceivedData();
}
}
private void sendCanData() {
if (!isCanOpen) {
showToast("请先打开 CAN 总线");
return;
}
String data = dataEditText.getText().toString().trim();
if (data.isEmpty()) {
showToast("请输入要发送的数据");
return;
}
// Convert hex string to byte array
byte[] dataArray = hexStringToByteArray(data);
if (dataArray == null) {
showToast("发送的数据格式不正确");
return;
}
try {
int result = systemCan.dev_sendCan(systemCan.fd, 0, 0, 0, dataArray.length, byteArrayToIntArray(dataArray));
if (result != 0) {
showToast("发送数据失败");
} else {
showToast("发送数据成功");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
showToast("发送数据出现异常");
Log.e(TAG, "Error sending CAN data: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private void openCan() {
if (isCanOpen) {
showToast("CAN 总线已经打开");
return;
}
try {
systemCan = new SystemCan(selectedCan, selectedBaudrate);
int fd = systemCan.dev_openCan(selectedCan);
if (fd != -1) {
systemCan.fd = fd;
showToast("打开 CAN 总线成功");
openCanButton.setEnabled(false);
isCanOpen = true;
} else {
showToast("打开 CAN 总线失败");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
showToast("打开 CAN 总线出现异常");
Log.e(TAG, "Error opening CAN: " + e.getMessage());
}
// 添加了额外的参数tq(时间量化器),propSeg(传播段时间),phaseSeg1(相位段1时间),phaseSeg2(相位段2时间)和sjw(同步跳转宽度)
/*runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
ShellUtils.CommandResult commandResult = ShellUtils.execCommand("ip link set " + selectedCan + " down && ip link set " + selectedCan + " type can tq 133 prop-seg 6 phase-seg1 6 phase-seg2 2 sjw 1 && ip link set " + selectedCan + " up", true);
//Log.d("SystemCan-test", + commandResult.result + "," + commandResult.successMsg + "," + commandResult.errorMsg);
}
});*/
}
private void closeCan() {
if (!isCanOpen) {
showToast("CAN 总线已经关闭");
openCanButton.setEnabled(true);
return;
}
try {
int result = systemCan.dev_closeCan(systemCan.fd);
if (result != 0) {
showToast("关闭 CAN 总线失败");
} else {
showToast("关闭 CAN 总线成功");
openCanButton.setEnabled(true);
isCanOpen = false;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
showToast("关闭 CAN 总线出现异常");
Log.e(TAG, "Error closing CAN: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
private void clearReceivedData() {
receivedDataList.clear();
receivedDataAdapter.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
private String getCurrentTimestamp() {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS");
return sdf.format(new Date());
}
private void scrollToBottom() {
scrollView.postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
scrollView.fullScroll(ScrollView.FOCUS_DOWN);
}
}, 100);
}在src/main/java/com/example/canapp/ReceivedDataAdapter.java文件中实现了App的can 接收数据DataAdapter功能,如下所示:
public class ReceivedDataAdapter extends ArrayAdapter<String> {
private Context context;
private List<String> dataList;
public ReceivedDataAdapter(Context context, List<String> dataList) {
super(context, 0, dataList);
this.context = context;
this.dataList = dataList;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return dataList.size();
}
@Override
public String getItem(int position) {
return dataList.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
ViewHolder viewHolder;
if (convertView == null) {
convertView = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.list_item_received_data, parent, false);
viewHolder = new ViewHolder();
viewHolder.timestampTextView = convertView.findViewById(R.id.timestampTextView);
viewHolder.dataTextView = convertView.findViewById(R.id.dataTextView);
convertView.setTag(viewHolder);
} else {
viewHolder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
String data = dataList.get(position);
String[] parts = data.split("收到数据:");
String timestamp = parts[0];
String canData = parts[1];
viewHolder.timestampTextView.setText(timestamp);
viewHolder.dataTextView.setText(canData);
return convertView;
}
private static class ViewHolder {
TextView timestampTextView;
TextView dataTextView;
}
}App的使用方法
可以使用Android Studio来运行的App,并在真机上进行测试。需要先打开CAN总线,然后输入要发送的数据,点击发送按钮,就可以向CAN设备发送一帧数据。还可以在ListView中查看接收到的数据列表,并清除已经接收到的数据。可以通过Spinner来切换不同的CAN设备和波特率,但是需要先关闭当前的CAN总线,再打开新的CAN总线。可以在Logcat中查看App的日志信息,以及发送和接收到的CAN数据。
我希望它能够帮助你和其他人了解和适配CAN通信的功能。如果你有任何问题,欢迎留言 & 支持三连 ~
























 2830
2830











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










