首先来看一个问题,在linux系统中,我们都知道fork会产生一个调用进程的复制,创建出一个新的进程,那么如果父进程有多个线程会不会复制父进程的多个线程呢?
答案:子进程创建出来时只有一个线程,就是调用fork()函数的那个线程。也就是说,父进程在复制子进程的时候,只会复制当前线程的执行状态,其它线程不会复制。(https://www.cnblogs.com/wenxuanh/p/12573966.html)
在linux下,经常会调用fork来产生一个子进程,如果出现既要考虑多线程,又要考虑多进程的情况,这个时候就要引入pthread_atfork函数了。

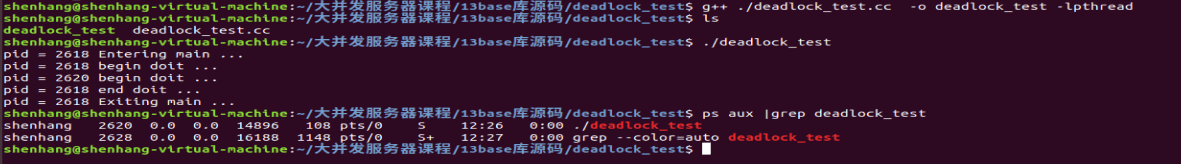
一个在多线程程序里fork造成死锁的例子:
父进程在创建了一个线程,并在线程函数doit中对mutex加锁(假设此时还未运行到解锁代码处);
父进程创建一个子进程,在子进程中调用doit,由于子进程会复制父进程的内存,所以这时候mutex处于锁的状态;
父进程在复制子进程的时候,只会复制当前线程的执行状态,其它线程不会复制。因此子进程会处于死锁的状态(阻塞在doit的加锁代码处)。
deadlock_test.cc
// 一个在多线程程序里fork造成死锁的例子
// 一个输出示例:
/*
pid = 19445 Entering main ...
pid = 19445 begin doit ...
pid = 19447 begin doit ...
pid = 19445 end doit ...
pid = 19445 Exiting main ...
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void* doit(void* arg)
{
printf("pid = %d begin doit ...\n",static_cast<int>(getpid()));
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
struct timespec ts = {2, 0};
nanosleep(&ts, NULL);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
printf("pid = %d end doit ...\n",static_cast<int>(getpid()));
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
printf("pid = %d Entering main ...\n", static_cast<int>(getpid()));
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, doit, NULL);
struct timespec ts = {1, 0};
nanosleep(&ts, NULL);
if (fork() == 0)
{
doit(NULL);
}
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
printf("pid = %d Exiting main ...\n",static_cast<int>(getpid()));
return 0;
}
ps aux |grep deadlock_test
killall deadlock_test
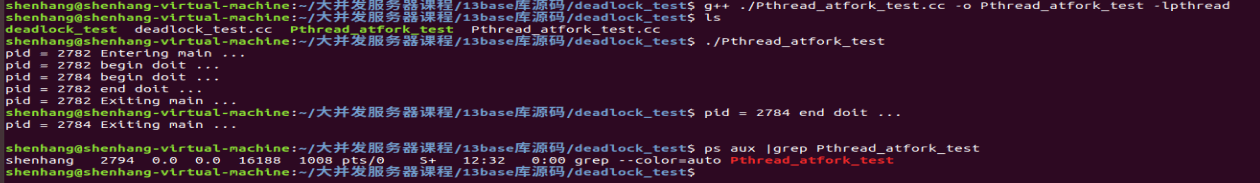
pthread_atfork解决死锁问题
解决做法的本质上就是在fork执行之前先调用prepare函数解锁,这样确保子进程调用doit时可以成功上锁。
Pthread_atfork_test.cc
#include <stdio.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <unistd.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
void* doit(void* arg)
{
printf("pid = %d begin doit ...\n",static_cast<int>(getpid()));
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
struct timespec ts = {2, 0};
nanosleep(&ts, NULL);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
printf("pid = %d end doit ...\n",static_cast<int>(getpid()));
return NULL;
}
void prepare(void)
{
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
}
void parent(void)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_atfork(prepare, parent, NULL);
printf("pid = %d Entering main ...\n", static_cast<int>(getpid()));
pthread_t tid;
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, doit, NULL);
struct timespec ts = {1, 0};
nanosleep(&ts, NULL);
if (fork() == 0)
{
doit(NULL);
}
pthread_join(tid, NULL);
printf("pid = %d Exiting main ...\n",static_cast<int>(getpid()));
return 0;
}





 本文探讨了在Linux环境下,使用fork函数时如何避免因多线程导致的死锁问题。通过具体示例展示了当父进程在进行多线程操作时调用fork可能引发的问题,并介绍了使用pthread_atfork函数解决此类死锁的方法。
本文探讨了在Linux环境下,使用fork函数时如何避免因多线程导致的死锁问题。通过具体示例展示了当父进程在进行多线程操作时调用fork可能引发的问题,并介绍了使用pthread_atfork函数解决此类死锁的方法。
















 717
717

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








