目录
一、类的定义
class为定义类的关键字,ClassName为类的名字,{}中为类的主体,注意类定义结束时后面分 号不能省略。
class className
{
// 类体:由成员函数和成员变量组成
}; // 一定要注意后面的分号
类的定义方式有两种:(1). 声明和定义全部放在类体中,成员函数如果在类中定义,编译器可能会将其当成内联函数处理;(2). 类声明放在.h文件中,成员函数定义放在.cpp文件中,成员函数名前需要加 类名::。
二、类的访问限定
类的访问限定符有public(公有)、private(私有)、protected(保护)。访问限定符只在编译时有用,当数据映射到内存后,没有任何访问限定符上的区别
(1)public修饰的成员在类外可以直接被访问,protected和private修饰的成员在类外不能直接被访问;
(2)访问权限作用域从该访问限定符出现的位置开始直到下一个访问限定符出现时为止;
(3)class的默认访问权限为private,struct为public。
三、类对象的大小
一个类的大小,实际就是该类中”成员变量”之和,当然要注意内存对齐 ,而空类比较特殊,编译器给了空类一个字节来唯一标识这个类的对象。
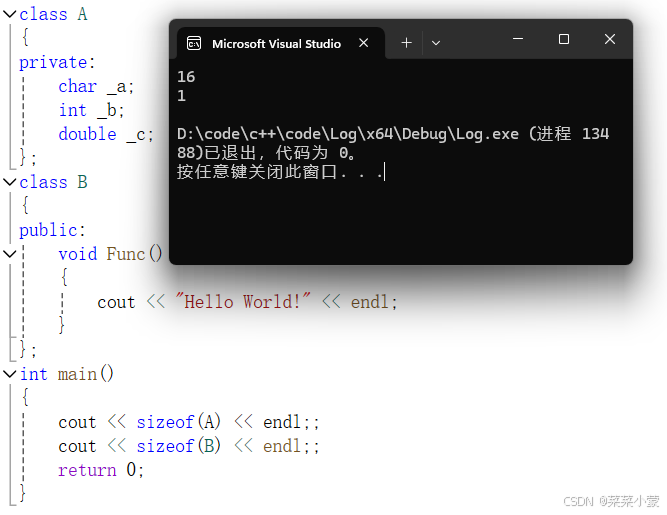
四、类对象的存储
类的非静态成员变量存储在类中(栈),在计算类的大小时,只计算成员变量的大小即可。
每个对象的成员变量都不相同,但每个变量所需要调用的成员函数都是相同的,所以把类的非静态成员函数全部放在代码区,形成一个公共的类函数代码区域,每个对象在调用函数时直接去该区域调用成员函数。
这样做的优势:每个对象在创建时,只要保存对象的成员变量,需要调用成员函数时,再去公共的类函数代码区域调用即可。

五、this指针
(一)概念
编译器给每个“非静态的成员函数“增加了一个隐藏的指针参数,让该指针指向当前对象(函数运行时调用该函数的对象),在函数体中所有“成员变量”的操作,都是通过该指针去访问。只不过所有的操作对用户是透明的,即用户不需要来传递,编译器自动完成。
(二)this指针的特性
this指针只能在成员函数内部使用。this指针的类型是 * const ,即在成员函数中,不能改变this的指向。this指针本质上是成员函数的形参,当对象调用成员函数时,将对象地址作为实参传递给this形参。this指针是成员函数隐藏的第一个参数,一般由编译器自动传递,无需用户传递。
需要注意,this指针是可以为空的,下面一段代码可以执行。
class A
{
private:
int _a;
public:
void Func()
{
cout << "Hello World!" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
A* p = nullptr;
p->Func();
return 0;
}而下面一段代码会报运行错误,因为p作为参数传递给函数Func,同时this指针接受参数为空,在成员函数体发生了空指针解引用。
class A
{
private:
int _a;
public:
void Func()
{
//cout << this->_a << endl;
cout << _a << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
A* p = nullptr;
p->Func();
return 0;
}六、类的六大默认成员函数
详见【C++六大默认成员函数】。
七、运算符重载
文章末尾附有运算符重载示例代码。
(一)运算符重载的概念
C++为了增强代码的可读性引入了运算符重载,运算符重载是具有特殊函数名的函数,也具有其返回值类型,函数名字以及参数列表,其返回值类型与参数列表与普通的函数类似。
函数名为:关键字operator后面接需要重载的运算符符号。
函数原型:返回值类型 operator操作符(参数列表)
(二)运算符重载的注意事项
(1)不能通过链接其他符号创建新的操作符:比如operator@ ,@是未知字符,只有运算符才能重载;
(2)运算符重载必须有类类型参数,且这个操作符有几个操作数就得有几个参数;
(3)运算符重载一般用于自定义类型,对于内置类型,其定义不可改变;
(4).* :: sizeof ?: . 注意以上5个运算符不能重载。
(5)++和--是单操作数的运算符,需注意,前置重载与普通运算符重载一致,后置重载需要在参数列表中加入一个int参数。
七、static成员
(一)概念
声明为static的类成员称为类的静态成员,用static修饰的成员变量,称之为静态成员变量;用 static修饰的成员函数,称之为静态成员函数。静态成员变量一定要在类外进行初始化。
(二)特性
(1)静态成员为所有类对象所共享,不属于某个具体的对象,存放在静态区;
(2)静态成员变量必须在类外定义,定义时不添加static关键字,类中只是声明;
(3)类静态成员可用 类名::静态成员 或者 对象.静态成员 来访问;
(4)静态成员函数没有隐藏的this指针,不能访问任何非静态成员;
(5)静态成员也是类的成员,受public、protected、private 访问限定符的限制;
(6)静态成员函数不能调用非静态成员函数;而非静态成员函数可以调用静态成员函数。
八、友元
友元提供了一种突破封装的方式,有时提供了便利。但是友元会增加耦合度,破坏了封装,所以 友元不宜多用。
(一)友元函数
文章末尾附有友元函数示例代码。
友元函数可以直接访问类的私有成员,它是定义在类外部的普通函数,不属于任何类,但需要在 类的内部声明,声明时需要加friend关键字。
(二)友元类
友元类的所有成员函数都可以是另一个类的友元函数,都可以访问另一个类中的非公有成员。
(1)友元关系是单向的,不具有交换性;
(2)友元关系不能传递;
(3)友元关系不能继承。
class A
{
friend class B;
private:
int _a;
void Func()
{
cout << _a << endl;
}
};
class B
{
private:
int _b;
A _A;
public:
void SetValue(int a)
{
//B是A的友元类,因此B可以访问A中所有非公有成员
_A._a = a;
_A.Func();
}
};九、内部类
(一)概念
如果一个类定义在另一个类的内部,这个内部类就叫做内部类。内部类是一个独立的类, 它不属于外部类,更不能通过外部类的对象去访问内部类的成员。外部类对内部类没有任何优越的访问权限。
内部类就是外部类的友元类,内部类可以通过外部类的对象参数来访问外部类中的所有成员。但是外部类不是内部类的友元。
(二)特性
(1)内部类可以定义在外部类的public、protected、private;
‘ (2)注意内部类可以直接访问外部类中的static成员,不需要外部类的对象/类名;
(3)sizeof(外部类)=外部类,和内部类没有任何关系。
class A
{
private:
int _a;
void Func()
{
cout << _a << endl;
}
public:
class B
{
public:
void SetValue(A& _A, int a)
{
//B是A的内部类,因此B可以访问A中所有非公有成员
_A._a = a;
_A.Func();
}
};
};
int main()
{
A a;
A::B b;
b.SetValue(a, 1);
return 0;
}代码:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
//友元函数
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d);
friend istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d);
private:
int _year;
int _month;
int _day;
int getMonthDay(int year, int day);
public:
Date(int year = 0, int month = 0, int day = 0);
Date(const Date& d);
//运算符重载
Date& operator=(const Date& d);
bool operator==(const Date& d) const;
bool operator!=(const Date& d) const;
bool operator>(const Date& d) const;
bool operator>=(const Date& d) const;
bool operator<(const Date& d) const;
bool operator<=(const Date& d) const;
Date operator+(int day) const;
Date& operator+=(int day);
Date operator-(int day) const;
Date& operator-=(int day);
int operator-(const Date& d) const;
Date& operator++();
Date operator++(int);
Date& operator--();
Date operator--(int);
};
int Date::getMonthDay(int year, int month)
{
static int MonthDay[13] = { 0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31 };
if (month == 2 && ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0)))
{
return 29;
}
return MonthDay[month];
}
Date::Date(int year, int month, int day)
:_year(year)
, _month(month)
, _day(day)
{}
Date::Date(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
}
Date& Date::operator=(const Date& d)
{
_year = d._year;
_month = d._month;
_day = d._day;
return *this;
}
bool Date::operator==(const Date& d) const
{
if (_year == d._year && _month == d._month && _day == d._day)
return true;
return false;
}
bool Date::operator!=(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this == d);
}
bool Date::operator>(const Date& d) const
{
if (this->_year > d._year)
return true;
else if (this->_year == d._year && this->_month > d._month)
return true;
else if (this->_year == d._year && this->_month == d._month && this->_day > d._day)
return true;
return false;
}
bool Date::operator>=(const Date& d) const
{
return (*this > d) || (*this == d);
}
bool Date::operator<(const Date& d) const
{
return !(*this > d);
}
bool Date::operator<=(const Date& d) const
{
return (*this < d) || (*this == d);
}
Date Date::operator+(int day) const
{
Date ret(*this);
ret += day;
return ret;
}
Date& Date::operator+=(int day)
{
if (day < 0)
return (*this -= day);
_day += day;
while (_day > getMonthDay(_year, _month))
{
_day -= getMonthDay(_year, _month);
++_month;
if (_month == 13)
{
++_year;
_month = 1;
}
}
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator-(int day) const
{
Date ret(*this);
ret -= day;
return ret;
}
Date& Date::operator-=(int day)
{
if (_day < 0)
return (*this += day);
_day -= day;
while (_day < 1)
{
--_month;
if (_month == 0)
{
_month = 12;
--_year;
}
_day += getMonthDay(_year, _month);
}
return *this;
}
int Date::operator-(const Date& d) const
{
Date max = *this;
Date min = d;
int flag = 1;
if (max < min)
{
max = d;
min = *this;
flag = -1;
}
int ret = 0;
while (min != max)
{
++min;
++ret;
}
return ret * flag;
}
Date& Date::operator++()
{
*this += 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator++(int)
{
Date ret(*this);
*this += 1;
return ret;
}
Date& Date::operator--()
{
*this -= 1;
return *this;
}
Date Date::operator--(int)
{
Date ret(*this);
*this -= 1;
return ret;
}
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Date& d)
{
out << d._year << "年" << d._month << "月" << d._day << "日";
return out;
}
istream& operator>>(istream& in, Date& d)
{
in >> d._year >> d._month >> d._day;
return in;
}























 496
496

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








