Towards Real World Human Parsing: Multiple-Human Parsing in the Wild
J Li , J Zhao , Y Wei , C Lang , Y Li
May 23 2017
https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.07206
这是今年5月份的一篇论文,我觉得有点意思所以就读了一下:
1、导引
之前很多做human parsing的工作都是考虑的一张图里面只有一个人,这种情况的确比较简单,因为现实世界很多时候的照片包含的人物不止一个,所以这篇文章的作者就考虑到这个问题,做了Multiple Human Parsing.
这篇文章的三个贡献点:
A、介绍了多人物分析问题,扩展了人物解析的研究范围,并在各种应用中更好地与真实世界情景相匹配。
B、他们新建了一个较大的Benchmark---Multiple Human Parsing (MHP) Dataset
C、他们提出来一个新的MH-Parser model用于multiple human parsing,结合了全局信息和局部信息,然后其表现超过了以往的那种简单的”detect-and-parse”的方法。
2、相关工作
A、Human parsing这一部分我就不多说了,介绍了以前human parsing的各种方法。
B、Instance-aware object segmentation
这里提到了一个工作:Multi-task Network Cascades for differentiating instances. 应该是一个做instance segmentation的工作,这个论文我也还没有看过,之后有时间会去看一下。这个工作的分割不是特别细,也就是说它停留在person这个level,没有进一步对body part进行segment,但是之后我还是准备看一下,毕竟是做instance segmentation的。
3、MHP Dataset
这个Dataset包含4980张Img,每一张都至少有两个person在图中。每个前景人物都被标注了用人类专家的18种语义标签。7个body parts: “hair”, “face”, “left leg”, “right leg”, “left arm”, “right arm”, and “torso skin”
11个fashion categories: “hat”, “sunglasses”, “upper clothes”, “skirt”, “pants”, “dress”, “belt”, “left shoe”, “right shoe”, “bag”, and “scarf” .
MHP数据集中总共有14,969个人物级别的注释。980张用作testing set,3000张用于training set, 1000张作为validation set。
4、Multiple-Human Parsing Methods
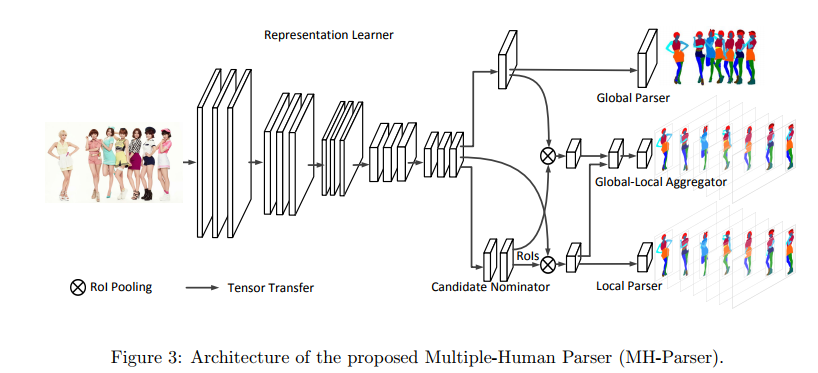
①MH-Parser
包含5个部分:
A、Representationlearner
这是主干网络,是一个CNN特征器,它提取的特征由后面几个模块共享,这里使用全卷积网络,以保持 spatial 信息。
B、Global parser
获取整幅图像的全局信息,就是对整幅图来做个parsing
C、Candidate nominator
包括三个子模块Region Proposal Network(RPN), abounding box classifier andabounding box regression,类似于 Faster RCNN,将每个人检测出来,得到矩形框
D、Local parser
针对每个含有人的矩形框,进行 semantic labels 语义标记
E、Global-localaggregator
同时将 local parser and the global parser 网络中隐含的信息输入,用于单人矩形框的semantic parsing predictions
②Detect-and-parse baseline
分为两个不同的阶段,detection stage和parsing stage. 在detection stage中,把representation learner和candidate nominator 作为detection model,在parsing stage中,把representation learner和local prediction作为parsing model.
注意这两个阶段的representation learner是相互独立不分享信息的。























 3400
3400

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








