互锁现象
在多线程中经常会出现线程间的互锁现象。
进程间的互锁,假设有两个线程,线程1的完成需要用线程2 的资源,线程2的完成需要用线程1的资源。当两个线程都启动后,线程1 等待线程2 的资源, 线程2 等待线程1 的资源,以致于两个线程都没办法完成,都在等待状态。这种现象就叫做线程间的互锁。
//线程1
public class LockRunnable1 implements Runnable {
private String lock1 = "lock1";
private String lock2 = "lock2";
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock1) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("我在等你把lock2给我!");
synchronized (lock2) {
}
}
}
}
//线程2
public class LockRunnable2 implements Runnable{
private String lock1 = "lock1";
private String lock2 = "lock2";
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock2) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("我在等你把lock1给我!");
synchronized (lock1) {
}
}
}
}
//测试
public class TestRunnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试互锁
LockRunnable1 run1 = new LockRunnable1();
LockRunnable2 run2 = new LockRunnable2();
Thread t1 = new Thread(run1, "小红");
Thread t2 = new Thread(run2,"小名");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
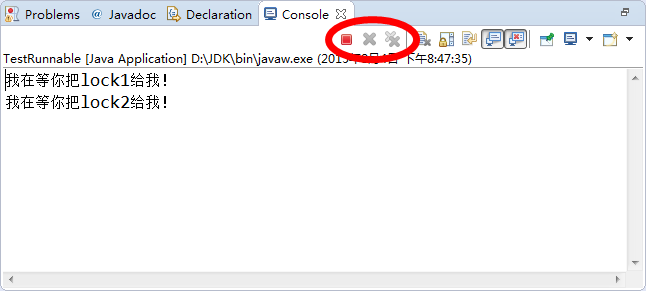
}运行结果:
从结果中可以看到,程序一直在运行。因为红色圆圈处一直处于运行状态!
如何解决互锁
可以通过调用同步锁的wait()和notify()方法来解决互锁问题。
首先说一下wait()方法,wait()方法必须用在同步锁中。调用wait()方法,线程进入等待状态,直到有notify()唤醒它。
nitify()方法同样也需要用在同步锁中。作用是将在等待状态的进程唤醒,进入运行状态。
//线程1
public class LockRunnable1 implements Runnable {
private String lock1 = "lock1";
private String lock2 = "lock2";
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("run1 开始运行!");
synchronized (lock1) {
//休眠1秒
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("run1释放lock1, 进入等待状态!");
try {
lock1.wait();//进入等待状态。
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("run1在等你把lock2给我!");
synchronized (lock2) {
System.out.println("run1获得lock2,继续运行!");
}
}
}
}
//线程2
public class LockRunnable2 implements Runnable{
private String lock1 = "lock1";
private String lock2 = "lock2";
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("run2开始运行!");
synchronized (lock2) {
//休眠1秒
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("run2在等run1把lock1给他!");
synchronized (lock1) {
System.out.println("run2获得lock1, 继续执行!");
//run2唤醒lock1
lock1.notify();
//休眠3S
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("run2 运行完毕!");
}
}
}
}
//测试
public class TestRunnable {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//测试互锁
LockRunnable1 run1 = new LockRunnable1();
LockRunnable2 run2 = new LockRunnable2();
Thread t1 = new Thread(run1, "小红");
Thread t2 = new Thread(run2,"小名");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
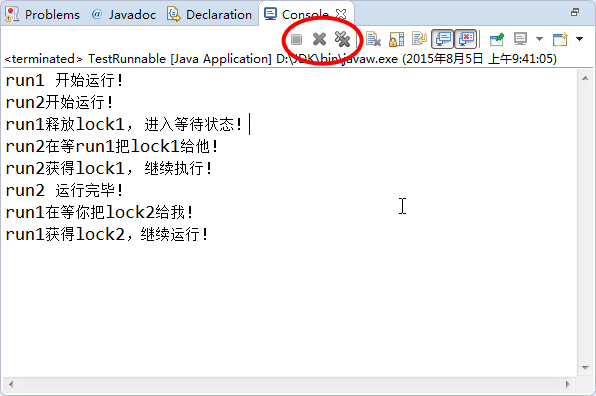
}运行结果:

























 7452
7452

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










