弄了个把星期总算有点自己的体会。。。还是以一道很老很简单的题来说
仓鼠球
总提交:239 测试通过:59
描述
一日,仓鼠君在一个由10×10的格子构成的竞技场里滚球,每一块格子高度不同;
仓鼠君有特别的滚球技巧,可以每次精准地向前后左右四个方向中的一个滚动一格;
仓鼠君只能从高的格子向相邻的相同高度或更低的格子滚动;
如果两个格子高度差超过100(不含100),那么仓鼠君不能向这个格子移动,否则会摔碎自己的球;
仓鼠君不会抛弃他的球。
现在,给你每个格子的高度,问仓鼠君能够到达的所有格子的数目(包括开始时的格子)(在任何一个路线中经过的格子都算在结果中)。
输入
输入第一行是一个整数T(1<=T<=20),代表测试数据的数量;
然后第一行是两个整数x和y,代表仓鼠君开始时的坐标(0<=x,y<=9);
然后是一个10×10的矩阵,表示每个格子的高度(0<=h<=200)。
输出
对于每组数据在一行内输出一个整数,表示仓鼠君能够到达的所有格子数目(包括开始时的格子)(在任何一个路线中经过的格子都算在结果中)。
样例输入
1
0 0
200 199 198 197 196 195 194 193 192 191
199 198 197 196 195 194 193 192 191 190
198 197 196 195 194 193 192 191 190 189
197 196 195 194 193 192 191 190 189 188
196 195 194 193 192 191 190 189 188 187
195 194 193 192 191 190 189 188 187 186
194 193 192 191 190 189 188 187 186 185
193 192 191 190 189 188 187 186 185 184
192 191 190 189 188 187 186 185 184 183
191 190 189 188 187 186 185 184 183 182样例输出
100dfs写法:
<strong>#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<time.h>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<iterator>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<map>
//#define ONLINE_JUDGE
#define eps 1e-8
#define INF 0x7fffffff
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define FOR(i,a) for((i)=0;i<(a);(i)++)
#define MEM(a) (memset((a),0,sizeof(a)))
#define sfs(a) scanf("%s",a)
#define sf(a) scanf("%d",&a)
#define sfI(a) scanf("%I64d",&a)
#define pf(a) printf("%d\n",a)
#define pfI(a) printf("%I64d\n",a)
#define pfs(a) printf("%s\n",a)
#define sfd(a,b) scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)
#define sft(a,b,c)scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<b;i++)
#define for2(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=b;i++)
#define for3(i,a,b)for(int i=(b);i>=a;i--)
#define MEM1(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define MEM2(a) memset(a,-1,sizeof(a))
#define LL __int64
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) {return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;}
template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) {return a / gcd(a, b) * b;}
template<class T> inline T Min(T a, T b) {return a < b ? a : b;}
template<class T> inline T Max(T a, T b) {return a > b ? a : b;}
using namespace std;
int n,m;
#define N 15
bool vis[N][N];
int pic[N][N];
int dfs(int x,int y){
int num = 0;
if(vis[x][y])
return num;
else{
num++;
vis[x][y] = true;
if(pic[x][y] >= pic[x][y+1] && pic[x][y] - pic[x][y+1] <= 100 && y + 1 <= 9)
num += dfs(x,y+1);
if(pic[x][y] >= pic[x][y-1] && pic[x][y] - pic[x][y-1] <= 100 && y - 1 >= 0)
num += dfs(x,y-1);
if(pic[x][y] >= pic[x-1][y] && pic[x][y] - pic[x-1][y] <= 100 && x - 1 >= 0)
num += dfs(x-1,y);
if(pic[x][y] >= pic[x+1][y] && pic[x][y] - pic[x+1][y] <= 100 && x + 1 <= 9)
num += dfs(x+1,y);
return num;
}
}
int main(){
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
#endif
int t,x,y;
sf(t);
while(t--){
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
sfd(x,y);
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 10; j++){
scanf("%d",&pic[i][j]);
}
}
pf(dfs(x,y));
}
return 0;
}</strong>
bfs写法:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<time.h>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<iterator>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<map>
//#define ONLINE_JUDGE
#define eps 1e-8
#define INF 0x7fffffff
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
#define FOR(i,a) for((i)=0;i<(a);(i)++)
#define MEM(a) (memset((a),0,sizeof(a)))
#define sfs(a) scanf("%s",a)
#define sf(a) scanf("%d",&a)
#define sfI(a) scanf("%I64d",&a)
#define pf(a) printf("%d\n",a)
#define pfI(a) printf("%I64d\n",a)
#define pfs(a) printf("%s\n",a)
#define sfd(a,b) scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)
#define sft(a,b,c)scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<b;i++)
#define for2(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=b;i++)
#define for3(i,a,b)for(int i=(b);i>=a;i--)
#define MEM1(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define MEM2(a) memset(a,-1,sizeof(a))
#define LL __int64
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) {return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;}
template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) {return a / gcd(a, b) * b;}
template<class T> inline T Min(T a, T b) {return a < b ? a : b;}
template<class T> inline T Max(T a, T b) {return a > b ? a : b;}
using namespace std;
int n,m;
#define N 15
bool vis[N][N];
int pic[N][N];
struct Point{
int x;
int y;
};
queue<Point> q;
const int go[4][2] = {{0,1},{0,-1},{1,0},{-1,0}};
bool Jud(Point next,Point first){
if(next.x < 0)
return false;
if(next.y < 0)
return false;
if(vis[next.x][next.y])
return false;
if(next.x >= 10)
return false;
if(next.y >= 10)
return false;
if(pic[first.x][first.y] - pic[next.x][next.y] > 100)
return false;
if(pic[next.x][next.y] > pic[first.x][first.y])
return false;
return true;
}
int bfs(int x,int y){
Point temp,next_step;
temp.x = x; temp.y = y;
q.push(temp);
int num = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
temp = q.front();
q.pop();
vis[temp.x][temp.y] = true; <span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//为什么只有这句不行?
num++;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++){
next_step.x = temp.x + go[i][0];
next_step.y = temp.y + go[i][1];
if(Jud(next_step,temp)){
q.push(next_step);
vis[next_step.x][next_step.y] = true; //这里始终有个问题,为什么要加这一句,只有上面那句为什么出错?
}
}
}
return num;
}
int main(){
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
#endif
int t,x,y;
sf(t);
while(t--){
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
while(!q.empty())
q.pop();
sfd(x,y);
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 10; j++){
scanf("%d",&pic[i][j]);
}
}
pf(bfs(x,y));
}
return 0;
}DFS的简单题:
Prime Ring Problem
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 34250 Accepted Submission(s): 15147
Note: the number of first circle should always be 1.
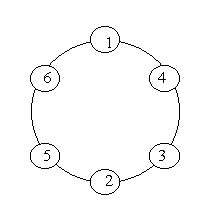
You are to write a program that completes above process.
Print a blank line after each case.
6 8
Case 1: 1 4 3 2 5 6 1 6 5 2 3 4 Case 2: 1 2 3 8 5 6 7 4 1 2 5 8 3 4 7 6 1 4 7 6 5 8 3 2 1 6 7 4 3 8 5 2
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<time.h>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<iterator>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<map>
//#define ONLINE_JUDGE
#define eps 1e-8
#define INF 0x7fffffff //INT_MAX
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f //int范围内可靠的无穷大
#define FOR(i,a) for((i)=0;i<(a);(i)++) //[i,a);
#define MEM(a) (memset((a),0,sizeof(a)))
#define sfs(a) scanf("%s",a)
#define sf(a) scanf("%d",&a)
#define sfI(a) scanf("%I64d",&a)
#define pf(a) printf("%d\n",a)
#define pfI(a) printf("%I64d\n",a)
#define pfs(a) printf("%s\n",a)
#define sfd(a,b) scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)
#define sft(a,b,c)scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<b;i++)
#define for2(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=b;i++)
#define for3(i,a,b)for(int i=(b);i>=a;i--)
#define MEM1(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define MEM2(a) memset(a,-1,sizeof(a))
#define LL __int64
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) {return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;}
template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) {return a / gcd(a, b) * b;}
template<class T> inline T Min(T a, T b) {return a < b ? a : b;}
template<class T> inline T Max(T a, T b) {return a > b ? a : b;}
using namespace std;
int n,m;
bool prime[40] = {0,0,1,1,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0};
int a[25];
int vis[25];
void dfs(int s){ //填第s个位置
if(s == n){
if(prime[a[s - 1] + 1]){
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++){
printf("%d%c",a[i],(i == n - 1 ? '\n' : ' '));
}
}
return ;
}
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
if(vis[i])
continue;
vis[i] = true; <span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//先标记
if(prime[i + a[s - 1]]){
a[s] = i;
dfs(s + 1);
}
vis[i] = false;<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>//记得复位
}
}
int main(){
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
#endif
int k = 0;
a[0] = 1;
while(sf(n)!=EOF){
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
printf("Case %d:\n",++k);
dfs(1);
putchar(10);
}
return 0;
}
典型BFS:
| Time Limit: 2000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 61445 | Accepted: 19198 |
Description
Farmer John has been informed of the location of a fugitive cow and wants to catch her immediately. He starts at a point N (0 ≤ N ≤ 100,000) on a number line and the cow is at a point K (0 ≤ K ≤ 100,000) on the same number line. Farmer John has two modes of transportation: walking and teleporting.
* Walking: FJ can move from any point X to the points X - 1 or X + 1 in a single minute
* Teleporting: FJ can move from any point X to the point 2 × X in a single minute.
If the cow, unaware of its pursuit, does not move at all, how long does it take for Farmer John to retrieve it?
Input
Output
Sample Input
5 17
Sample Output
4代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<string.h>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
#include<time.h>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<iterator>
#include<math.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<map>
//#define ONLINE_JUDGE
#define eps 1e-8
#define INF 0x7fffffff //INT_MAX
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f //int范围内可靠的无穷大
#define FOR(i,a) for((i)=0;i<(a);(i)++) //[i,a);
#define MEM(a) (memset((a),0,sizeof(a)))
#define sfs(a) scanf("%s",a)
#define sf(a) scanf("%d",&a)
#define sfI(a) scanf("%I64d",&a)
#define pf(a) printf("%d\n",a)
#define pfI(a) printf("%I64d\n",a)
#define pfs(a) printf("%s\n",a)
#define sfd(a,b) scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)
#define sft(a,b,c)scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c)
#define for1(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<b;i++)
#define for2(i,a,b) for(int i=(a);i<=b;i++)
#define for3(i,a,b)for(int i=(b);i>=a;i--)
#define MEM1(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define MEM2(a) memset(a,-1,sizeof(a))
#define LL __int64
const double PI = acos(-1.0);
template<class T> T gcd(T a, T b) {return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;}
template<class T> T lcm(T a, T b) {return a / gcd(a, b) * b;}
template<class T> inline T Min(T a, T b) {return a < b ? a : b;}
template<class T> inline T Max(T a, T b) {return a > b ? a : b;}
using namespace std;
int n,m;
#define N 100000
bool vis[N+10];
struct Node{
int position;
int time;
Node(){
position = 0;
time = 0;
}
};
queue<Node> q;
bool Jud(Node temp){
if(temp.position < 0 || temp.position > N || vis[temp.position] )
return false;
return true;
}
int bfs(){
while(!q.empty())
q.pop();
Node temp,next_step;
temp.position = n;
vis[n] = true;
q.push(temp);
int ans_time = 0;
while(!q.empty()){
temp = q.front();
q.pop();
if(temp.position == m){
ans_time = temp.time;
break;
}
next_step.position = temp.position - 1;
next_step.time = temp.time + 1;
if (Jud(next_step)) {
q.push(next_step);
vis[next_step.position] = true;
}
next_step.position = temp.position + 1;
next_step.time = temp.time + 1;
if (Jud(next_step)) {
q.push(next_step);
vis[next_step.position] = true;
}
next_step.position = temp.position * 2;
next_step.time = temp.time + 1;
if (Jud(next_step)) {
q.push(next_step);
vis[next_step.position] = true;
}
}
return ans_time;
}
int main(){
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
#endif
while(sfd(n,m)!=EOF){
if(n >= m)
pf(n - m);
else{
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
pf(bfs());
}
}
return 0;
}
总结:
以上几个例子基本上是bfs和dfs的一般写法。。。当然还有根据bfs和dfs拓展的算法。。以后往上加。
对了 杭电有道题!1728 我已经连错三天了。。。








 本文通过仓鼠球和Prime Ring Problem问题,探讨BFS(广度优先搜索)和DFS(深度优先搜索)的基本使用。仓鼠球问题中,需要计算仓鼠能到达的所有格子数。Prime Ring Problem则涉及FJ追赶逃犯的路径优化问题。文章总结了这两种算法的一般写法,并提及杭电1728题作为拓展应用。
本文通过仓鼠球和Prime Ring Problem问题,探讨BFS(广度优先搜索)和DFS(深度优先搜索)的基本使用。仓鼠球问题中,需要计算仓鼠能到达的所有格子数。Prime Ring Problem则涉及FJ追赶逃犯的路径优化问题。文章总结了这两种算法的一般写法,并提及杭电1728题作为拓展应用。














 175
175

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








