以罗马尼亚问题为例,学习人工智能的搜索算法
Romania problem
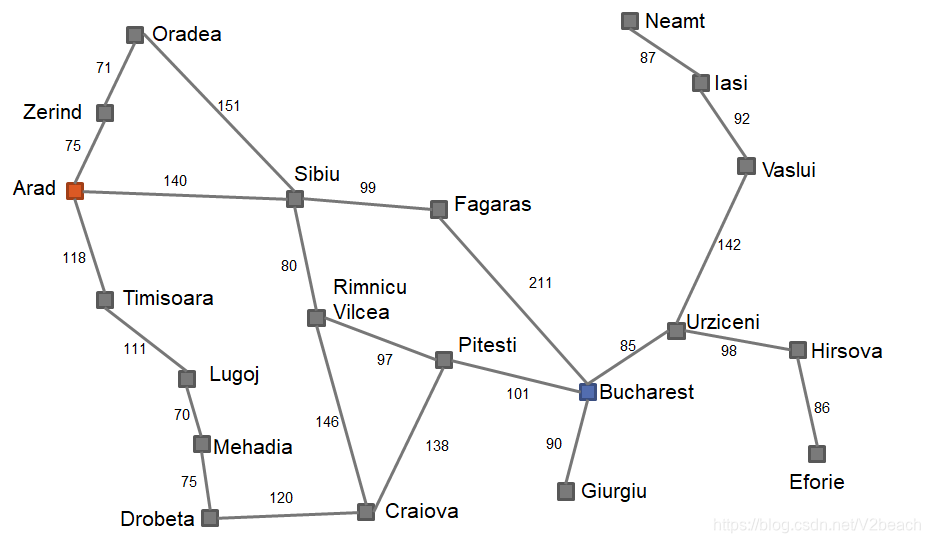
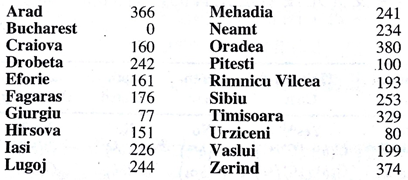
给出各个城市之间的距离及代价,包括A*算法需要的直线距离,求解从A到B点的最短路径。这里分别使用两种搜索算法求解–DFS和Astar。因为本问题的数据量较小,均使用邻接矩阵来表示图,程序均用C++实现。
无信息搜索算法:深度优先搜索
算法思路
使用图的深度优先算法求解,所以需要找出每一条路径,然后根据其总距离求出最短路径,图的深度优先搜索主要思路是,在图中从起点开始往任意有弧的节点扩展,直到没有出度(或在本题中找到目标节点)后保存为一条路径,把图中所有的点全部遍历一遍为止。
程序源码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#define VERTEX 13
using namespace std;//A must?
struct AdjacencyMatrix {
string vertex[VERTEX];
int edges[VERTEX][VERTEX];
int isTraversed[VERTEX] = { 0 };
vector<int> path;
vector<pair<vector<int>, int>> pathcost;//?!
};
class Solution {
public:
void createGraph(AdjacencyMatrix &graph) {
// 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12
int map[VERTEX][VERTEX] = { { 0, 75, -1,118, -1, -1, -1,140, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },//0
{ -1, 0, 71, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },//1
{ -1, -1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1,151, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },//2
{ -1, -1, -1, 0,111, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },//3
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, 70, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },//4
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, 75, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },//5
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, -1, -1,120, -1, -1, -1 },//6
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, 80, -1, 99, -1, -1 },//7
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0,146, -1, 97, -1 },//8
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, -1,138, -1 },//9
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, -1,211 },//10
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0,101 },//11
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0 } //12
};//13 points
for (int i = 0; i < VERTEX; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < VERTEX; j++)
if (map[i][j] != -1)
map[j][i] = map[i][j];
memcpy(graph.edges, map, sizeof(map));
graph.vertex[0] = "Arad";
graph.vertex[1] = "Zerind";
graph.vertex[2] = "Oradea";
graph.vertex[3] = "Timisoara";
graph.vertex[4] = "Lugoj";
graph.vertex[5] = "Mehadia";
graph.vertex[6] = "Drobeta";
graph.vertex[7] = "Sibiu";
graph.vertex[8] = "Rimnicu-Vilcea";
graph.vertex[9] = "Craiova";
graph.vertex[10] = "Fagaras";
graph.vertex[11] = "Pitesti";
graph.vertex[12] = "Bucharest";
}
void outputGraph(AdjacencyMatrix &graph) {
for (int i = 0; i < VERTEX; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < VERTEX; j++)
if (graph.edges[i][j] > 0)
cout << graph.vertex[i] << " -> " << graph.vertex[j] << " : " << graph.edges[i][j] << endl;
}
int nextOutdegree(AdjacencyMatrix graph, int interrupt, int loc) {
for (int index = interrupt + 1; index < VERTEX; index++) {
if (graph.edges[loc][index] > 0 && graph.isTraversed[index] == 0)
//cout << index << endl;
return index;
}
return -1;
}
int computePathCost(AdjacencyMatrix graph) {
int cost = 0, index = 0;
for (; index < graph.path.size() - 1; index++)
cost += graph.edges[graph.path[index]][graph.path[index + 1]];
cost += graph.edges[graph.path[index]][12];
return cost;
}
int minimumPathCost(vector<pair<vector<int>, int>> pathcost) {
int minIndex = 0, index = 1;
for (; index < pathcost.size(); index++)
if (pathcost[minIndex].second >= pathcost[index].second)
minIndex = index;
return minIndex;
}
void depthFirstSearch(AdjacencyMatrix &graph, int start, int end) {
int loc = 0, cost = 0;
graph.isTraversed[start] = 1;
graph.path.push_back(start);
while ((loc = nextOutdegree(graph, loc, start)) != -1) {
if (loc == end) {
cout << "Path: ";
for (int cur = 0; cur < graph.path.size(); cur++) {
cout << graph.vertex[graph.path[cur]] << " ";
cost = computePathCost(graph);
graph.pathcost.push_back(pair<vector<int>, int>(graph.path, cost));
}
cout << graph.vertex[end] << ", Cost: " << cost << endl;//Here is an error.
break;
}
depthFirstSearch(graph, loc, end);
graph.path.pop_back();
graph.isTraversed[loc] = 0;//Go back.
//cout << "back path: " << loc << endl;
}
}
/*void breadthFirstSearch(AdjacencyMatrix &graph) {
//really?
}*/
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int start = 0, end = 12, index = 0;
AdjacencyMatrix graph;
Solution sol;
sol.createGraph(graph);
sol.outputGraph(graph);
sol.depthFirstSearch(graph, start, end);
index = sol.minimumPathCost(graph.pathcost);
cout << endl << "So, mincost path: ";
for (int cur = 0; cur < graph.pathcost[index].first.size(); cur++)
cout << graph.vertex[graph.pathcost[index].first[cur]] << " -> ";
cout << graph.vertex[end] << endl;//Here is an error.
vector<int>().swap(graph.path);//Clear and release memory.
system("pause");
return 0;
}
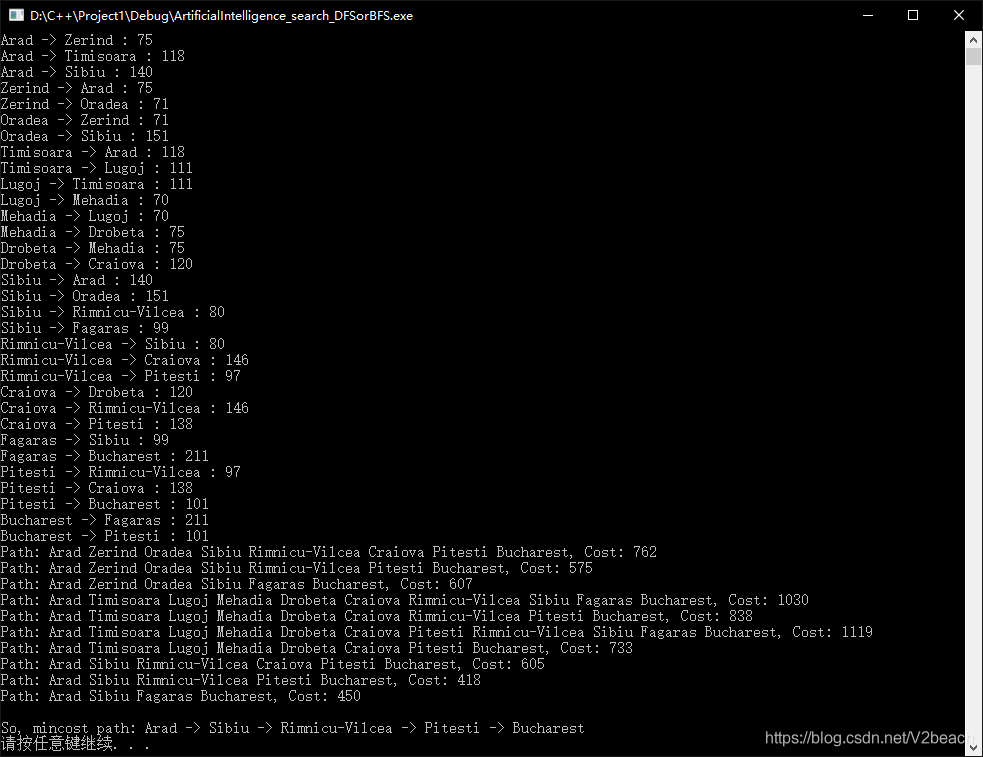
最后输出的So, mincost path: Arad -> Sibiu -> Rimnicu-Vilcea -> Pitesti -> Bucharest即为结果。
代码分析
流程图描述
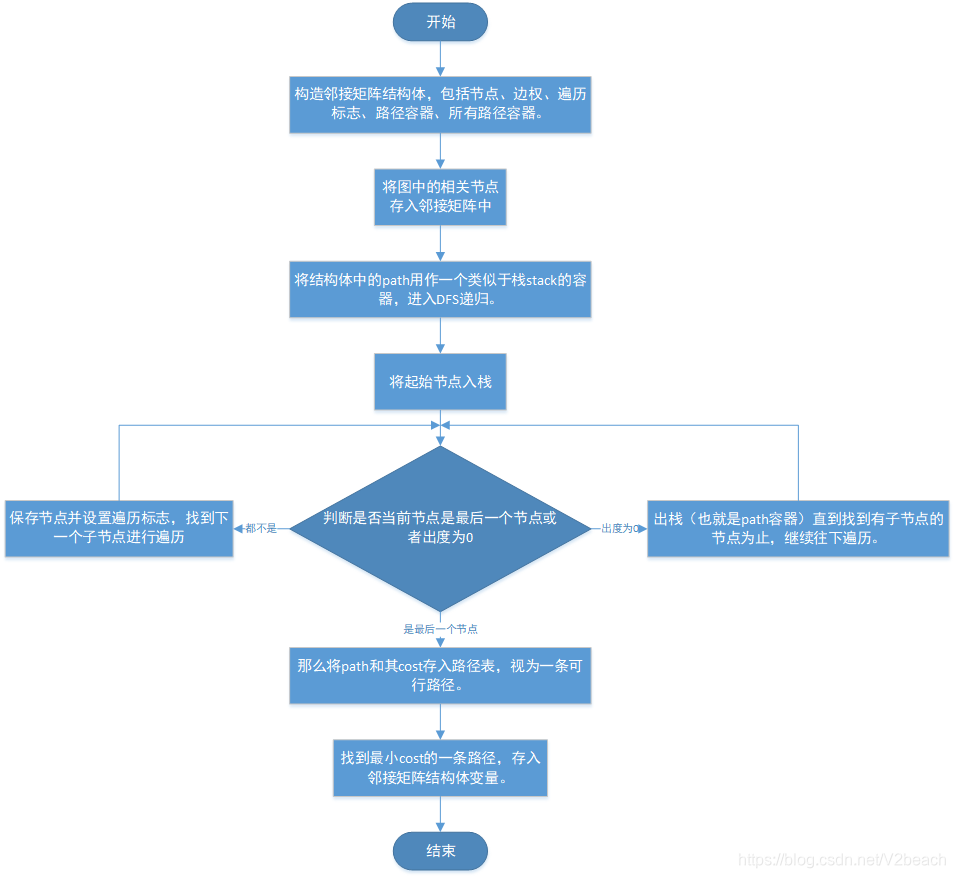
感觉图和代码都还算清晰,就不用自然语言描述了。
有信息搜索算法:A*搜索
算法思路
部分A*算法的思路来自https://www.gamedev.net/articles/programming/artificial-intelligence/a-pathfinding-for-beginners-r2003/,要维护两个表,分别是open list和close list,由公式
1.把起点加入 open list 。
2.重复如下过程:
a.遍历 open list ,查找 F 值最小的节点,把它作为当前要处理的节点。
b.把这个节点移到 close list 。
c.对当前方格的 8 个相邻方格的每一个方格?
Ⅰ.如果它是不可抵达的或者它在 close list 中,忽略它。否则,做如下操作。
Ⅱ.如果它不在 open list 中,把它加入 open list ,并且把当前方格设置为它的父亲,记录该方格的 F , G 和 H 值。
Ⅲ.如果它已经在 open list 中,检查这条路径 ( 即经由当前方格到达它那里 ) 是否更好,用 G 值作参考。更小的 G 值表示这是更好的路径。如果是这样,把它的父亲设置为当前方格,并重新计算它的 G 和 F 值。如果 open list 是按 F 值排序的话,改变后可能需要重新排序。
d.停止,当
Ⅰ.把终点加入到了 open list 中,此时路径已经找到了,或者
Ⅱ.查找终点失败,并且 open list 是空的,此时没有路径。
3.保存路径。从终点开始,每个方格沿着父节点移动直至起点,这就是所求路径。
程序源码
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#define VERTEX 13
using namespace std;//A must?
//https://www.gamedev.net/articles/programming/artificial-intelligence/a-pathfinding-for-beginners-r2003/
struct AstarNode {
int id;
AstarNode *parent;
AstarNode() :
id(-1), parent(NULL) {}
AstarNode(int id) :
id(id), parent(NULL) {}
AstarNode(int id, AstarNode *parent) :
id(id), parent(parent) {}
};
struct AdjacencyMatrix {
string vertex[VERTEX];
int edges[VERTEX][VERTEX];
int direct[VERTEX];
AstarNode openlist[VERTEX];
AstarNode closelist[VERTEX];
int fvalue[VERTEX];
int isTraversed[VERTEX] = { 0 };
vector<int> path;
};
class Solution {
public:
void createGraph(AdjacencyMatrix &graph) {
// 00 01 02 03 04 05 06 07 08 09 10 11 12
int map[VERTEX][VERTEX] = { { 0, 75, -1,118, -1, -1, -1,140, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },//0
{ -1, 0, 71, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },//1
{ -1, -1, 0, -1, -1, -1, -1,151, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },//2
{ -1, -1, -1, 0,111, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },//3
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, 70, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },//4
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, 75, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1 },//5
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, -1, -1,120, -1, -1, -1 },//6
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, 80, -1, 99, -1, -1 },//7
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0,146, -1, 97, -1 },//8
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, -1,138, -1 },//9
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0, -1,211 },//10
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0,101 },//11
{ -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1, 0 } //12
};//13 points
for (int i = 0; i < VERTEX; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < VERTEX; j++)
if (map[i][j] != -1)
map[j][i] = map[i][j];
memcpy(graph.edges, map, sizeof(map));
graph.vertex[0] = "Arad"; graph.direct[0] = 366;
graph.vertex[1] = "Zerind"; graph.direct[1] = 374;
graph.vertex[2] = "Oradea"; graph.direct[2] = 380;
graph.vertex[3] = "Timisoara"; graph.direct[3] = 329;
graph.vertex[4] = "Lugoj"; graph.direct[4] = 244;
graph.vertex[5] = "Mehadia"; graph.direct[5] = 241;
graph.vertex[6] = "Drobeta"; graph.direct[6] = 242;
graph.vertex[7] = "Sibiu"; graph.direct[7] = 253;
graph.vertex[8] = "Rimnicu-Vilcea"; graph.direct[8] = 193;
graph.vertex[9] = "Craiova"; graph.direct[9] = 160;
graph.vertex[10] = "Fagaras"; graph.direct[10] = 176;
graph.vertex[11] = "Pitesti"; graph.direct[11] = 100;
graph.vertex[12] = "Bucharest"; graph.direct[12] = 0;
/*for (int index = 0; index < VERTEX; index++) {
cout << &graph.openlist[index] << endl;
}*/
}
void outputGraph(AdjacencyMatrix &graph) {
for (int i = 0; i < VERTEX; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < VERTEX; j++)
if (graph.edges[i][j] > 0)
cout << graph.vertex[i] << " -> " << graph.vertex[j] << " : " << graph.edges[i][j] << endl;
}
inline int computeF(AdjacencyMatrix graph, AstarNode node) {
if (node.parent == NULL)
return graph.direct[node.id];
return graph.edges[node.parent->id][node.id] + graph.direct[node.id];
}
AstarNode minimumF(AdjacencyMatrix graph) {
int Fmin = INT_MAX;
int Findex = 0;
int F;//F = G + H, G is cost, H is estimated value.
for (int index = 1; index < VERTEX; index++)
if (graph.openlist[index].id != -1 && graph.closelist[index].id == -1
&& (F = graph.fvalue[index]) < Fmin) {
Fmin = F;
Findex = index;
}
//cout << Findex << " ";
return graph.openlist[Findex];
}
int nextOutdegree(AdjacencyMatrix graph, int interrupt, int loc) {
for (int index = interrupt + 1; index < VERTEX; index++) {
if (graph.edges[loc][index] > 0 && graph.isTraversed[index] == 0)
//cout << index << endl;
return index;
}
return -1;
}
bool extendOpenList(AdjacencyMatrix &graph, int id) {
graph.closelist[id] = graph.openlist[id];
int current = 0;
if (id == VERTEX - 1)
return false;
while ((current = nextOutdegree(graph, current, id)) != -1) {
//AstarNode *extended = new AstarNode();//Why???
graph.openlist[current].id = current;
graph.openlist[current].parent = &graph.closelist[id];
graph.isTraversed[current] = 1;
graph.fvalue[current] = computeF(graph, graph.openlist[current]);
//cout << current << " ";
}
return true;
}
void AstarSearch(AdjacencyMatrix &graph, int start, int end) {
AstarNode root = { start, NULL };
//cout << &root << endl;
graph.openlist[start] = root;
graph.isTraversed[start] = 1;
graph.fvalue[start] = computeF(graph, root);
while (extendOpenList(graph, root.id)) {
cout << root.id << " ";
root = minimumF(graph);
}
root = graph.closelist[end];
cout << root.id << endl;
AstarNode *p = &root;
while (p != NULL) {
graph.path.push_back(p->id);//逆向
p = p->parent;
//cout << p->id << endl;
}
}
};
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int start = 0, end = 12;
AdjacencyMatrix graph;
Solution sol;
sol.createGraph(graph);
sol.outputGraph(graph);
sol.AstarSearch(graph, start, end);
cout << endl << "So, path: ";
for (int cur = graph.path.size() - 1; cur > 0; cur--)
cout << graph.vertex[graph.path[cur]] << " -> ";
cout << graph.vertex[graph.path[0]] << endl;
vector<int>().swap(graph.path);
system("pause");
return 0;
}

最后输出的path: Arad -> Sibiu -> Rimnicu-Vilcea -> Pitesti -> Bucharest即为结果。
代码分析
流程图描述
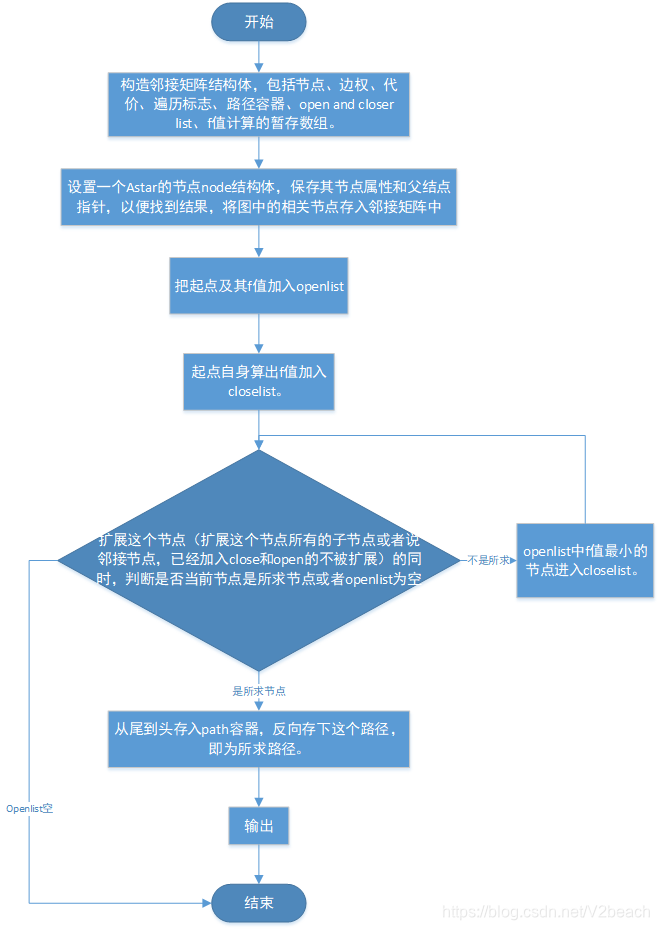
小结
固定疯玩三天per month,Live and drink, friend。
此文为人工智能导论实验报告,顺便发表在博客,转载请注明出处。

























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








