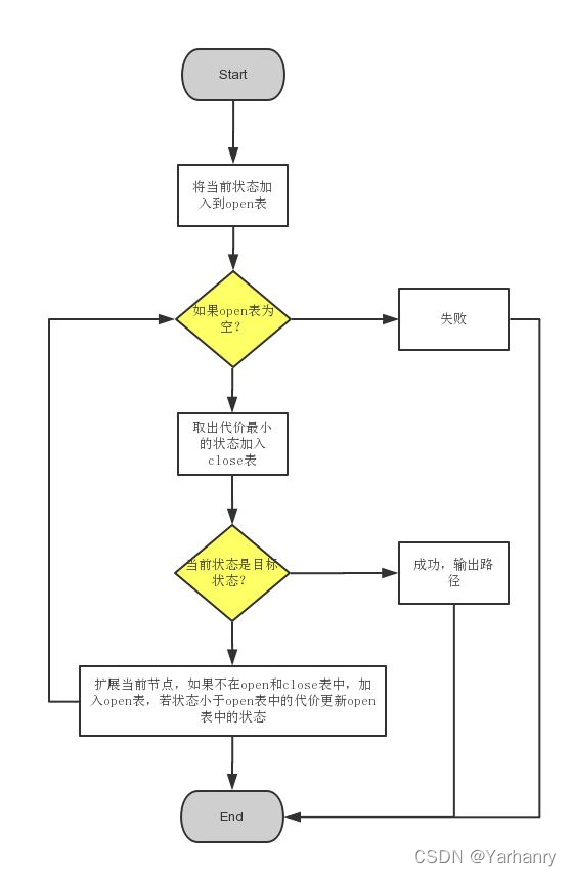
实验内容
本实验要求用广度优先算法、深度优先算法和A*算法求解“罗马尼亚度假问题”,即找到从初始地点 Arad到 目的地点 Bucharest 的一条最佳路径
实验原理
广度优先搜索
从图的一个未遍历的节点出发,先遍历这个节点的相邻节点,再依次遍历每个相邻节点的相邻节点,找到目标节点或完全遍历结束。

深度优先搜索
从图中一个未访问的顶点 V开始,沿着一条路一直走到底,然后从这条路尽头的节点回退到上一个节点,再从另一条路开始走到底,不断递归重复此过程,直到找到目标节点或所有的顶点都遍历完成。

A*算法
通过下面这个函数来计算每个节点的优先级:
f(n) = g(n) + h(n)
其中:
f(n)是节点n的综合优先级。当我们选择下一个要遍历的节点时,我们总会选取综合优先级最高(值最小)的节点。
g(n) 是节点n距离起点的代价。
h(n)是节点n距离终点的预计代价,这也就是A*算法的启发函数。
实验数据
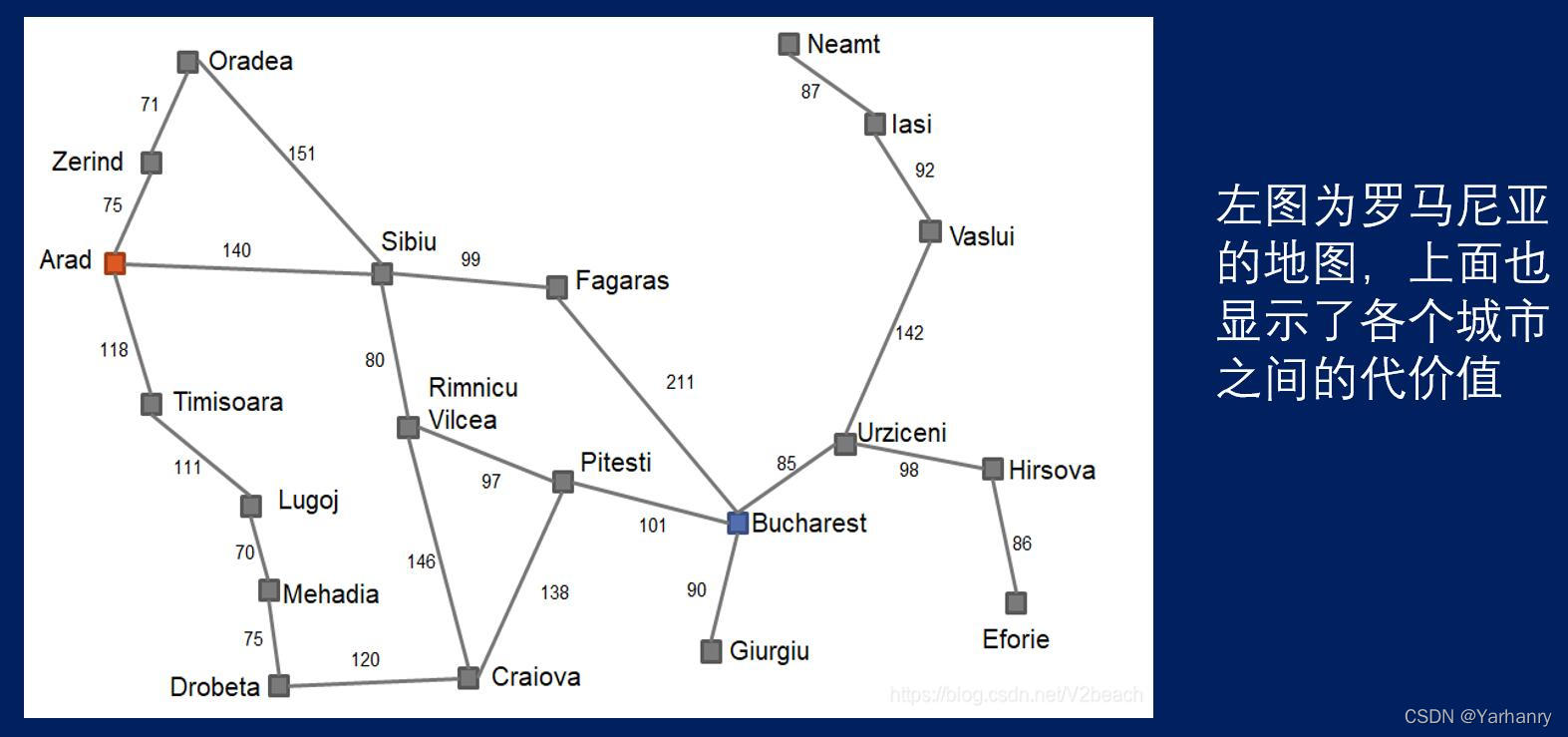
城市名:
Arad, Bucharest, Craiova,Drobeta, Eforie, Fagaras,Giurgiu, Hirsova, Iasi,Lugoj, Mehadia,
Neamt,Oradea, Pitesti, Rimnicu,Sibiu, Timisoara, Urziceni,Vaslui, Zerind
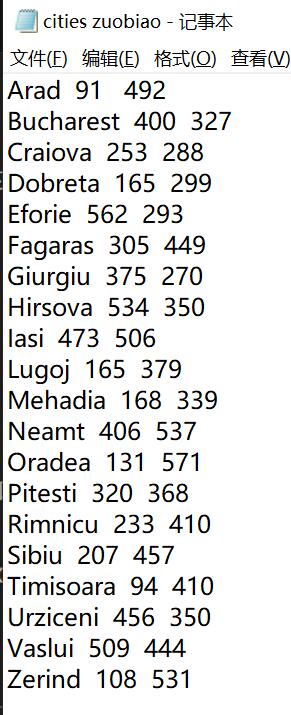
每个城市对应的坐标信息:(用在A*算法处算出h(n),当前节点到目标节点距离)
Arad=(91, 492), Bucharest=(400, 327), Craiova=(253, 288),
Drobeta=(165, 299), Eforie=(562, 293), Fagaras=(305, 449),
Giurgiu=(375, 270), Hirsova=(534, 350), Iasi=(473, 506),
Lugoj=(165, 379), Mehadia=(168, 339), Neamt=(406, 537),
Oradea=(131, 571), Pitesti=(320, 368), Rimnicu=(233, 410),
Sibiu=(207, 457), Timisoara=(94, 410), Urziceni=(456, 350),
Vaslui=(509, 444), Zerind=(108, 531))
实验要求
1.给出各种搜索算法得到的具体路径、相应的代价、经过的节点数、open表和close表。
2.这几种方法效果做对比,例如时间维度。
3.可自选出发地和目标地。
实验过程
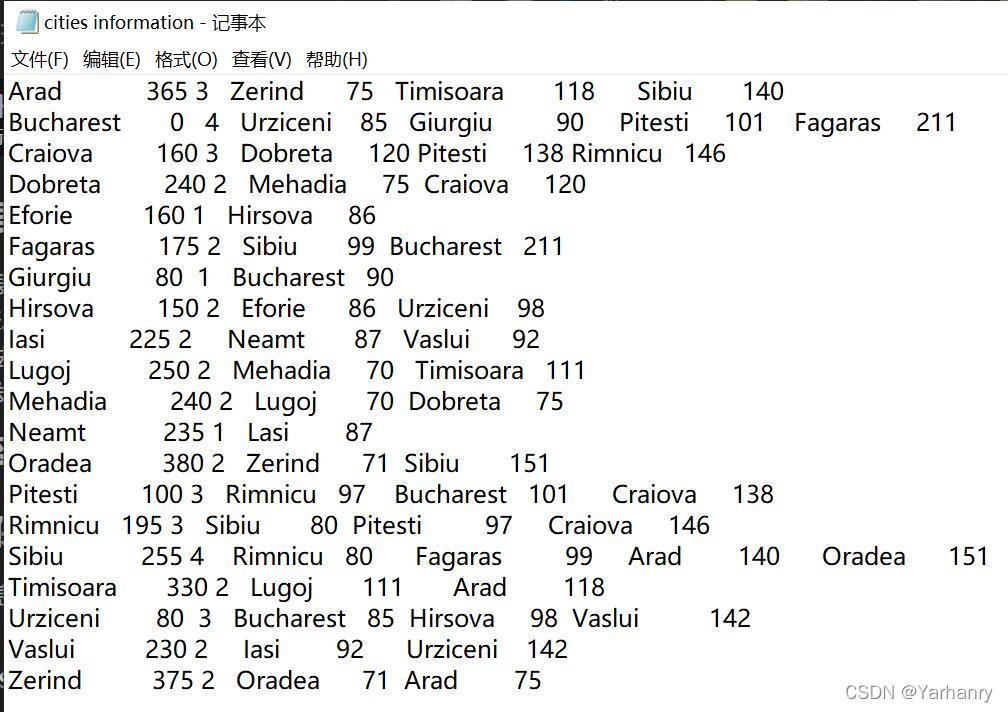
数据保存
我把数据信息分别保存到如下图中,方便后续可再添加


代码展示
城市信息文件读取
def file_input(file1, file2): # 城市信息文件的读取
global graph
global state_num
with open(file1, 'r', encoding='utf8') as f1:
# state_num = len(f.readlines()) # 城市数量 不可用此法求行数,读完后光标会移到末尾,信息为空了
for line in f1.readlines(): # 读取每一行城市信息
state_num += 1 # 计算城市数量(行数)
line = list(line.split())
t = State(line[0], int(line[2]))
line = line[3:]
for i, j in zip(range(0, len(line), 2), range(0, t.neighbor_num)):
t.nextstate[j] = {line[i]: int(line[i + 1])} # 存取该城市所有相邻城市的信息
graph[t.name] = t # 添加当前城市
f1.close()
with open(file2, 'r', encoding='utf8') as f2:
for line in f2.readlines():
line = str(line).split()
cities_name.extend(line)
f2.close()
def zuobiao(file3): # 读取每个城市的坐标信息,放在字典里面
global cost
with open(file3, 'r', encoding='utf8') as f3:
for line in f3.readlines(): # 读取每一行城市信息
line = list(str(line).split())
cost[line[0]] = line[1:] # 存的坐标信息是str型
f3.close()
宽度优先搜索
def BFS(start, goal): # 宽度优先搜索
close = [] # 已拓展的城市,存的是名字
open = deque() # 待拓展的城市,存的是名字
open.append(start)
while open:
print("当前open表的状态是:", open, end="")
print(" 当前close表的状态是:", close)
city = open.popleft()
if (city not in close):
if (city == goal): # 找到目标城市
close.append(city)
print("当前open表的状态是:", open, end="")
print(" 当前close表的状态是:", close)
print("宽度优先搜索的搜索路径是:")
S_route(close, 'BFS')
return
else:
close.append(city)
for i in range(graph[city].neighbor_num):
for j in graph[city].nextstate[i]:
open.append(j)
print("搜索失败")
深度优先搜索
def DFS(start, goal):
close = [] # 已拓展的城市,存的是名字
open = [] # 待拓展的城市,存的是名字,模拟栈
open.append(start)
while open:
print("当前open表的状态是:", open, end="")
print(" 当前close表的状态是:", close)
city = open.pop()
if (city not in close):
if (city == goal): # 找到目标城市
close.append(city)
print("当前open表的状态是:", open, end="")
print(" 当前close表的状态是:", close)
print("深度优先搜索的搜索路径是:")
S_route(close, 'DFS')
return
else:
close.append(city)
for i in range(graph[city].neighbor_num):
for j in graph[city].nextstate[i]:
open.append(j)
print("搜索失败")
A*算法
f(n) = g(n) + h(n)按综合优先级重新排序open表,g(n)是到达此结点已经花费的代价,h(n)是从该结点到目标结点所花代价.f(n)小的排前面
def compute_des(g): # 计算当前各点到goal的h(n)(欧式距离)
global destination
for i in cost:
if (i == g):
destination[i] = 0
else:
destination[i] = math.sqrt((int(cost[i][0]) - int(cost[g][0])) *
(int(cost[i][0]) - int(cost[g][0])) +
(int(cost[i][1]) - int(cost[g][1])) *
(int(cost[i][1]) - int(cost[g][1])))
def sot(C1, C2):
C1 = graph[C1]
C2 = graph[C2]
if (dic[C1.name] + destination[C1.name] <
dic[C2.name] + destination[C2.name]): # 总代价小的排前面
return -1
if (dic[C1.name] + destination[C1.name] >
dic[C2.name] + destination[C2.name]):
return 1
if (dic[C1.name] + destination[C1.name] == dic[C2.name] +
destination[C2.name]): # 总代价相等时,h(n)小的排前面
if (destination[C1.name] < destination[C2.name]):
return -1
return 0
def Astar(start, goal):
open = deque() # 待拓展的城市,存的是名字
close = [] # 已拓展的城市,存的是名字
open.append(start)
compute_des(goal) # 调用函数求h(n)
while open:
current = [] # 存每一轮当前城市的邻居城市,每一轮新的循环更新
print("当前open表的状态是:", open, end="")
print(" 当前close表的状态是:", close)
city = open.popleft()
if (city not in close):
if (city == goal): # 找到目标城市
close.append(city)
print("当前open表的状态是:", open, end="")
print(" 当前close表的状态是:", close)
print("A*搜索的搜索路径是:")
S_route(close, 'A*')
return
else:
close.append(city)
for i in range(graph[city].neighbor_num):
for j in graph[city].nextstate[i]:
current.append(j)
open.append(j)
# 获取从起点到当前点代价值信息,不能从上往下计算(就是存下面邻居点的代价值,而不是往回求上面邻居节点代价值)因为这是图搜索有回路,会存储多条路径。只能从下往上计算,等当前所有的城市加入到open表后
for g in range(len(current)):
for q in range(graph[close[-1]].neighbor_num):
if (list(graph[close[-1]].nextstate[q].keys())[0] == current[g]
):
if (close[-1] == start):
dic[current[g]] = list(
graph[close[-1]].nextstate[q].values())[0]
else:
dic[current[g]] = list(graph[close[-1]].nextstate[q].
values())[0] + dic[close[-1]]
open = deque(
sorted(open, key=functools.cmp_to_key(sot))
) # f(n) = g(n) + h(n)按综合优先级重新排序open表,g(n)是到达此结点已经花费的代价,h(n)是从该结点到目标结点所花代价.f(n)小的排前面
print("搜索失败")
总代码
from collections import deque
import functools
import time
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class State(object): # 每一个城市的信息
def __init__(self, name, neighbor_num):
self.name = name # 城市名
self.neighbor_num = neighbor_num # 相邻的城市个数
self.nextstate = {
} # 相邻城市的信息 !!!!!可以不在建立对象的时候传参数,但一定要在构造函数里面,不然此字典就是所有对象公有的,会随时改变.{0:{'名':路径},...}
state_num = 0 # 城市数量
graph = {} # 保存罗马尼亚的图:'城市名':城市信息
cities_name = [] # 保存各城市的名字
daijia = {} # 存储每种算法的最小代价值
cost = {} # 存储每个城市的坐标,计算h(n)
def file_input(file1, file2): # 城市信息文件的读取
global graph
global state_num
with open(file1, 'r', encoding='utf8') as f1:
# state_num = len(f.readlines()) # 城市数量 不可用此法求行数,读完后光标会移到末尾,信息为空了
for line in f1.readlines(): # 读取每一行城市信息
state_num += 1 # 计算城市数量(行数)
line = list(line.split())
t = State(line[0], int(line[2]))
line = line[3:]
for i, j in zip(range(0, len(line), 2), range(0, t.neighbor_num)):
t.nextstate[j] = {line[i]: int(line[i + 1])} # 存取该城市所有相邻城市的信息
graph[t.name] = t # 添加当前城市
f1.close()
with open(file2, 'r', encoding='utf8') as f2:
for line in f2.readlines():
line = str(line).split()
cities_name.extend(line)
f2.close()
def zuobiao(file3): # 读取每个城市的坐标信息,放在字典里面
global cost
with open(file3, 'r', encoding='utf8') as f3:
for line in f3.readlines(): # 读取每一行城市信息
line = list(str(line).split())
cost[line[0]] = line[1:] # 存的坐标信息是str型
f3.close()
def show(): # 图信息展示
print("State numbers :", state_num)
for i, k in zip(graph, range(len(graph))):
print("State" + str(k + 1) + ':', 'name:' + graph[i].name)
for key, value in graph[i].nextstate.items():
for j in value:
print(' ' + 'neighbor' + str(key + 1) + ':', 'name:',
j + ' ' + 'path_cost:' + str(value[j]))
def S_route(arr, go): # 展示搜索路径
cost = 0 # 总花费
reached = [] # 存储已经计算过路径值的城市
for i, j in zip(range(len(arr)), range(len(arr) - 1, -1, -1)):
if (i == len(arr) - 1):
print(arr[i])
else:
print(arr[i] + "-->", end="")
for k in range(graph[arr[j]].neighbor_num):
for g in graph[arr[j]].nextstate[k]:
if (g not in reached and g in arr
): # 判断,如果该城市不在已计算过的列表以及在close表中,则加上路径值,从下往上计算
cost += graph[arr[j]].nextstate[k][g]
reached.append(g)
daijia[go] = cost
print("总代价为:", cost)
print("经过的节点数为:", len(arr))
def BFS(start, goal): # 宽度优先搜索
close = [] # 已拓展的城市,存的是名字
open = deque() # 待拓展的城市,存的是名字
open.append(start)
while open:
print("当前open表的状态是:", open, end="")
print(" 当前close表的状态是:", close)
city = open.popleft()
if (city not in close):
if (city == goal): # 找到目标城市
close.append(city)
print("当前open表的状态是:", open, end="")
print(" 当前close表的状态是:", close)
print("宽度优先搜索的搜索路径是:")
S_route(close, 'BFS')
return
else:
close.append(city)
for i in range(graph[city].neighbor_num):
for j in graph[city].nextstate[i]:
open.append(j)
print("搜索失败")
def DFS(start, goal):
close = [] # 已拓展的城市,存的是名字
open = [] # 待拓展的城市,存的是名字,模拟栈
open.append(start)
while open:
print("当前open表的状态是:", open, end="")
print(" 当前close表的状态是:", close)
city = open.pop()
if (city not in close):
if (city == goal): # 找到目标城市
close.append(city)
print("当前open表的状态是:", open, end="")
print(" 当前close表的状态是:", close)
print("深度优先搜索的搜索路径是:")
S_route(close, 'DFS')
return
else:
close.append(city)
for i in range(graph[city].neighbor_num):
for j in graph[city].nextstate[i]:
open.append(j)
print("搜索失败")
dic = {} # 存放从起始点到该点的代价值
destination = {} # 存放当前各点到goal的h(n)
def compute_des(g): # 计算当前各点到goal的h(n)(欧式距离)
global destination
for i in cost:
if (i == g):
destination[i] = 0
else:
destination[i] = math.sqrt((int(cost[i][0]) - int(cost[g][0])) *
(int(cost[i][0]) - int(cost[g][0])) +
(int(cost[i][1]) - int(cost[g][1])) *
(int(cost[i][1]) - int(cost[g][1])))
def sot(C1, C2):
C1 = graph[C1]
C2 = graph[C2]
if (dic[C1.name] + destination[C1.name] <
dic[C2.name] + destination[C2.name]): # 总代价小的排前面
return -1
if (dic[C1.name] + destination[C1.name] >
dic[C2.name] + destination[C2.name]):
return 1
if (dic[C1.name] + destination[C1.name] == dic[C2.name] +
destination[C2.name]): # 总代价相等时,h(n)小的排前面
if (destination[C1.name] < destination[C2.name]):
return -1
return 0
def Astar(start, goal):
open = deque() # 待拓展的城市,存的是名字
close = [] # 已拓展的城市,存的是名字
open.append(start)
compute_des(goal) # 调用函数求h(n)
while open:
current = [] # 存每一轮当前城市的邻居城市,每一轮新的循环更新
print("当前open表的状态是:", open, end="")
print(" 当前close表的状态是:", close)
city = open.popleft()
if (city not in close):
if (city == goal): # 找到目标城市
close.append(city)
print("当前open表的状态是:", open, end="")
print(" 当前close表的状态是:", close)
print("A*搜索的搜索路径是:")
S_route(close, 'A*')
return
else:
close.append(city)
for i in range(graph[city].neighbor_num):
for j in graph[city].nextstate[i]:
current.append(j)
open.append(j)
# 获取从起点到当前点代价值信息,不能从上往下计算(就是存下面邻居点的代价值,而不是往回求上面邻居节点代价值)因为这是图搜索有回路,会存储多条路径。只能从下往上计算,等当前所有的城市加入到open表后
for g in range(len(current)):
for q in range(graph[close[-1]].neighbor_num):
if (list(graph[close[-1]].nextstate[q].keys())[0] == current[g]
):
if (close[-1] == start):
dic[current[g]] = list(
graph[close[-1]].nextstate[q].values())[0]
else:
dic[current[g]] = list(graph[close[-1]].nextstate[q].
values())[0] + dic[close[-1]]
open = deque(
sorted(open, key=functools.cmp_to_key(sot))
) # f(n) = g(n) + h(n)按综合优先级重新排序open表,g(n)是到达此结点已经花费的代价,h(n)是从该结点到目标结点所花代价.f(n)小的排前面
print("搜索失败")
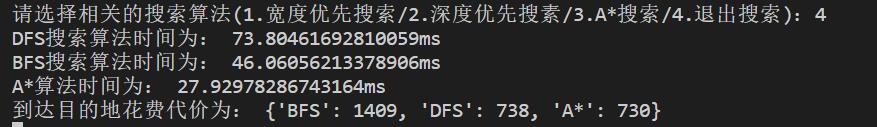
def compare(): # 算法时间维度,到达目的地花费代价做对比,可将此可视化
print("DFS搜索算法时间为:", str((end1 - start1) * 1000) + 'ms') # 单位为ms
print("BFS搜索算法时间为:", str((end2 - start2) * 1000) + 'ms')
print("A*算法时间为:", str((end3 - start3) * 1000) + 'ms')
print("到达目的地花费代价为:", daijia)
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False
algorithm = ('DFS', 'BFS', 'A*')
TIME = [(end1 - start1) * 1000, (end2 - start2) * 1000,
(end3 - start3) * 1000]
plt.bar(algorithm, TIME) # 可视化为条形图
plt.title('不同算法运行时间(ms)')
plt.show()
file_input("D:/cities information.txt","D:/cities name.txt")
zuobiao("D:/cities zuobiao.txt")
while (1):
num = int(input("请选择相关的搜索算法(1.宽度优先搜索/2.深度优先搜素/3.A*搜索/4.退出搜索):"))
if (num == 4):
break
show()
st, go = map(int, input("请选择开始州以及目标州的序号(1-20),以空格分隔:").split())
if (num == 1 and 1 <= st <= 20 and 1 <= go <= 20):
start1 = time.time() # 记录开始时间
BFS(cities_name[st - 1], cities_name[go - 1])
end1 = time.time() # 记录结束时间
elif (num == 2 and 1 <= st <= 20 and 1 <= go <= 20):
start2 = time.time() # 记录开始时间
DFS(cities_name[st - 1], cities_name[go - 1])
end2 = time.time() # 记录结束时间
elif (num == 3 and 1 <= st <= 20 and 1 <= go <= 20):
start3 = time.time() # 记录开始时间
Astar(cities_name[st - 1], cities_name[go - 1])
end3 = time.time() # 记录结束时间
else:
print("您的输入有误,请重新输入!") # 程序健壮性
# compare()
实验结果
坐标给出数据并不是特别好,A算法这里得到的最优路径是有回溯的。这里分别从算法运行所需时间,与到达目的地所花费的代价来比较三种算法,可以看出A算法的性能是最佳的。
























 857
857











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










