目录
1.管道通信的4种情况
1.1管道内没有数据&&写端不关闭
代码验证
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
void Write(int fd)
{
char buffer[128];
int cnt = 0;
while(1)
{
sleep(1000);//sleep不向管道写入
sprintf(buffer,"I am childProcess,I'm writing pid:%d cnt = %d\n",getpid(),cnt);
write(fd,buffer,sizeof(buffer));
cnt++;
}
}
void Read(int fd)
{
char buffer[1024];
while(1)
{
read(fd,buffer,sizeof(buffer)-1);
printf("i am father process,I am reading\nmessage:%s\n",buffer);
}
}
int main()
{
int fdarry[2] = {0};
int ret = pipe(fdarry);
if(ret == -1)
{
printf("Create pipe fail");
return -1;
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == 0)
{
//子进程写
close(fdarry[0]);
Write(fdarry[1]);
}
close(fdarry[1]);
Read(fdarry[0]);
wait(NULL);
return 0;
}运行结果
什么也没读出来,说明读端一直在阻塞等待。
1.2管道内数据被写满&&写端不关闭
同上,什么也读不出来,管道写满,写端阻塞等待。
1.3写端写了一部分,关闭写端
代码验证
#include<stdio.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<sys/stat.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
void Write(int fd)
{
char buffer[128];
int cnt = 0;
while(1)
{
sprintf(buffer,"I am childProcess,I'm writing pid:%d cnt = %d\n",getpid(),cnt);
write(fd,buffer,sizeof(buffer));
if(cnt == 10)
{
break;
}
cnt++;
sleep(1);
}
printf("close write\n");
close(fd);
}
void Read(int fd)
{
char buffer[1024];
while(1)
{
size_t n = read(fd,buffer,sizeof(buffer)-1);
if(n > 0)
{
printf("i am father process,I am reading\nmessage:%s\n",buffer);
}
else if(n == 0)
{
printf("read end\n");
break;
}
else
{
printf("read error\n");
break;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int fdarry[2] = {0};
int ret = pipe(fdarry);
if(ret == -1)
{
printf("Create pipe fail\n");
return -1;
}
pid_t pid = fork();
if(pid == 0)
{
//子进程写
close(fdarry[0]);
Write(fdarry[1]);
_exit(0);
}
close(fdarry[1]);
Read(fdarry[0]);
int status = 0;
pid_t rid = waitpid(pid,&status,0);
if(rid = pid)
{
printf("pid:%d exitsignal:%d exitcode:%d\n",rid,status&0x7f,WEXITSTATUS(status));
}
return 0;
}
运行结果
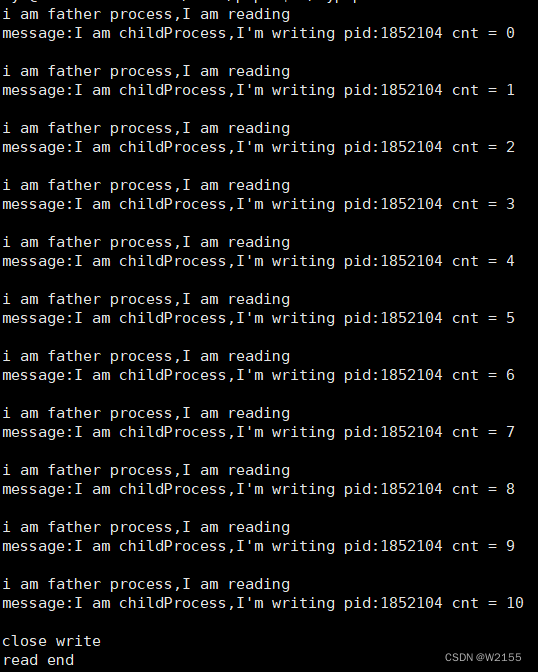
说明代码会把管道的数据读完,然后读到文件末尾,结束读取。
1.4读端不读直接关闭,写端再写
代码验证
close(fdarry[1]);
close(fdarry[0]);运行结果
![]()
子进程的退出信号是13,
说明读端关闭,os会终止写进程,使用信号13杀死写进程。






















 1672
1672











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








