As the Internet of Things (IoT) and embedded systems continue to evolve, wireless connectivity technology has become a key element in driving innovation and enabling device interconnection. Qualcomm, as one of the leaders in the field of wireless communications, leads the development of wireless connection technology. Among them, Wi-Fi chip series such as QCN9074, QCN9024 and QCN9274 have become its latest highlights, providing excellent wireless connection performance for various devices.
QCN9074: The connection choice for the Internet of Things
QCN9074 is a Wi-Fi and Bluetooth combination chip specially designed for IoT devices. It supports 802.11ac Wi-Fi standard and Bluetooth standard. This design makes QCN9074 an ideal choice for connecting future IoT application scenarios such as smart homes and industrial automation. Its excellent wireless connection performance and stability provide efficient and reliable interconnection capabilities for devices.
QCN9024: The long-lasting choice for low-power Bluetooth
QCN9024 is dedicated to Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) connectivity and plays a key role in long-running scenarios such as wearable devices and health monitoring devices. By supporting the Bluetooth low energy standard, QCN9024 not only ensures long-term operation and stable connection of the device, but also reduces energy consumption and extends the service life of the device.
QCN9274: The leader in high-performance Wi-Fi
As a chip launched by Qualcomm to support high-performance Wi-Fi connectivity, QCN9274 not only supports the 802.11ac Wi-Fi standard, but also provides Bluetooth connectivity. In embedded systems, such as smart home centers, industrial control equipment, etc., QCN9274 meets the demand for larger bandwidth and high-speed connections through its high-performance Wi-Fi connection, providing fast and stable wireless connections for devices.
These three Wi-Fi chip series have their own characteristics in design and provide flexible solutions for different application scenarios. QCN9074's comprehensive connectivity solution makes it suitable for IoT devices, QCN9024's low-power Bluetooth connectivity provides the possibility of long battery life for wearable devices and health monitoring devices, and QCN9274's high-performance Wi-Fi connectivity Become a leader in embedded systems.
These families of Qualcomm chips provide product designers with a wide range of options and play a critical role whether they are connecting smart homes, embedded systems, or providing wireless communications for wearable devices. Qualcomm promotes the advancement of wireless communication technology through continuous innovation, making chips such as QCN9074, QCN9024 and QCN9274 attract much attention in the market. The leading position of this series of chips not only demonstrates Qualcomm's technical strength, but also injects new vitality into the future of the entire industry, enabling wireless communication technology to better serve the growing Internet of Things and embedded systems.
And there are also differences between WIFI 6 and WIFI 7
What is WiFi 6?
Announced in 2019, Wi-Fi 6 brought huge improvements with the introduction of ODFMA, power consumption improvements, and two-way MU-MIMO. Operating at 2.4 and 5 GHz frequencies, efficiency delivers a considerable throughput increase of over 30% over the previous generation.
What is WiFi 7?
The latest WiFi technology, WIFI7 products have been officially launched and is undergoing extensive revisions since its initial draft in 2021. 802.11be, aka WiFi 7, doubles the bandwidth with a channel frequency of 320Hz. With a fourfold increase in QAM and the addition of spatial streams, speed throughput reaches 30 Gbps while operating on all three frequency bands of 2.4, 5 and 6 GHz.
Speed and availability
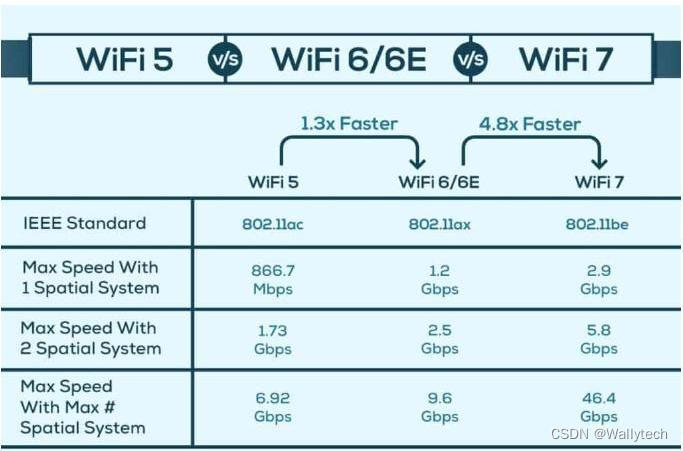
When comparing WiFi 6 and 6E in terms of speed capabilities, they appear to offer 9.6 Gbps of throughput, which is a huge jump compared to the speeds offered by the Wi-Fi 5 standard, which is capped at 6.9 Gbps. learn more.
To take advantage of the efficiencies of Gen 6 wireless standards, you'll need OEMs to integrate them into the latest client devices, such as smartphones, tablets, gaming consoles, and more.
The WiFi 7 standard triples theoretical speed capacity to up to 30 Gbps. WiFi 7 speeds will require a new set of manufacturing standards for high-performance gadgets and IoT devices designed to operate at multiple frequencies.
frequency band
Wi-Fi 6 operates on two main frequencies, 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. As wireless devices increase, both frequencies become crowded.
WiFi 7 operates on three frequency bands: 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz and 6 GHz, similar to 6E and improves efficiency in other areas.
channel width
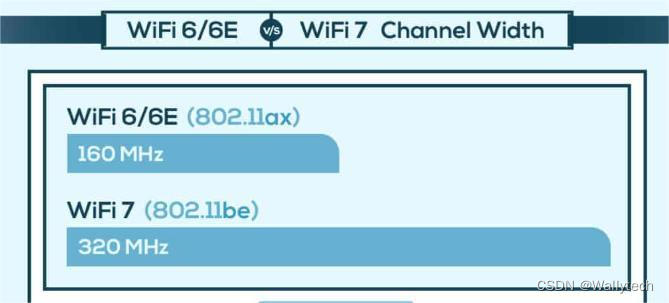
While the second wave of 802.11ac saw the use of wider 80 MHz channels, a huge leap overall was achieved with the introduction of 160 MHz channels in WiFi 6 routers.
The new generation of WiFi 7 wireless devices will take advantage of the wider 320 MHz channel to achieve superior efficiency and throughput levels.
QAM modulation
QAM modulation determines how data is packaged and transmitted over radio frequencies. The denser the modulation, the greater the amount of data that can be transmitted easily. The rise of high-quality 4K streaming and AR/VR content is testing the limits of Wi-Fi 5 running at 256-QAM.
Wi-Fi 6 proposes higher modulation, operating at 1024-QAM. Wi-Fi 7 goes a step further, bringing greater efficiency with denser modulation of 4096-QAM. This effectively reflects the throughput speed and enables higher speeds such as 30 Gbps.
data flow
The 6th generation wireless standard brings two-way MU-MIMO to practical applications and doubles the number of spatial streams to eight, surpassing Wi-Fi 5’s 4×4 MU-MIMO. This will allow up to 8 simultaneous connections to access the internet without losing speed throughput.
Wi-Fi 6 uses two-way 8 x 8 MU-MIMO. WiFi 7 increases the number of spatial streams to 16. This will allow up to 16 devices to boot data at high speeds.
The next generation of IoT devices will take advantage of this efficiency brought by the latest wireless technologies.
Access Point
In Wi-Fi 6, client devices can only use one frequency band at a time, 2.4/5/6 GHz. Smart Connect features allow devices to automatically switch between these bands based on signal quality and interference.
With Wi-Fi 7, it's a whole new ballgame. The introduction of MLO (Multiple Link Operation) allows client devices to send and receive data across different frequency bands and channels. This reduces communication delays to a minimum. This gives you a wireless experience similar to wired internet.
Significantly improved reliability when using AR applications and online gaming.
Conclusion
A router with the Wi-Fi 6 standard is sufficient for the average home user. The majority of client devices in use are Wi-Fi 5, which will remain relevant for the foreseeable future
WiFi 7's speeds are much higher than what's available to home users, making it overkill. It will be more suitable for commercial spaces and mid-sized offices.
By:Wallystech





















 86
86











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








