目录
反射
Class
Field[] 抽象其属性用的
Method[] 抽象其方法用的
/**
* 反射的测试
*/
public static void classTest() {
Class<Student> clazz = Student.class; //得到一个Student类的模板
Field[] field = clazz.getFields(); //以数组形式所有公共属性
for(Field fie:field){
System.out.println("Student的公共属性"+fie.getName());
}
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();//返回所有属性的数组
for (Field field2 : fields) {
System.out.println("Student类的属性:"+field2.getName());
}
Student zhangsan = new Student();
//将私有属性age的值设置成13
try {
Field age = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");
age.setAccessible(true); //检验修饰符。默认为false。先将"age"的检验修饰符改为true,即不检验可以访问
age.set(zhangsan, 13);
age.setAccessible(false); //需要将其改为false。
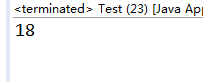
System.out.println(zhangsan.getAge());
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}工厂设计模式
先建一个File文件 指向类名(包名.类名)
建一个工厂类
创建一个Properties对象
load方法读File文件
public class Person {
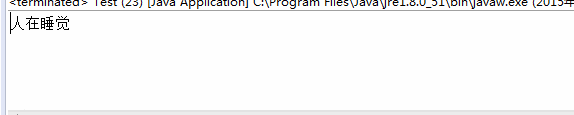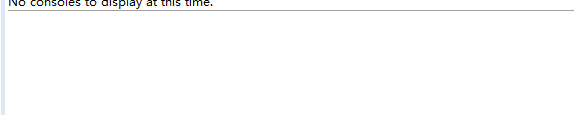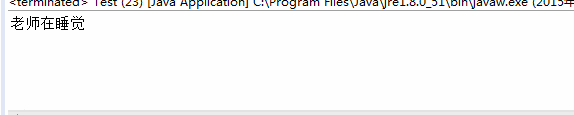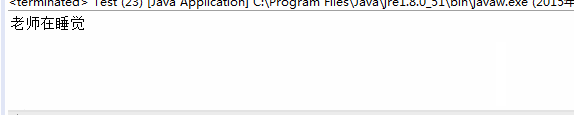
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("人在睡觉");
}
}
public class Student extends Person {
@AnnotationStudent(value = 18) // 自定义注解 在AnnotationStudent类中
private int age;
private String name;
public String clothes;
public char sex;
public Student() {
/**
* 注解的用法
*/
// 通过将注解的值赋给age
Class clazz = this.getClass();
try {
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");// 先得到属性后得到注解
AnnotationStudent as = field.getAnnotation(AnnotationStudent.class);
if (as != null) {// 如果注解类中存在此注解,执行下边的
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(this, as.value());
field.setAccessible(false);
}
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("学生在睡觉");
}
}
public class Teacher extends Person{
private String name;
private int age;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("老师在睡觉");
}
}
/**
* 工厂设计模式 工厂类 创建一个Properties对象
*
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Factory {
public Person createPerson() {
Person person = null;
Properties p = new Properties();
try {
// load方法读File文件
p.load(new FileInputStream("config.properties"));
// 得到类名
String clazzName = p.getProperty("person");
// Class反射得到一个关于类的模板
Class clazz = getClass().forName(clazzName);
// 通过模板得到所要得到的对象
person = (Person) clazz.newInstance();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InstantiationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return person;
}
}
/**
* 工厂设计模式
* 先建一个File文件 指向类名(包名.类名)
* 建一个工厂类
*
*/
public static void factoryTest() {
Person person = new Factory().createPerson();
person.sleep();
}注解
注解
@Override//这个方法是复写了父类的方法
自定义注解
例:学生类中的注解
/**
* 自定义注解AnnotationStudent
* @author Administrator
*
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)//表示此注解的范围
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)//表示此注解只能注释属性
public @interface AnnotationStudent {
int value();
}
//学生类
public class Student extends Person {
@AnnotationStudent(value = 18) // 自定义注解 在AnnotationStudent类中
private int age;
private String name;
public Student() {
/**
* 注解的用法
*/
// 通过将注解的值赋给age
Class clazz = this.getClass();
try {
Field field = clazz.getDeclaredField("age");// 先得到属性后得到注解
AnnotationStudent as = field.getAnnotation(AnnotationStudent.class);
if (as != null) {// 如果注解类中存在此注解,执行下边的
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(this, as.value());//将注解中的值赋给age
field.setAccessible(false);
}
} catch (NoSuchFieldException | SecurityException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 注解的测试 Student类 与 AnnotationStudent中
*/
public static void annotationTest() {
Student zhangsan = new Student();
System.out.println(zhangsan.getAge());
}结果
例:班级类中有教师的属性,此属性是教师类的对象,将注解中的值赋给教师对象
/**
* 老师类的注解
* @author Administrator
*
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
public @interface TeacherAnnotation {
int age() default 20;//默认值20
String name();
}
/**
* 班级类,注解的用法
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Clazz {
//将注解的值赋给教师的对象
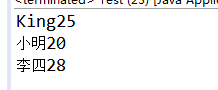
@TeacherAnnotation(age = 25,name = "King")
private Teacher javaTeacher;
@TeacherAnnotation(age = 28,name = "李四")
private Teacher mathTeacher;
@TeacherAnnotation(name = "小明")
private Teacher englishTeacher;
private int clzzNum;
private String clazzName;
public Clazz() {
//反射与注解的应用
Class clazz = this.getClass();//得到一个班级的模板
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();//得到模板中的所有属性(将教师类也看成属性)
for (Field field : fields) {
TeacherAnnotation ta = field.getAnnotation(TeacherAnnotation.class);//看看是不是拥有注解
if (ta!=null) {
int age = ta.age();
String name = ta.name();
Teacher teacher = new Teacher();//创建一个Teacher对象
teacher.setAge(age);//将注解的年龄和姓名赋给Teacher的对象teacher
teacher.setName(name);
field.setAccessible(true);
try {
field.set(this, teacher); //将teacher赋给当前Clazz的属性
} catch (IllegalArgumentException | IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
field.setAccessible(false);
}
}
}
public Teacher getJavaTeacher() {
return javaTeacher;
}
public void setJavaTeacher(Teacher javaTeacher) {
this.javaTeacher = javaTeacher;
}
public Teacher getMathTeacher() {
return mathTeacher;
}
public void setMathTeacher(Teacher mathTeacher) {
this.mathTeacher = mathTeacher;
}
public Teacher getEnglishTeacher() {
return englishTeacher;
}
public void setEnglishTeacher(Teacher englishTeacher) {
this.englishTeacher = englishTeacher;
}
}线程
进程:相对于系统来讲,分配的一段空间,只有所属应用可以访问


Thread
继承Thread类,重写run()方法,测试类中用start()方法启动线程
/**
* 继承Thread类的线程
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class MyThread extends Thread{
// private static int ticket = 200; //static是总的票数,线程共有
private int ticket = 200;
public MyThread() {
}
public MyThread(String name) {
super(name);
}
@Override
public void run() {
while (ticket>0) {
System.out.println(getName()+"卖出了"+ticket+"张票");//getName()得到线程的名称
ticket--;
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
/**
* 继承Thread类的线程的测试
*/
public static void extendsThreadTest() {
MyThread t1 = new MyThread("售票员一");
MyThread t2 = new MyThread("售票员二");
MyThread t3 = new MyThread("售票员三");
MyThread t4 = new MyThread("售票员四");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
}Runnable
实现Runnable()接口,重写run()方法,测试中声明类的对象,Thread t = new Thread(类的对象)
/**
* 实现了Runnable接口
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
private int ticket = 10;
private String lock = "sakfh";
@Override
public void run() {
while (ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
//同步代码块,需要加一个锁,所得类型"对象"
synchronized (lock) {
//因为1 2 3 4如果都进来,可能会出现<0的状况
if (ticket>0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖票号" + ticket);
ticket--;
}
}
}
}
}
public static void implementsRunnableTest() {
MyRunnable runnable = new MyRunnable();
//此时t1,t2,t3,t4共享了runnable中的数据
Thread t1 = new Thread(runnable,"售票员1");
Thread t2 = new Thread(runnable,"售票员2");
Thread t3 = new Thread(runnable,"售票员3");
Thread t4 = new Thread(runnable,"售票员4");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
System.out.println("线程执行完成");
}线程锁 synchronized
public void run() {
while (ticket > 0) {
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
//同步代码块,需要加一个锁,所得类型"对象"
synchronized (lock) {
//因为1 2 3 4如果都进来,可能会出现<0的状况
if (ticket>0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖票号" + ticket);
ticket--;
}
}
}
}/**
* 银行卡,两人取钱,如果存款如果不足100,无法提取
* 用了一个线程锁,一人取钱时,另一个不能取
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class Post implements Runnable{
private int count = 1100;
private int money = 100;
private String lock = "akfhk";
@Override
public void run() {
while (count>=100) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (lock) {
if (count>=100) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"取钱:"+money+" "+"还剩余"+(count-money));
count -=money;
}else {
System.out.println("余额"+count+",不足100无法取款");
}
}
}
}
}线程的状态
阻塞join()
须执行完.join()的线程后下执行
public static void implementsRunnableTest() {
MyRunnable runnable = new MyRunnable();
//此时t1,t2,t3,t4共享了runnable中的数据
Thread t1 = new Thread(runnable,"售票员1");
t1.start();
try {
t1.join(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("线程执行完成");
}线程锁等待
wait() notify();
两个线程相同锁,用wait()先释放当前锁,notify()唤醒原wait的锁
//仓库,里边有生产的东西
public class Product {
private int pro = 0;
public int getPro() {
return pro;
}
public void setPro(int pro) {
this.pro = pro;
}
public synchronized void consumer() {
if (getPro()==1) {
System.out.println("消费者消费");
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
setPro(0);
notify();
}
}
public synchronized void product() {
if (getPro()==0) {
System.out.println("生产者生产");
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (InterruptedException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
setPro(1);
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class Producer implements Runnable{
private Product pro;
public Producer(Product pro) {
this.pro = pro;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e2) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e2.printStackTrace();
}
// synchronized (pro) {
// if (pro.getPro()==0) {
// System.out.println("生产者生产");
// try {
// Thread.sleep(3000);
// } catch (InterruptedException e1) {
// // TODO Auto-generated catch block
// e1.printStackTrace();
// }
// pro.setPro(1);
// try {
// pro.wait();
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// // TODO Auto-generated catch block
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
// }
pro.product();
}
}
}
public class Consumer implements Runnable{
private Product pro;
public Consumer(Product pro) {
this.pro = pro;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(true){
// synchronized (pro) {
// if (pro.getPro()==1) {
// System.out.println("消费者消费");
// try {
// Thread.sleep(2000);
// } catch (InterruptedException e) {
// // TODO Auto-generated catch block
// e.printStackTrace();
// }
// pro.setPro(0);
//
// pro.notify();
// }
// }
pro.consumer();
}
}
}
//测试wait和notify
public static void factory() {
Product product = new Product();
Producer producer = new Producer(product);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(product);
Thread t1 = new Thread(producer);
Thread t2 = new Thread(consumer);
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}网络与线程的结合
TCP/IP的线程的结合:
读信息的线程
写信息的线程
服务器端实现读、写信息 创建ServerSocket
客户端实现读、写信息 创建Server端口
/**
* 服务器的主线程,里边创建了ServerSocket
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class MyServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8080);
Socket socket = server.accept();
//读的线程
Thread read = new Thread(new MyRead(socket));
//写的线程
Thread write = new Thread(new MyWrite(socket));
read.start();
write.start();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 客户端的主线程,里边创建了Socket
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class MyClient{
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Socket socket = new Socket("localhost", 8080);
//读的线程
Thread read = new Thread(new MyRead(socket));
//写的线程
Thread write = new Thread(new MyWrite(socket));
read.start();
write.start();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 读的线程
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class MyRead implements Runnable{
private Socket socket;
//将端口传输过来
public MyRead(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
while(true){
String msg = br.readLine();
System.out.println("说:"+msg);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 写的线程
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class MyWrite implements Runnable{
private Socket socket;
public MyWrite(Socket socket) {
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(os));
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
bw.write(scanner.next()+"\n");
bw.flush();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}界面版的即时聊天
/**
* 服务器的界面
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class StartServer extends JFrame {
private JPanel contentPane;
private JTextField textField;
private Socket socket;
private JList list;
private boolean isServer = true;
private DefaultListModel<String> model;
public boolean isServer() {
return isServer;
}
public void setServer(boolean isServer) {
this.isServer = isServer;
}
/**
* Launch the application.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
StartServer frame = new StartServer();
frame.setVisible(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* Create the frame.
*/
public StartServer() {
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100, 100, 450, 300);
contentPane = new JPanel();
contentPane.setBorder(new EmptyBorder(5, 5, 5, 5));
setContentPane(contentPane);
contentPane.setLayout(null);
JButton button = new JButton("启动服务");
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
try {
//点击事件,服务启动
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8080);
System.out.println("服务器启动");
socket = server.accept();
System.out.println("有客户端接入");
Thread t1 = new Thread(new ServerRead(StartServer.this));
t1.start();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
button.setBounds(331, 21, 93, 23);
contentPane.add(button);
JButton button_1 = new JButton("发送");
button_1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
serverWrite();
}
});
button_1.setBounds(331, 214, 93, 23);
contentPane.add(button_1);
textField = new JTextField();
textField.setBounds(24, 215, 296, 21);
contentPane.add(textField);
textField.setColumns(10);
list = new JList();
list.setBounds(24, 10, 296, 191);
model = new DefaultListModel<>();
JScrollPane scroll = new JScrollPane(list);
scroll.setBounds(24, 10, 296, 191);
list.setModel(model);
contentPane.add(scroll);
JButton button_2 = new JButton("关闭服务");
button_2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
}
});
button_2.setBounds(331, 54, 93, 23);
contentPane.add(button_2);
}
/**
* 服务器端读的方法
*/
public void serverRead(){
try {
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String words = br.readLine();
model.addElement("客户端说:"+words);
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 服务器端写的方法
*/
public void serverWrite() {
try {
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(os));
String words = textField.getText();
bw.write(words+"\n");
textField.setText("");
model.addElement("我说:"+words);
bw.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 服务器端写的线程
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class ServerRead implements Runnable{
private StartServer startServer;
public ServerRead(StartServer startServer) {
this.startServer = startServer;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(startServer.isServer()){
startServer.serverRead();
}
}
}
/**
* 客户端的界面
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class StartClient extends JFrame {
private JPanel contentPane;
private JTextField textField;
private Socket socket;
private JList list;
private DefaultListModel<String> model;
private boolean isClient = true;
private boolean isConnectClient = true;
public boolean isClient() {
return isClient;
}
public void setClient(boolean isClient) {
this.isClient = isClient;
}
/**
* Launch the application.
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
try {
StartClient frame = new StartClient();
frame.setVisible(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
/**
* Create the frame.
*/
public StartClient() {
setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
setBounds(100, 100, 450, 300);
contentPane = new JPanel();
contentPane.setBorder(new EmptyBorder(5, 5, 5, 5));
setContentPane(contentPane);
contentPane.setLayout(null);
JButton button = new JButton("连接服务器");
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
try {
//点击事件启动服务
System.out.println("客户端启动");
socket = new Socket("localhost", 8080);
System.out.println("成功连接服务器");
Thread t1 = new Thread(new ClientRead(StartClient.this));
t1.start();
} catch (UnknownHostException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
button.setBounds(331, 23, 93, 23);
contentPane.add(button);
JButton button_1 = new JButton("发送");
button_1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent arg0) {
clickWrite();
}
});
button_1.setBounds(331, 229, 93, 23);
contentPane.add(button_1);
textField = new JTextField();
textField.setBounds(10, 230, 311, 21);
contentPane.add(textField);
textField.setColumns(10);
list = new JList();
model = new DefaultListModel<>();
list.setModel(model);
list.setBounds(10, 10, 311, 208);
JScrollPane scroll = new JScrollPane(list);
scroll.setBounds(10, 10, 311, 208);
contentPane.add(scroll);
JButton button_2 = new JButton("断开服务器");
button_2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent arg0) {
}
});
button_2.setBounds(331, 56, 93, 23);
contentPane.add(button_2);
}
/**
* 客户端的写的方法
*/
public void clickWrite() {
try {
OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(os));
String words = textField.getText();
bw.write(words+"\n");
textField.setText("");
model.addElement("我说:"+words);
bw.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 客户端的读的方法
*/
public void clientRead() {
try {
InputStream is = socket.getInputStream();
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
String words = br.readLine();
model.addElement("服务器说:"+words);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 客户端读的线程
* @author Administrator
*
*/
public class ClientRead implements Runnable{
private StartClient startClient;
public ClientRead(StartClient startClient) {
this.startClient = startClient;
}
@Override
public void run() {
while(startClient.isClient()){
//调用客户端的读的方法
startClient.clientRead();
}
}
}






















 9568
9568

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








