目录
0.写在开头
本篇文章旨在实现各种数据结构,实现为主,介绍为辅(或者说基本不介绍),要看具体详情可以参考《在 JavaScript 中学习数据结构与算法》这篇博客
1.栈
栈(Stack):后进先出LIFO
class Stack {
constructor(items){
this.items = items||[]
}
push(el){ // 入栈
this.items.push(el)
}
pop(){ // 出栈
return this.items.pop()
}
clear(){ //清空
this.items=[]
}
get peek(){ // 末位
return this.items[this.items.length-1]
}
get isEmpty(){
return !this.items.length
}
get size(){
return this.items.length
}
}
2.队列
队列(Queue):先进先出FIFO
class Queue {
constructor(items){
this.items = items || []
}
addEl(el){ // 入队
this.items.push(el)
}
delEl(){ // 出队
return this.items.shift()
}
clear(){ // 清空
this.items = []
}
get header(){ // 首位
return this.items[0]
}
get isEmpty(){
return !this.items.length
}
get size(){
return this.items.length
}
}
2.1 优先队列
优先队列是队列的变种,由项的priority的值决定其在队列中的优先级
class PriorityQueue extends Queue {
constructor(items){
super(items)
}
addEl(el,priority){ // priority越小优先级越高
const queueEl = {el,priority}
let preIndex = this.items.findIndex(item=>item.priority>queueEl.priority)
if(preIndex>-1) this.items.splice(preIndex,0,queueEl)
else this.items.push(queueEl)
}
}
2.2 循环队列
循环队列是队列的另一个变种,可以实现队列索引循环
class LoopQueue extends Queue {
constructor(items){
super(items)
}
getIndex(index){
let len = this.items.length
return index>len?(index%len):index
}
find(index){
return this.items[this.getIndex(index)]
}
}
3.链表
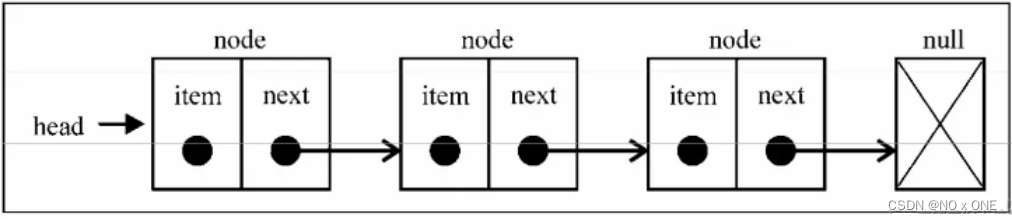
链表(LinkedList):每个元素都有一个next保存下一个元素的指针,第一个元素为head,如下图所示:
class LinkedList {
constructor(){
this.head = null
this.length = 0
}
static createNode(el){
const node = Object.create(null)
node.el = el
node.next = null
return node
}
append(el){ // 添加
const node = LinkedList.createNode(el)
if(!this.head) this.head = node
else{
let preNode = this.head
while(preNode.next) preNode = preNode.next
preNode.next = node
}
this.length++
}
insert(index,el){ // 插入
if(index>=0&&index<=this.length){
const node = LinkedList.createNode(el)
let curEl = this.head
if(index===0){
this.head = node
node.next = curEl
}
else{
let preEl = null
let curIndex = 0
while (curIndex++ < index) {
preEl = curEl
curEl = curEl.next
}
preEl.next = node
node.next = curEl
}
this.length++
return true
}
return false
}
removeAt(index){
if(index>=0&&index<length){
let curEl = this.head
if(index===0){
this.head = curEl.next
}
else{
let preEl = null
let curIndex = 0
while (curIndex++ < index) {
preEl = curEl
curEl = curEl.next
}
preEl.next = curEl.next
}
this.length--
return curEl.el
}
return null
}
remove(el){
return this.removeAt(this.findIndex(el))
}
findIndex(el){
let curEl = this.head
let index = -1
while (curEl) {
if(el===curEl.el) return index+1
index++
curEl = curEl.next
}
return index
}
selectNode(cb){ // 筛选
let curNode = this.head
while(curNode){
if(cb(curNode.el)) return curNode
curNode = curNode.next
}
return null
}
get isEmpty(){
return !this.length
}
get size(){
return this.length
}
}
3.1 双向链表
指定最后一个元素为end,
class DoublyLinkedList extends LinkedList {
constructor(){
super()
this.end = null
}
insert(el,index){
if(index>=0&&index<=this.length){
const node = super.createNode(el)
let curNode = this.head
let preNode = null
let curIndex = 0
if(index===0){ // 首位
if(!this.head){
this.head = node
this.end = node
}else{
this.head = node
node.next = curNode
curNode.pre = node
}
}
else if(index ===this.length){ // 末位
curNode = this.end
this.end = node
curNode.next = node
node.pre = curNode
}
else{ // 中间
while (curIndex++ < this.length) {
preNode = curNode
curNode = curNode.next
}
preNode.next = node
node.pre = preNode
node.next = curNode
curNode.pre = node
}
this.length++
return true
}
return false
}
}
// 循环链表、双向循环链表(略)
4.集合
集合(set):每一个元素形如{value:value},无key,每个元素都是唯一的
class Set {
constructor(){
this.items = Object.create(null)
}
has(value){
return this.items.hasOwnProperty(value)
}
add(value){
if(!this.has(value)){ // 保证唯一
this.items[value] = value
return true
}
return false
}
remove(value){
if(this.has(value)){
delete this.items[value]
return true
}
return false
}
get size(){
return Object.keys(this.items).length
}
get isEmpty(){
return !this.size
}
get values(){
return Object.keys(this.items)
}
union(set){ // 并集
let res = new Set()
this.values.forEach((key,val)=>res.add(val))
set.values.forEach((key,val)=>res.add(val))
return res
}
intersection(set){ // 交集
let res = new Set()
this.values.forEach((key,val)=>set.has(val)&&res.add(val))
return res
}
difference(set){ // 差集
let res = new Set()
this.values.forEach((key,val)=>!set.has(val)&&res.add(val))
return res
}
isSubsetOf(set){ // 子集
return this.size<=set.size && this.values.every((key,val)=>set.has(val))
}
}
5.字典
字典(Dictionary):每一个元素形如{ key: value },且能保证每个key-value是唯一的
class Dictionary {
constructor(){
this.items = {}
}
set(key,val){
this.items[key] = val
return this // 链式调用
}
get(key){
return this.items[key]
}
remove(key){
delete this.items[key]
return this
}
get keys(){
return Object.keys(this.items)
}
get values(){
return Object.values(this.items) // ES7
// **
return Object.keys(this.items).reduce((pre,cur)=>{
pre.push(this.items[cur])
return pre
},[])
// **
}
}
6.哈希表
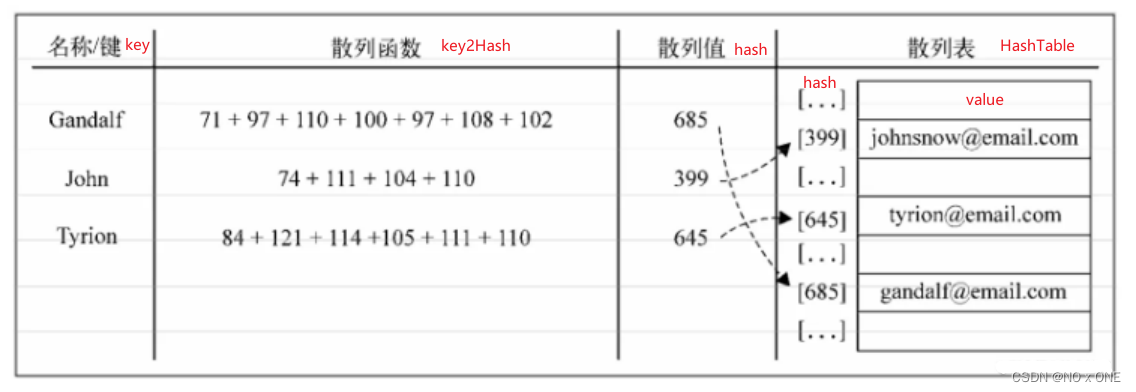
哈希表(HashTable):使用hash值代替key,使用[]代替{key:value},从而避免遍历整个数据结构来达到最快取值的功能,典型的牺牲空间换取时间,如下图所示:
class HashTable{
constructor(){
this.table = []
}
static key2Hash(key){
let hash = 0
for(let code of key) hash += code.charCodeAt()
return hash%37
}
put(key,val){
this.table[HashTable.key2Hash(key)] = val
}
get(key){
return this.table[HashTable.key2Hash(key)]
}
remove(key){
this.table[HashTable.key2Hash(key)] = undefined
}
}
6.1 哈希值重复的冲突解决
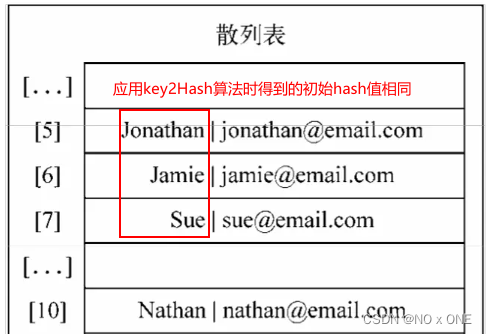
使用哈希表有一个潜在的问题,那就是使用hash值代替key值时,有时候可能不同的key值会得到相同的hash值,例如'az'和'by',这里介绍三种解决方法
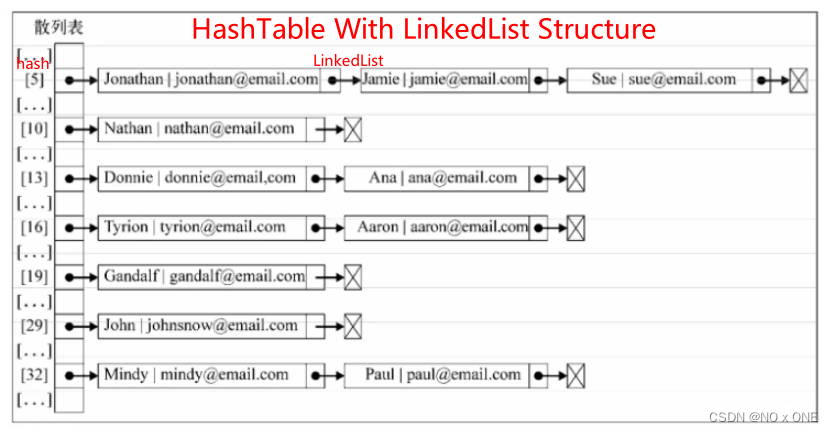
6.1.1 链地址法
核心思想:链表+哈希表,哈希表项以链表结构存储,
class HashTable{
constructor(){
this.table = []
}
static key2Hash(key){
let hash = 0
for(let code of key) hash += code.charCodeAt()
return hash%37
}
put(key,val){
const hash = HashTable.key2Hash(key)
if(this.table[hash]===undefined) this.table[hash] = new LinkedList()
this.table[hash].append({key,val})
}
get(key){
const hash = HashTable.key2Hash(key)
let linkList = this.table[hash]
return linkList===undefined? undefined :linkList.selectNode(node=>Object.is(node.key,key))
// function getNodeVal(node){
// if(!node||!node.el) return undefined // 到末位
// if(Object.is(node.el.key,key)) return node.el.value
// return getNodeVal(node.next)
// }
// return getNodeVal(linkList.head)
}
remove(key){
const hash = HashTable.key2Hash(key)
let linkList =this.table[hash]
if(linkList===undefined) return undefined
const node = linkList.selectNode(node=>Object.is(node.key,key))
return linkList.remove(node)
// function removeNodeVal(node) {
// if(!node||!node.el) return false // 到末位
// if(Object.is(node.el.key,key)){
// linkList.remove(node.el)
// if(linkList.isEmpty) this.table[hash] = undefined // 由于指针的原因,这里要使用this.table[hash]
// return true
// }
// return removeNodeVal(node)
// }
// return removeNodeVal(linkList.head)
}
}
6.1.2 线性探查
核心思想:若存在重复的hash值,则hash++,直到没有重复
class HashTable{
constructor(){
this.table = []
}
static key2Hash(key){
let hash = 0
for(let code of key) hash += code.charCodeAt()
return hash%37
}
put(key,value){
const hash = HashTable.key2Hash(key)
while (this.table[hash]!==undefined){
if(Object.is(this.table[hash].key,key)) return // 唯一key
}
this.table[hash] = {key,value}
}
get(key){
const hash = HashTable.key2Hash(key)
while(this.table[hash]){
if(Object.is(this.table[hash].key,key)) return this.table[hash].value
hash++
}
return undefined
}
remove(key){
const hash = HashTable.key2Hash(key)
while(this.table[hash]){
if(Object.is(this.table[hash].key,key)){
this.table[hash] =undefined
return true
}
hash++
}
return false
}
}
6.1.3 优化key2Hash算法
降低hash值重复率
static key2Hash(key){
let hash = 0
for(let code of key) hash += code.charCodeAt()
return hash%37
}
// 改进,hash重复率更低,也可以插入时间戳
static key2Hash2(key) {
let hash = 5381
for (let code of key) hash = hash * 33 + code.charCodeAt()
return hash % 1013
}
7.树
二叉搜索树
二叉树中的节点最多只能有两个子节点:一个是左侧子节点,另一个是右侧子节点
二叉搜索树(BST,Binary Search Tree)是二叉树的一种,在左侧节点存储(比父节点)小的值, 在右侧节点存储(比父节点)大(或者等于)的值,结构如下图所示
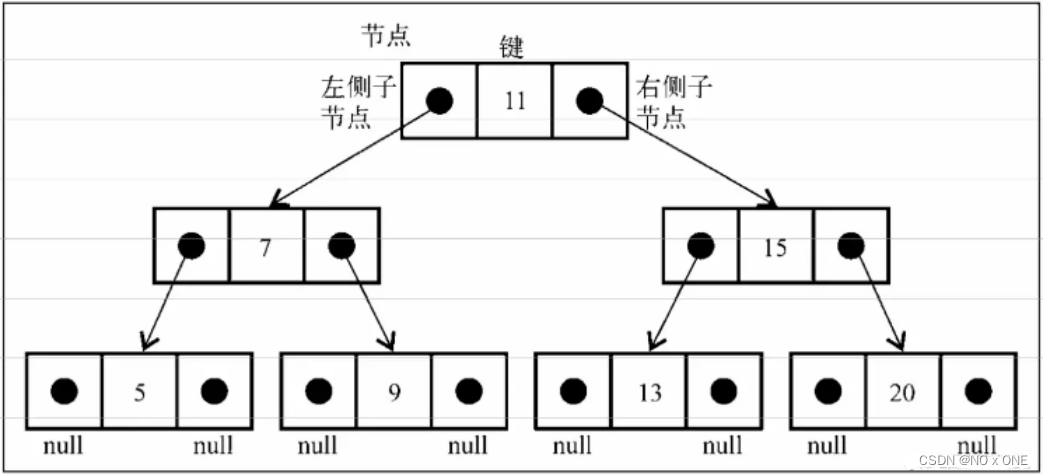
class BinarySearchTree{
constructor(){
this.root = null
}
static getNode(key){
const node = Object.create(null)
node.key = key
node.left = null
node.right = null
return node
}
insert(key){
const newNode = BinarySearchTree.getNode(key)
if(!this.root) return this.root = newNode
function insetNode(node,newNode) {
if(newNode.key<node.key){ // left
if(node.left === null) return node.left = newNode
else insetNode(node.left,newNode)
}
else{ // right
if(node.right === null) return node.right = newNode
else insetNode(node.right,newNode)
}
}
insetNode(this.root,newNode)
//** 用while循环代替递归函数
let curNode = this.root
let direction = newNode.key<curNode.key?'left':'right'
while(curNode[direction]){
curNode=curNode[direction]
direction = newNode.key<curNode.key?'left':'right'
}
curNode[direction] = newNode
//**
}
}
创建二叉树
const tree = new BinarySearchTree()
tree.insert(11)
tree.insert(7)
tree.insert(5)
tree.insert(3)
tree.insert(9)
tree.insert(8)
tree.insert(10)
tree.insert(13)
tree.insert(12)
tree.insert(14)
tree.insert(20)
tree.insert(18)
tree.insert(25)
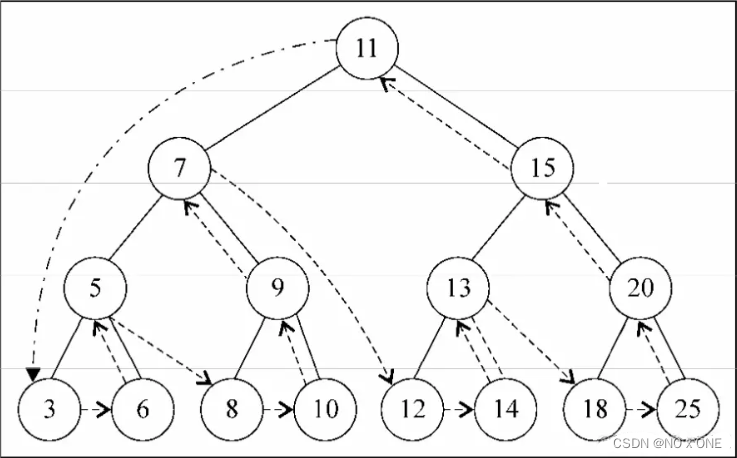
结构如下,自己看
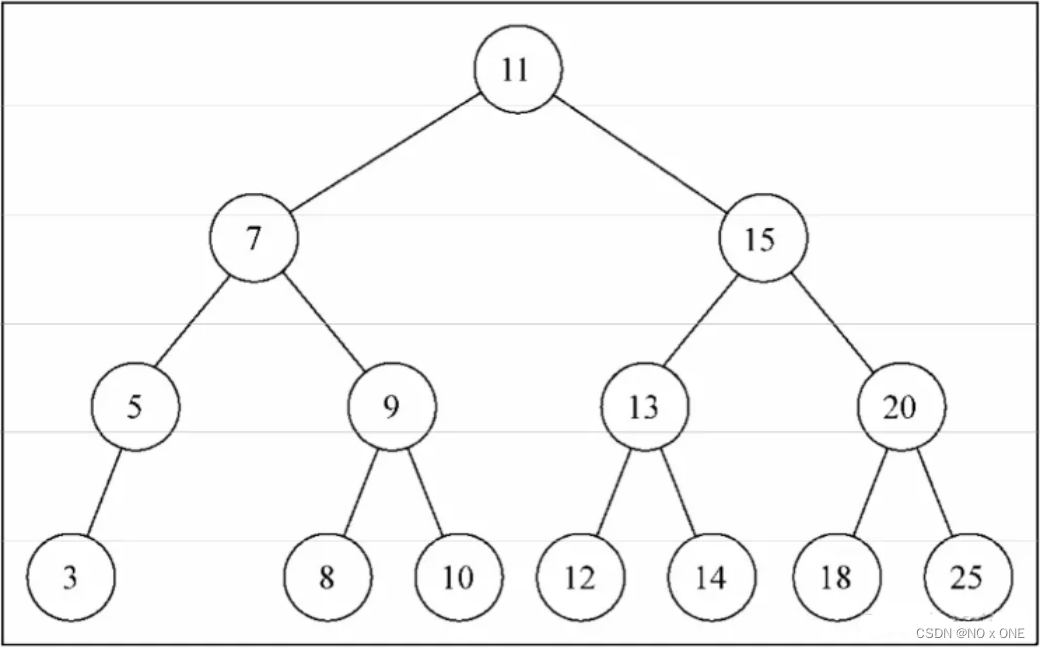
7.1 树的遍历
遍历一颗树是指访问树的每个节点并对它们进行某种操作(这里的操作这个词翻译成编程术语就是cb回调)的过程,有三种方式:中序、先序、后序
7.1.1 中序
中序遍历是一种以上行(即最小到最大)的顺序访问BST所有节点的遍历方式
class BinarySearchTree{
// ...
inOrderTranverse(cb){
function tranverse(node,cb){
if(node!==null){
tranverse(node.left,cb) // 以最小节点为起点
cb(node.key) // 回调
tranverse(node.right,cb)
}
}
tranverse(this.root,cb)
}
}
// 中序遍历可以用于排序
let arr = []
tree.inOrderTranverse(node=>arr.push(node))
console.log(arr) // [3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 18, 20, 25]
过程如下
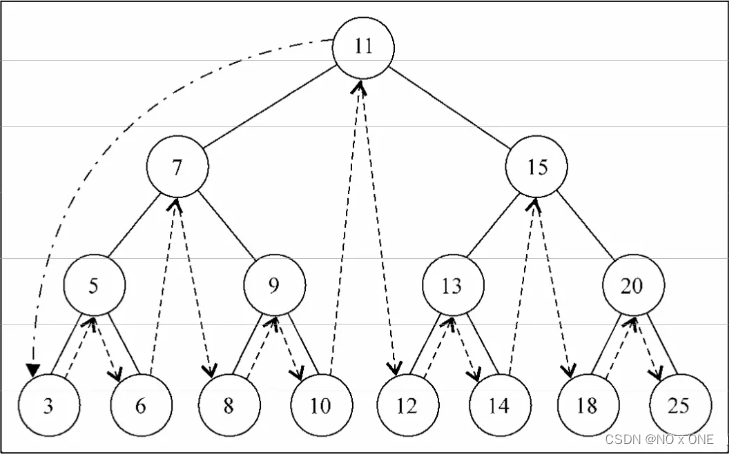
7.1.2 先序
先序遍历是以优先于后代节点的顺序访问每个节点
class BinarySearchTree{
// ...
preOrderTraverse(cb){
function tranverse(node,cb) {
if(node!==null){
cb(node)
tranverse(node.left,cb)
tranverse(node.right,cb)
}
}
tranverse(this.root,cb)
}
}
过程如下
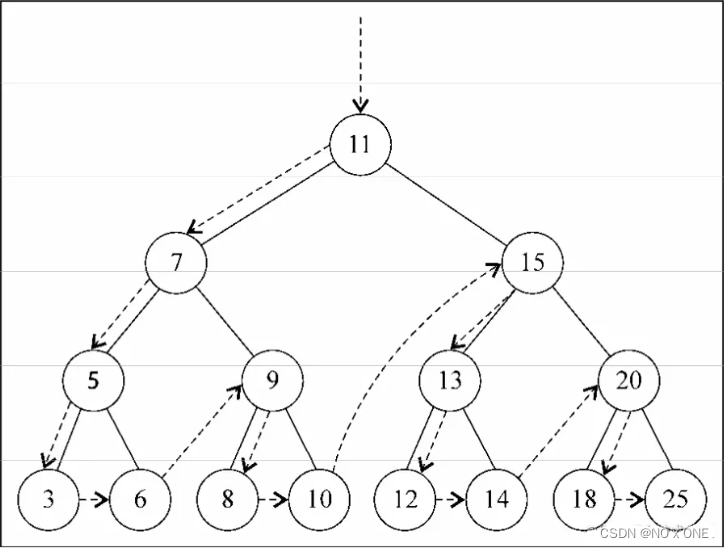
7.1.3 后序
后序遍历则是先访问节点的后代节点,再访问节点本身,与先序正好相反
class BinarySearchTree{
// ...
postOrderTraverse(cb){
function tranverse(node,cb) {
if(node!==null){
tranverse(node.left,cb)
tranverse(node.right,cb)
cb(node)
}
}
tranverse(this.root,cb)
}
}
过程如下,自己看
7.2 节点操作
7.2.1 搜索最大值和最小值
前面说过了二叉搜索树的特点就是小的放左边,大的放右边
min(node=this.root){ // 默认为根节点
while(node&&node.left) node = node.left
return node
//**
function getMin(node){
if(!node) return node
if(node.left) return getMin(node.left)
else return node
}
getMin(node)
//**
}
max(node=this.root){
while(node.right) node = node.right
return node
}
7.2.2 搜索特定节点
search(key){
let curNode = this.root
while(curNode&&curNode.key!==key){
if(key<curNode.key) curNode = curNode.left
else curNode = curNode.right
}
return curNode?curNode:false
//**
function searchNode(node,key) {
if(!node) return false
if(node.key===key) return node
if(key<node.key) return searchNode(node.left,key)
else return searchNode(node.right,key)
}
searchNode(this.root,key)
//**
}
7.2.3 移除特定节点(todo)
AVL树,RB树(todo)
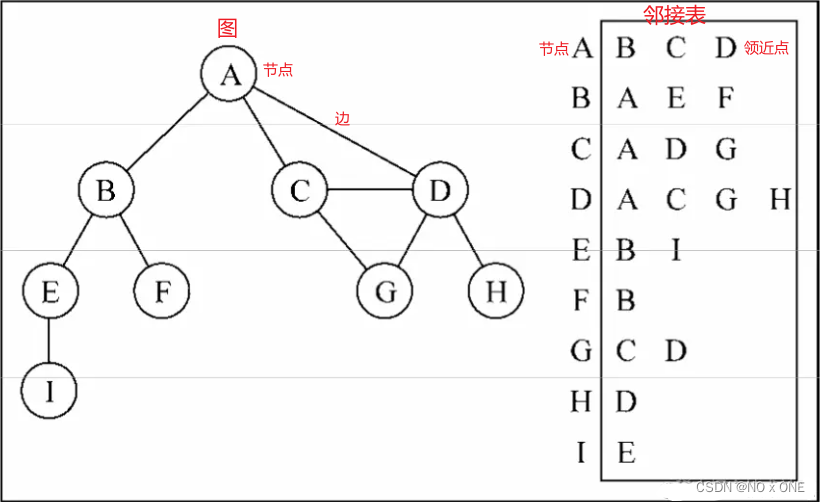
8.图
class Graph{
constructor(vertices=[]){
if(Object.prototype.toString.call(vertices)!=='[object Array]') throw new Error(`只能传数组噢`)
this.vertices=vertices
this.adjList = new Dictionary() // 邻接表
if(this.vertices.length) this.vertices.forEach(v=>this.adjList.set(v,[]))
}
addVertex(v){
this.vertices.push(v)
this.adjList.set(v,[])
}
addEdge(v,w){
this.adjList.get(v).push(w)
this.adjList.get(w).push(v)
}
toString(){
return this.vertices.reduce((pre,cur)=>{
return this.adjList.get(cur).reduce((pre,cur)=>{
return `${pre} ${cur}`
},`${pre}\n${cur}:`)
},'')
//** 以下可以增加代码维护难度 (若你老板对你不好,可以这样写)
return this.vertices.reduce((pre,cur)=>this.adjList.get(cur).reduce((pre,cur)=>`${pre} ${cur}`,`${pre}\n${cur}`),'')
//**
}
创建树
const graph = new Graph(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I'])
graph.addEdge('A', 'B')
graph.addEdge('A', 'C')
graph.addEdge('A', 'D')
graph.addEdge('C', 'D')
graph.addEdge('C', 'G')
graph.addEdge('D', 'G')
graph.addEdge('D', 'H')
graph.addEdge('B', 'E')
graph.addEdge('B', 'F')
graph.addEdge('E', 'I')
console.log(''+graph)
/**
* A: B C D
* B: A E F
* C: A D G
* D: A C G H
* E: B I
* F: B
* G: C D
* H: D
* I: E
*/
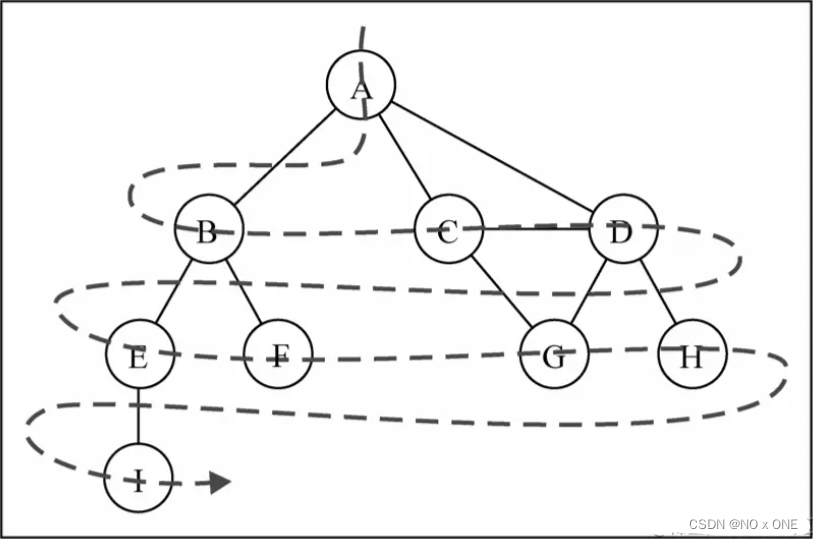
8.1 图遍历
图遍历算法的思想是:先指定第一次被访问的节点,并且追踪其下还有哪些节点还没有被完全探索
有两种遍历算法:广度优先搜索(Breadth-First Search,BFS)、深度优先搜索(Depth-First Search,DFS)
8.1.1 广度优先搜索
广度优先搜索(Breadth-First Search,BFS)是先宽后深地访问节点,实现思想:维护两个队列,分别用于存储已读和待读节点,两者具有互斥性,不断递归访问相邻的节点和同时标为已读
class Graph{
// ...
bfs(v,cb){
const readList = [] // 已读队列
const adjList = this.adjList
let pending = [v||this.vertices[0]] // 待读队列
while (pending.length) {
let key = pending.shift()
readList.push(key)
cb&&cb(key)
adjList.get(key).forEach(v=>{
if(!readList.includes(v)&&!pending.includes(v)){ // 互斥,保证只读一遍
pending.push(v)
}
})
}
//** 下面是另一种方法(我个人还是喜欢用while循环来代替递归,递归会浪费函数作用域内存,而且不优雅)
;(function read(vertices) {
vertices.forEach(key=>{
readList.push(pending.shift())
cb&&cb(key)
adjList.get(key).forEach(v=>{
if(!pending.includes(v)&&!readList.includes(v)){ // 互斥,保证只读一遍
pending.push(v)
}
})
pending.length&&read(pending)
})
})(pending)
//**
}
}
}
遍历看看
/**
* graph邻接表
* A: B C D
* B: A E F
* C: A D G
* D: A C G H
* E: B I
* F: B
* G: C D
* H: D
* I: E
*/
graph.bfs(null,v=>console.log(v)) // A B C D E F G H I
使用广度搜索计算到各节点到顶点的最短路径
class Graph{
// ...
bfs(v,cb){
const readList = []
const distances = []
const predecessors = []
const adjList = this.adjList
let pending = [v||this.vertices[0]]
while (pending.length) {
let key = pending.shift()
cb&&cb(key)
readList.push(key)
distances[key] = distances[key] || 0
predecessors[key] = predecessors[key]||null
adjList.get(key).forEach(v=>{
if(!readList.includes(v)&&!pending.includes(v)){
pending.push(v)
distances[v] = distances[key]+1
predecessors[v] = key
}
})
}
return {distances,predecessors}
}
getAllPath(fromV) {
let res = Object.create(null)
fromV = fromV || this.vertices[0]
const vertices = this.vertices
const { distances,predecessors } = this.bfs(fromV)
vertices.forEach(toV=>{
if(!!distances[toV]){
let preV = predecessors[toV]
let curPath = `${toV}`
while (fromV!==preV) {
curPath =`${preV} => ${curPath}`
preV = predecessors[preV]
}
curPath = `${fromV} => ${curPath}`
res[toV] = curPath
}
})
return res
}
}
/**
* graph邻接表
* A: B C D
* B: A E F
* C: A D G
* D: A C G H
* E: B I
* F: B
* G: C D
* H: D
* I: E
*/
console.log(graph.bfs())
// distances: [A: 0, B: 1, C: 1, D: 1, E: 2, F: 2, G: 2, H: 2 , I: 3]
// predecessors: [A: null, B: "A", C: "A", D: "A", E: "B", F: " B", G: " C", H: "D", I: "E"]
console.log(graph.getAllPath())
/**
* B: "A => B"
* C: "A => C"
* D: "A => D"
* E: "A => B => E"
* F: "A => B => F"
* G: "A => C => G"
* H: "A => D => H"
* I: "A => B => E => I"
*
*/
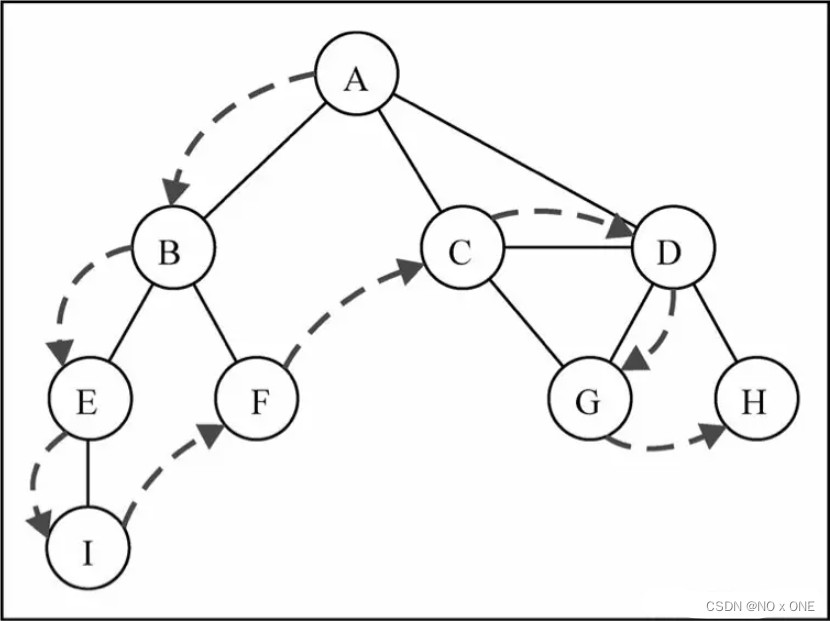
8.1.2 深度优先搜索
深度优先搜索(Depth-First Search,DFS)是先深后宽,实现思想:从第一个指定的顶点开始遍历图,沿着路径直到这条路径最后一个顶 点被访问了,接着原路回退并探索下一条路径,维护一个已读队列即可
class Graph{
// ...
dfs(cb){
const readList = []
const adjList =this.adjList
const len = this.vertices.length
function read(vertices){
vertices.forEach(key=>{
if(readList.includes(key)) return
readList.push(key)
cb&&cb(key)
if(readList.length!==len) read(adjList.get(key))
})
}
read(this.vertices)
}
}
/**
* graph邻接表
* A: B C D
* B: A E F
* C: A D G
* D: A C G H
* E: B I
* F: B
* G: C D
* H: D
* I: E
*/
graph.dfs(val=>console.log(val)) // A B E I F C D G H
优化,加入前导节点标记predecessors 、遍历节点开始时所在轮次readTimes和遍历完所有子节点所在轮次finishedTimes
class Graph{
dfs(cb){
const readList = []
const adjList =this.adjList
const len = this.vertices.length
let readT = 0
const finishedTimes = Object.create(null)
const readTimes = Object.create(null)
const predecessors = Object.create(null)
function read(vertices,predecessor){
vertices.forEach(key=>{
readT++
if(adjList.get(key).every(v=>readList.includes(v))&&!finishedTimes[key]){
finishedTimes[key] = readT // 完成遍历某节点的所有邻接点
}
if(readList.includes(key)) return
readTimes[key] = readT
readList.push(key)
cb&&cb(key)
predecessors[key] = predecessors[key] || predecessor || null
if(readList.length!==len) read(adjList.get(key),key)
})
}
read(this.vertices)
return { readTimes, finishedTimes, predecessors }
}
}
/**
* graph邻接表
* A: B C D
* B: A E F
* C: A D G
* D: A C G H
* E: B I
* F: B
* G: C D
* H: D
* I: E
*/
console.log(graph.dfs())
// readTimes: {A: 1, B: 2, C: 10, D: 12, E: 4, F: 8, G: 15, H: 18, I: 6 } 第2轮开始遍历到B节点
// finishedTimes: {A: 13, B: 9, C: 16, D: 20, E: 7, F: 8, G: 15, H: 18, I: 6 } 第9轮 "确认" 遍历完B节点下的所有子节点(这里的确认即这轮不再遍历下去,而是跳过)
// predecessors: {A: null, B: 'A', C: 'A', D: 'C', E: 'B', F: 'B', G: 'D', H: ''D', I: 'E'}























 4106
4106











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








