1.开闭原则
1.1 定义
对一个软件实体 如接口、类、模块 修改关闭、扩展打开, 对框架进行抽象,具体实现放在扩展里面。
1.2优点
提高代码的可复用性和代码的可维护性。
1.3 demo
源码地址:design-pattern: 学习记录 - Gitee.com
背景1:现在网上各种培训课程很多,比如java、大数据、人工智能等,这些课程有相同的属性:课程代码、课程名称、还有课程价格等等,可以将这些相同属性抽离出来,然后具体课程可以具体的进行实现。
/**
* 课程的抽象
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 00:05
*/
public interface ICourse {
String getId();
String getName();
BigDecimal getPrice();
}
/**
* 课程的一个具体实现
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 00:09
*/
public class JavaCourse implements ICourse {
private String id;
private String name;
private BigDecimal price;
public JavaCourse(String id, String name, BigDecimal price) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public BigDecimal getPrice() {
return price;
}
}
public class OpenCloseTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ICourse course = new JavaCourse("1", "java架构", new BigDecimal(10000));
System.out.println("课程id:" + course.getId()
+ "\n课程名称:《" + course.getName() + "》"
+ "\n课程价格:" + course.getPrice()
);
}
result:
课程id:1
课程名称:《java架构》
课程价格:10000背景2:同一个课程在不同的时间段也有相应的优惠,这个时候如果每次活动之前去临时改动代码修改课程的价格肯定是高危操作,所以这个时候应该对该功能进行扩展
/**
* 对JavaCourse 进行扩展来实现课程优惠的场景
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 00:17
*/
public class DiscountJavaCourse extends JavaCourse {
public DiscountJavaCourse(String id, String name, BigDecimal price) {
super(id, name, price);
}
public BigDecimal getDsicountPrice() {
return super.getPrice().multiply(new BigDecimal(0.6));
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 00:10
*/
public class OpenCloseTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ICourse course2 = new DiscountJavaCourse("1", "java架构", new BigDecimal(10000));
System.out.println("课程id:" + course2.getId()
+ "\n课程名称:《" + course2.getName() + "》"
+ "\n课程原价:" + course2.getPrice()
+ "\n课程售价:" + ((DiscountJavaCourse) course2).getDsicountPrice()
);
}
}
result:
课程id:1
课程名称:《java架构》
课程原价:10000
课程售价:5999.99999999999977795539507496869191527366638183593750000至于上面课程精度为啥不是6000的问题,是因为BigDecimal字符串和双精度类型的构造函数里执行的代码不同 可通过 ((DiscountJavaCourse) course2).getDsicountPrice().toString() 解决
2.依赖倒置原则
2.1定义
高层代码不依赖底层代码,两者都可以依赖抽象,抽象不依赖细节,细节依赖抽象,面向接口编程,而不是面向实现编程
2.2优点
解耦,提高代码的可维护性和可读性,降低修改代码带来的风险
2.3demo
源码地址:design-pattern: 学习记录 - Gitee.com
背景1 :小明在现在正在学习java、c课程 上代码:
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 10:32
*/
public class XiaoMing {
public void studyJavaCourse(){
System.out.println("小明正在学java课程");
}
public void studyCCourse(){
System.out.println("小明正在学C课程");
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 10:33
*/
public class DipTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
XiaoMing xiaoMing = new XiaoMing();
xiaoMing.studyCCourse();
xiaoMing.studyJavaCourse();
}
}背景2 :如果小明又要开始学c++课程,那么低层代码(XiaoMing)得修改,高层代码(DipTest)也得修改,这个是高层代码对低层代码产生了依赖,所以我们要对这种依赖进行抽象,上代码:
/**
* 对study 进行抽象
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 10:37
*/
public interface ICourse {
void study();
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 10:32
*/
public class XiaoMing {
// ===============v1 版本=======
// public void studyJavaCourse(){
// System.out.println("小明正在学java课程");
// }
// public void studyCCourse(){
// System.out.println("小明正在学C课程");
// }
// ===============v2 版本=======
public void study(ICourse course) {
course.study();
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 10:33
*/
public class DipTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// === v1 依赖细节 如果哪天又要学其他课程 那么调用方(this)和被调用方(XiaoMing)都要修改============
// XiaoMing xiaoMing = new XiaoMing();
// xiaoMing.studyCCourse();
// xiaoMing.studyJavaCourse();
// ============= v2 依赖抽象============
XiaoMing xiaoMing = new XiaoMing();
xiaoMing.study(new JavaCourse());
xiaoMing.study(new CCourse());
}
}背景3:v2版本是依赖抽象,依赖注入的原型,这个时候不管你实现怎么去实现,只要能保证我的抽象保持稳定就好,同时可以用构造的方式来进行注入,上代码:
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 10:32
*/
public class XiaoMing {
// ===============v1 版本=======
// public void studyJavaCourse(){
// System.out.println("小明正在学java课程");
// }
// public void studyCCourse(){
// System.out.println("小明正在学C课程");
// }
// ===============v2 版本=======
// public void study(ICourse course) {
// course.study();
// }
// ===============v3 版本=======
private ICourse course;
public XiaoMing(ICourse course) {
this.course = course;
}
public void study(){
course.study();
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 10:33
*/
public class DipTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ============= v1 依赖细节 如果哪天又要学其他课程 那么调用方(this)和被调用方(XiaoMing)都要修改============
// XiaoMing xiaoMing = new XiaoMing();
// xiaoMing.studyCCourse();
// xiaoMing.studyJavaCourse();
// ============= v2 依赖抽象============
// XiaoMing xiaoMing = new XiaoMing();
// xiaoMing.study(new JavaCourse());
// xiaoMing.study(new CCourse());
// ============= v3 如果XiaoMing 是单例的话这样也不妥============
XiaoMing xiaoMing = new XiaoMing(new JavaCourse());
xiaoMing.study();
XiaoMing xiaoMing1 = new XiaoMing(new CCourse());
xiaoMing1.study();
}
}背景4:这种构造注入的情况如果是单例的话这样就会出现不能重复new 的问题,所以 可以通过set 进行注入,上代码:
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 10:32
*/
public class XiaoMing {
// ===============v1 版本=======
// public void studyJavaCourse(){
// System.out.println("小明正在学java课程");
// }
// public void studyCCourse(){
// System.out.println("小明正在学C课程");
// }
// ===============v2 版本=======
// public void study(ICourse course) {
// course.study();
// }
// ===============v3 版本=======
// private ICourse course;
//
// public XiaoMing(ICourse course) {
// this.course = course;
// }
//
// public void study(){
// course.study();
// }
// ===============v4 版本=======
private ICourse course;
public void setCourse(ICourse course) {
this.course = course;
}
public void study(){
course.study();
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 10:33
*/
public class DipTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// ============= v1 依赖细节 如果哪天又要学其他课程 那么调用方(this)和被调用方(XiaoMing)都要修改============
// XiaoMing xiaoMing = new XiaoMing();
// xiaoMing.studyCCourse();
// xiaoMing.studyJavaCourse();
// ============= v2 依赖抽象============
// XiaoMing xiaoMing = new XiaoMing();
// xiaoMing.study(new JavaCourse());
// xiaoMing.study(new CCourse());
// ============= v3 如果XiaoMing 是单例的话这样也不妥============
// XiaoMing xiaoMing = new XiaoMing(new JavaCourse());
// xiaoMing.study();
//
// XiaoMing xiaoMing1 = new XiaoMing(new CCourse());
// xiaoMing1.study();
// ============= v4============
XiaoMing xiaoMing = new XiaoMing();
xiaoMing.setCourse(new JavaCourse());
xiaoMing.study();
xiaoMing.setCourse(new CCourse());
xiaoMing.study();
}
}
result:
小明正在学java课程
小明正在学C课程看下类图: 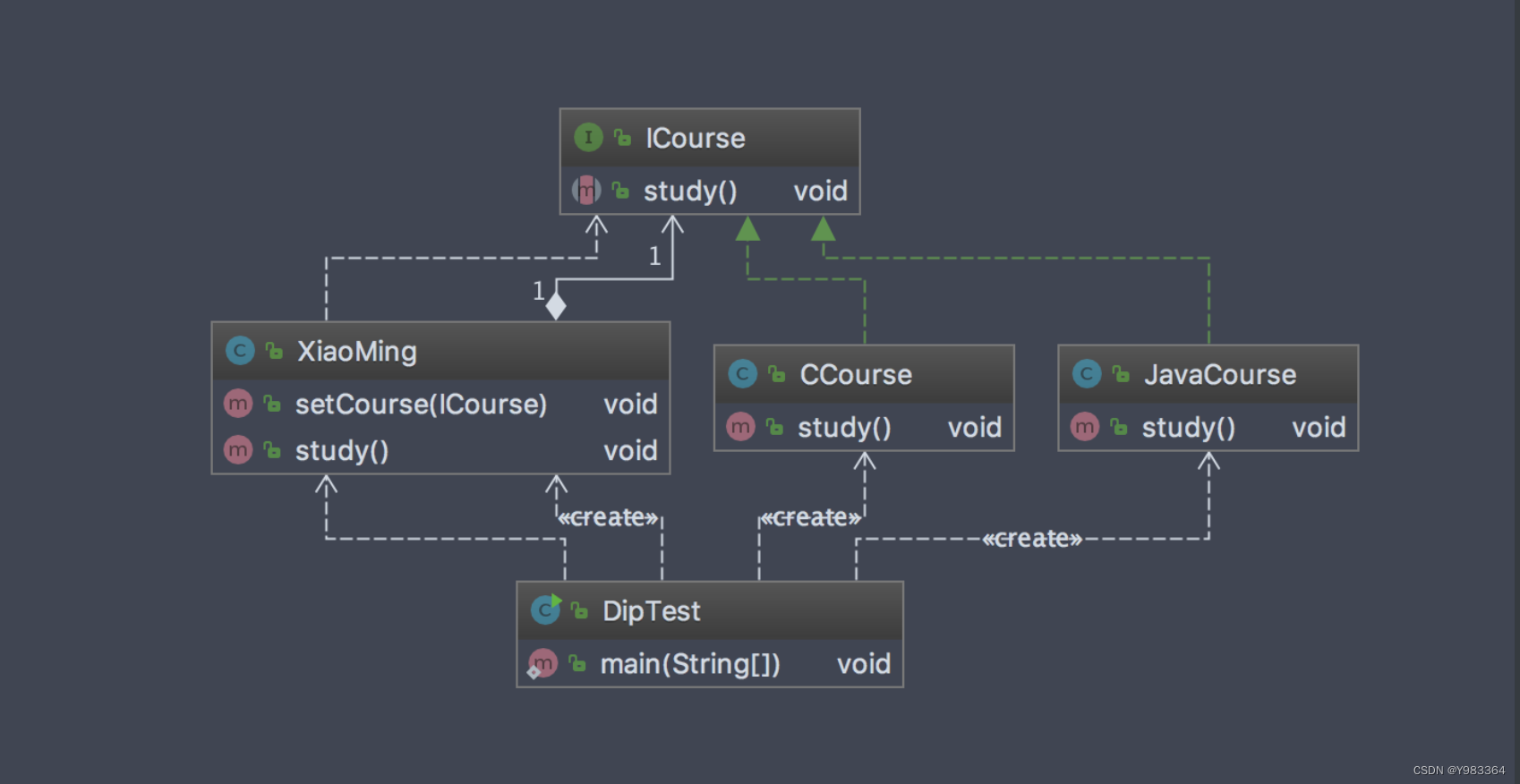
3.单一职责原则
3.1定义
一个类、方法、接口修改的原因只有一个
3.2优点
1.提高代码的可读性
2.提高代码的可维护性
3.降低代码的复杂程度
4.降低维护代码带来的风险
3.3demo
源码地址:design-pattern: 学习记录 - Gitee.com
背景1:当我们一个类做的事情比较多,比如我一个课程实现直播课和录播课的功能,这个时候直播课的业务逻辑需要调整时要修改这个类,如果是录播课要调整时也要修改这个类,所以违背了单一职责的原则,上代码:
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 11:37
*/
public class Course {
public void study(String courseName) {
if ("直播课".equals(courseName)) {
System.out.println("直播课不能快进");
}else {
System.out.println("录播课可以反复观看");
}
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 11:38
*/
public class SimpleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Course course = new Course();
course.study("直播课");
course.study("录播课");
}
}以上违背了单一职责的设计原则
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 11:41
*/
public class LiveCourse {
public void study() {
System.out.println("直播课不能快进");
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 11:42
*/
public class RePlayCourse {
public void study() {
System.out.println("录播课可以反复观看");
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 11:38
*/
public class SimpleTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LiveCourse liveCourse = new LiveCourse();
liveCourse.study();
RePlayCourse rePlayCourse = new RePlayCourse();
rePlayCourse.study();
}
}
这个时候不管是你调整直播课还是录播课,都不会相互影响,降低修改带来的风险
背景2:接口的情况,一个课程有课程的基本信息,还有课程的学习权限,如果放在一个接口里面存在基本信息修改或者学习权限修改的时候,也会相互收到影响,上代码:
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 11:43
*/
public interface ICourse {
// 课程名称
String courseName();
// 视频流
byte[] corseVideo();
// 课程学习
void studyCourse();
}
//违背了单一职责原则这个时候就要拆开,在各个功能变更时相互不影响
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 11:45
*/
public interface ICourseInfo {
// 课程名称
String courseName();
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 11:46
*/
public interface ICourseManage {
// 视频流
byte[] corseVideo();
// 课程学习
void studyCourse();
}背景3:在方法层面,如果一个方法做的事情太多,也会存在类似的情况,上代码:
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 11:45
*/
public class Method {
public void updateUserInfo(String userCode, String userName, boolean ifUpdateName) {
if (ifUpdateName) {
userName = "xxx";
} else {
userCode = "code";
}
}
}用一个参数变量作为修改某个具体信息的路由,用起来虽然很方便,但真正代码逻辑复杂之后,修改起来还是有一点风险的,也增加了测试回归量
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 12:29
*/
public class Method {
public void updateUserCode(String userCode) {
userCode = "code";
}
public void updateUserName(String userName) {
userName = "xxx";
}
}直接拆成两个方法,可读性很强,一眼就能看出来该方法是干嘛的,批次更改也互补影响
4.接口隔离原则
4.1定义
有许多专门的接口,而不是一个臃肿的同一接口,实现需要实现的接口。注意:
1.一个类的另外一个类的依赖是建立在最小接口的基础上
2.建立单一的接口,不要建立庞大臃肿的接口
3.细化一个接口的方法,尽量的少
4.注意适度
4.2优点
实现高类聚、低耦合
提高可读性、拓展性和可维护性
4.3demo
源码地址:design-pattern: 学习记录 - Gitee.com
背景:拿动物的属性举例子,动物有吃、飞、游泳等行为,如果我们把这些行为抽象到一个接口里面,那我们在实现狗这个动物时会发现不该实现的方法也得去实现,比如说飞,另外鸟也是的,鸟是没有游泳的行为的,上代码:
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 13:08
*/
public interface IAnimal {
void eat();
void fly();
void swin();
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 13:10
*/
public class Dog implements IAnimal {
public void eat() {
}
public void fly() {
}
public void swin() {
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 13:10
*/
public class Bird implements IAnimal {
public void eat() {
}
public void fly() {
}
public void swin() {
}
}这个时候dog 类的fly 就是一个空实现,bird的swin也是一个空实现
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 13:14
*/
public interface IEatAnimal {
void eat();
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 13:14
*/
public interface IFlyAnimal {
void fly();
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 13:14
*/
public interface ISwinAnimal {
void swin();
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 13:15
*/
public class Bird implements IEatAnimal,IFlyAnimal {
public void eat() {
}
public void fly() {
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 13:14
*/
public class Dog implements IEatAnimal,ISwinAnimal {
public void eat() {
}
public void swin() {
}
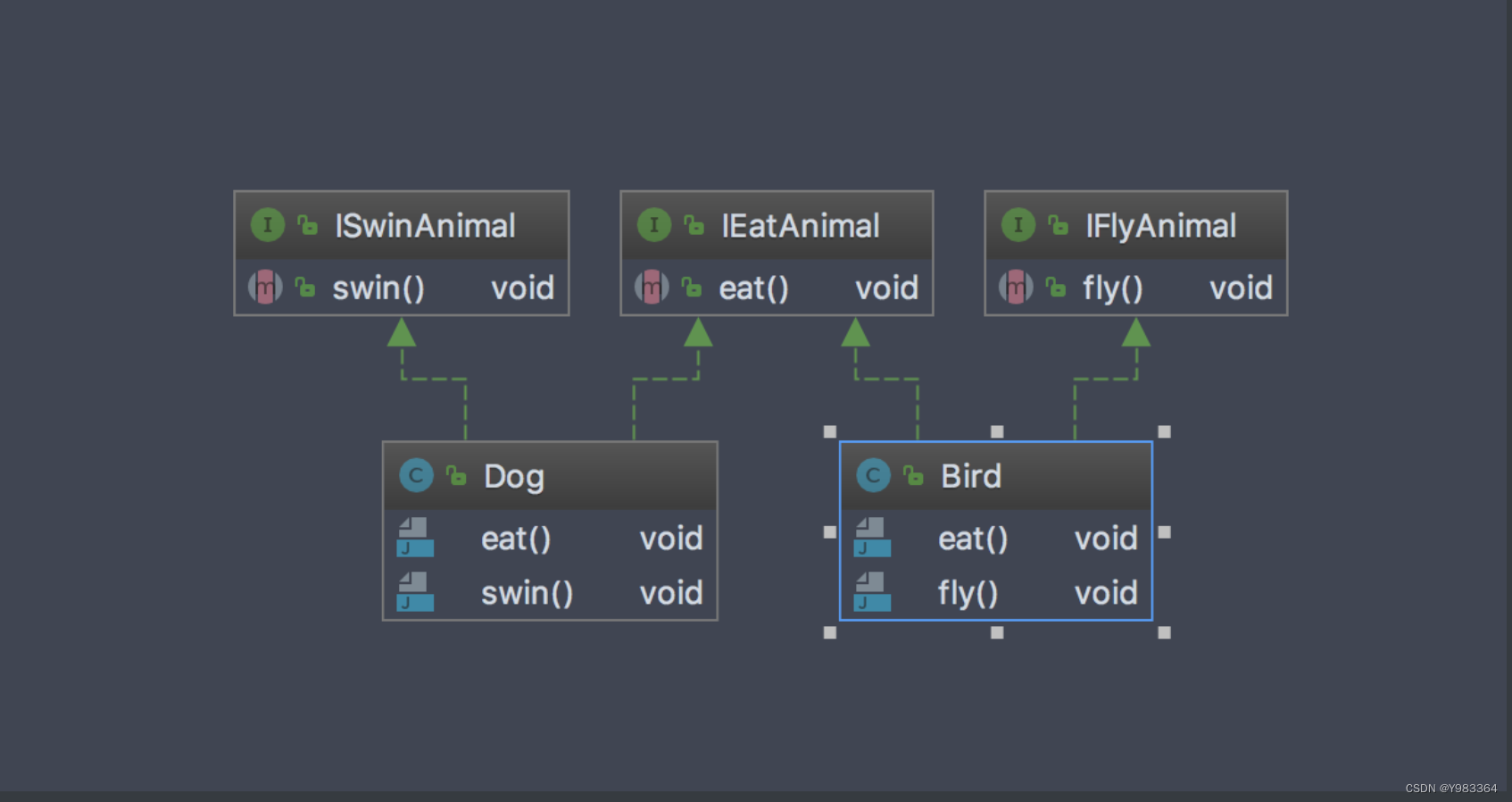
}让我们看看类图这个结构就很清晰:
5.迪米特法则
5.1定义
一个对象对所调用的对象要保持最少知道,也叫最少知道原则
朋友:出现在输入参数、输出参数、成员变量的类为成员朋友类,方法体内部的内不属于朋友
5.2优点
解耦
5.3demo
源码地址:design-pattern: 学习记录 - Gitee.com
背景1:老师让组长去统计学生交的作业数,直接上代码再说问题:
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 13:49
*/
public class Teacher {
public void checkTaskNumber(GroupLeader groupLeader) {
List<Task> taskList = new ArrayList<Task>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
taskList.add(new Task());
}
groupLeader.statistics(taskList);
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 13:51
*/
public class GroupLeader {
public void statistics(List<Task> taskList){
System.out.println("作业数:" + taskList.size());
}
}
这个是结果也没得问题,但是真正的场景中,老师不不用关心具体的作业的,所以在老师这个对象里面就不应该知道具体的作业
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 13:49
*/
public class Teacher {
public void checkTaskNumber(GroupLeader groupLeader) {
groupLeader.statistics();
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 13:51
*/
public class GroupLeader {
public void statistics(){
List<Task> taskList = new ArrayList<Task>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
taskList.add(new Task());
}
System.out.println("作业数:" + taskList.size());
}
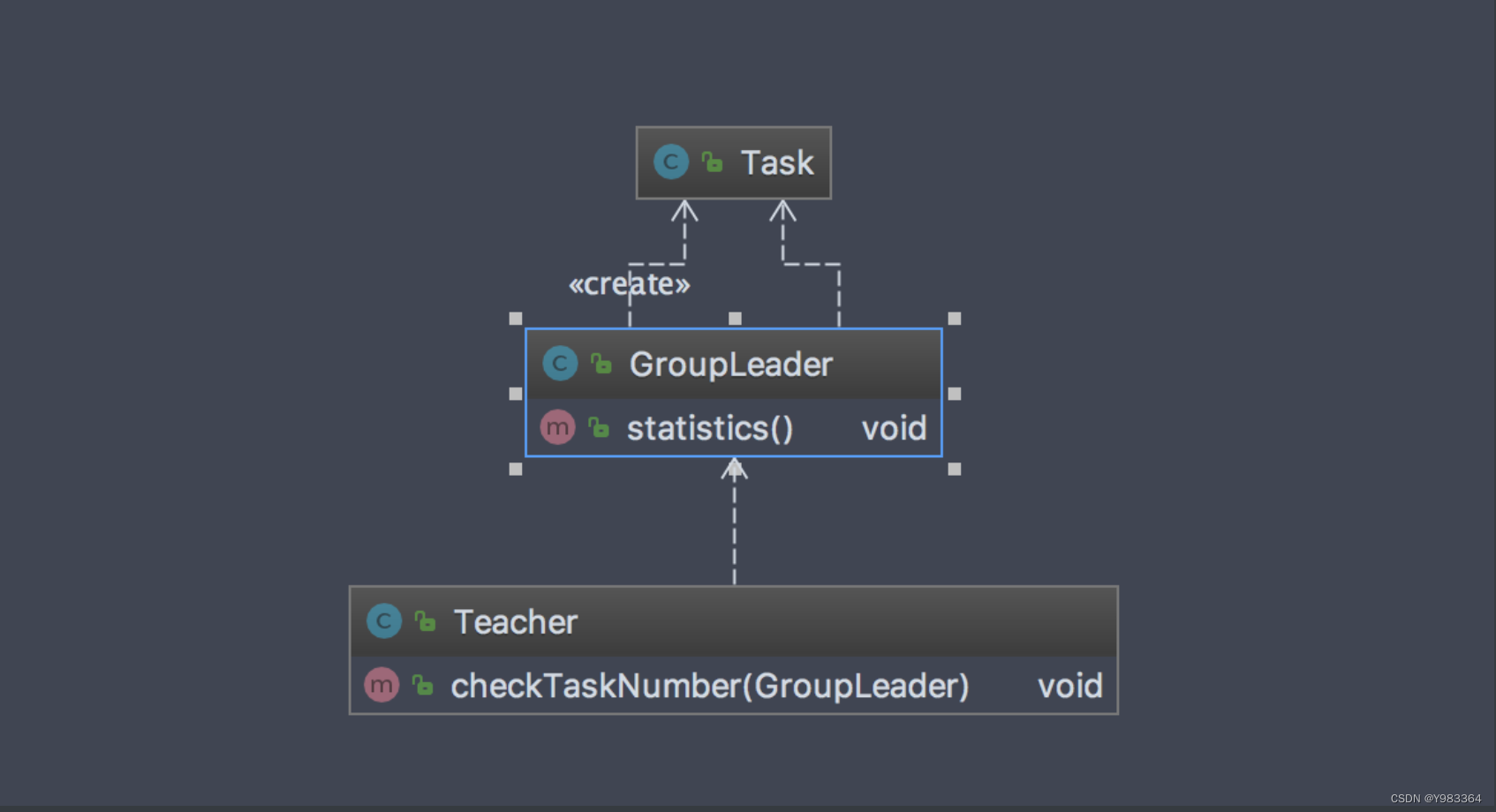
}这个时候代码就很清晰了,老师只管让组长去统计就好了,不需要了解具体的作业,再看看类图:
6.合成复用原则
6.1定义
类之间的关联关系尽量用组合、聚合的形式,尽量少用继承关系
聚合has-a:电脑和U盘,在一起可以工作,拔出来也可以独立的工作
组合contains-a:组合在一起具有相同的生命周期,比如人的手脚、头,缺一不可
继承is-a:狗跟动物,管理关系非常强,动物的公用特征抽离出来到顶层设计中,方便管理
6.2优点
降低类与类之间的耦合度,提高代码的可维护性,一个类的修改尽量影响到更少的类
6.3demo
源码地址:design-pattern: 学习记录 - Gitee.com
背景1:在dao层因为要用到数据库连接 DBcoonection,那这个时候可以继承DBcoonection然后再做对应的增删改查,但是这个时候明显是不合理的,因为这样coon的信息都会暴露给dao,所以这个时候就可以用复用原则,上代码:
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 15:08
*/
public class DBConnection {
public String getDbConnection(){
return "获取数据库连接";
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 15:09
*/
public class ProductDao {
private DBConnection dbConnection;
public void setDbConnection(DBConnection dbConnection){
this.dbConnection = dbConnection;
}
public void add(){
String coon = dbConnection.getDbConnection();
System.out.println("获取了数据库连接");
}
}这样就是典型的合成复用原则,但是如果后面又有其他类型的数据连接的时候就需要改动,违背了开闭原则,所以还得进一步优化
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 15:08
*/
public abstract class DBConnection {
abstract String getDbConnection();
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 15:12
*/
public class MysqlConnection extends DBConnection {
@Override
String getDbConnection() {
return "获取mysql数据库连接";
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 15:12
*/
public class OracleConnection extends DBConnection {
@Override
String getDbConnection() {
return "获取oracle数据库连接";
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 15:09
*/
public class ProductDao {
private DBConnection dbConnection;
public void setDbConnection(DBConnection dbConnection){
this.dbConnection = dbConnection;
}
public void add(){
String coon = dbConnection.getDbConnection();
System.out.println(coon);
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 15:13
*/
public class CopTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ProductDao productDao = new ProductDao();
productDao.setDbConnection(new MysqlConnection());
productDao.add();
}
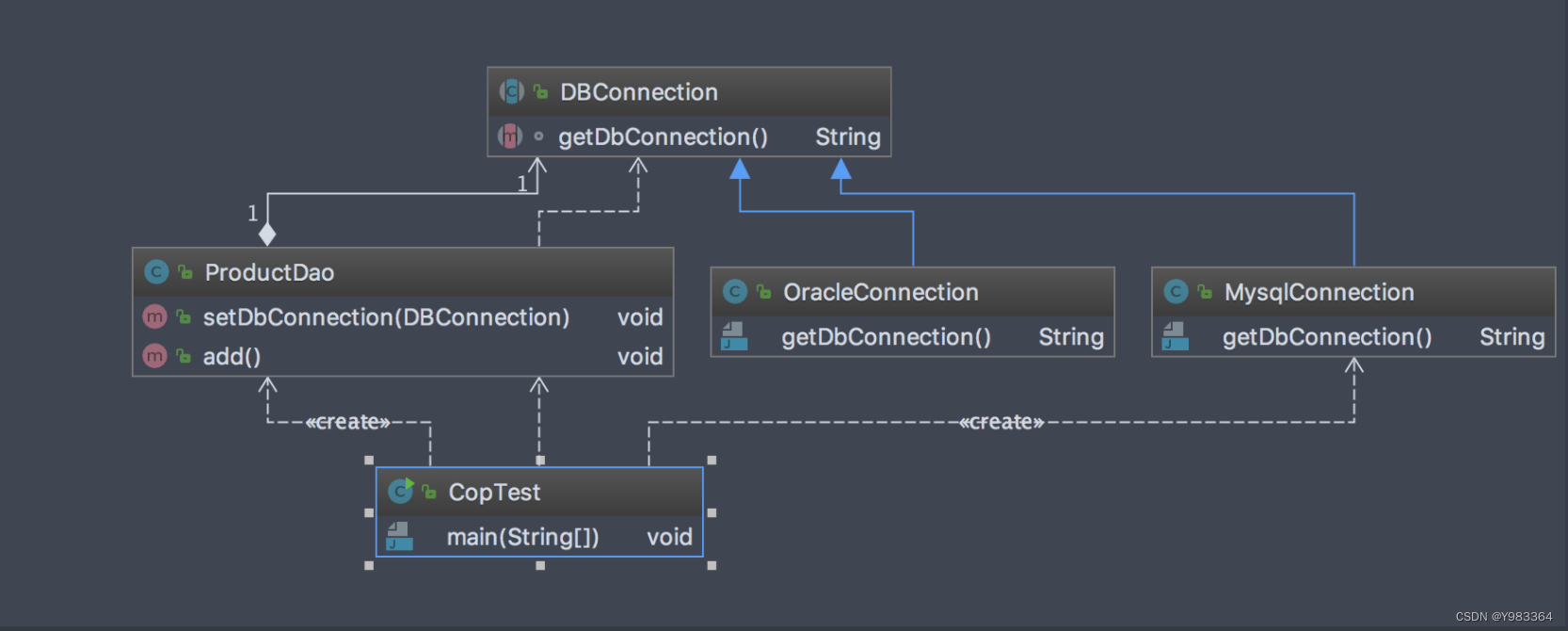
}看下类图:
7. 里氏替换原则
7.1定义
如果对每一个类型为T1的对象哦o1,都有类型为T2的对象o2,使得以T1定义的所有程序p在所有的对象o1都替换成o2时,程序p的行为没有发生变化,那么类型T2是类型T1 的子类
7.2定义拓展
一个软件实体如果适用一个父类的话,那一定适用于其子类,所有引用父类的地方必须能透明的使用其子类对象,子类对象能够替换父类对象,而程序逻辑不变
7.3引申含义
子类可以扩展父类的功能,但不能改变父类原有的功能
含义1:子类可以实现父类的抽象方法,单不能覆盖父类的非抽象方法
含义2:子类可以增加自己特有的方法
含义3:单子类的方法重载父类的方法时,方法的前置条件(入参)要比父类方法输入参数更为宽松
含义4:当子类的方式实现父类的方法时(重写、重载或实现抽象方法),后置条件(返回值)要比父类的严格或相等
7.4demo
源码地址:design-pattern: 学习记录 - Gitee.com
场景1:长方形有长宽,正方形只有边长,这个时候我们用正方形继承长方形看看
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:05
*/
public class Rectangle {
private long height;
private long width;
public long getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(long height) {
this.height = height;
}
public long getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(long width) {
this.width = width;
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:05
*/
public class Square extends Rectangle {
private long length;
public long getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(long length) {
this.length = length;
}
@Override
public long getHeight() {
return getLength();
}
@Override
public void setHeight(long height) {
setLength(height);
}
@Override
public long getWidth() {
return getLength();
}
@Override
public void setWidth(long width) {
setLength(width);
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:05
*/
public class SimpleTest {
public static void resize(Rectangle rectangle){
while (rectangle.getWidth() >= rectangle.getHeight()){
rectangle.setHeight(rectangle.getHeight() + 1);
System.out.println("Width:" +rectangle.getWidth() +",Height:" + rectangle.getHeight());
}
System.out.println("Resize End,Width:" +rectangle.getWidth() +",Height:" + rectangle.getHeight());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
rectangle.setWidth(20);
rectangle.setHeight(18);
resize(rectangle);
}
}
执行结果:
Width:20,Height:19
Width:20,Height:20
Width:20,Height:21
Resize End,Width:20,Height:21这个时候我们拿子类 Square 做同样操作看看
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:05
*/
public class SimpleTest {
public static void resize(Rectangle rectangle){
while (rectangle.getWidth() >= rectangle.getHeight()){
rectangle.setHeight(rectangle.getHeight() + 1);
System.out.println("Width:" +rectangle.getWidth() +",Height:" + rectangle.getHeight());
}
System.out.println("Resize End,Width:" +rectangle.getWidth() +",Height:" + rectangle.getHeight());
}
// public static void main(String[] args) {
// Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
// rectangle.setWidth(20);
// rectangle.setHeight(18);
// resize(rectangle);
// }
public static void main(String[] args) {
Square square = new Square();
square.setLength(10);
resize(square);
}
}
执行结果:
发现会一直执行下去,因为while 是恒等的,正方形边长一样得出结论:这个不遵循里式替换原则 这个继承是有点问题的
场景2:那我们在做个调整,抽象出一个四边形,然后再用长方形、正方形去实现这个四边形,再看看效果
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:10
*/
public interface QuadRangle {
long getWidth();
long getHeight();
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:11
*/
public class Rectangle implements QuadRangle {
private long height;
private long width;
public long getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(long height) {
this.height = height;
}
public long getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(long width) {
this.width = width;
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:10
*/
public class Square implements QuadRangle {
private long length;
public long getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(long length) {
this.length = length;
}
public long getWidth() {
return length;
}
public long getHeight() {
return length;
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:10
*/
public class IspTest {
public static void resize(QuadRangle rectangle){
while (rectangle.getWidth() >= rectangle.getHeight()){
// rectangle.setHeight(rectangle.getHeight() + 1);
System.out.println("Width:" +rectangle.getWidth() +",Height:" + rectangle.getHeight());
}
System.out.println("Resize End,Width:" +rectangle.getWidth() +",Height:" + rectangle.getHeight());
}
// public static void main(String[] args) {
// Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle();
// rectangle.setWidth(20);
// rectangle.setHeight(18);
// resize(rectangle);
// }
public static void main(String[] args) {
Square square = new Square();
square.setLength(10);
resize(square);
}
}会发现,这里直接会报错,因为抽象里面是没有set方法的,这样就杜绝了一个继承泛滥的问题
场景3:子类重载父类的方法时,入参要不父类更宽松
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:42
*/
public class Child extends Base {
public void method(Map map){
System.out.println("执行子类Map入参方法");
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:42
*/
public class Child extends Base {
public void method(Map map){
System.out.println("执行子类Map入参方法");
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:42
*/
public class MethodParamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base child = new Child();
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
child.method(hashMap);
}
}
执行结果:
父类执行
我们这个时候根据定义把
Base child = new Child();
替换成
Child child = new Child();
执行结果:
父类执行
执行结果不变,证明遵循了里式替换原则这个时候我们再测一下把父类的体检变更更严格再看看效果
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:42
*/
public class Base {
public void method(Map map){
System.out.println("父类执行");
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:42
*/
public class Child extends Base {
public void method(HashMap map){
System.out.println("执行子类Map入参方法");
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:42
*/
public class MethodParamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base child = new Child();
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
child.method(hashMap);
}
}
执行结果:
父类执行
我们这个时候根据定义把
Base child = new Child();
替换成
Child child = new Child();
执行结果:
执行子类Map入参方法
执行结果改变了,证明了子类重载方法入参更严格确实违背了里式替换原则场景4:当子类的方式实现父类的方法时(重写、重载或实现抽象方法),后置条件(返回值)要比父类的严格或相等
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:50
*/
public abstract class Base {
public abstract Map method();
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:50
*/
public class Child extends Base {
@Override
public HashMap method() {
HashMap hashMap = new HashMap();
System.out.println("执行子类的method");
hashMap.put("msg","子类method");
return hashMap;
}
}
/**
* create by yufeng on 2021/7/3 16:50
*/
public class MethodReturnTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base child = new Child();
System.out.println(child.method());
}
}
执行结果:
执行子类的method
{msg=子类method}
我们这个时候根据定义把
Base child = new Child();
替换成
Child child = new Child();
执行结果:
执行子类的method
{msg=子类method}
执行结果不变,证明遵循了里式替换原则
这个时候我们把子类的后置条件弄得更宽松看看是否遵循里式替换原则
结果发现 编译器直接报错,证明这个后置条件 就强制遵循了里式替换原则






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








