(1)针对前面的遗传算法部分,给出程序汇总如下:
%-------------函数说明----------------
%
% 主函数
%---------------------------------------
function main()
clear
clc
popsize = 100; %种群大小
chromlength = 10; %二进制编码长度
pc = 0.6; %交叉概率
pm = 0.001; %变异概率
pop = initpop(popsize,chromlength); %初始种群
for i=1:100
[objvalue] = cal_objvalue(pop); %计算适应度值(函数值)
fitvalue = objvalue;
[newpop] = selection(pop,fitvalue); %选择操作
[newpop] = crossover(newpop,pc); %交叉操作
[newpop] = mutation(newpop,pm); %变异操作
pop = newpop; %更新种群
[bestindividual,bestfit]=best(pop,fitvalue);%寻找最优解
x2 = binary2decimal(bestindividual);
x1 = binary2decimal(newpop);
[y1] = cal_objvalue(newpop);
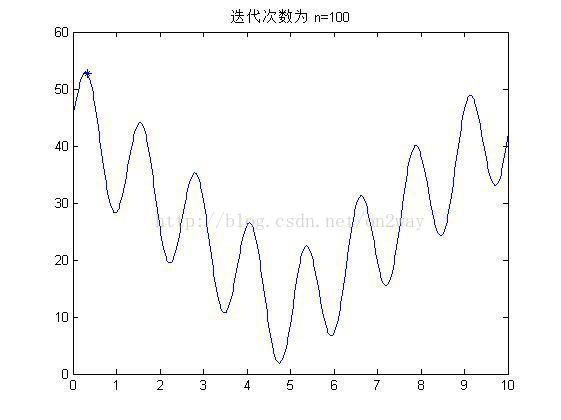
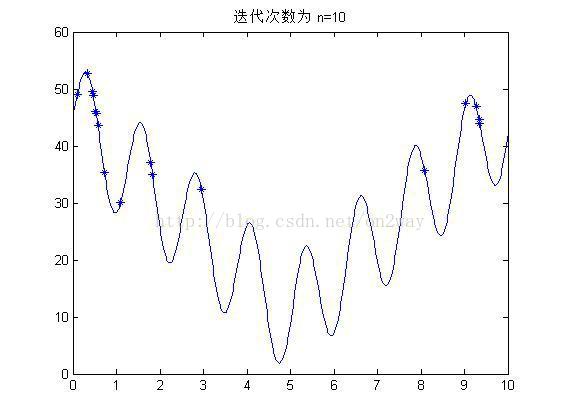
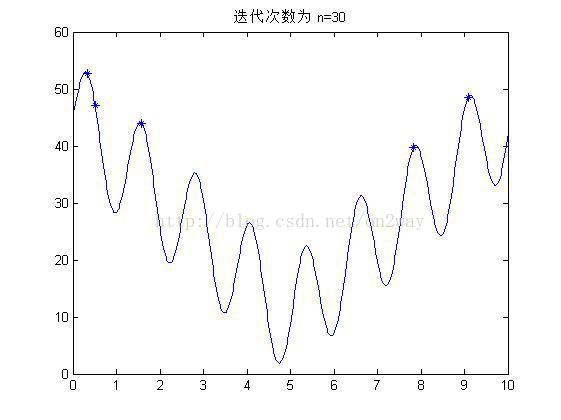
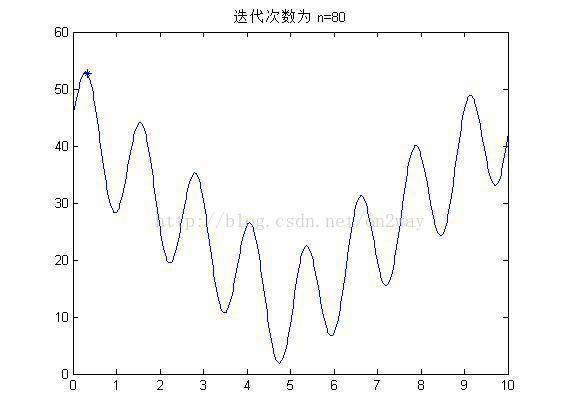
if mod(i,10)==0
figure;
fplot('10*sin(5*x)+7*abs(x-5)+10',[0 10]);
hold on;
title(['迭代次数为 n=' num2str(i)]);
plot(x1,y1,'*');
end
end
fprintf('the best X is --->>%5.2f\n',x2);
fprintf('the best Y is --->>%5.2f\n',bestfit);
%-------------函数说明----------------
% 初始化种群大小
% 输入变量:
% popsize:种群大小
% chromlength:染色体长度--》转化的二进制长度
% 输出变量:
% pop:种群
%---------------------------------------
function pop = initpop(popsize,chromlength)
pop = round(rand(popsize,chromlength));
%-------------函数说明----------------
% 二进制转化十进制函数
% 输入变量:
% 二进制种群
% 输出变量:
% 十进制数值
%---------------------------------------
function pop2 = binary2decimal(pop)
[px,py]=size(pop);
for i=1:py
pop1(:,i) = 2.^(py-i).*pop(:,i);
end
%sum(.,2)对行求和,得到列的向量
temp = sum(pop1,2);
pop2 = temp*10/1023;
%-------------函数说明----------------
% 计算函数目标值
% 输入变量:
% 二进制数值
% 输出变量:
% 目标函数值
%---------------------------------------
function [objvalue]=cal_objvalue(pop)
x = binary2decimal(pop);
%转化二进制数为x变量的变化域范围的数值
% x = temp*10/1023;
% objvalue = 10*sin(5*x)+7*cos(4*x);
% objvalue = 10*sin(x)+7*x+10
objvalue = 10*sin(5*x)+7*abs(x-5)+10;
%-------------函数说明----------------
%
% 输入变量:
% pop : 二进制种群
% fitvalue : 适应度值
% 输出变量:
% newpop:选择以后的二进制种群
%---------------------------------------
function [newpop] = selection(pop,fitvalue)
%构造轮盘
[px,py]=size(pop);
totalfit = sum(fitvalue);
p_fitvalue = fitvalue/totalfit;
p_fitvalue = cumsum(p_fitvalue);%概率求和排序
%-------
ms = sort(rand(px,1));%从小到大排列
fitin = 1;
newin = 1;
while newin<=px
if (ms(newin))<p_fitvalue(fitin)
newpop(newin,:)=pop(fitin,:);
newin=newin+1;
else fitin=fitin+1;
end
end
%-------------函数说明----------------
%
% 输入变量:
% pop:二进制的父代种群数
% pc:交叉的概率
% 输出变量:
% newpop:交叉后的种群数
%---------------------------------------
function [newpop]=crossover(pop,pc)
[px,py]=size(pop);
newpop = ones(size(pop));
for i=1:2:px-1
if(rand<pc)
cpoint = round(rand*py);
newpop(i,:) = [pop(i,1:cpoint),pop(i+1,cpoint+1:py)];
newpop(i+1,:) = [pop(i+1,1:cpoint),pop(i,cpoint+1:py)];
else
newpop(i,:)=pop(i,:);
newpop(i+1,:)=pop(i+1,:);
end
end
%-------------函数说明----------------
%
% 输入变量:
% pop : 二进制种群
% pm : 变异概率
% 输出变量:
% newpop : 变异以后的种群
%---------------------------------------
function [newpop] = mutation(pop,pm)
[px,py] = size(pop);
newpop = ones(size(pop));
for i=1:px
if(rand<pm)
mpoint = round(rand*py);
if mpoint<=0
mpoint=1;
end
newpop(i,:) = pop(i,:);
if newpop(i,mpoint)==0
newpop(i,mpoint)=1;
else newpop(i,mpoint)=0;
end
else
newpop(i,:)=pop(i,:);
end
end
%-------------函数说明----------------
%
% 输入变量:
% pop : 种群
% fitvalue : 种群适应度
%
% 输出变量:
% bestindividual : 最佳个体(二进制个体)
% bestfit : 最佳适应度值
%---------------------------------------
function [bestindividual,bestfit]=best(pop,fitvalue)
[px,py]=size(pop);
bestindividual = pop(1,:);
bestfit = fitvalue(1);
for i=2:px
if fitvalue(i)>bestfit
bestindividual = pop(i,:);
bestfit = fitvalue(i);
end
end
(2)实验结果






















 4591
4591

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








