1. Which feature on a Cisco router permits the forwarding of traffic for which there is no specific route?
- next-hop
- gateway of last resort
- route source
- outgoing interface
Explanation: A default static route is used as a gateway of last resort to forward unknown destination traffic to a next hop/exit interface. The next-hop or exit interface is the destination to send traffic to on a network after the traffic is matched in a router. The route source is the location a route was learned from.
2. Which three advantages are provided by static routing? (Choose three.)
- Static routing does not advertise over the network, thus providing better security.
- Configuration of static routes is error-free.
- Static routes scale well as the network grows.
- Static routing typically uses less network bandwidth and fewer CPU operations than dynamic routing does.
- The path a static route uses to send data is known.
- No intervention is required to maintain changing route information.
3. What are two functions of dynamic routing protocols? (Choose two.)
- to maintain routing tables
- to assure low router overhead
- to avoid exposing network information
- to discover the network
- to choose the path that is specified by the administrator
4. What is an advantage of using dynamic routing protocols instead of static routing?
- easier to implement
- more secure in controlling routing updates
- fewer router resource overhead requirements
- ability to actively search for new routes if the current path becomes unavailable
5. What happens to a static route entry in a routing table when the outgoing interface associated with that route goes into the down state?
- The static route is removed from the routing table.
- The router polls neighbors for a replacement route.
- The router automatically redirects the static route to use another interface.
- The static route remains in the table because it was defined as static.
Explanation: When the interface associated with a static route goes down, the router will remove the route because it is no longer valid.
6. What is a characteristic of a static route that matches all packets?
- It uses a single network address to send multiple static routes to one destination address.
- It identifies the gateway IP address to which the router sends all IP packets for which it does not have a learned or static route.
- It backs up a route already discovered by a dynamic routing protocol.
- It is configured with a higher administrative distance than the original dynamic routing protocol has.
Explanation: A default static route is a route that matches all packets. It identifies the gateway IP address to which the router sends all IP packets for which it does not have a learned or static route. A default static route is simply a static route with 0.0.0.0/0 as the destination IPv4 address. Configuring a default static route creates a gateway of last resort.
7. When would it be more beneficial to use a dynamic routing protocol instead of static routing?
- in an organization where routers suffer from performance issues
- on a stub network that has a single exit point
- in an organization with a smaller network that is not expected to grow in size
- on a network where there is a lot of topology changes
Explanation: Dynamic routing protocols consume more router resources, are suitable for larger networks, and are more useful on networks that are growing and changing.
8. Which route would be used to forward a packet with a source IP address of 192.168.10.1 and a destination IP address of 10.1.1.1?
- C 192.168.10.0/30 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1
- O 10.1.1.0/24 [110/65] via 192.168.200.2, 00:01:20, Serial0/1/0
- S* 0.0.0.0/0 [1/0] via 172.16.1.1
- S 10.1.0.0/16 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0
Explanation: Even though OSPF has a higher administrative distance value (less trustworthy), the best match is the route in the routing table that has the most number of far left matching bits.
9. Refer to the exhibit. What is the administrative distance value of the route for router R1 to reach the destination IPv6 address of 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::A?

- 120
- 110
- 1
- 4
Explanation: The RIP route with the source code R is used to forward data to the destination IPv6 address of 2001:DB8:CAFE:4::A. This route has an AD value of 120.
10. Which value in a routing table represents trustworthiness and is used by the router to determine which route to install into the routing table when there are multiple routes toward the same destination?
- administrative distance
- metric
- outgoing interface
- routing protocol
Explanation: The administrative distance represents the trustworthiness of a particular route. The lower an administrative distance, the more trustworthy the learned route is. When a router learns multiple routes toward the same destination, the router uses the administrative distance value to determine which route to place into the routing table. A metric is used by a routing protocol to compare routes received from the routing protocol. An exit interface is the interface used to send a packet in the direction of the destination network. A routing protocol is used to exchange routing updates between two or more adjacent routers.
11. Refer to the exhibit. This network has two connections to the ISP, one via router C and one via router B. The serial link between router A and router C supports EIGRP and is the primary link to the Internet. If the primary link fails, the administrator needs a floating static route that avoids recursive route lookups and any potential next-hop issues caused by the multiaccess nature of the Ethernet segment with router B. What should the administrator configure?

- Create a static route pointing to Fa0/0 with an AD of 1.
- Create a static route pointing to 10.1.1.1 with an AD of 95.
- Create a static route pointing to 10.1.1.1 with an AD of 1.
- Create a fully specified static route pointing to Fa0/0 with an AD of 1.
- Create a fully specified static route pointing to Fa0/0 with an AD of 95.
12. Refer to the graphic. Which command would be used on router A to configure a static route to direct traffic from LAN A that is destined for LAN C?
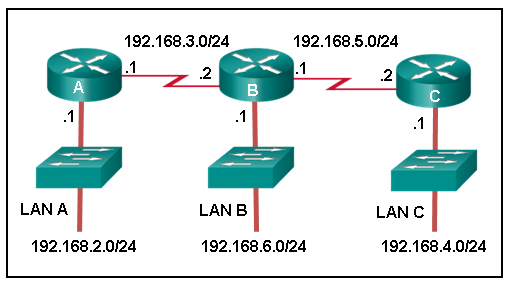
- A(config)# ip route 192.168.3.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.1
- A(config)# ip route 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.0 192.168.4.0
- A(config)# ip route 192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.5.2
- A(config)# ip route 192.168.5.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.2
- A(config)# ip route 192.168.4.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.3.2
Explanation: The destination network on LAN C is 192.168.4.0 and the next-hop address from the perspective of router A is 192.168.3.2.
13. On which two routers would a default static route be configured? (Choose two.)
- any router where a backup route to dynamic routing is needed for reliability
- the router that serves as the gateway of last resort
- any router running an IOS prior to 12.0
- stub router connection to the rest of the corporate or campus network
- edge router connection to the ISP
Explanation: A stub router or an edge router connected to an ISP has only one other router as a connection. A default static route works in those situations because all traffic will be sent to one destination. The destination router is the gateway of last resort. The default route is not configured on the gateway, but on the router sending traffic to the gateway. The router IOS does not matter.
14. Refer to the exhibit. This network has two connections to the ISP, one via router C and one via router B. The serial link between router A and router C supports EIGRP and is the primary link to the Internet. If the primary link fails, the administrator needs a floating static route that avoids recursive route lookups and any potential next-hop issues caused by the multiaccess nature of the Ethernet segment with router B. What should the administrator configure?
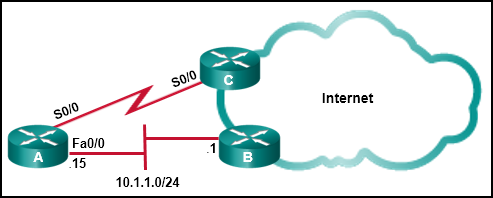
- Create a static route pointing to 10.1.1.1 with an AD of 95.
- Create a fully specified static route pointing to Fa0/0 with an AD of 1.
- Create a fully specified static route pointing to Fa0/0 with an AD of 95.
- Create a static route pointing to 10.1.1.1 with an AD of 1.
- Create a static route pointing to Fa0/0 with an AD of 1.
Explanation: A floating static route is a static route with an administrative distance higher than that of another route already in the routing table. If the route in the table disappears, the floating static route will be put into the routing table in its place. Internal EIGRP has an AD of 90, so a floating static route in this scenario would need to have an AD higher than 90. Also, when creating a static route to a multiaccess interface like a FastEthernet segment a fully specified route should be used, with both a next-hop IP address and an exit interface. This prevents the router from doing a re








 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








