本文的笔记顺序就是阅读muduo库的推荐顺序。
文章目录
1.noncopyable
要点
类如其名,继承自它的类,不能通过拷贝构造和赋值运算符来创建一个相同的对象。只保留了构造和析构。
比较巧妙的也在于对于每一个不可复制的类,不需要一一delete掉赋值和拷贝构造,只需要继承自这个类即可。

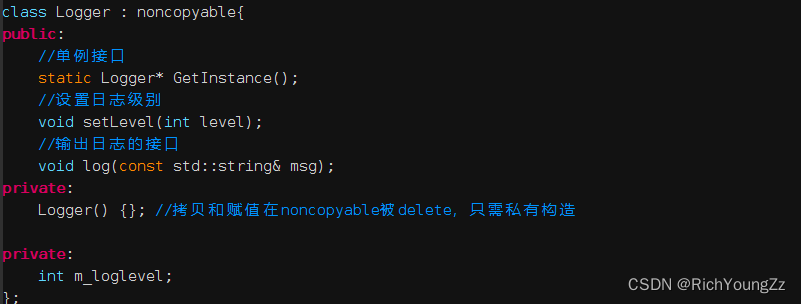
2.Logger
要点
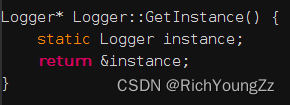
这里,值得一提的是,Logger是个局部静态变量创建的单例。这里有两点需要注意:
- 因为是static静态变量,所以可以保证这个变量在创建以后一直存在于内存;
- 应用了C++11的特性来保证线程安全:如果当变量在初始化的时候,并发同时进入声明语句,并发线程将会阻塞等待初始化结束
代码
剩下的Logger代码就没什么好说的了,这个Logger也是极其简陋,只是打印出时间 + 日志级别 + 我们备注的字符串而已。
//Logger.h
#pragma once
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include "noncopyable.h"
/*
* 这个日志做成了单例类,这样宏定义的话,感觉存在线程安全的问题
* 有可能输出的是一个线程的level,但是输出的是另一个线程的msg
* 这里我觉得后期还有值得修改的地方
*/
#define LOG_INFO(logFormat, ...) \
do { \
char msg[2048] = {0}; \
snprintf(msg, 2048, logFormat, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
mymuduo::Logger::GetInstance()->setLevel(mymuduo::LogLevel::INFO); \
mymuduo::Logger::GetInstance()->log(msg); \
} while(0)
#ifdef MDDEBUG
#define LOG_DEBUG(logFormat, ...) \
do { \
char msg[2048] = {0}; \
snprintf(msg, 2048, logFormat, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
mymuduo::Logger::GetInstance()->setLevel(mymuduo::LogLevel::DEBUG); \
mymuduo::Logger::GetInstance()->log(msg); \
} while(0)
#else
#define LOG_DEBUG(logFormat, ...)
#endif
#define LOG_ERROR(logFormat, ...) \
do { \
char msg[2048] = {0}; \
snprintf(msg, 2048, logFormat, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
mymuduo::Logger::GetInstance()->setLevel(mymuduo::LogLevel::ERROR); \
mymuduo::Logger::GetInstance()->log(msg); \
} while(0)
#define LOG_FATAL(logFormat, ...) \
do { \
char msg[2048] = {0}; \
snprintf(msg, 2048, logFormat, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
mymuduo::Logger::GetInstance()->setLevel(mymuduo::LogLevel::FATAL); \
mymuduo::Logger::GetInstance()->log(msg); \
exit(-1); \
} while(0)
namespace mymuduo {
enum LogLevel {
INFO, //跟踪中间流程
DEBUG, //调试时候使用
ERROR, //某些运行时候遇到错误,但是大多是逻辑上的,不会导致程序中断
FATAL //致命错误,会导致程序crash
};
/*
* 日志类,单例
*/
class Logger : noncopyable{
public:
//单例接口
static Logger* GetInstance();
//设置日志级别
void setLevel(int level);
//输出日志的接口
void log(const std::string& msg);
private:
Logger() {}; //拷贝和赋值在noncopyable被delete,只需私有构造
private:
int m_loglevel;
};
}
//Logger.cc
#include "Logger.h"
#include "Timestamp.h" //自己写的头文件尽量在源文件中声明,源文件被编译后是在so库中,这样对外暴露的就会少
namespace mymuduo {
Logger* Logger::GetInstance() {
static Logger instance;
return &instance;
}
void Logger::setLevel(int level) {
m_loglevel = level;
}
void Logger::log(const std::string& msg){
std::ostringstream oss;
switch(m_loglevel) {
case INFO:
oss << " [INFO] ";
break;
case DEBUG:
oss << " [DEBUG] ";
break;
case ERROR:
oss << " [ERROR] ";
break;
case FATAL:
oss << " [FATAL] ";
break;
}
oss << Timestamp::now().toString()
<< " "
<< msg
<< std::endl;
std::cout << oss.str();
}
}
/*
//测试Logger和Timestamp两个类
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
LOG_INFO("i love %s %d years %s %d", "yzz", 3000, __FILE__, __LINE__);
LOG_DEBUG("i love %s %d years", "yzz", 3000);
LOG_ERROR("i love %s %d years", "yzz", 3000);
LOG_FATAL("i love %s %d years", "yzz", 3000);
return 0;
}
*/
存在的问题
这里还有一点需要我非常注意,注意看我的宏定义,这两行,我自认为输出日志的时候是存在"线程安全"问题的,有可能出现一个线程的LogLevel拼接上了另一个备注字符串。暂时还没有改,不过不可能加锁,一个线程因为输出日志加锁,那还不如不要这个功能。
mymuduo::Logger::GetInstance()->setLevel(mymuduo::LogLevel::DEBUG);
mymuduo::Logger::GetInstance()->log(msg);
3.Timestamp
要点
仅仅提供两个功能,一个是获取当前的时间戳的静态成员函数,这里返回的是一个Timestamp类的对象。另外一个功能是将时间戳转换当成我们熟知的年月日格式,利用到了头文件提供的localtime函数与strftime函数,非常方便。
代码
//Timestamp.h
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <time.h>
namespace mymuduo {
/*
* 时间类,可以获取当前时间并转换成我们熟知的年月日格式
*/
class Timestamp {
public:
Timestamp();
explicit Timestamp(int64_t time_);
//获取当前时间
static Timestamp now();
//转换为年月日格式
std::string toString() const;
private:
int64_t m_time;
};
}
//Timestamp.cc
#include "Timestamp.h"
namespace mymuduo {
Timestamp::Timestamp() : m_time(0) {
}
Timestamp::Timestamp(int64_t time_) : m_time(time_) {
}
Timestamp Timestamp::now() {
return Timestamp(time(NULL));
}
std::string Timestamp::toString() const {
struct tm tm_ = *localtime(&m_time);
char buf[64];
strftime(buf, sizeof(buf), "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", &tm_);
return buf;
}
}
4.InetAddress
要点
这个类没什么要点,保存着一个sockaddr_in结构体,学过网络编程的肯定都知道,就是传入port端口号和ip地址,用sockaddr_in来保存。外加了一些输出ip、port之类锦上添花的功能而已。
代码
//InetAddress.h
#pragma once
#include <sstream>
#include <string>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <string.h>
namespace mymuduo {
/*
* socket地址信息类,存储ip地址以及端口号的地址信息类型,暂时只支持ipv4
*/
class InetAddress {
public:
InetAddress(uint16_t port = 80, std::string ip = "127.0.0.1");
explicit InetAddress(const sockaddr_in& addr); //单参数的构造函数加explicit才有用
std::string toIp() const;
uint16_t toPort() const;
std::string toIpPort() const;
const sockaddr_in* getSockAddr() const; //跟muduo有所不同,减少一次类型转换
void setSockAddr(const sockaddr_in &addr); //设置底层的sockaddr_in
private:
struct sockaddr_in m_addr;
};
}
//InetAddress.cc
#include "InetAddress.h"
namespace mymuduo {
InetAddress::InetAddress(uint16_t port, std::string ip) {
memset(&m_addr, 0, sizeof(m_addr));
m_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
m_addr.sin_port = htons(port);
m_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip.c_str());
}
InetAddress::InetAddress(const sockaddr_in& addr)
:m_addr(addr){
}
std::string InetAddress::toIp() const {
//二进制网络字节序ip转点分十进制ip
return inet_ntoa(m_addr.sin_addr);
}
uint16_t InetAddress::toPort() const {
//网络字节序转主机字节序
return ntohs(m_addr.sin_port);
}
std::string InetAddress::toIpPort() const {
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << inet_ntoa(m_addr.sin_addr) //ip地址
<< ':'
<< ntohs(m_addr.sin_port); //端口号port
return oss.str();
}
const sockaddr_in* InetAddress::getSockAddr() const {
return &m_addr;
}
void InetAddress::setSockAddr(const sockaddr_in &addr) {
m_addr = addr;
}
}
/*
//测试InetAddress类
#include <iostream>
int main(){
mymuduo::InetAddress addr(8080);
std::cout << addr.toIp() << std::endl;
std::cout << addr.toIpPort() << std::endl;
std::cout << addr.toPort() << std::endl;
return 0;
}
*/
5.Channel
要点
这个是非常核心的一个类。
-
可以把Channel理解为一个包装,它封装了四个很重要的东西,socket_fd、它关注的事件events、实际发生的事件revents,以及不同事件发生时候对应的回调函数。
-
对每个Channel,我们会通过轮询的方式,将它放入一个EventLoop里,由EventLoop来监听Channel里面关注的事件是否有发生,发生的话就会运行Channel里面对应的事件函数。
-
使用
using EventCallback = std::function<void()>
代替
typedef std::function<void()> EventCallback;
-
它这里所使用的函数回调并非通过函数指针,而已通过function函数对象。
-
类里的函数几乎都是用来对它关注的事件events、实际发生的事件revents,以及不同事件发生时候对应的回调函数进行修改的,EventLoop和socket_fd是在构造Channel对象的时候就传入的。还有一些函数就是对前面这些东西进行查询的,不过在函数后加了const,如下:
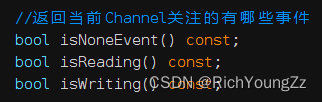
只是让我们来查询Channel的一些信息,而无法修改Channel里面封装的成员变量 -
注释里面有挺多关于代码逻辑的,可以细看一波。
代码
//Channel.h
#pragma once
#include <functional>
#include <memory>
#include <utility>
#include <assert.h>
#include "noncopyable.h"
#include "Timestamp.h" //这个必须包含,Timestamp用作函数参数,需要确定大小
namespace mymuduo {
//类的前向声明,有关头文件放源代码里面声明,这样减少暴露
class EventLoop;
/*
* Channel可以理解为通道
* 封装了两部分内容:
* 1.封装了socket_fd和其感兴趣的事件,例如EPOLLIN、EPOLLOUT等事件(读、写之类的)
* 2.封装了Channel得到Poller返回的时候,需要回调的具体事件
*/
class Channel : noncopyable {
public:
//typedef std::function<void()> EventCallback;
//typedef std::function<void(Timestamp)> ReadEventCallback;
using EventCallback = std::function<void()>; //事件回调
using ReadEventCallback = std::function<void(Timestamp)>; //只读事件的回调
Channel(EventLoop* loop, int fd);
~Channel();
//Channel得到Poller返回后,根据返回结果调用不同的EventCallback
void handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime);
//设置函数回调对象
void setReadCallback(ReadEventCallback callbackFunction);
void setWriteCallback(EventCallback callbackFunction);
void setCloseCallback(EventCallback callbackFunction);
void setErrorCallback(EventCallback callbackFunction);
//在Poller里面有removeChannel的接口,tie()就是防止Channel被我们手动remove后,还在执行回调函数
void tie(const std::shared_ptr<void>&);
//获得Event信息的函数
int fd() const;
int events() const;
int index();
//暴露接口给Poller设置revents
void set_revents(int revents);
//给Channel添加关注事件的接口
void enableReading();
void disableReading();
void enableWriting();
void disableWriting();
void disableAll(); //移除所有事件
//返回当前Channel关注的有哪些事件
bool isNoneEvent() const;
bool isReading() const;
bool isWriting() const;
//设置该Channel在EPollPoller里面的状态 new added deleted
void set_index(int idx);
//获得Channel所属事件循环
EventLoop* ownerLoop();
//应该是从事件循环删除这个Channel
void remove();
private:
/*在前面给Channel添加关注事件的时候,不只是修改m_events就行,还给使用epoll_ctl改
*epoll_ctl这部分操作封装在update里面
*/
void update();
//处理受保护的Event
void handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime);
private:
/*
* 这里是标识符的作用,该类所有对象都通用
* 如果这个对象关注读事件的话,那么(m_events & kReadEvent) == 1
* 如果这个对象关注写事件的话,那么(m_events & kWriteEvent) == 1
* m_revents类似
* 以此来判断Channel有什么事件
*/
static const int sc_kNoneEvent;
static const int sc_kReadEvent;
static const int sc_kWriteEvent;
EventLoop *m_loop; //该事件所属的事件循环
const int mc_fd; //事件的fd
int m_events; //该fd注册的事件,EPOLLIN、EPOLLOUT实际上都是一个整形
int m_revents; //real events Poller返回该fd上实际发生的事件
int m_index; //该Channel在EPollPoller中的状态 new added deleted
std::weak_ptr<void> m_tiePtr; //void表示什么类型都可以接收
bool tied_; //在此绑定自己用的,相当于share_from_this
//weak_ptr起一个检测一个对象是否还存在的作用,如果存在则可以提升为强指针,否则nullptr
//绑定不同事件的回调函数,起着类似函数指针的作用,实际上是函数对象
//可以根据Poller返回的m_revents,进行不同函数的回调
ReadEventCallback m_readCallback;
EventCallback m_writeCallback;
EventCallback m_closeCallback;
EventCallback m_errorCallback;
//标记当前Channel是否在处理事件,是否在事件循环Loop中
bool m_eventHandling;
bool m_addedToLoop;
};
}
//Channel.cc
#include "Channel.h"
#include "EventLoop.h"
#include "Logger.h"
#include <sys/epoll.h>
namespace mymuduo {
const int Channel::sc_kNoneEvent = 0;
//EPOLLPRI是带外数据,紧急数据的意思,即使缓冲区有数据,也得先接收这个
const int Channel::sc_kReadEvent = EPOLLIN | EPOLLPRI;
const int Channel::sc_kWriteEvent = EPOLLOUT;
//构造函数
Channel::Channel(EventLoop *loop, int fd)
:m_loop(loop),
mc_fd(fd),
m_events(Channel::sc_kNoneEvent),
m_revents(Channel::sc_kNoneEvent),
m_index(-1),
tied_(false),
m_eventHandling(false),
m_addedToLoop(false) {
}
//析构函数
Channel::~Channel() {
/*
//调用析构的时候,需要Event不在处理事件,并且也不在Loop里面
assert(m_eventHandling == false);
assert(m_addedToLoop == false);
//暂时不理解,之后回来看***************
if(m_loop->isInLoopThread()) {
assert(!m_loop->hasChannel(this));
}
//这个析构函数并没有释放资源,都是断言,可以暂时不需要
*/
}
/*让Channel去调用回调函数去处理事件
*这里为什么有一个if呢
*因为如果我们调用了m_tiePtr来监听,那么就先看看能不能提成强智能指针
*如果能的话,那么说明Channel还是存在的,就执行
*或者是根本没有尝试去监听,那么就直接执行
*/
void Channel::handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime) {
if(tied_) {
std::shared_ptr<void> guard = m_tiePtr.lock();
if(guard) {
handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);
}
}
else {
handleEventWithGuard(receiveTime);
}
}
/*
* 下面是设置回调函数
* 这里为什么使用std::move是有说法的
* funtcion实际上是函数对象类,本质上是类class
* 但凡涉及类,就会存在拷贝构造和移动构造的问题
* 1.先大概知道拷贝构造会涉及内存的复制,而移动构造仅仅是内存的移动
* 2.callbackFunction作为一个左值,但是在set函数结束以后就不再使用了
* 3.所以我们可以再它销毁之前,使用std::move()将其转换成右值
* 4.这样在类似m_readCallback = std::move(callbackFunction);语句的时候,调用的是移动构造而非拷贝构造
* 5.这样直接占据了callbackFunction的内存,而非重新复制一份,大大提高了效率
*/
void Channel::setReadCallback(ReadEventCallback callbackFunction) {
m_readCallback = std::move(callbackFunction);
}
void Channel::setWriteCallback(EventCallback callbackFunction) {
m_writeCallback = std::move(callbackFunction);
}
void Channel::setCloseCallback(EventCallback callbackFunction) {
m_closeCallback = std::move(callbackFunction);
}
void Channel::setErrorCallback(EventCallback callbackFunction) {
m_errorCallback = std::move(callbackFunction);
}
/*
* 设置回调函数到此为止
*/
//用weak_ptr<void> tie来观察强智能指针 这里也有点不理解************
void Channel::tie(const std::shared_ptr<void> &obj) {
m_tiePtr = obj;
tied_ = true;
}
//获得Event信息的函数
int Channel::fd() const {
return mc_fd;
}
int Channel::events() const {
return m_events;
}
int Channel::index() {
return m_index;
}
//暴露接口给Poller设置revents
void Channel::set_revents(int revents) {
m_revents = revents;
}
//给Channel添加关注事件的接口
void Channel::enableReading() {
m_events |= sc_kReadEvent;
update();
}
void Channel::disableReading() {
m_events &= ~sc_kReadEvent;
update();
}
void Channel::enableWriting() {
m_events |= sc_kWriteEvent;
update();
}
void Channel::disableWriting() {
m_events &= ~sc_kWriteEvent;
update();
}
void Channel::disableAll() {
m_events = sc_kNoneEvent;
update();
}
//返回当前Channel关注的有哪些事件
bool Channel::isNoneEvent() const {
return m_events == sc_kNoneEvent;
}
bool Channel::isReading() const {
return m_events & sc_kReadEvent;
}
bool Channel::isWriting() const {
return m_events & sc_kWriteEvent;
}
//index其实是Channel在EPollPoller里面的状态,是new,还是added,还是deleted
void Channel::set_index(int idx) {
m_index = idx;
}
//获得Channel所属事件循环
EventLoop* Channel::ownerLoop() {
return m_loop;
}
//Channel通知EventLoop把自己移除
void Channel::remove() {
assert(isNoneEvent());
m_addedToLoop = false;
m_loop->removeChannel(this);
}
/* 改变Channel关注的事件后,需要update()调用到EventLoop,
* EventLoop再去通知Poller,使得Poller修改epoll里该fd关注的事件
*/
void Channel::update() {
m_addedToLoop = true;
m_loop->updateChannel(this);
}
//根据Poller通知Channel发生的具体事件,由Channel执行响应回调事件
void Channel::handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime) {
LOG_INFO("Channel fd: %d, handleEvent revents: %d\n", mc_fd, m_revents);
m_eventHandling = true;
//检测到fd读写关闭的处理
//如果发现这个fd的读写都关闭了,并且没有EPOLLIN,也就是没有待读取数据
if((m_revents & EPOLLHUP) && (m_revents & EPOLLIN) == 0) {
if(m_closeCallback) {
m_closeCallback();
}
}
//检测到错误时候的处理
//如果发现这个fd出现错误,原版是&(POLLERR | POLLNVAL)
//而POLLNVAL是指这个fd没有被打开,除非人为故意,否则永远不会出现这种情况
if(m_revents & EPOLLERR) {
if(m_errorCallback) {
m_errorCallback();
}
}
//检测到读事件的时候处理
//EPOLLRDHUP指不再往内核缓冲区加内容。已在内核缓冲区的内容,依然能读取到
//感觉EPOLLRDHUP可有可无
if(m_revents & (EPOLLIN | EPOLLPRI | EPOLLRDHUP)) {
if(m_readCallback) {
m_readCallback(receiveTime);
}
}
//检测到写事件的时候处理
if(m_revents & EPOLLOUT) {
if(m_writeCallback) {
m_writeCallback();
}
}
m_eventHandling = false;
}
}
/*
//测试Channel类
int main() {
//mymuduo::Channel a;
return 0;
}
*/
6.Poller
要点
-
内置一个unordered_map<int, Channel*>,原muduo里面使用的是map。因为我们Epoll监听的是socket_fd,我们通过unordered_map,来找到对应Channel
-
Poller只是一个抽象类。设计好epoll、更新Channel、删除Channel的接口,具体实现放到继承这个抽象类的子类中去实现。
-
还有一个接口可以获取默认Poller
代码
//Poller.h
#pragma once
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <map>
#include "noncopyable.h"
#include "Timestamp.h"
namespace mymuduo {
class Channel;
class EventLoop;
/*
* muduo库中事件分发器的核心,IO多路复用模块
* 这是一个抽象类,很多纯虚函数,可以继承成select、poll、epoll
* 当然我们只去实现epoll_wait
*/
class Poller : noncopyable {
public:
using ChannelList = std::vector<Channel*>;
Poller(EventLoop *loop);
virtual ~Poller() = default;
//给IO复用部分提供的接口
//poll接口相当于就是epoll_wait
virtual Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList *activeChannels) = 0;
virtual void updateChannel(Channel *channel) = 0;
virtual void removeChannel(Channel *channel) = 0;
//判断当前channel是否在当前Poller中
virtual bool hasChannel(Channel *channel) const;
//获取该接口获取每个EventLoop下默认的IO复用的Poller
static Poller* newDefaultPoller(EventLoop *loop);
/*
* 有趣的是,newDefaultPoller方法并不会在Poller.cc实现
* 因为虽然返回的是一个Poller基类的指针,但是实际上指向的是一个EpollPoller的对象
* 如果在Poller.cc里面这么实现了,需要包含EpollPoller的头文件
* 基类头文件包含子类头文件,这样的设计显然是不合理的
* 所以在实现EpollPoller以后,我们会另外去实现一个DefaultPoller.cc来实现整个函数
*/
protected:
//存储该Poller正在监听的Channel
using ChannelMap = std::unordered_map<int, Channel*>; //应该比map更高效
//key值是fd,value则是该fd所属的Channel
ChannelMap m_channel_items;
private:
EventLoop *m_loop; //该Poller所属的事件循环EventLoop
};
}
//Poller.cc
#include "Poller.h"
#include "Channel.h"
namespace mymuduo {
Poller::Poller(EventLoop *loop)
:m_loop(loop) {
}
//判断当前channel是否在当前Poller中
bool Poller::hasChannel(Channel *channel) const {
auto it = m_channel_items.find(channel->fd());
return (it != m_channel_items.end() && it->second == channel) ? true : false;
}
}
7.EPollPoller
原muduo库里面有PollPoller,但是我并没有去实现,只实现了EPollPoller
要点
-
这里传给epoll_wait接收数据的地方不是普通数组,而是vector数组,初始长度定为16,之后如果填满了,则两倍扩容。
-
struct epoll_event结构体有个void* ptr指针,可以携带数据,muduo在此将该socket_fd对应的Channel*传入。
-
我们之前在Channel类里面写的index成员变量,其实就是为了标记这个Channel是否已经被添加到了EPollPoller中。根据是否被添加,我们在更新它关注的事件的时候,选择是EPOLL_CTL_ADD还是EPOLL_CTL_MOD。
-
EPollPoller监听到有事件发生的Channel,会填充到ChannelList *activeChannels中。EventLoop接收到这个ChannelList以后,就会开始执行每个Channel发生对应事件时候需要运行的函数。
-
Channel需要更新的时候,是先汇报给EventLoop,EventLoop再调用自己的EPollPoller提供的接口来完成update()和remove()等。
代码
//EPollPoller.h
#pragma once
#include "Poller.h"
#include "Timestamp.h"
#include <vector>
#include <sys/epoll.h>
namespace mymuduo {
class Channel;
class EPollPoller : public Poller {
public:
EPollPoller(EventLoop *loop); //epoll_create epollfd
~EPollPoller() override; //close epollfd
//重写Poller里的IO复用接口,主要内容还是epoll_ctl、epoll_wait等
Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList *activeChannels) override; //epoll_wait
void updateChannel(Channel *channel) override; //epoll_ctl add/mod
void removeChannel(Channel *channel) override; //epoll_ctl del
private:
//初始化vector长度用
static const int s_kInitEventListSize = 16;
//供上面三个重写的接口调用
//填写活跃的连接
void fillActiveChannels(int numEvents, ChannelList *activeChannels) const;
//更新Channel
void update(int operation, Channel *channel);
using EventList = std::vector<struct epoll_event>;
int m_epollfd;
EventList m_event_vec;
};
}
//EPollPoller.cc
#include "EPollPoller.h"
#include "Logger.h"
#include "Channel.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <assert.h>
namespace mymuduo {
//标记Channel在当前Poller里面的状态的时候会使用到
const int kNew = -1; //Channel.index = c_kNew; 代表当前Channel是新的,未加入EPollPoller
const int kAdded = 1; //Channel.index = c_kAdded; 代表当前Channel已经加入EpollPoller
const int kDeleted = 2; //Channel.index = c_kDeleted; 代表当前Channel已经被该EPollPoller删除
EPollPoller::EPollPoller(EventLoop *loop)
:Poller(loop),
m_epollfd(::epoll_create1(EPOLL_CLOEXEC)),//EPOLL_CLOEXEC在子进程启用时,会关闭父进程打开的fd
m_event_vec(s_kInitEventListSize) //初始化vector
{
//如果epollfd都没创建成功,那么汇报异常然后退出即可.
if(m_epollfd < 0) {
LOG_FATAL("epoll_create1 fail, errno : %d\n", errno);
}
}
EPollPoller::~EPollPoller() {
::close(m_epollfd);
}
//重写Poller基类的IO复用接口
//Channel update/remove -> EventLoop update/remove -> EPollPoller update/remove
Timestamp EPollPoller::poll(int timeoutMs, ChannelList *activeChannels) {
//activeChannels是一个接收发生事情channel的vector
//EPollPoller填充activeChannels给EventLoop
//EventLoop在根据这个activeChannels通知相应channel回调
int numEvents = ::epoll_wait(m_epollfd,
&*m_event_vec.begin(),
static_cast<int>(m_event_vec.size()),
timeoutMs);
int savedErrno = errno;
Timestamp now_time(Timestamp::now());
if(numEvents > 0) {
fillActiveChannels(numEvents, activeChannels);
if(static_cast<size_t>(numEvents) == m_event_vec.size()) {
//把vector填满了,说明事件很可能大于vector了,需要我们扩容vector接收更多事件
m_event_vec.resize(m_event_vec.size() << 1);
}
}
else if(numEvents == 0) {
//LOG_INFO("nothing happend");
}
else {
//如果不是系统调用被中断,而是其他原因的话,我们就要看看
if(savedErrno != EINTR) {
LOG_ERROR("EPollPoller::poll() error = %d", savedErrno);
}
}
return now_time;
}
void EPollPoller::updateChannel(Channel *channel) {
LOG_INFO("fun %s: fd = %d, events = %d, index = %d\n",__FUNCTION__, channel->fd(), channel->events(), channel->index());
const int index = channel->index();
/*
* 一个channel在此有两种情况
* 1.kNew,还没有加入EPollPoller
* 2.kDeleted,已经加入了EPollPoller,但是没有关注事件
* 也就是kNoneEvents,这时候channel还在EPollPoller,但不在epoll_wait监听
*/
int fd = channel->fd();
if(index == kNew || index == kDeleted) {
if(index == kNew) {
//要新添加,需要assert保证该fd没有存在EPollPoller中
assert(m_channel_items.find(fd) == m_channel_items.end());
m_channel_items[fd] = channel;
}
else { //index == c_kDeleted
//要把Deleted的重新加回去,需要保证channel已经在EPollPoller中,只是没有加入epoll_wait而已
assert(m_channel_items.find(fd) != m_channel_items.end());
assert(m_channel_items[fd] == channel);
}
channel->set_index(kAdded);
update(EPOLL_CTL_ADD, channel);
}
else {
//index == c_kAdded
//先保证channel已经添加到了EPollPoller里
assert(m_channel_items.find(fd) != m_channel_items.end());
assert(m_channel_items[fd] == channel);
assert(index == kAdded);
//如果该fd已经不关注事件了,就直接从epoll_wait删除
if(channel->isNoneEvent()) {
update(EPOLL_CTL_DEL, channel);
channel->set_index(kDeleted);
}
else {
//否则就修改
update(EPOLL_CTL_MOD, channel);
}
}
}
void EPollPoller::removeChannel(Channel *channel) {
/*
* 删除一个fd要保证如下几件事
* 1.该channel的fd在EPollPoller中
* 2.该fd对应的确实是当前channel
* 3.该channel的fd没有关注的事件了
* 4.channel->index() == c_kAdded | c_kDeleted,说明该channel是在这个EPollPoller中的
*/
int fd = channel->fd();
int index = channel->index();
assert(m_channel_items.find(fd) != m_channel_items.end());
assert(m_channel_items[fd] == channel);
assert(channel->isNoneEvent());
assert(index == kAdded | index == kDeleted);
int num = m_channel_items.erase(fd);
assert(num == 1);
//如果index == c_kAdded,说明还在epoll_wait中,否则,就已经不在epoll_wait中了
if(index == kAdded) {
update(EPOLL_CTL_DEL, channel);
}
//从EPollPoller删除以后,设置一下index状态即可
channel->set_index(kNew);
}
//填写活跃链接
void EPollPoller::fillActiveChannels(int numEvents, ChannelList *activeChannels) const {
assert(static_cast<size_t>(numEvents) <= m_event_vec.size()); //保证事件数量没有问题
for(int i = 0; i < numEvents; ++i) {
Channel* channel = static_cast<Channel*>(m_event_vec[i].data.ptr); //epoll时携带数据发挥作用了
#ifndef MDDEBUG
int fd = channel->fd();
auto it = m_channel_items.find(fd);
assert(it != m_channel_items.end());
assert(it->second == channel);
#endif
//如果这个fd和channel正常挂钩,那么直接把这个channel填入接收信息的activeChannels
channel->set_revents(m_event_vec[i].events);
activeChannels->emplace_back(channel);
}
}
//更新Channel通道
//也就是修改epoll_ctl
void EPollPoller::update(int operation, Channel *channel) {
struct epoll_event ev;
int fd = channel->fd();
memset(&ev, 0, sizeof(ev));
ev.events = channel->events();
ev.data.ptr = channel; //epoll_event中有个void *ptr指针,可以携带数据,可以携带我们的channel
ev.data.fd = fd;
if(::epoll_ctl(m_epollfd, operation, fd, &ev) < 0) {
if(operation == EPOLL_CTL_DEL) {
//如果是删除的话,没删掉这个fd,并不会影响其他fd运行
LOG_ERROR("epoll op = %s, fd = %d error\n", "EPOLL_CTL_DEL", fd);
}
else {
//如果是加入或者修改失败,那就影响到当前fd的运行了
LOG_FATAL("epoll op = %s, fd = %d error\n", "EPOLL_CTL_MOD|EPOLL_CTL_ADD", fd);
}
}
}
}
8.CurrentThread
要点
-
使用了__thread关键字,创建了对于当前线程而已的"全局变量",而非整个程序的全局变量。类似C++thread_local关键字。每启动一个线程就会创建一个具有__thread关键字的变量。
-
这个程序是为了获取当前线程在Linux内核中的线程ID也就是tid,这里调用的是syscall而非pthread_self。syscall获得的才是系统内核中真正的tid,对于pthread_self()而言,不同的进程中的线程可以有相同的pthread_self()返回。
-
使用了__builtin_expect()语句,__builtin_expect()括号内的情况大概率不会发生,所以告诉CPU先预加载后面的语句。
代码
//CurrentThread.h
#pragma once
namespace mymuduo {
namespace CurrentThread {
//__thread说明这个"全局"变量,不是真正意义上的全局
//不是整个程序的全局,而是这个线程的全局
//当有线程启动了,就会拷贝一个__thread标识的变量,这个变量只有该线程可见
//C++提供了thread_local关键字,作用类似
extern __thread int t_cachedTid;
extern __thread char t_tidString[32];
extern __thread int t_tidStringLength;
extern __thread const char* t_threadName;
void cacheTid();
inline int tid() {
//__builtin_expect是在告诉CPU,t_cacheTid == 0情况几乎不会出现
//预加载return t_cachedTid;语句就行了 这样提高了CPU的效率
if(__builtin_expect(t_cachedTid == 0, 0)) {
cacheTid();
}
return t_cachedTid;
}
}
}
#include "CurrentThread.h"
#include <sys/syscall.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
namespace mymuduo {
namespace CurrentThread {
__thread int t_cachedTid = 0;
__thread char t_tidString[32];
__thread int t_tidStringLength = 6;
__thread const char* t_threadName = "unknow";
void cacheTid() {
//syscall得到的tid才是Linux系统内核里面的tid
//pthread_self并不是,不同的进程中可能有相同的pthread_self()
if(t_cachedTid == 0) {
t_cachedTid = static_cast<pid_t>(::syscall(SYS_gettid));
}
}
}
}
9.EventLoop
这是muduo库里面极其重要的一部分。
要点
-
首先,有一个__thread关键字的指针,指向当前创建的EventLoop,保证每个线程只有一个EventLoop。
-
一个EventLoop管理多个Channel和一个EPollPoller,Channel和EPollPoller之间无法直接联系,必须通过EventLoop暴露的接口。
-
在EventLoop下会创建一个eventfd作为wakeupFd。mainLoop在接收到新连接以后,会轮询选择一个subLoop,并且通过这个subLoop的wakeupFd去唤醒它,并且分发新连接的Channel给它。
-
当你调用这个EventLoop的loop()函数以后,EventLoop就会调用自己的EPollPoller开始epoll_wait(),并且返回一个有事件发生的Channel列表,EventLoop去通知这个列表的Channel执行相应回调。
-
atomic变量是采用CAS无锁同步实现的
CAS 操作包含三个操作数 —— 内存位置(V)、预期原值(A)和新值(B)。
如果内存位置的值与预期原值相匹配,那么处理器会自动将该位置值更新为新值,否则不作任何处理 -
这里线程通信采用eventfd实现,其他实现方式还有管道、socketpair
管道的通信是半双工的,socketpair虽然是全双工的,但是跟网络有关,效率不如eventfd
eventfd可以绑定成epoll_fd监听的对象,mainReactor收到新用户连接以后,用轮询算法选择subReactor,通过这个m_wakeupFd来唤醒
代码
//EventLoop.h
#pragma once
#include <functional>
#include <vector>
#include <atomic>
#include <memory>
#include <mutex>
#include "noncopyable.h"
#include "Timestamp.h"
namespace mymuduo{
class Poller;
class Channel;
/*
* 时间循环类,主要的部分就是多个Channel和一个Poller
* Channel可以视作是Event信息及其对应处理的集合
* Poller是Epoll的抽象,muduo里面其实有poll和epoll的接口,在此我们只实现epoll
*/
class EventLoop : noncopyable {
public:
using Functor = std::function<void()>;
EventLoop();
~EventLoop();
//开启事件循环
void loop();
//退出事件循环
void quit();
//Poller返回时候的时间
Timestamp pollReturnTime() const;
//在当前EventLoop中执行的回调
void runInLoop(Functor callbackFunction);
//把这个回调cb函数放入队列,唤醒该cb所属的EventLoop执行回调
void queueInLoop(Functor callbackFunction);
//mainReactor唤醒其余subReactor时候使用
void wakeup();
//EventLoop提供接口给channel,让channel通过这个接口加入Poller中
void updateChannel(Channel *channel);
void removeChannel(Channel *channel);
bool hasChannel(Channel *channel);
//查询当前线程和运行的EventLoop是否是同一个tid
bool isInLoopThread() const;
private:
//应该是提供接口给public调用
void handleRead();
void doPendingFunctors();
using ChannelList = std::vector<Channel*>;
//标记当前EventLoop是在运行还是退出
std::atomic_bool m_looping;
std::atomic_bool m_quit;
std::atomic_bool m_eventHanding;
/*
* atomic变量是采用CAS无锁同步实现的
* CAS 操作包含三个操作数 —— 内存位置(V)、预期原值(A)和新值(B)。
* 如果内存位置的值与预期原值相匹配,那么处理器会自动将该位置值更新为新值,否则不作任何处理
*/
//记录当前EventLoop所在线程的tid
const pid_t m_threadId;
//Poller返回事件时候的时间
Timestamp m_pollReturnTime;
std::unique_ptr<Poller> m_poller; //每个EventLoop都管理有一个Poller
/*
* 这里线程通信采用eventfd实现,其他实现方式还有管道、socketpair
* 管道的通信是半双工的,socketpair虽然是全双工的,但是跟网络有关,效率不如eventfd
* eventfd可以绑定成epoll_fd监听的对象,mainReactor收到新用户连接以后,用轮询算法选择subReactor,通过这个m_wakeupFd来唤醒
*/
int m_wakeupFd;
std::unique_ptr<Channel> m_wakeupChannel; //和其他fd一样,都对应有一个channel,通过回调来完成任务
ChannelList m_activeChannels;
Channel *m_currentActiveChannel; //断言assert使用到
std::atomic_bool m_callingPengdingFunctors; //表示当前EventLoop是否有需要执行的回调操作
std::vector<Functor> m_pendingFunctors; //存储当前EventLoop需要执行的所有回调操作
std::mutex m_mutex; //保护m_pendingFunctors线程安全的互斥锁
};
}
//EventLoop.cc
#include "EventLoop.h"
#include "CurrentThread.h"
#include "Logger.h"
#include "Channel.h"
#include "Poller.h"
#include <sys/eventfd.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
namespace mymuduo {
//指向当前线程的EventLoop,也可以检测一个线程是否创建EventLoop,防止创建多个
__thread EventLoop *t_loopInThisThread = nullptr;
const int kPollTimeMs = 10000; //默认10s的epoll_wait阻塞时间
//全局函数,用于创建eventfd使用
int createEventfd() {
//将该fd设置为非阻塞 | 在fork出子进程,子进程调用exec执行其他程序的时候,就会在子进程关闭这个fd
int evtfd = ::eventfd(0, EFD_NONBLOCK | EFD_CLOEXEC);
if(evtfd < 0) {
LOG_ERROR("Failed in createEventfd\n");
abort();
}
return evtfd;
}
EventLoop::EventLoop()
:m_looping(false),
m_quit(false),
m_eventHanding(false),
m_threadId(CurrentThread::tid()),
m_poller(Poller::newDefaultPoller(this)),
m_wakeupFd(createEventfd()),
m_wakeupChannel(new Channel(this, m_wakeupFd)),
m_currentActiveChannel(nullptr),
m_callingPengdingFunctors(false) {
if(t_loopInThisThread) {
//一个线程只有一个EventLoop
LOG_FATAL("Another EventLoop exists in this thread : %d\n", m_threadId);
}
else {
t_loopInThisThread = this;
}
//设置wakeupFd的回调操作
m_wakeupChannel->setReadCallback(std::bind(&EventLoop::handleRead, this));
m_wakeupChannel->enableReading();
}
EventLoop::~EventLoop() {
//将wakeupFd及其channel设置为不关注任何事件,并且从Poller中移除
//一般析构函数需要手动释放的是指针、文件描述符fd、new申请的资源
//在EventLoop中,我们申请的指针都是new出来的,并且交给!智能指针!去管理了,所以我们在此只用关闭文件描述符
m_wakeupChannel->disableAll();
m_wakeupChannel->remove();
::close(m_wakeupFd);
t_loopInThisThread = nullptr;
}
void EventLoop::loop() {
assert(!m_looping);
m_looping = true;
m_quit = false;
LOG_INFO("EventLoop %p start looping", this);
while(!m_quit) {
//清空ChannelList并且开始epoll_wait监听
m_activeChannels.clear();
//这里会监听两种fd,一种是client_fd,另一种是eventfd(唤醒EventLoop时候用)
m_pollReturnTime = m_poller->poll(kPollTimeMs, &m_activeChannels);
//可以在此给ChannelList里的Channel排序
m_eventHanding = true;
for(Channel *channel : m_activeChannels) {
//EventLoop通知Channel进行响应事件处理
m_currentActiveChannel = channel;
m_currentActiveChannel->handleEvent(m_pollReturnTime);
}
m_eventHanding = false;
m_currentActiveChannel = nullptr;
//执行当前EventLoop所需的回调
/*
* mainLoop => accept => fd => channel => subLoop
* mainLoop需要分发fd给subLoop,不需要subLoop从阻塞队列里面取
* 1.完成这个过程,需要mainLoop事先注册回调
* 2.wakeup subLoop
* 3.subLoop来执行mainLoop注册的这个回调
*/
doPendingFunctors();
}
LOG_INFO("EventLoop %p stop looping", this);
m_looping = false;
}
/*
* 退出EventLoop有两种情况
* 1.loop所在线程自己退出loop,那么一定会是自己处理完了epoll_wait,处理完自己的事情以后申请退出,这个就不需要我们多作处理
* 2.其他线程要让这个loop退出,但是这个时候loop可能还在处理自己的事情
* 我们回去看loop()函数,这个函数只可能在m_poller->poll()阻塞住,那么我们就要wakeup()发送信号,让它立即结束阻塞,退出loop
*/
void EventLoop::quit() {
m_quit = true;
if(!isInLoopThread()) {
wakeup();
}
}
Timestamp EventLoop::pollReturnTime() const {
return m_pollReturnTime;
}
void EventLoop::runInLoop(Functor callbackFunction) {
/*
* 如果当前Loop在当前线程,那么就直接执行这个callbackFunction函数的回调
* 否则的话,说明当前Loop并不在当前线程中,没有资格执行callbackFunction函数
* 那么就放入一个队列(实质是vector)中,等待到自己的线程再去执行
*/
if(isInLoopThread()) {
callbackFunction();
}
else {
queueInLoop(std::move(callbackFunction));
}
}
void EventLoop::queueInLoop(Functor callbackFunction) {
/*
* 这是一个智能锁
* 在其声明周期内会持有这把锁(如果这把锁没被锁的话,否则阻塞)
* 在{}结束以后,它会自动释放这把锁
* 至于为什么放入vector要加锁呢,那是因为可能有多个线程都发生这件事
*/
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(m_mutex);
m_pendingFunctors.emplace_back(std::move(callbackFunction));
}
if(!isInLoopThread() || m_callingPengdingFunctors == true) {
wakeup();
}
}
//通过向eventfd写入数据,来唤醒subReactor
void EventLoop::wakeup() {
uint64_t one = 1;
ssize_t n = write(m_wakeupFd, &one, sizeof(one));
if(n != sizeof(one)) {
LOG_ERROR("EventLoop::wakeup() writes %d bytes instead of 8\n", n);
}
}
void EventLoop::updateChannel(Channel *channel) {
assert(channel->ownerLoop() == this);
//调用Poller接口
m_poller->updateChannel(channel);
}
void EventLoop::removeChannel(Channel *channel) {
assert(channel->ownerLoop() == this);
//要删除这个channel的话,需要保证这个channel已经被currentActiveChannel记录
//或者是这个channel没有事件要处理
if(m_eventHanding) {
assert(m_currentActiveChannel == channel
||
std::find(m_activeChannels.begin(), m_activeChannels.end(), channel) == m_activeChannels.end());
}
m_poller->removeChannel(channel);
}
bool EventLoop::hasChannel(Channel *channel) {
return m_poller->hasChannel(channel);
}
bool EventLoop::isInLoopThread() const {
return m_threadId == CurrentThread::tid();
}
//把wakeup写入的数据给读空
//因为我们的epoll是水平触发,为了防止被一直唤醒,需要读空数据
void EventLoop::handleRead() {
uint64_t one = 1;
ssize_t n = read(m_wakeupFd, &one, sizeof(one));
if(n != sizeof(one)) {
LOG_ERROR("EventLoop::wakeup() reads %d bytes instead of 8\n", n);
}
}
void EventLoop::doPendingFunctors() {
std::vector<Functor> tempPendingFunctors;
m_callingPengdingFunctors = true;
/*
* 这一部分拿局部vector来存储这个Loop的vector非常巧妙
* 因为你在执行这个Loop的回调的时候,很有可能还有别的地方向这个Loop注册回调
* 我们可以把向Loop注册回调看作写事件,把Loop执行回调看作读事件
* 这么做相当于"读写分离"
* 拿局部变量存储了Functor以后,"读"和"写"就可以并发进行了,而不是读需要等写的锁,写需要等读的锁,显然这样更加高效
* 当然,为了保证线程安全,下面加的一次锁还是需要的
*/
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(m_mutex);
tempPendingFunctors.swap(m_pendingFunctors);
}
for(const Functor& functor : tempPendingFunctors) {
functor();
}
m_callingPengdingFunctors = false;
}
}
10.Thread
要点
- 这只是一个简单的线程类,对线程的主函数进行了一层封装,可以给线程赋予名字并且记录线程tid,并且创建这个线程类的对象时,仅仅是传入线程主函数,而线程什么时候开始,由你什么时候调用类中start()函数来决定,还可以调用类中join()函数来将线程设置为join()状态。
- 在其中,使用了信号量。Thread类及其所在线程,需要成功创建完新线程,获取到新线程的tid才能正常使用,所以使用了信号量来保证同步。
- 总的来说,Thread类主要是起到一个记录线程信息,开启线程的作用。
- Thread类开启子线程以后,子线程的第一步就是获取tid,也就是39行
Thread::start()所处线程和子线程是两个线程,如果不加信号量来阻塞的话,调用完Thread::start()不能保证子线程创建并运行
而加了信号量阻塞,只有子线程创建并且获取tid之后,Thread::start()才正常结束,信号量在此作一个保证子线程成功创建的作用
代码
//Thread.h
#pragma once
#include "noncopyable.h"
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string>
#include <atomic>
#include <memory>
#include <thread>
#include <functional>
namespace mymuduo {
class Thread : noncopyable {
public:
using ThreadFunc = std::function<void()>;
explicit Thread(ThreadFunc, const std::string &name = std::string());
~Thread();
void start();
void join();
/*
* 获取成员变量值的函数
*/
bool started() const;
pid_t tid() const;
const std::string& name() const;
static int numCreated();
private:
void setDefaultName(); //设置线程的默认名字
bool m_started; //记录线程是否启动
bool m_joined; //记录线程是否是join状态
/*
* 何为join,如果线程是join状态,那么相当于把这个线程和主线程合并
* 主线程要等待这个线程结束,才会一起结束
* 如果这个线程设置了detach分离状态,而非join,那么它和主线程的运行就独立了
*/
std::shared_ptr<std::thread> m_threadPtr;
/*
* 这里不能直接设置一个std::thread的对象,一旦设置,就会直接启动一个线程
* 我们这里选择设置一个指针,那么什么时候启动线程就是我们自己决定了
*/
pid_t m_tid;
ThreadFunc m_func; //线程的主函数
std::string m_name; //线程名字
static std::atomic_int m_numCreated; //记录我们创建线程的数量
};
}
#include "Thread.h"
#include "CurrentThread.h"
#include <semaphore.h> //信号量头文件
namespace mymuduo {
std::atomic_int m_numCreated(0);
Thread::Thread(ThreadFunc func, const std::string& name)
:m_started(false),
m_joined(false),
m_tid(0),
m_func(std::move(func)),
m_name(name) {
setDefaultName();
}
Thread::~Thread() {
if(m_started == true && m_joined == false) {
//如果线程已经运行,并且没有设置成join状态,那么就设置成分离线程
m_threadPtr->detach();
}
}
//Thread类就是为了记录一个新线程的各种信息而存在的
void Thread::start() {
m_started = true;
//初始化一个信号量
sem_t sem;
sem_init(&sem, false, 0);//第二个参数为true代表进程间使用
//开启线程
//lambda表达式作为线程的主函数
m_threadPtr = std::shared_ptr<std::thread>(new std::thread([&]() {
//获取该线程的tid
m_tid = CurrentThread::tid();
sem_post(&sem); //信号量+1
m_func(); //这才是线程的真正该执行的函数
}));
/*Thread类开启子线程以后,子线程的第一步就是获取tid,也就是39行
Thread::start()所处线程和子线程是两个线程,如果不加信号量来阻塞的话,调用完Thread::start()不能保证子线程创建并运行
而加了信号量阻塞,只有子线程创建并且获取tid之后,Thread::start()才正常结束,信号量在此作一个保证子线程成功创建的作用
*/
sem_wait(&sem);
}
void Thread::join() {
//完成一些简单设置即可
m_joined = true;
m_threadPtr->join();
}
bool Thread::started() const {
return m_started;
}
pid_t Thread::tid() const {
return m_tid;
}
const std::string& Thread::name() const {
return m_name;
}
int Thread::numCreated() {
return m_numCreated;
}
void Thread::setDefaultName() {
int threadNum = ++m_numCreated;
if(m_name.empty()) {
char buf[16];
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "Thread%d", threadNum);
m_name = buf;
}
}
}
11.EventLoopThread
要点
- EventLoopThread将EventLoop和Thread绑定了起来,之前的EventLoop和Thread都是这个类下的一个成员。
- Thread所需要的线程主函数,在EventLoopThread里已经写好了,主要内容就是创建一个EventLoop,开始loop()。Thread类中运行的线程主函数即是EventLoopThread的一个成员函数。
- 当然,EventLoop是在新开启的线程Thread中创建,而非在建立EventLoopThread对象的时候创建,所以等EventLoop创建完以后,需要在EventLoopThread保存。但是EventLoopThread所在线程和创建EventLoop并非同一个线程,而是并发的,所以使用了条件变量,保证EventLoop被成功创建以后,再保存到EventLoopThread的指针中,防止出错。
代码
//EventLoopThread.h
#pragma once
#include "noncopyable.h"
#include "Thread.h"
#include <functional>
#include <mutex>
#include <string>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <memory>
namespace mymuduo {
class EventLoop;
class EventLoopThread : noncopyable {
public:
using ThreadInitCallback = std::function<void(EventLoop*)>;
EventLoopThread(const ThreadInitCallback& cb = ThreadInitCallback(),//线程初始化回调默认空函数
const std::string& name = std::string());
~EventLoopThread();
EventLoop* startLoop();
private:
void threadFunc();
EventLoop* m_loop;
bool m_exiting;
Thread m_thread;
//下面互斥锁和条件变量暂时不知道有什么用
std::mutex m_mutex;
std::condition_variable m_cond;
ThreadInitCallback m_callback;
};
}
//EventLoopThread.cc
#include "EventLoopThread.h"
#include "EventLoop.h"
namespace mymuduo {
EventLoopThread::EventLoopThread(const ThreadInitCallback& cb, const std::string& name)
:m_loop(nullptr),
m_exiting(false),
m_thread(std::bind(&EventLoopThread::threadFunc, this), name),
m_mutex(),
m_cond(), //C++11的条件变量不需要放入互斥锁来初始化
m_callback(cb) {
}
EventLoopThread::~EventLoopThread() {
m_exiting = true;
if(m_loop != nullptr) {
m_loop->quit();
m_thread.join();
}
}
EventLoop* EventLoopThread::startLoop() {
//先启动一个线程
m_thread.start();
EventLoop* loop = nullptr;
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(m_mutex);
//这个EventLoopThread的startLoop函数和threadFunc运行在不同线程
//条件变量和互斥锁是为了等待子线程创建完一个EventLoop
while(m_loop == nullptr) {
m_cond.wait(lock);
}
loop = m_loop;
}
return loop;
}
//下面这个函数是在EventLoopThread构造函数中,提供给新线程使用的
void EventLoopThread::threadFunc() {
//新线程中直接创建一个EventLoop
EventLoop loop;
if(m_callback) {
m_callback(&loop);
}
{
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(m_mutex);
m_loop = &loop;
m_cond.notify_one();
}
//开启EventLoop,将会调用Poller开始监听事件,在此阻塞!
loop.loop();
//当程序到这,说明EventLoop结束了,那么需要清空一下我们记录的m_loop
std::unique_lock<std::mutex> lock(m_mutex);
m_loop = nullptr;
}
}
12.EventLoopThreadPool
要点
- 这是一个管理线程池的类,内含baseLoop(也就是mainLoop),我们可以通过这个类设置线程池中线程的数量,以及开启线程池的使用。
- baseLoop是在main函数中,直接创建一个EventLoop分配给TcpServer,而一层层下来给到EventLoopThreadPool中的baseLoop保存。
- 线程池中用一个vector存储池中所有线程类的指针,还有一个vector存储每个线程中唯一的EventLoop。轮询的时候就是依次分配vector中的EventLoop。如果没有subLoop那么就会分配mainLoop出去。
代码
#pragma once
#include "noncopyable.h"
#include <string>
#include <memory>
#include <functional>
#include <vector>
namespace mymuduo {
class EventLoop;
class EventLoopThread;
class EventLoopThreadPool : noncopyable {
public:
using ThreadInitCallback = std::function<void(EventLoop*)>;
EventLoopThreadPool(EventLoop* baseLoop, const std::string& nameArg);
~EventLoopThreadPool();
void setThreadNum(int numThreads);
void start(const ThreadInitCallback& cb = ThreadInitCallback());//开启线程池使用,默认空函数
EventLoop* getNextLoop(); //轮询得到接收Channel的EventLoop
EventLoop* getLoopForHash(size_t hashCode); //通过Hash来获得,暂且不实现
std::vector<EventLoop*> getAllLoops();
bool started() const;
const std::string& name() const;
private:
EventLoop* m_baseLoop;
/*
* 在main函数中,我们会申请一个EventLoop给TcpServer,那个就是作为mainLoop使用的
* 而那个mainLoop,我们在此会用baseLoop这个指针来进行保存
* 如果我们不调用setThreadNum的话,mainLoop和subLoop就是同一个
*/
std::string m_name;
bool m_started;
int m_numThreads;
int m_next; //轮询时候使用,下一个接收Channel的EventLoop的编号
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<EventLoopThread> > m_threads_vec; //存储EventLoop线程类对应的指针
std::vector<EventLoop*> m_loops_vec; //存储每个线程里面唯一的那个EventLoop
};
}
#include "EventLoopThreadPool.h"
#include "EventLoopThread.h"
#include "EventLoop.h"
namespace mymuduo {
EventLoopThreadPool::EventLoopThreadPool(EventLoop* baseLoop, const std::string& nameArg)
:m_baseLoop(baseLoop),
m_name(nameArg),
m_started(false),
m_numThreads(0),
m_next(0) {
}
EventLoopThreadPool::~EventLoopThreadPool() {
/*
* 这里不需要任何操作,线程会由智能指针帮我们释放,而EventLoop是EventLoopThread里面函数的
* 局部变量,用的是栈区空间,也不需要我们手动释放
*/
}
//供TcpServer的setThreadNum函数底层调用
void EventLoopThreadPool::setThreadNum(int numThreads) {
m_numThreads = numThreads;
}
void EventLoopThreadPool::start(const ThreadInitCallback& cb) {
m_started = true;
for(int i = 0; i < m_numThreads; ++i) {
char buf[m_name.size() + 16];
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), "%s%d", m_name.c_str(), i);
EventLoopThread* temp = new EventLoopThread(cb, buf);
m_threads_vec.emplace_back(std::unique_ptr<EventLoopThread>(temp));
m_loops_vec.emplace_back(temp->startLoop());
}
//如果外部没有调用setThreadNum,也就是mainLoop和subLoop合体,共用一个我们在主函数创建的Loop
//那么就会执行下面这里而不进for循环
if(m_numThreads == 0 && cb) {
cb(m_baseLoop);
}
}
EventLoop* EventLoopThreadPool::getNextLoop() {
EventLoop* loop = m_baseLoop;
//如果有多个subLoop,那么就轮询来分配,否则就直接给mainLoop
if(!m_loops_vec.empty()) {
loop = m_loops_vec[++m_next];
if(static_cast<size_t>(m_next) >= m_loops_vec.size()) {
m_next = 0;
}
}
return loop;
}
std::vector<EventLoop*> EventLoopThreadPool::getAllLoops() {
if(m_loops_vec.empty()) {
//如果只有mainLoop,那么就创建一个只存mainLoop的vector
return std::vector<EventLoop*>(1, m_baseLoop);
}
else {
return m_loops_vec;
}
}
bool EventLoopThreadPool::started() const {
return m_started;
}
const std::string& EventLoopThreadPool::name() const {
return m_name;
}
}




















 117
117











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








