顺序表的准备工作,头文件以及结构体
![]() ,在编译器中对于顺序表的头文件后缀为.h
,在编译器中对于顺序表的头文件后缀为.h
其内部所需要的内容有如下:
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int SLDataType;
typedef struct SeqList
{
SLDataType* arr;
int size; //有效数据的个数
int capacity; //空间的大小
}SL;
//初始化
void SLInit(SL*ps);
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL*ps);
//打印
void SLPrint(SL* ps);
//扩容
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps);
//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps);
//头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x);
//头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps);下面我们依次来对顺序表进行分解,然后详细的说明

顺序表的初始化
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}顺序表的销毁
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
顺序表的打印
//打印
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n")
} 
顺序表的扩容
//扩容
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)//空间大小和元素大小相同所以需要增容
{
//判断之前的空间是否为0
SLDataType newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
//空间不够开辟的新空间大小
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newcapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)//判断是否开辟了新空间
{
perrnor("realloc fail!");
return;
}
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
ps->arr = tmp;
}
}顺序表的尾插
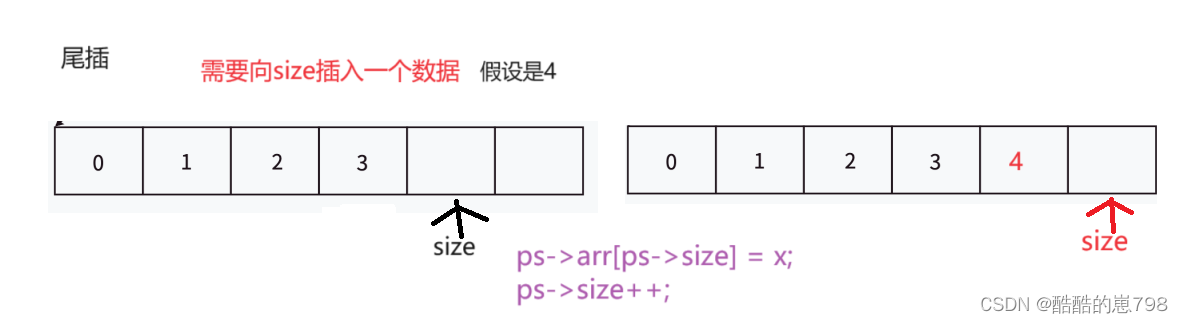
//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);//判断空间足不足够,不够扩容
ps->arr[ps->size++] = x;//size在使用完之后需要++往后推一个空间
//ps->arr[ps->size] = x;
//++ps->size;
//ps->size++也可以
}尾插的测试

顺序表的尾删
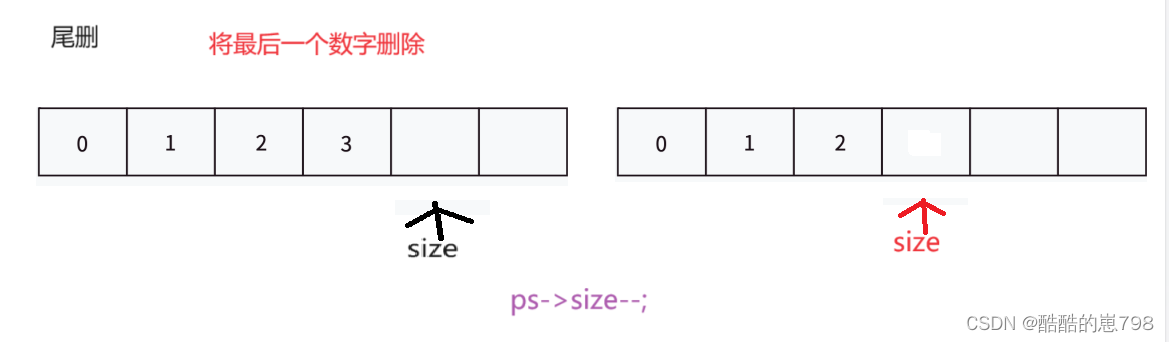
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
//顺序表不能为空
//ps->arr[ps->size - 1] = -1;
ps->size--;
}尾删的测试

顺序表的头插
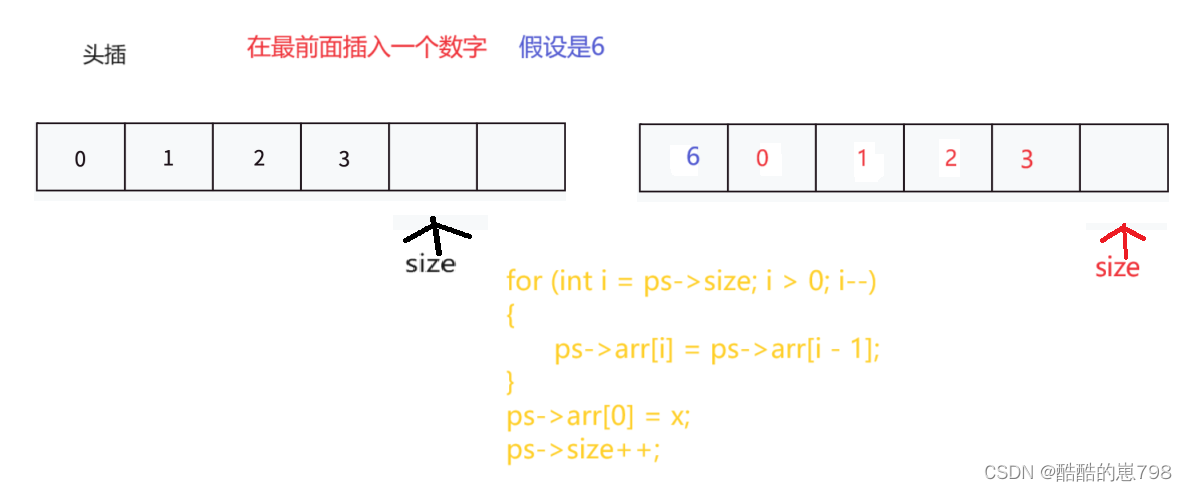
//头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);//判断空间足不足够
for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];
}
ps->arr[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
头插的测试 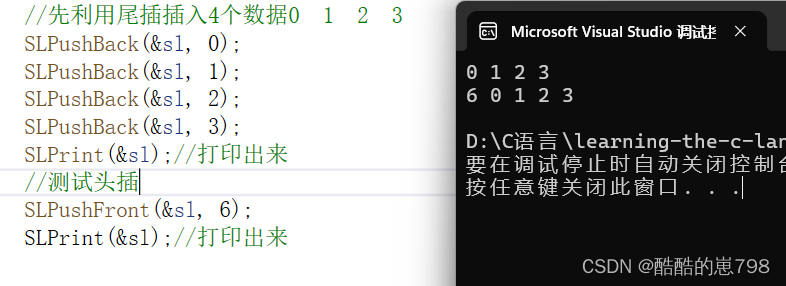
顺序表的头删
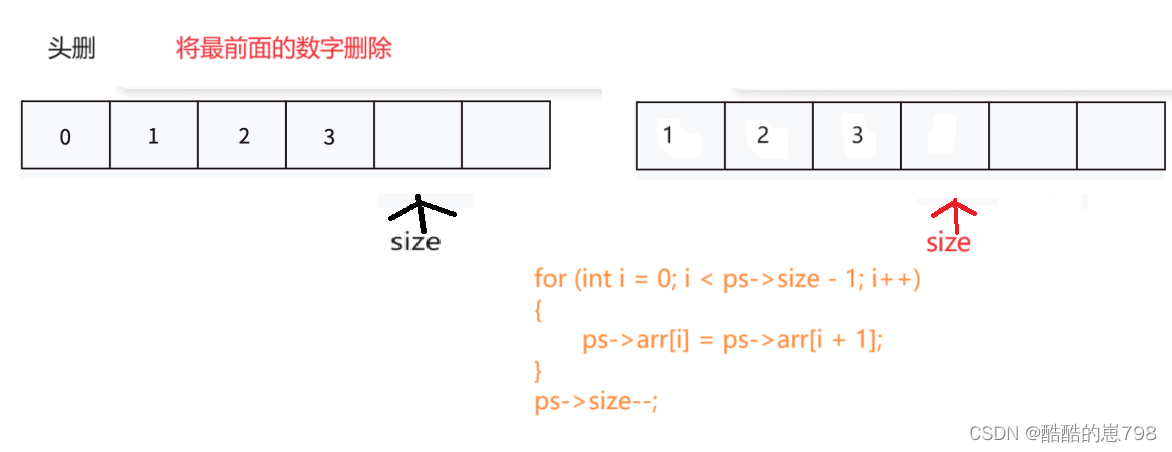
//头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}头删的测试

顺序表指定位置插入数据

//指定某一个位置插入数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
for (int i = ps->size; i > pos; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
指定位置插入测试
中间插入数据

首元素插入数据

末尾插入数据

顺序表指定位置删除数据
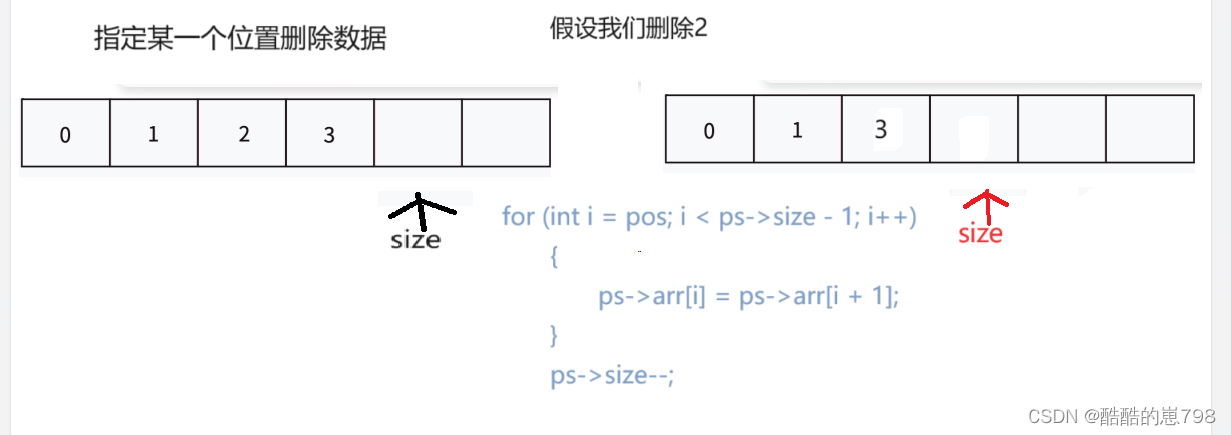
//指定某一个位置删除数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}指定位置删除测试
删除中间数据
删除第一个数据

删除最后一个数据
 在顺序表中查找一个数据
在顺序表中查找一个数据
//寻找一个数字
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (x == ps->arr[i])
{
printf("找到了!");
return i;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
}测试查找0

测试查找99

顺序表所有内容的总结 !!!
#include"SeqList.h"
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//打印
void SLPrint(SL* ps)
{
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//扩容
void SLCheckCapacity(SL* ps)
{
if (ps->size == ps->capacity)
{
SLDataType newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
SLDataType* tmp = (SLDataType*)realloc(ps->arr, newcapacity * sizeof(SLDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail!");
return;
}
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
ps->arr = tmp;
}
}
//尾插
void SLPushBack(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);//判断空间足不足够
ps->arr[ps->size] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//尾删
void SLPopBack(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
ps->size--;
}
//头插
void SLPushFront(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);//判断空间足不足够
for (int i = ps->size; i > 0; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];
}
ps->arr[0] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//头删
void SLPopFront(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
//指定某一个位置插入数据
void SLInsert(SL* ps, int pos, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
SLCheckCapacity(ps);
for (int i = ps->size; i > pos; i--)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i - 1];
}
ps->arr[pos] = x;
ps->size++;
}
//指定某一个位置删除数据
void SLErase(SL* ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->size);
for (int i = pos; i < ps->size - 1; i++)
{
ps->arr[i] = ps->arr[i + 1];
}
ps->size--;
}
//寻找一个数字
int SLFind(SL* ps, SLDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (x == ps->arr[i])
{
printf("找到了!");
return i;
}
else
{
printf("没有找到");
return -1;
}
}
}
//销毁
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->arr);
ps->arr = NULL;
ps->size = ps->capacity = 0;
}#include"SeqList.h"
void SLTest01()
{
SL sl;
SLInit(&sl);
//先利用尾插插入4个数据0 1 2 3
SLPushBack(&sl, 0);
SLPushBack(&sl, 1);
SLPushBack(&sl, 2);
SLPushBack(&sl, 3);
SLPrint(&sl);//打印出来
//测试头插
//SLPushFront(&sl, 6);
//SLPrint(&sl);//打印出来6 0 1 2 3
//测试头删
//SLPopFront(&sl);
//SLPrint(&sl);//1 2 3
//测试尾删
//SLPopBack(&sl);
//SLPrint(&sl);//0 1 2
//测试指定某一个位置插入数据
//SLInsert(&sl, 3, 10);
//SLPrint(&sl);//0 1 2 10 3
//SLInsert(&sl, 0, 10);
//SLPrint(&sl);//10 0 1 2 3
//SLInsert(&sl, 4, 10);
//SLPrint(&sl);//0 1 2 3 10
//测试指定某一个位置删除数据
//SLErase(&sl, 1);
//SLPrint(&sl);//0 2 3
//SLErase(&sl, 0);
//SLPrint(&sl);//1 2 3
// SLErase(&sl, 4);
//SLPrint(&sl);//0 1 2
//测试有没有找到
SLFind(&sl, 99);
//SLFind(&sl, 0);
//......
SLDestroy(&sl);
}
int main()
{
SLTest01();
return 0;
}




















 3737
3737











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








