在编程中,我们经常需要对txt文件进行读写操作,有时候由于编解码问题,txt读写会出现乱码问题。下面介绍一种基于ofstream和ifstream的txt文件读写方法,并介绍txt文件读写的乱码解决方案。
1.txt文件写入
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
ofstream outfile("1.txt",ios::ate); //打开文件,设置写入方式为覆盖写入
if(!outfile)
{
cout<<"txt文件打开失败!"<<endl;
exit(0);
}
outfile<<"写入txt文件示例.\n";
outfile<<"成功写入.\n";
outfile.close();
}txt里面的写入内容如下:
成功写入。
2.txt文件读出
对上面读入内容的txt进行读出操作,代码如下:
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char txt[100];
ifstream infile;
infile.open("1.txt");
if(!infile.is_open())
{
cout<<"txt文件打开失败"<<endl;
exit(0);
}
while(!infile.eof())
{
infile.getline(txt,100);
cout<<txt<<endl;
}
infile.close();
getchar();
}读出结果为:
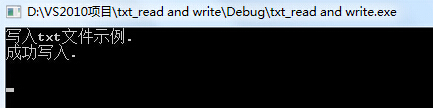
读出结果正确。
3.txt读写乱码问题
有时候由于txt文件编码问题的不同,会导致读写的时候出现乱码,通常的txt编码方式有:
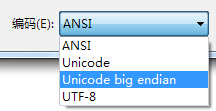
上面默认的编码方式为ANSI,如果我们现在将它另存为1.txt,但编码格式变为UTF-8,那么读出结果会变成:
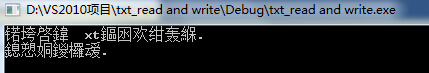
发现结果完全错误,这时候我们需要编解码转换,具体代码如下:
#include <fstream>
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
string UTF8ToGB(const char* str)
{
string result;
WCHAR *strSrc;
LPSTR szRes;
//获得临时变量的大小
int i = MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, str, -1, NULL, 0);
strSrc = new WCHAR[i+1];
MultiByteToWideChar(CP_UTF8, 0, str, -1, strSrc, i);
//获得临时变量的大小
i = WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP, 0, strSrc, -1, NULL, 0, NULL, NULL);
szRes = new CHAR[i+1];
WideCharToMultiByte(CP_ACP, 0, strSrc, -1, szRes, i, NULL, NULL);
result = szRes;
delete []strSrc;
delete []szRes;
return result;
}
int main()
{
char txt[100];
string msg;
ifstream infile;
infile.open("2.txt");
if(!infile.is_open())
{
cout<<""<<endl;
exit(0);
}
while(!infile.eof())
{
infile.getline(txt,100);
msg=UTF8ToGB(txt);
cout<<msg<<endl;
}
infile.close();
getchar();
}将读出结果进行上述转换,发现结果又正确了。






















 1268
1268

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








