Java实现BP神经网络
算法讲解
BP(Back-propagation,反向传播)神经网络是最传统的神经网络。BP神经网络的过程主要分为两个阶段,第一阶段是信号的前向传播,从输入层经过隐含层,最后到达输出层;第二阶段是误差的反向传播,从输出层到隐含层,最后到输入层,依次调节隐含层到输出层的权重和偏置,输入层到隐含层的权重和偏置。
前向传播
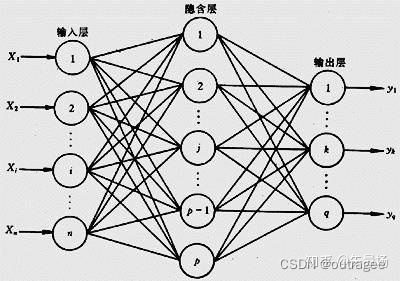
隐含层中每一个值
H
j
H_j
Hj都是由输入层的数据进行线性运算与非线性运算的结合得到的。
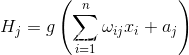
前向传播(Forward Propagation): 在前向传播中,神经网络将输入数据通过一系列的权重和激活函数的计算,逐层向前传递,最终生成预测结果。具体步骤如下:
- 将输入数据传递给第一层(输入层),每个输入与对应的神经元相连接。
- 对于每一层,计算该层的加权和,加权和等于前一层的输出与权重的乘积之和,并加上偏置项。
- 对加权和进行激活函数的计算,例如Sigmoid、ReLU等,得到该层的输出。本例使用sigmod
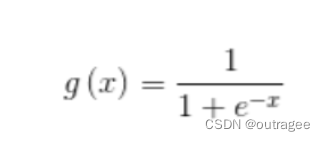
- 将该层的输出作为下一层的输入,继续进行加权和和激活函数的计算,直到达到输出层,输出最终的预测结果。
反向传播
反向传播(Backward Propagation): 在反向传播过程中,通过计算损失函数的梯度,将误差从输出层传递回输入层,以便调整网络中的权重和偏置项。具体步骤如下:
- 计算输出层的预测误差,根据预测结果与真实标签之间的差异。 通过使用链式法则,将输出层的误差传递回前一层,计算前一层的误差。本例使用均方误差
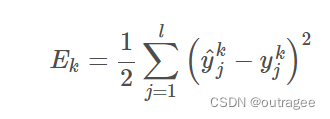
- 更新网络中的权重和偏置项,以最小化损失函数。这可以通过梯度下降等优化算法来实现,其中每个权重和偏置项的更新方向与其对应的梯度成反方向。
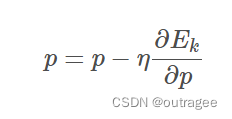
其中 p p p是待更新变量,另一个是学习率
代码设计
抽象类GeneralAnn
这个类实现了一些具体且固定的Ann流程方法,如:读取文件并为属性赋值的构造方法、实现模型训练的train()方法以及实现激活函数的argmax()方法。但是核心的正向传播forward()与反向传播backPropagation()是抽象的,未实现。
package bp;
import weka.core.Instances;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Random;
//数据读取与基本结构
public abstract class GeneralAnn {
/**
* The whole dataset.
*/
Instances dataset;
/**
* Number of layers. It is counted according to nodes instead of edges.
*/
int numLayers;
/**
* The number of nodes for each layer, e.g., [3, 4, 6, 2] means that there
* are 3 input nodes (conditional attributes), 2 hidden layers with 4 and 6
* nodes, respectively, and 2 class values (binary classification).
*/
int[] layerNumNodes;
/**
* Momentum coefficient.
*/
public double mobp;
/**
* Learning rate.
*/
public double learningRate;
/**
* For random number generation.
*/
Random random = new Random();
/**
********************
* The first constructor.
* @param paraFilename
* The arff filename.
* @param paraLayerNumNodes
* The number of nodes for each layer (may be different).
* @param paraLearningRate
* Learning rate.
* @param paraMobp
********************
*/
public GeneralAnn(String paraFilename, int[] paraLayerNumNodes, double paraLearningRate,
double paraMobp) {
// Step 1. Read data.
try {
FileReader tempReader = new FileReader(paraFilename);
dataset = new Instances(tempReader);
// The last attribute is the decision class.
dataset.setClassIndex(dataset.numAttributes() - 1);
tempReader.close();
} catch (Exception ee) {
System.out.println("Error occurred while trying to read \'" + paraFilename
+ "\' in GeneralAnn constructor.\r\n" + ee);
System.exit(0);
} // Of try
// Step 2. Accept parameters.
layerNumNodes = paraLayerNumNodes;
numLayers = layerNumNodes.length;
// Adjust if necessary.
layerNumNodes[0] = dataset.numAttributes() - 1;
layerNumNodes[numLayers - 1] = dataset.numClasses();
learningRate = paraLearningRate;
mobp = paraMobp;
}//Of the first constructor
/**
********************
* Forward prediction.
*
* @param paraInput
* The input data of one instance.
* @return The data at the output end.
********************
*/
public abstract double[] forward(double[] paraInput);
/**
********************
* Back propagation.
*
* @param paraTarget
* For 3-class data, it is [0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0] or [1, 0, 0].
*
********************
*/
public abstract void backPropagation(double[] paraTarget);
/**
********************
* Train using the dataset.
********************
*/
public void train() {
double[] tempInput = new double[dataset.numAttributes() - 1];
double[] tempTarget = new double[dataset.numClasses()];
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
// Fill the data.
for (int j = 0; j < tempInput.length; j++) {
tempInput[j] = dataset.instance(i).value(j);
} // Of for j
// Fill the class label.
Arrays.fill(tempTarget, 0);
tempTarget[(int) dataset.instance(i).classValue()] = 1;
// Train with this instance.
forward(tempInput);
backPropagation(tempTarget);
} // Of for i
}// Of train
/**
********************
* Get the index corresponding to the max value of the array.
*
* @return the index.
********************
*/
public static int argmax(double[] paraArray) {
int resultIndex = -1;
double tempMax = -1e10;
for (int i = 0; i < paraArray.length; i++) {
if (tempMax < paraArray[i]) {
tempMax = paraArray[i];
resultIndex = i;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
return resultIndex;
}// Of argmax
/**
********************
* Test using the dataset.
*
* @return The precision.
********************
*/
public double test() {
double[] tempInput = new double[dataset.numAttributes() - 1];
double tempNumCorrect = 0;
double[] tempPrediction;
int tempPredictedClass = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < dataset.numInstances(); i++) {
// Fill the data.
for (int j = 0; j < tempInput.length; j++) {
tempInput[j] = dataset.instance(i).value(j);
} // Of for j
// Train with this instance.
tempPrediction = forward(tempInput);
//System.out.println("prediction: " + Arrays.toString(tempPrediction));
tempPredictedClass = argmax(tempPrediction);
if (tempPredictedClass == (int) dataset.instance(i).classValue()) {
tempNumCorrect++;
} // Of if
} // Of for i
System.out.println("Correct: " + tempNumCorrect + " out of " + dataset.numInstances());
return tempNumCorrect / dataset.numInstances();
}// Of test
}//Of class GeneralAnn
Ann具体实现类SimpleAnn
在该类中具体实现了forward与backPropagation方法
package bp;
/**
* Back-propagation neural networks. The code comes from
* https://mp.weixin.qq.com
* /s?__biz=MjM5MjAwODM4MA==&mid=402665740&idx=1&sn=18d84d72934e59ca8bcd828782172667
*
* @author 彭渊 revised by minfanphd@163.com
*/
public class SimpleAnn extends GeneralAnn{
/**
* The value of each node that changes during the forward process. The first
* dimension stands for the layer, and the second stands for the node.
*/
public double[][] layerNodeValues;
/**
* The error on each node that changes during the back-propagation process.
* The first dimension stands for the layer, and the second stands for the
* node.
*/
public double[][] layerNodeErrors;
/**
* The weights of edges. The first dimension stands for the layer, the
* second stands for the node index of the layer, and the third dimension
* stands for the node index of the next layer.
*/
public double[][][] edgeWeights;
/**
* The change of edge weights. It has the same size as edgeWeights.
*/
public double[][][] edgeWeightsDelta;
/**
********************
* The first constructor.
*
* @param paraFilename
* The arff filename.
* @param paraLayerNumNodes
* The number of nodes for each layer (may be different).
* @param paraLearningRate
* Learning rate.
* @param paraMobp
* Momentum coefficient.
********************
*/
public SimpleAnn(String paraFilename, int[] paraLayerNumNodes, double paraLearningRate,
double paraMobp) {
super(paraFilename, paraLayerNumNodes, paraLearningRate, paraMobp);
// Step 1. Across layer initialization.
layerNodeValues = new double[numLayers][];
layerNodeErrors = new double[numLayers][];
edgeWeights = new double[numLayers - 1][][];
edgeWeightsDelta = new double[numLayers - 1][][];
// Step 2. Inner layer initialization.
for (int l = 0; l < numLayers; l++) {
layerNodeValues[l] = new double[layerNumNodes[l]];
layerNodeErrors[l] = new double[layerNumNodes[l]];
// One less layer because each edge crosses two layers.
if (l + 1 == numLayers) {
break;
} // of if
// In layerNumNodes[l] + 1, the last one is reserved for the offset.
edgeWeights[l] = new double[layerNumNodes[l] + 1][layerNumNodes[l + 1]];
edgeWeightsDelta[l] = new double[layerNumNodes[l] + 1][layerNumNodes[l + 1]];
for (int j = 0; j < layerNumNodes[l] + 1; j++) {
for (int i = 0; i < layerNumNodes[l + 1]; i++) {
// Initialize weights.
edgeWeights[l][j][i] = random.nextDouble();
} // Of for i
} // Of for j
} // Of for l
}// Of the constructor
/**
********************
* Forward prediction.
*
* @param paraInput
* The input data of one instance.
* @return The data at the output end.
********************
*/
public double[] forward(double[] paraInput) {
// Initialize the input layer.
//首先将输入放进第一层中
for (int i = 0; i < layerNodeValues[0].length; i++) {
layerNodeValues[0][i] = paraInput[i];
} // Of for i
// Calculate the node values of each layer.
//循环numLayers-1次,将一次输入的数据根据权重进行向量乘法到下一层中,直到网络全部被填满
double z;
for (int l = 1; l < numLayers; l++) {
for (int j = 0; j < layerNodeValues[l].length; j++) {
// Initialize according to the offset, which is always +1
//用z变量存储矩阵乘法的值,累加完毕后放入layerNodeValues中
z = edgeWeights[l - 1][layerNodeValues[l - 1].length][j];
// Weighted sum on all edges for this node.
for (int i = 0; i < layerNodeValues[l - 1].length; i++) {
z += edgeWeights[l - 1][i][j] * layerNodeValues[l - 1][i];
} // Of for i
// Sigmoid activation.
// This line should be changed for other activation functions.
//在填满网络后用激活函数处理,得到输出
layerNodeValues[l][j] = 1 / (1 + Math.exp(-z));
} // Of for j
} // Of for l
return layerNodeValues[numLayers - 1];
}// Of forward
/**
********************
* Back propagation and change the edge weights.
*
* @param paraTarget
* For 3-class data, it is [0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0] or [1, 0, 0].
********************
*/
public void backPropagation(double[] paraTarget) {
// Step 1. Initialize the output layer error.
//初始化误差数组
int l = numLayers - 1;
for (int j = 0; j < layerNodeErrors[l].length; j++) {
layerNodeErrors[l][j] = layerNodeValues[l][j] * (1 - layerNodeValues[l][j])
* (paraTarget[j] - layerNodeValues[l][j]);
} // Of for j
// Step 2. Back-propagation even for l == 0
while (l > 0) {
l--;
// Layer l, for each node.
for (int j = 0; j < layerNumNodes[l]; j++) {
double z = 0.0;
// For each node of the next layer.
for (int i = 0; i < layerNumNodes[l + 1]; i++) {
if (l > 0) {
z += layerNodeErrors[l + 1][i] * edgeWeights[l][j][i];
} // Of if
// Weight adjusting.
edgeWeightsDelta[l][j][i] = mobp * edgeWeightsDelta[l][j][i]
+ learningRate * layerNodeErrors[l + 1][i] * layerNodeValues[l][j];
edgeWeights[l][j][i] += edgeWeightsDelta[l][j][i];
if (j == layerNumNodes[l] - 1) {
// Weight adjusting for the offset part.
edgeWeightsDelta[l][j + 1][i] = mobp * edgeWeightsDelta[l][j + 1][i]
+ learningRate * layerNodeErrors[l + 1][i];
edgeWeights[l][j + 1][i] += edgeWeightsDelta[l][j + 1][i];
} // Of if
} // Of for i
// Record the error according to the differential of Sigmoid.
// This line should be changed for other activation functions.
layerNodeErrors[l][j] = layerNodeValues[l][j] * (1 - layerNodeValues[l][j]) * z;
} // Of for j
} // Of while
}// Of backPropagation
/**
********************
* Test the algorithm.
********************
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] tempLayerNodes = { 4, 8, 8, 3 };
SimpleAnn tempNetwork = new SimpleAnn("C:\\Users\\hp\\Desktop\\deepLearning\\src\\main\\java\\resources\\iris.arff", tempLayerNodes, 0.01,
0.6);
for (int round = 0; round < 5000; round++) {
tempNetwork.train();
} // Of for n
double tempAccuracy = tempNetwork.test();
System.out.println("The accuracy is: " + tempAccuracy);
}// Of main
}// Of class SimpleAnn





















 1437
1437











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








