多态
多态基本介绍
方法或对象具有多种形态。是面向对象的第三大特征,多态是建立在封装和继承基础之上的。
例如
A a = new A() ;
//通过不同的参数个数去调用sum方法,就回去调用不同的方法
//因此对sum方法来说,就是多态的实现
System.out.println( a.sum(10,30) ) ;
System.out.println( a.sum(10,30,50) ) ;
多态细节
- 多态的前提是:两个对象(类)存在继承关系
多态的向上转型
- 本质:父类的引用指向子类的对象
- 语法:父类类型 引用名 = new 子类类型();
- 特点:
- 编译类型看左边,运行类型看右边。
- 可以调用父类中的成员(需遵守访问权限),不能调用子类中的特有成员(属性和方法)。
- 最终运行效果看子类的具体实现。
public class Poly {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//编译类型看左边,运行类型看右边
Animal animal = new Cat();
//但是不能调用子类的特有成员
//因为在编译阶段,能调用哪些成员,是由编译类型决定的
animal.CathMourse() //编译错误
//可以调用父类中的所有成员(需遵守访问权限)
//最终运行效果看子类的具体实现
animal.eat(); //输出 猫吃老鼠
animal.run();
animal.sleep();
animal.show();
}
}
class Animal{
String name = "动物" ;
int age = 10 ;
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("睡觉");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("吃饭");
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("奔跑");
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("表演");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("猫吃老鼠");
}
public void CathMourse(){
System.out.println("猫抓老鼠");
}
}
多态的向下转型
- 语法: 子类类型 引用名 = (子类类型) 父类引用 ;
- 只能强转父类的引用,不能强转父类的对象
- 要求父类的引用必须指向的是当前目标类型的对象
- 可以调用子类类型中的所有成员
public class Next {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal animal = new Cat() ;
//向下转型
Cat cat = (Cat)animal ;
cat.eat(); //输出猫吃老鼠
//可以调用子类类型中的所有成员
cat.CathMourse(); //输出猫抓老鼠
cat.run(); //输出 跑步
cat.show(); //输出 表演
cat.sleep(); //输出 睡觉
}
}
class Animal{
String name = "动物" ;
int age = 10 ;
public void sleep(){
System.out.println("睡觉");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("吃饭");
}
public void run(){
System.out.println("奔跑");
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("表演");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
public void eat(){
System.out.println("猫吃老鼠");
}
public void CathMourse(){
System.out.println("猫抓老鼠");
}
}
多态注意事项
-
属性没有重写之说!属性的值看编译类型
public class Deatil { public static void main(String[] args) { //属性没有重写之说!属性的值看编译类型 Sub sub = new Sub(); //编译类型为sub 运行类型为sub System.out.println(sub.count); // 20 Base base = new Sub() ; //编译类型为base 运行类型为sub System.out.println(base.count); //10 } } class Base{ int count = 10 ; } class Sub extends Base{ int count = 20 ; } -
instanceOf 比较操作符,用于判断对象的运行类型是否为xx类型或xx类型的子类型
Java动态绑定机制
- 当调用对象方法的时候,该方法会和该对象的内存地址/运行类型绑定
- 当调用对象属性时,没有动态绑定机制,哪里声明,哪里使用(就近原则)
public class DynamicBinding {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A a = new B() ; //向上转型
//运行类型为B
System.out.println(a.sum()); //40 B的sum方法与B的i
System.out.println(a.sum1()); //30 B的sum1方法与B的i
System.out.println(a.i); //10 属性值看编译类型
}
}
class A{
public int i = 10 ;
public int getI() {
return i;
}
public int sum(){
return getI() + 10 ;
}
public int sum1(){
return i + 10 ;
}
}
class B extends A{
public int i = 20 ;
@Override
public int getI() {
return i;
}
public int sum(){
return getI() + 20 ;
}
public int sum1(){
return i + 10 ;
}
}
多态数组
数组的定义类型为父类类型,里面保存的实际元素类型为子类型。
public class Dynamic {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person[] person = new Person[5] ;
person[0] = new Person("张三" , 20) ;
person[1] = new Student("李四" , 20 , 100) ;
person[2] = new Student("王五" , 23 , 50) ;
person[3] = new Teacher("赵六" , 20 , 46300) ;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
//person[i]编译类型是Person,运行类型是根据实际情况由JVM判断
System.out.println(person[i].say()); //动态绑定机制
}
}
}
public class Person {
private String name ;
private int age ;
public Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String say(){
return name + "\t" + age ;
}
}
public class Student extends Person{
private int score ;
public Student(String name, int age , int score) {
super(name, age);
this.score = score ;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
public String say(){
return "学生 " + super.say() + "\t" + "score " + this.score ;
}
}
public class Teacher extends Person{
private int salary ;
public Teacher(String name, int age , int salary ) {
super(name, age);
this.salary = salary ;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String say(){
return "老师 " + super.say() + "\t" + "薪水:" + this.salary ;
}
}
输出
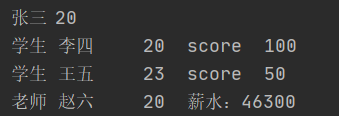
多态参数
方法定义的形参类型为父类类型,实参类型允许为子类类型
例题
定义员工类Employee,包含姓名和月工资[private],以及计算年工资getAnnual的方法。普通员工和经理继承了员工,经理类多了奖金bonus属性和管理manage方法,普通员工类多了work方法,普通员工和经理类要求分别重写getAnnual方法
测试类中添加一个方法showEmpAnnal(Employee e),实现获取任何员工对象的年工资,并在main方法中调用该方法[e.getAnnual()]
测试类中添加一个方法,testWork,如果是普通员工,则调用work方法,如果是经理,则调用manage方法
public class Worker extends Employee{
public Worker(String name, int salary) {
super(name, salary);
}
public String work(){
return "员工" + getName() + " 正在工作" ;
}
public int getAnnual(){
return getSalary() * 12 ;
}
}
public class Manager extends Employee{
private int bonus ;
public Manager(String name, int salary , int bonus) {
super(name, salary);
this.bonus = bonus ;
}
public int getAnnual(){
return getSalary() * 12 + this.bonus ;
}
public String manager(){
return "经理" + getName() + " 正在管理" ;
}
public int getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(int bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
}
public class Employee {
private String name ;
private int salary ;
public Employee(String name, int salary) {
this.name = name;
this.salary = salary;
}
public int getAnnual(){
return this.salary * 12 ;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Worker worker = new Worker("张三", 20000);
Manager manager = new Manager("李四" , 10000 , 60000);
Test test = new Test();
//多态参数
//showEmpAnnual()方法形参类型为父类类型,实参类型允许为子类类型
test.showEmpAnnual(worker);
test.showEmpAnnual(manager);
test.testWork(worker);
test.testWork(manager);
}
public static void showEmpAnnual( Employee emp ){
System.out.println(emp.getAnnual());
}
public static void testWork( Employee emp){
if( emp instanceof Worker ){
//向下转型
System.out.println( ( (Worker)emp ).work() );
}
else if( emp instanceof Manager ){
System.out.println( ((Manager)emp).manager() );
}
}
}






















 111
111











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








