1.什么是Services
Service是android 系统中的四大组件之一(Activity、Service、BroadcastReceiver、ContentProvider),它跟Activity的级别差不多,但不能自己运行只能后台运行,并且可以和其他组件进行交互。service可以在很多场合的应用中使用,比如播放多媒体的时候用户启动了其他Activity这个时候程序要在后台继续播放,比如检测SD卡上文件的变化,再或者在后台记录你地理信息位置的改变等等,总之服务总是藏在后台的。
Service的启动有两种方式:context.startService() 和 context.bindService()`-
2.startService 方式启动Services怎么做(启动和停止及生命周期)
1.其他组件调用startService()方法可以启动一个Service,接着,Service会回调onStartCommand()生命周期方法。startService()方法中传入一个Intent参数,用于显式指定目标Service的名字,并携带data以供Service使用,该Intent参数将回传至onStartCommand()方法中。
比如说,Activity需要向在线数据库中上传数据,那么可以调用startService()启动一个Service,并将数据传入Intent的data中,接着,onStartCommand()方法会接收这个Intent并开启一个线程将数据上传至网络,当数据上传完成后,该Service将停止并被destroy。
2.一般使用如下两种方式创建一个start Service:
继承Service类:请务必在Service中开启线程来执行耗时操作,因为Service运行在主线程中。
继承IntentService类:IntentService继承于Service,若Service不需要同时处理多个请求,那么使用IntentService将是最好选择:您只需要重写onHandleIntent()方法,该方法接收一个回传的Intent参数,您可以在方法内进行耗时操作,因为它默认开启了一个子线程,操作执行完成后也无需手动调用stopSelf()方法,onHandleIntent()会自动调用该方法。
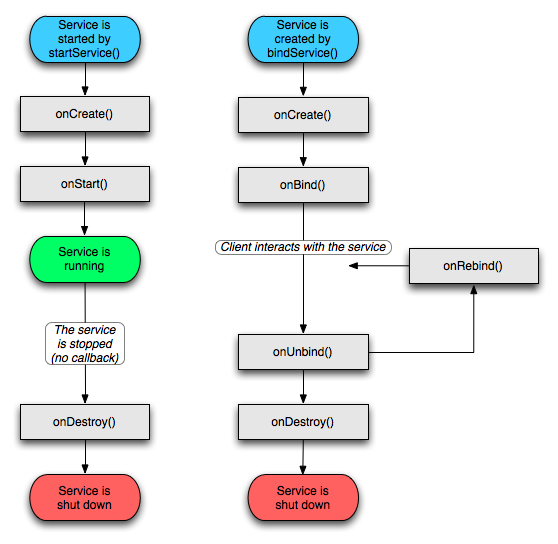
3.context.startService() 启动流程:
context.startService() -> onCreate() -> onStart() -> Service running -> context.stopService() -> onDestroy() -> Service stop
3.bindService 方式启动Services怎么做(绑定和解绑及生命周期)
1.通过其他组件调用bindService()方法可以绑定一个Service以保持长连接(long-standing connection),这时一般不允许其他组件调用startService()启动Service。
2.当其他组件需要与Service交互或者需要跨进程通信时,可以创建一个bound Service。
3.为创建一个bound Service,必须重写onBind()回调,该方法返回一个IBinder接口。该接口时组件与Service通信的桥梁。组件调用bindService()与Service绑定,该组件可获取IBinder接口,一旦获取该接口,就可以调用Service中的方法。一旦没有组件与Service绑定,系统将destroy它,您不必手动停止它。
4.为创建一个bound Service,必须定义一个接口 ,该接口指定组件与Service如何通信。定义的接口在组件与Service之间,且必须实现IBinder接口。这正是onBind()的返回值。一旦组件接收了IBinder,组件与Service便可以开始通信。
5.多个组件可同时与Service绑定,当组件与Service交互结束后,可调用unbindService()方法解绑。bound Service比start Service要复杂,故我将在后续单独翻译。
ontext.bindService()启动流程:
context.bindService() -> onCreate() -> onBind() -> Service running -> onUnbind() -> onDestroy() -> Service stop
5.IntentServices有什么不同
ntentService是Service的子类,根据需要处理异步请求(以intent表示)。客户端通过调用startService(Intent) 发送请求,该Service根据需要启动,使用工作线程处理依次每个Intent,并在停止工作时停止自身。
这种“工作队列处理器”模式通常用于从应用程序的主线程中卸载任务。 IntentService类的存在是为了简化这种模式。 要使用它,扩展IntentService并实现onHandleIntent(Intent)。 IntentService将收到Intents,启动一个工作线程,并根据需要停止该服务。
所有请求都在单个工作线程处理 - 它们可能需要很长的时间(并且不会阻止应用程序的主循环),但是一次只会处理一个请求。
6. IntentServices怎么用,注意事项
在IntentService中处理下载请求(模拟),并将进度更新到Ui。
MyIntentService.java代码如下:
public class MyIntentService extends IntentService {
private final static String TAG = "MyIntentService";
public static final String ACTION_DOWN_IMG = "down.image";
public static final String ACTION_DOWN_VID = "down.vid";
public static final String ACTION_DOWN_PROGRESS = "com.zpengyong.down.progress";
public static final String ACTION_SERVICE_STATE = "com.zpengyong.service.state";
public static final String PROGRESS = "progress";
public static final String SERVICE_STATE = "service_state";
//构造方法 一定要实现此方法否则Service运行出错。
public MyIntentService() {
super("MyIntentService");
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.i(TAG, "onCreate");
sendServiceState("onCreate");
}
@Override
public void onStart(Intent intent, int startId) {
super.onStart(intent, startId);
Log.i(TAG, "");
}
@Override
protected void onHandleIntent(Intent intent) {
Log.i(TAG, "onHandleIntent thread:"+Thread.currentThread());
String action = intent.getAction();
if(action.equals(ACTION_DOWN_IMG)){
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
try{ //模拟耗时操作
Thread.sleep(50);
}catch (Exception e) {
}
sendProgress(i);
}
}else if(action.equals(ACTION_DOWN_VID)){
for(int i = 0; i < 100; i++){
try{ //模拟耗时操作
Thread.sleep(70);
}catch (Exception e) {
}
sendProgress(i);
}
}
Log.i(TAG, "onHandleIntent end");
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.i(TAG, "onDestroy");
sendServiceState("onDestroy");
}
//发送Service的状态
private void sendServiceState(String state){
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(ACTION_SERVICE_STATE);
intent.putExtra(SERVICE_STATE, state);
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
//发送进度
private void sendProgress(int progress){
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(ACTION_DOWN_PROGRESS);
intent.putExtra(PROGRESS, progress);
sendBroadcast(intent);
}
}使用IntentService的方法:
继承IntentService。
实现不带参数的构造方法,并且调用父类IntentService的构造方法。
实现onHandleIntent方法。






















 3749
3749











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








