Problem Description
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
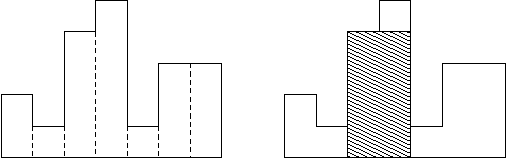
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.

Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that 1 <= n <= 100000. Then follow n integers h1, ..., hn, where 0 <= hi <= 1000000000. These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3 4 1000 1000 1000 1000 0
Sample Output
8 4000
/*
矩形面积额。不会做
有个小想法,但目测会TLE
枚举每个长方形,然后往左右扩散,如果遇到比他低的就停止
这样等下面积就是rec[i].h*(rec[i].r-rec[i].l)
好吧,想了想目测实现并不难。
从左往右读入矩形,如果这个矩形跟前一个矩形等高,rec[i].l=rec[i-1].l
如果这个矩形比前一个矩形还要高,rec[i].l=i-1;
如果这个矩形比前一个矩形要矮。
int j=i-1;
while(rec[rec[j].l].h>=rec[i].h)
{
j=rec[j].l;
}
rec[i].l=j;
这样的话,对任意的i,rec[i].l就已经处理好了。
现在要处理rec[i].r,只需要像刚才找rec[i].l一样找,不过得从右边往左边循环一遍
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 100008
struct REC
{
int l,r,h;//l和r分别用来存左边和右边第一个比他低的
}rec[100008];
inline int max(int a,int b)
{
return a>b?a:b;
}
int main()
{
int n;//lh和rh来模拟栈,就是等下来
while(scanf("%d",&n)!=EOF&&n)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&rec[i].h);
if(i==1)
{
rec[i].l=0;
rec[0].h=-1;
continue;
}
if(rec[i].h==rec[i-1].h)
{
rec[i].l=rec[i-1].l;
continue;
}
if(rec[i].h>rec[i-1].h)
{
rec[i].l=i-1;
}
if(rec[i].h<rec[i-1].h)
{
int j=i-1;
while(rec[rec[j].l].h>=rec[i].h)
{
j=rec[j].l;
}
rec[i].l=rec[j].l;
}
}//这个循环实现了读取数据和给每个矩形找到左边第一比他低的矩形的id
//接下来我要反向循环一遍,给每个矩形找到右边第一个比他低的矩形的id
for(int i=n;i>=1;i--)
{
if(i==n)
{
rec[i].r=n+1;
rec[n+1].h=-1;
continue;
}
if(rec[i].h>rec[i+1].h)
{
rec[i].r=i+1;
continue;
}
if(rec[i].h==rec[i+1].h)
{
rec[i].r=rec[i+1].r;
continue;
}
if(rec[i].h<rec[i+1].h)
{
int j=i+1;
while(rec[rec[j].r].h>=rec[i].h)
{
j=rec[j].r;
}
rec[i].r=rec[j].r;
}
}//这样,所有矩形的左右都找到了
long long int maxs=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
maxs=max(maxs,long long int(rec[i].h)*long long int(rec[i].r-rec[i].l-1));
}
printf("%d\n",maxs);
}
return 0;
}






















 3984
3984











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








