代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<malloc.h>
//定义一个双向链表节点
typedef struct DoubleLinkedNode {
char data;
struct DoubleLinkedNode* previous;
struct DoubleLinkedNode* next;
}DLNode, * DLNodePtr;
//初始化/创建头节点
DLNodePtr initLinkList() {
DLNodePtr tempHeader = (DLNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct DoubleLinkedNode));
tempHeader->data = '\0';
tempHeader->previous = NULL;
tempHeader->next = NULL;
return tempHeader;
}
//打印表,从p1的数据开始
void printList(DLNodePtr paraHeader) {
DLNodePtr p = paraHeader->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%c", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("\r\n");
}
//在链表的某个位置后面插入一个节点
void insertElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar, int paraPosition) {
DLNodePtr p, q, r;
//判断要求位置是否超出表长,p为链表表头
p = paraHeader;
for (int i = 0; i < paraPosition; i++) {
p = p->next;
if (p == NULL) {
printf("The position %d is beyond the scope of the list.", paraPosition);
return;
}
}
//q为要插入的节点
q = (DLNodePtr)malloc(sizeof(struct DoubleLinkedNode));
q->data = paraChar;
//把q插到p后面,及p在要求的位置上(原先为pr,插入后为pqr)
r = p->next;
q->next = p->next;
q->previous = p;
p->next = q;
if (r != NULL) {//考虑p是否为链表末尾,即插入q后没有下一个节点
r->previous = q;
}
}
//删除表中的某个节点(只一位)
void deleteElement(DLNodePtr paraHeader, char paraChar) {
DLNodePtr p, q, r;
p = paraHeader;
//p从头到尾或者p的下一个的数据为要求数据时才停止
while ((p->next != NULL) && (p->next->data != paraChar)) {
p = p->next;
}
//没有该数据的情况
if (p->next == NULL) {
printf("The char '%c' does not exist.\r\n", paraChar);
return;
}
//删除
q = p->next;
r = q->next;
p->next = r;
if (r != NULL) {
r->previous = p;
}
//释放
free(q);
}
void insertDeleteTest() {
DLNodePtr tempList = initLinkList();
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'H', 0);
insertElement(tempList, 'e', 1);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 2);
insertElement(tempList, 'l', 3);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 4);
insertElement(tempList, '!', 5);
printList(tempList);
deleteElement(tempList, 'e');
deleteElement(tempList, 'a');
deleteElement(tempList, 'o');
printList(tempList);
insertElement(tempList, 'o', 1);
printList(tempList);
}
void basicAddressTest() {
DLNode tempNode1, tempNode2;
tempNode1.data = 4;
tempNode1.next = NULL;
tempNode2.data = 6;
tempNode2.next = NULL;
printf("The first node: %d, %d, %d\r\n",
&tempNode1, &tempNode1.data, &tempNode1.next);
printf("The second node: %d, %d, %d\r\n",
&tempNode2, &tempNode2.data, &tempNode2.next);
tempNode1.next = &tempNode2;
}
void main() {
insertDeleteTest();
basicAddressTest();
}运行结果:

分析及体会:
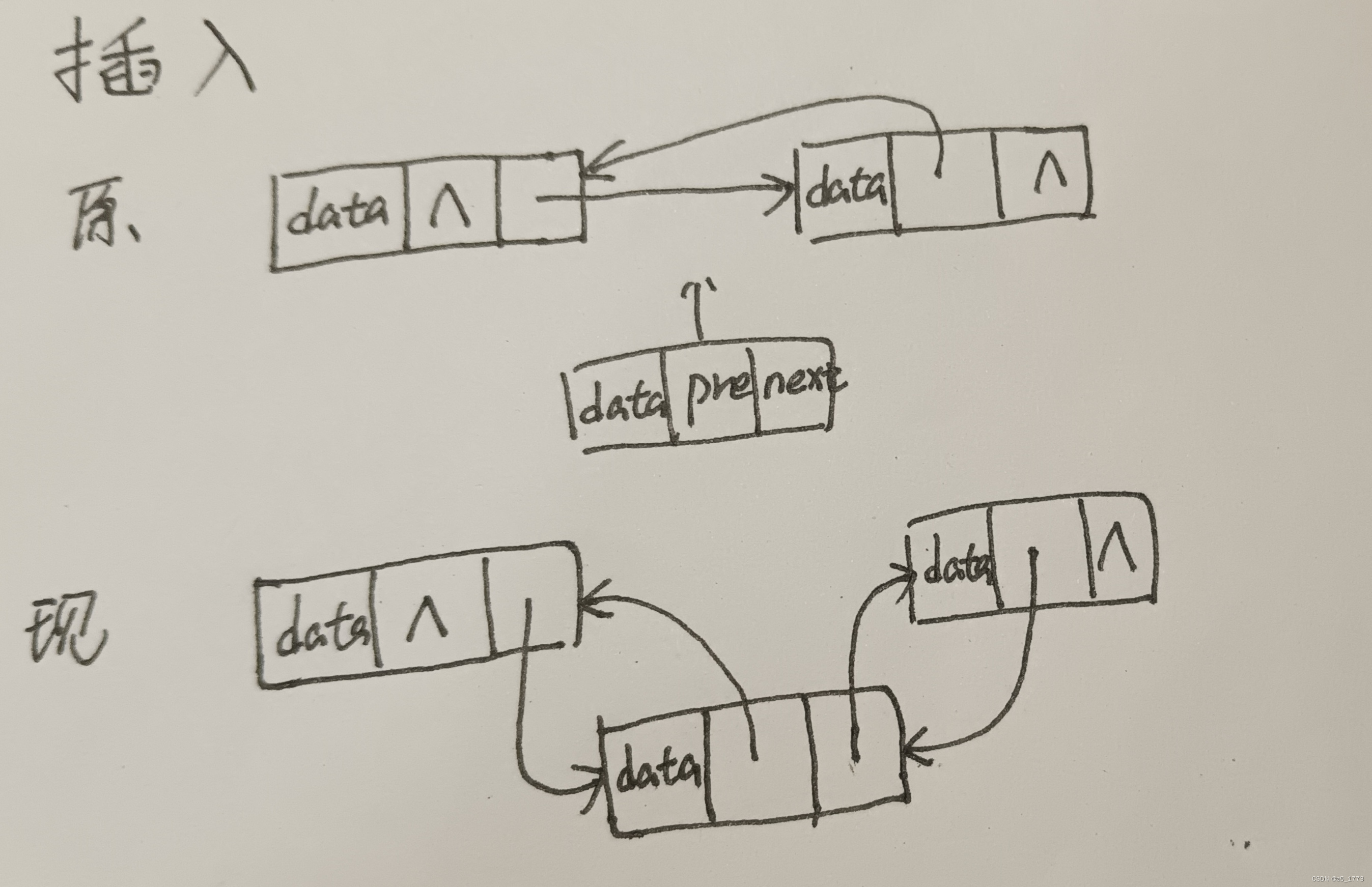
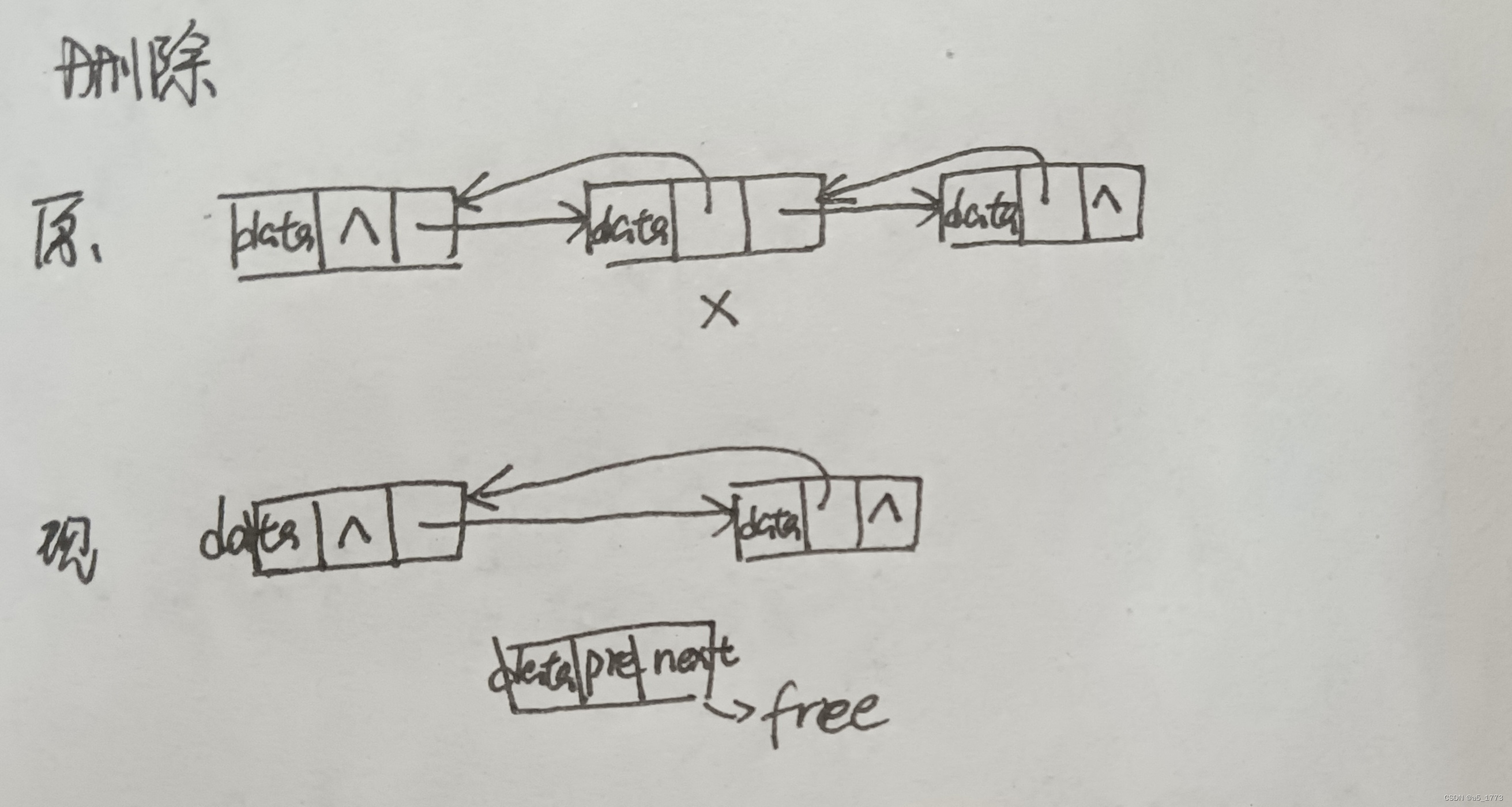
该代码可以实现双向链表建立、插入、删除的功能。与单向链表相比,双向链表每个节点都增加了一个指向前面节点的指针,这使得它在进行遍历等功能时更加高效,与此同时,其所需存储空间也就更大,操作更复杂更容易混乱。





















 117
117











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








