基础
数据结构
ngx_conf_t
struct ngx_conf_s {
//当前解析到的命令名
char *name;
//当前命令的所有参数
ngx_array_t *args;
//使用的cycle
ngx_cycle_t *cycle;
//所使用的内存池
ngx_pool_t *pool;
//这个pool将会在配置解析完毕后释放。
ngx_pool_t *temp_pool;
//这个表示将要解析的配置文件
ngx_conf_file_t *conf_file;
//配置log
ngx_log_t *log;
//主要为了提供模块的层次化
void *ctx;
//模块类型
ngx_uint_t module_type;
//命令类型
ngx_uint_t cmd_type;
//模块自定义的handler
ngx_conf_handler_pt handler;
//自定义handler的conf
char *handler_conf;
};ngx_command_t
struct ngx_command_s {
ngx_str_t name;
ngx_uint_t type;
char *(*set)(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf);
ngx_uint_t conf;
ngx_uint_t offset;
void *post;
};
http{}也可以看做一行配置命令,只不过它的参数有点长,它解析参数的方法是ngx_http_block,其他event,server都是类似的。
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_commands[] = {
{ ngx_string("http"),
NGX_MAIN_CONF|NGX_CONF_BLOCK|NGX_CONF_NOARGS,
ngx_http_block,
0,
0,
NULL },
ngx_null_command
};具体流程:
这是一个递归的过程。nginx首先解析core模块的配置。core模块提供一些块指令,这些指令引入其他类型的模块,nginx遇到这些指令,就重新迭代解析过程,解析其他模块的配置。这些模块配置中又有一些块指令引入新的模块类型或者指令类型,nginx就会再次迭代,解析这些新的配置类型。比如nginx遇到“events”指令,就重新调用ngx_conf_parse()解析event模块配置,解析完以后ngx_conf_parse()返回,nginx继续解析core模块指令,直到遇到“http”指令。nginx再次调用ngx_conf_parse()解析http模块配置的http级指令,当遇到“server”指令时,nginx又一次调用ngx_conf_parse()解析http模块配置的server级指令。
ngx_init_cycle 函数
获取
ngx_max_module
个指针空间,用来保存每个模块的配置信息.
cycle->conf_ctx = ngx_pcalloc(pool, ngx_max_module * sizeof(void *));获取模块中属于 NGX_CORE_MODULE 类的模块,如果需要创建配置信息就创建相应的配置信息,并且将地址保存在先前创建好的 cycle->conf_ctx 地址空间中,完成核心模块配置文件的创建过程。
for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {
if (ngx_modules[i]->type != NGX_CORE_MODULE) {
continue;
}
module = ngx_modules[i]->ctx;
if (module->create_conf) {
rv = module->create_conf(cycle);
if (rv == NULL) {
ngx_destroy_pool(pool);
return NULL;
}
cycle->conf_ctx[ngx_modules[i]->index] = rv;
}
}
此时内存布局:
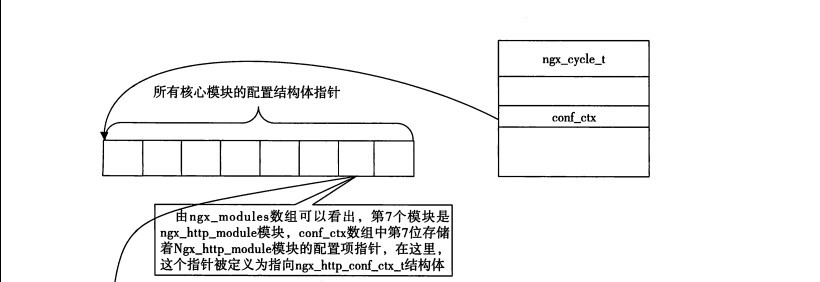
对conf进行必要初始化:
conf.ctx = cycle->conf_ctx;
conf.cycle = cycle;
conf.pool = pool;
conf.log = log;
conf.module_type = NGX_CORE_MODULE;
conf.cmd_type = NGX_MAIN_CONF;
#if 0
log->log_level = NGX_LOG_DEBUG_ALL;
#endif
if (ngx_conf_param(&conf) != NGX_CONF_OK) {
environ = senv;
ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf);
return NULL;
}
if (ngx_conf_parse(&conf, &cycle->conf_file) != NGX_CONF_OK) {
environ = senv;
ngx_destroy_cycle_pools(&conf);
return NULL;
}ngx_conf_parse 指令解析函数
char *
ngx_conf_parse(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_str_t *filename)
{
char *rv;
ngx_fd_t fd;
ngx_int_t rc;
ngx_buf_t buf;
ngx_conf_file_t *prev, conf_file;
enum {
parse_file = 0,
parse_block,
parse_param
} type;
/*
该函数存在三种运行方式,并非一定需要打开配置文件
*/
#if (NGX_SUPPRESS_WARN)
fd = NGX_INVALID_FILE;
prev = NULL;
#endif
/*
filename 的值为 nginx.conf 的路径
*/
if (filename) {
/* 打开配置文件 */
fd = ngx_open_file(filename->data, NGX_FILE_RDONLY, NGX_FILE_OPEN, 0);
...
/*
保存cf->conf_file 的上文
*/
prev = cf->conf_file;
/*
定义cf->conf_file 当前的变量信息
*/
cf->conf_file = &conf_file;
/*
接下来是对,conf_file 的参数进行设置,为了方便阅读省略此处代码
*/
...
/*
将函数的运行模式定位为 parse_file ,配置文件模式。
*/
type = parse_file;
/*
其它两个else 是定义其他模式,在解析nginx.conf时并不会使用到
*/
} else if (cf->conf_file->file.fd != NGX_INVALID_FILE) {
type = parse_block;
} else {
type = parse_param;
}
/*
完成对配置文件信息的,初步设置之后,就开始对配置文件进行解析。
*/
for ( ;; ) {
/*
获取从配置文件nginx.conf中读取的指令名,对于 ngx_conf_read_token 下面给出来返回参数的详细英文注释
*/
rc = ngx_conf_read_token(cf);
/*
* ngx_conf_read_token() may return
*
* NGX_ERROR there is error
* NGX_OK the token terminated by ";" was found
* NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START the token terminated by "{" was found
* NGX_CONF_BLOCK_DONE the "}" was found
* NGX_CONF_FILE_DONE the configuration file is done
*/
/*
如果错误,调转到done处执行
*/
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
goto done;
}
/*
如果如到“}”符号,跳转到done处执行,出现错误跳到failed处
*/
if (rc == NGX_CONF_BLOCK_DONE) {
if (type != parse_block) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0, "unexpected \"}\"");
goto failed;
}
goto done;
}
/*
如果配置文件全部解析完成,调转到done处执行。
*/
if (rc == NGX_CONF_FILE_DONE) {
if (type == parse_block) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"unexpected end of file, expecting \"}\"");
goto failed;
}
goto done;
}
/*
如果遇到“{"但出现错误,调转到failed 处执行
*/
if (rc == NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START) {
if (type == parse_param) {
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0,
"block directives are not supported "
"in -g option");
goto failed;
}
}
/*
前面对可能出现的情况都进行了相应的跳转,那么剩下的就是读取 指令正确后执行的过程了,主要分为两种,一种为NGX_OK 一般指令的进行如:worker_processes
另一种 NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START 就是以{作为结束符指令的执行,如:events、http 这类有二级指令的。
rc == NGX_OK || rc == NGX_CONF_BLOCK_START
*/
if (cf->handler) {
/*
指令执行前是否要进行些处理工作
* the custom handler, i.e., that is used in the http's
* "types { ... }" directive
*/
rv = (*cf->handler)(cf, NULL, cf->handler_conf);
if (rv == NGX_CONF_OK) {
continue;
}
if (rv == NGX_CONF_ERROR) {
goto failed;
}
ngx_conf_log_error(NGX_LOG_EMERG, cf, 0, rv);
goto failed;
}
/*
下一个关键函数 ngx_conf_handler
*/
rc = ngx_conf_handler(cf, rc);
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
goto failed;
}
}
failed:
rc = NGX_ERROR;
done:
/*
一些完成后的处理,释放资源或者 出错处理。省略
*/
...
/*
恢复上下文
*/
cf->conf_file = prev;
}
if (rc == NGX_ERROR) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
return NGX_CONF_OK;
}ngx_conf_handler 指令处理函数
handler的作用就是给那些已经申请好的conf结构内容赋上响应配置文件中的值,即调用cmd->set。
static ngx_int_t
ngx_conf_handler(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_int_t last)
{
...
for (i = 0; ngx_modules[i]; i++) {
/* 查找与指令想对应的模块 module*/
if (ngx_modules[i]->type != NGX_CONF_MODULE
&& ngx_modules[i]->type != cf->module_type)
{
continue;
}
/*
读取模块的指令集
*/
cmd = ngx_modules[i]->commands;
if (cmd == NULL) {
continue;
}
for ( /* void */ ; cmd->name.len; cmd++) {
/*
遍历指令集中的指令,并找寻 从配置文件中读取到的 指令相对应的 内容
*/
if (name->len != cmd->name.len) {
continue;
}
if (ngx_strcmp(name->data, cmd->name.data) != 0) {
continue;
}
/* 判断下指令类型 是否正确*/
if (!(cmd->type & cf->cmd_type)) {
if (cmd->type & NGX_CONF_MULTI) {
multi = 1;
continue;
}
goto not_allowed;
}
...
/*判断指令参数是否正确*/
if (!(cmd->type & NGX_CONF_ANY)) {
if (cmd->type & NGX_CONF_FLAG) {
if (cf->args->nelts != 2) {
goto invalid;
}
} else if (cmd->type & NGX_CONF_1MORE) {
}
...
}
/*
通过指令的类型,来设置执行指令时需要的 模块前期创建的 cf_ctx里面的配置信息,朔源就是 cycle->conf_ctx 当然它指向的 上下文 可能已经发生了改变
*/
conf = NULL;
if (cmd->type & NGX_DIRECT_CONF) { conf = ((void **) cf->ctx)[ngx_modules[i]->index]; }
...
/*
执行指令对应的 功能函数!!
*/
rv = cmd->set(cf, cmd, conf);
/*
如果执行成功,返回 成功。
*/
if (rv == NGX_CONF_OK) {
return NGX_OK;
}
/*
至此,配置文件的指令执行就结束了。后面都是一些出错处理,在此省略。
*/
...
}
}
...
}//可以看到没有direct_conf,因为http包含有二级模块。
static ngx_command_t ngx_http_commands[] = {
{ ngx_string("http"),
NGX_MAIN_CONF|NGX_CONF_BLOCK|NGX_CONF_NOARGS,
ngx_http_block,//注意这里
0,
0,
NULL },
ngx_null_command
};
static char *
ngx_http_block(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *conf)
{
char *rv;
ngx_uint_t mi, m, s;
ngx_conf_t pcf;
ngx_http_module_t *module;
ngx_http_conf_ctx_t *ctx;
ngx_http_core_loc_conf_t *clcf;
ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t **cscfp;
ngx_http_core_main_conf_t *cmcf;
/* the main http context */
ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_conf_ctx_t));
if (ctx == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
//最核心的地方,可以看到修改了传递进来的conf
*(ngx_http_conf_ctx_t **) conf = ctx;
/* count the number of the http modules and set up their indices */
ngx_http_max_module = 0;
for (m = 0; ngx_modules[m]; m++) {
if (ngx_modules[m]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) {
continue;
}
//然后保存了对应模块的索引.
ngx_modules[m]->ctx_index = ngx_http_max_module++;
}
/* the http main_conf context, it is the same in the all http contexts */
//创建HTTP对应的conf,因为每个级别(main/ser/loc)都会包含模块的conf.
ctx->main_conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool,
sizeof(void *) * ngx_http_max_module);
if (ctx->main_conf == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
/*
* the http null srv_conf context, it is used to merge
* the server{}s' srv_conf's
*/
ctx->srv_conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *) * ngx_http_max_module);
if (ctx->srv_conf == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
/*
* the http null loc_conf context, it is used to merge
* the server{}s' loc_conf's
*/
ctx->loc_conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *) * ngx_http_max_module);
if (ctx->loc_conf == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
/*
* create the main_conf's, the null srv_conf's, and the null loc_conf's
* of the all http modules
*/
for (m = 0; ngx_modules[m]; m++) {
if (ngx_modules[m]->type != NGX_HTTP_MODULE) {
continue;
}
module = ngx_modules[m]->ctx;
mi = ngx_modules[m]->ctx_index;
if (module->create_main_conf) {
ctx->main_conf[mi] = module->create_main_conf(cf);
if (ctx->main_conf[mi] == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
}
if (module->create_srv_conf) {
ctx->srv_conf[mi] = module->create_srv_conf(cf);
if (ctx->srv_conf[mi] == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
}
if (module->create_loc_conf) {
ctx->loc_conf[mi] = module->create_loc_conf(cf);
if (ctx->loc_conf[mi] == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
}
....................................
//保存当前使用的cf,因为我们只是在解析HTTP时需要改变当前的cf,
pcf = *cf;
//保存当前模块的上下文
cf->ctx = ctx;
..........................................
/* parse inside the http{} block */
//设置模块类型和命令类型
cf->module_type = NGX_HTTP_MODULE;
cf->cmd_type = NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF;
//开始解析,这里注意传递进去的文件名是空
rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL);
if (rv != NGX_CONF_OK) {
goto failed;
}
/*
* init http{} main_conf's, merge the server{}s' srv_conf's
* and its location{}s' loc_conf's
*/
.........................................
/*
* http{}'s cf->ctx was needed while the configuration merging
* and in postconfiguration process
*/
//回复cf
*cf = pcf;
......................................
return NGX_CONF_OK;
failed:
*cf = pcf;
return rv;
}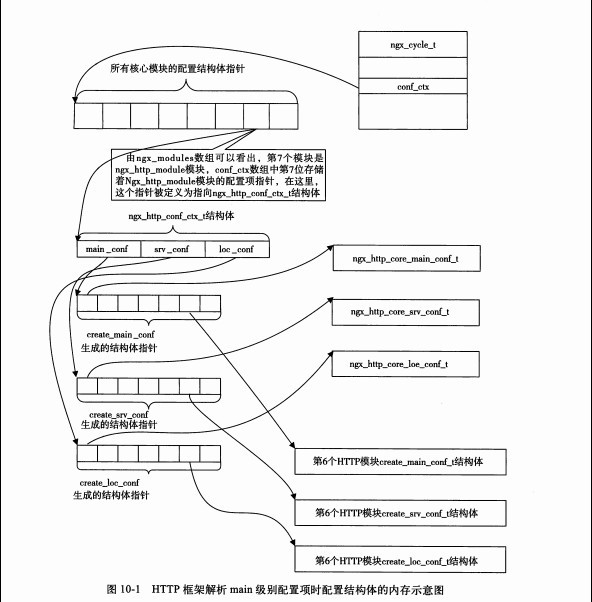
我们来看server这个命令的解析:
{ ngx_string("server"),
NGX_HTTP_MAIN_CONF|NGX_CONF_BLOCK|NGX_CONF_MULTI|NGX_CONF_NOARGS,
ngx_http_core_server,
0,
0,
NULL },
static char *
ngx_http_core_server(ngx_conf_t *cf, ngx_command_t *cmd, void *dummy)
{
char *rv;
void *mconf;
ngx_uint_t i;
ngx_conf_t pcf;
ngx_http_module_t *module;
struct sockaddr_in *sin;
ngx_http_conf_ctx_t *ctx, *http_ctx;
ngx_http_listen_opt_t lsopt;
ngx_http_core_srv_conf_t *cscf, **cscfp;
ngx_http_core_main_conf_t *cmcf;
ctx = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(ngx_http_conf_ctx_t));
if (ctx == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
http_ctx = cf->ctx;
//main conf不变
ctx->main_conf = http_ctx->main_conf;
/* the server{}'s srv_conf */
//创建新的srv和loc conf.
ctx->srv_conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *) * ngx_http_max_module);
if (ctx->srv_conf == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
/* the server{}'s loc_conf */
ctx->loc_conf = ngx_pcalloc(cf->pool, sizeof(void *) * ngx_http_max_module);
if (ctx->loc_conf == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
............................
/* the server configuration context */
cscf = ctx->srv_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index];
cscf->ctx = ctx;
cmcf = ctx->main_conf[ngx_http_core_module.ctx_index];
//保存所有的servers,可以看到是保存在main中的。这样子最后在HTTP main中就可以取到这个srv conf.
cscfp = ngx_array_push(&cmcf->servers);
if (cscfp == NULL) {
return NGX_CONF_ERROR;
}
*cscfp = cscf;
/* parse inside server{} */
//解析,可以看到设置type为srv_conf.
pcf = *cf;
cf->ctx = ctx;
cf->cmd_type = NGX_HTTP_SRV_CONF;
rv = ngx_conf_parse(cf, NULL);
//恢复cf.
*cf = pcf;
........................
}
return rv;
}此时内存:
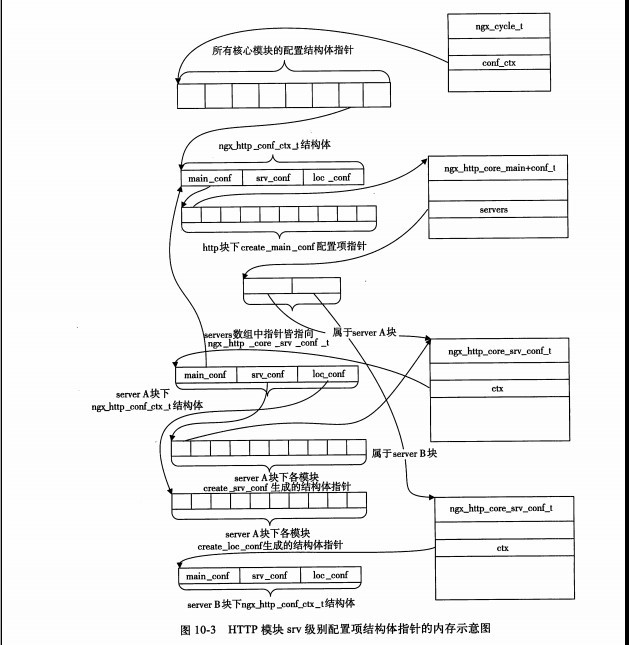
location解析完后内存:
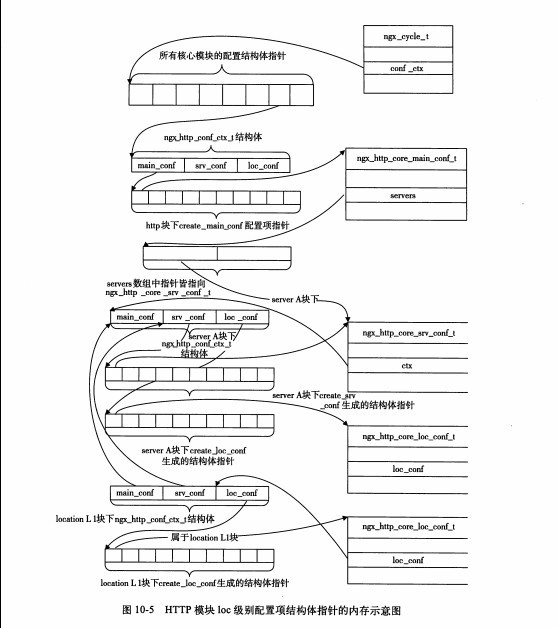
二级模块解析:





















 1104
1104

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








