官网demo地址:
 这篇讲的是如何使用聚合处理大量点数据。
这篇讲的是如何使用聚合处理大量点数据。
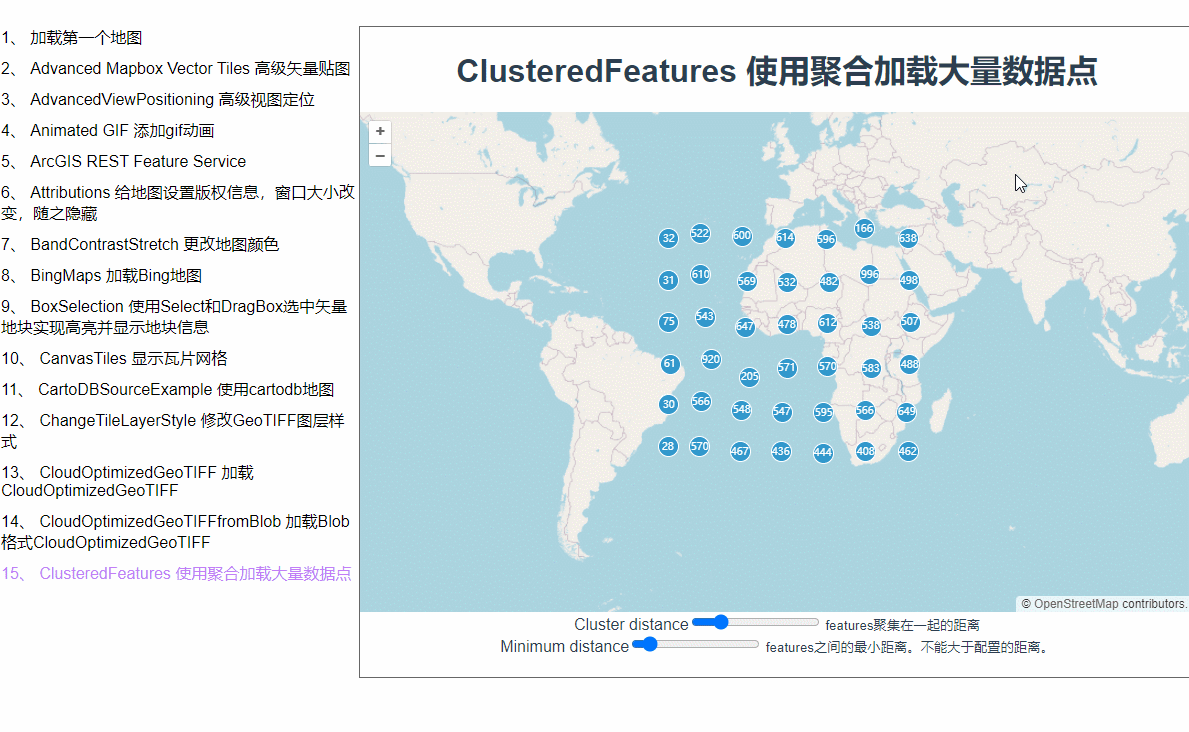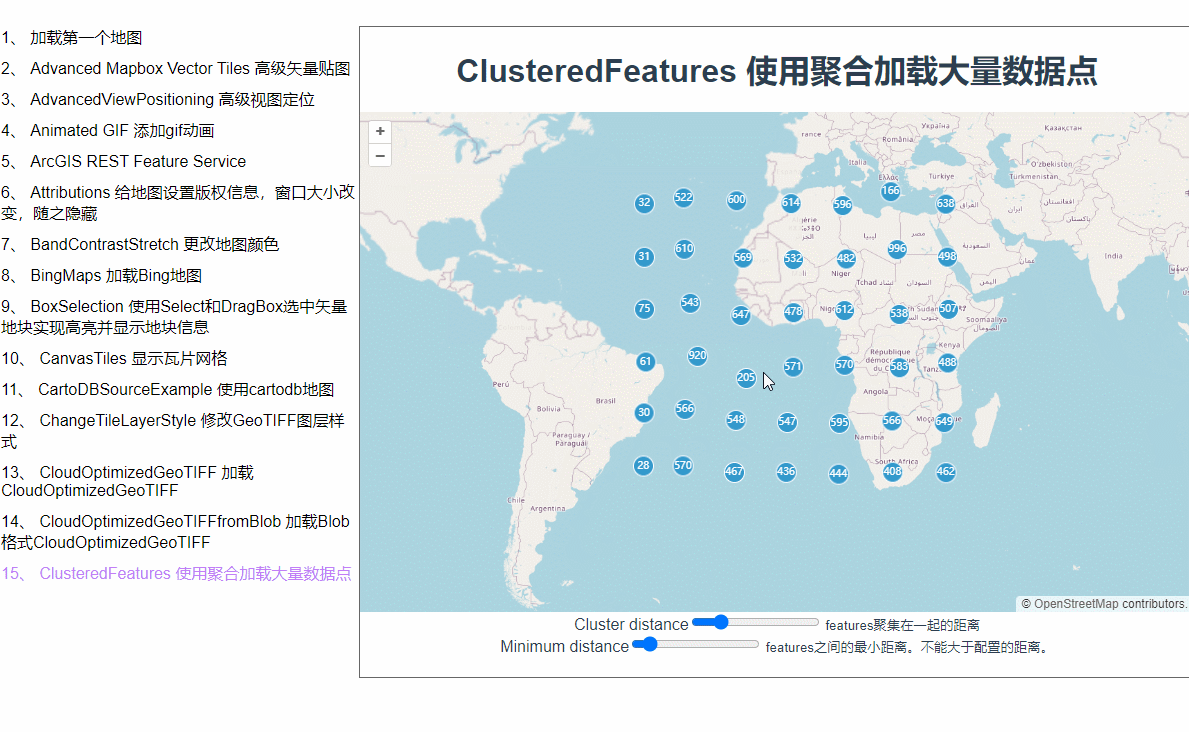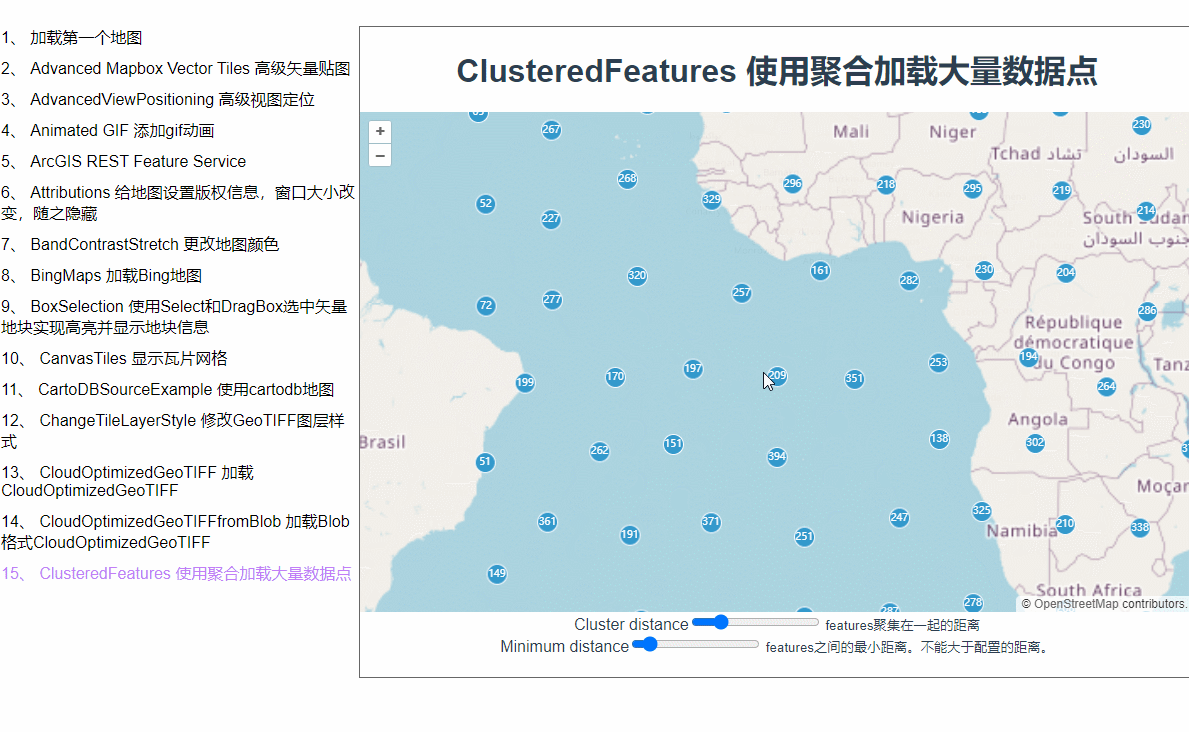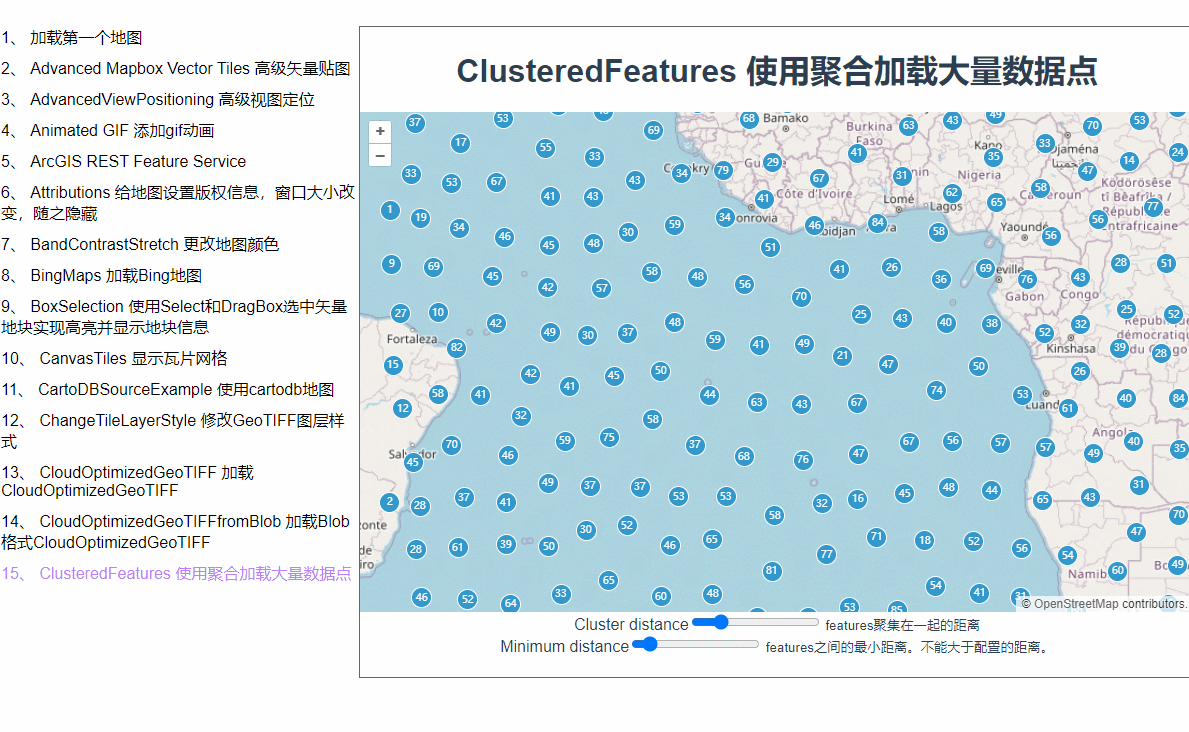
为什么会用聚合呢?当我们在地图上加载了大量矢量点位数据之后,地图就会卡顿,而在地图层级缩放层级较小的时候根本也看不见点位的具体信息。这时候,使用聚合就是一个比较好的解决方案。地图缩小的时候它会将紧挨着的许多点位合并成一个矢量点,放大到一定程度才会显示具体点位信息。
首先,来生成一些点位坐标数组
const count = 20000;
const features = new Array(count);
const e = 4500000;
for (let i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
const coordinates = [
2 * e * Math.random() - e,
2 * e * Math.random() - e,
];
features[i] = new Feature(new Point(coordinates));
}此时,features里面就是两万个点位的feature。然后把它们加载到矢量数据源上
const source = new VectorSource({
features: features,
});接着创建聚合类,Cluster的source是一个矢量数据源。distance表示的是feature与feature之间的距离,因为这个示例中有一个滑块动态设置间距,所以这里要设置一下minDistance最小距离。
const clusterSource = new Cluster({
distance: this.distanceInput,
minDistance: this.minDistanceInput,
source: source,
});然后把source加载图层上。
this.clusterLayer = new VectorLayer({
source: clusterSource,
});来看下效果:

点位都出来了,接下来加点样式配置。在实例化VectorLayer时加一个style配置,函数里会返回每一个feature,每一个feature上都有一个features属性,记录着它的下级features数组,聚合的原理就是把几个相邻的点通过计算合成一个feature,我猜features里面记录的就是合成这个feature所用的数组。style后面的这个函数是个高频触发的函数,地图稍微移动一下都会触发,所以这里的使用styleCache对象做了缓存效果,以每个feature的features数组的长度作为key,这样就不用每次都重新new Style了。
const styleCache = {};
this.clusterLayer = new VectorLayer({
source: clusterSource,
style: function (feature) {
const size = feature.get("features").length;
let style = styleCache[size];
if (!style) {
style = new Style({
image: new CircleStyle({
radius: 10,
stroke: new Stroke({
color: "#fff",
}),
fill: new Fill({
color: "#3399CC",
}),
}),
text: new Text({
text: size.toString(),
fill: new Fill({
color: "#fff",
}),
}),
});
styleCache[size] = style;
}
return style;
},
});注册地图点击事件,点击每一个feature就会把地图视角定位到点击的feature处。
this.map.on("click", (e) => {
this.clusterLayer.getFeatures(e.pixel).then((clickedFeatures) => {
if (clickedFeatures.length) {
// Get clustered Coordinates
console.log("clickedFeatures[0]", clickedFeatures);
const features = clickedFeatures[0].get("features");
// console.log('features',features);
const polygon = clickedFeatures[0].getGeometry();
if (features.length > 1) {
console.log(
"features.map((r) => r.getGeometry().getCoordinates())",
features.map((r) => r.getGeometry().getCoordinates())
);
const extent = boundingExtent(
features.map((r) => r.getGeometry().getCoordinates())
);
this.map
.getView()
.fit(extent, { duration: 1000, padding: [50, 50, 50, 50] });
}
}
});
});features.map((r) => r.getGeometry().getCoordinates()) 这段获取了组成这个feature用到的所有坐标数组。

使用boundingExtent(坐标数组)方法,可以计算出extent边界值。

最后再使用fit方法进行定位,duration表示动画时间。
this.map.getView().fit(extent, { duration: 1000, padding: [50, 50, 50, 50] });小细节:
fit方法的第一个参数可以接受extent(边界值)或者geometry(几何形状)。

而这里为什么要用extent而不是geometry呢?使用geometry定位看看。
const polygon = clickedFeatures[0].getGeometry();
this.map.getView().fit(extent, { duration: 1000, padding: [50, 50, 50, 50] });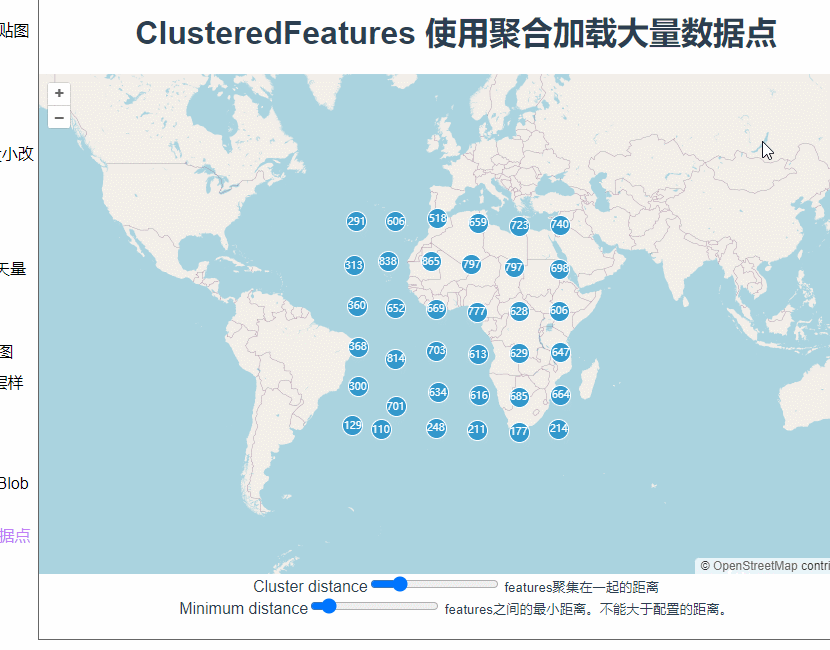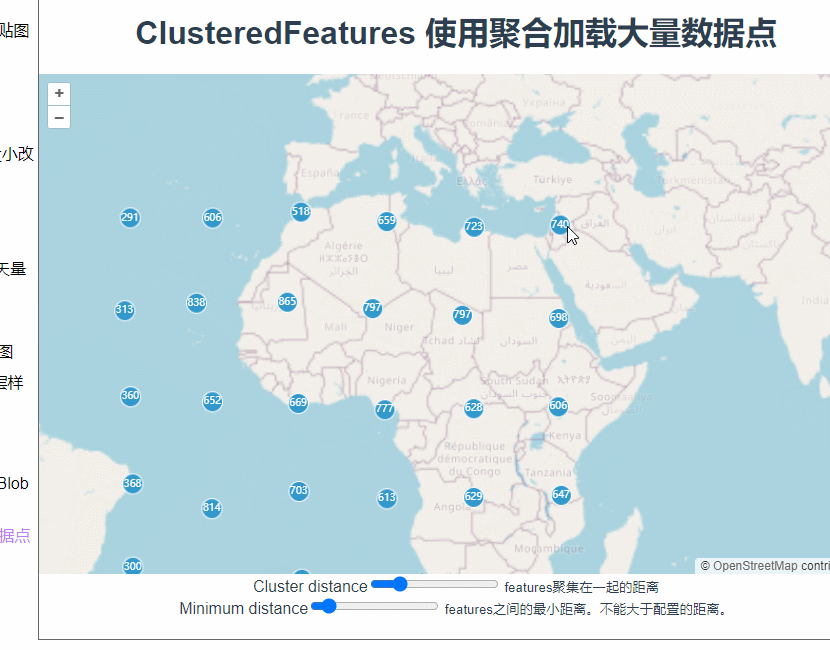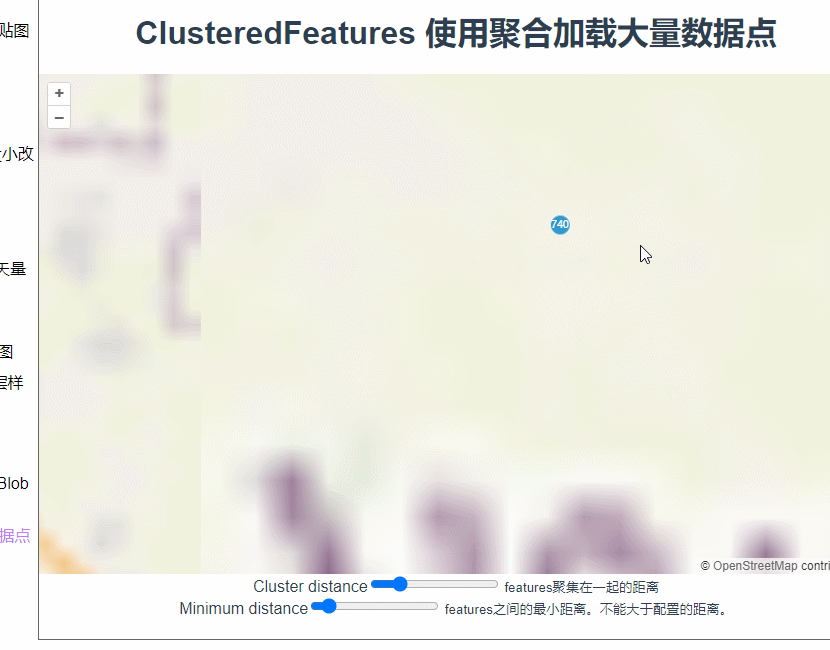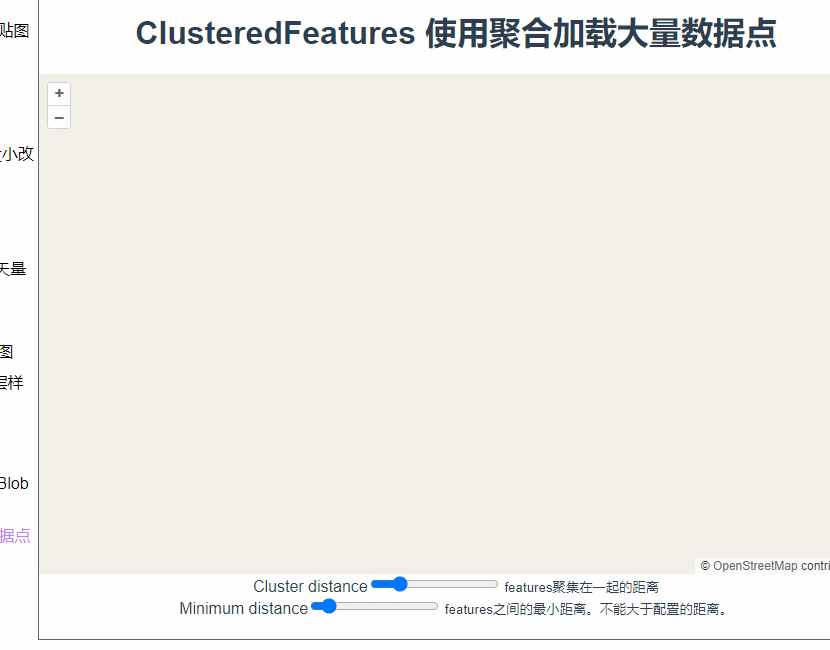
额。。。定位到了一个不知道的地方。
这是因为聚合里面,图层上的feature本来就是根据缩放层级变化的,定位过程中刚刚点击的那个feature已经不见了。而且这里我们希望地图视角移动到一个刚好能显示所有下级features的位置。所以这里使用extent更为合适。
完整代码:
<template>
<div class="box">
<h1>ClusteredFeatures 使用聚合加载大量数据点</h1>
<div id="map"></div>
<form>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="distance" class="col-form-label pb-0"
>Cluster distance</label
>
<input
id="distance"
class="form-range"
type="range"
min="0"
max="200"
step="1"
@change="distanceInputFun"
v-model.number="distanceInput"
/>
<small class="form-text text-muted"> features聚集在一起的距离 </small>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="min-distance" class="col-form-label pb-0"
>Minimum distance</label
>
<input
id="min-distance"
class="form-range"
type="range"
min="0"
max="200"
step="1"
@change="minDistanceInputFun"
v-model.number="minDistanceInput"
/>
<small class="form-text text-muted">
features之间的最小距离。不能大于配置的距离。
</small>
</div>
</form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Feature from "ol/Feature.js";
import Map from "ol/Map.js";
import Point from "ol/geom/Point.js";
import View from "ol/View.js";
import { Circle as CircleStyle, Fill, Stroke, Style, Text } from "ol/style.js";
import { Cluster, OSM, Vector as VectorSource } from "ol/source.js";
import { Tile as TileLayer, Vector as VectorLayer } from "ol/layer.js";
import { boundingExtent } from "ol/extent.js";
export default {
name: "",
components: {},
data() {
return {
map: null,
clusterLayer: null,
distanceInput: 40,
minDistanceInput: 20,
};
},
computed: {},
created() {},
mounted() {
this.initMap();
this.addUnderLayer();
this.addClusterLayer();
this.map.on("click", (e) => {
this.clusterLayer.getFeatures(e.pixel).then((clickedFeatures) => {
if (clickedFeatures.length) {
// Get clustered Coordinates
console.log("clickedFeatures[0]", clickedFeatures);
const features = clickedFeatures[0].get("features");
// console.log('features',features);
if (features.length > 1) {
console.log(
"features.map((r) => r.getGeometry().getCoordinates())",
features.map((r) => r.getGeometry().getCoordinates())
);
const extent = boundingExtent(
features.map((r) => r.getGeometry().getCoordinates())
);
const polygon = clickedFeatures[0].getGeometry();
this.map.getView().fit(extent, { duration: 0, padding: [50, 50, 50, 50] });
}
}
});
});
},
methods: {
distanceInputFun() {
this.clusterLayer
.getSource()
.setDistance(parseInt(this.distanceInput, 10));
},
minDistanceInputFun() {
this.clusterLayer
.getSource()
.setDistance(parseInt(this.minDistanceInput, 10));
},
addClusterLayer() {
const count = 20000;
const features = new Array(count);
const e = 4500000;
for (let i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
const coordinates = [
2 * e * Math.random() - e,
2 * e * Math.random() - e,
];
features[i] = new Feature(new Point(coordinates));
}
const source = new VectorSource({
features: features,
});
const clusterSource = new Cluster({
distance: this.distanceInput,
minDistance: this.minDistanceInput,
source: source,
});
const styleCache = {};
this.clusterLayer = new VectorLayer({
source: clusterSource,
style: function (feature) {
const size = feature.get("features").length;
let style = styleCache[size];
if (!style) {
style = new Style({
image: new CircleStyle({
radius: 10,
stroke: new Stroke({
color: "#fff",
}),
fill: new Fill({
color: "#3399CC",
}),
}),
text: new Text({
text: size.toString(),
fill: new Fill({
color: "#fff",
}),
}),
});
styleCache[size] = style;
}
return style;
},
});
this.map.addLayer(this.clusterLayer);
},
addUnderLayer() {
const raster = new TileLayer({
source: new OSM(),
});
this.map.addLayer(raster);
},
initMap() {
this.map = new Map({
layers: [],
target: "map",
view: new View({
center: [0, 0],
zoom: 2,
}),
});
},
},
};
</script>
<style lang="scss" scoped>
#map {
width: 100%;
height: 500px;
}
.box {
height: 100%;
}
</style>
























 2364
2364

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








