Solitaire
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 4721 Accepted Submission(s): 1421
Problem Description
Solitaire is a game played on a chessboard 8x8. The rows and columns of the chessboard are numbered from 1 to 8, from the top to the bottom and from left to right respectively.
There are four identical pieces on the board. In one move it is allowed to:
> move a piece to an empty neighboring field (up, down, left or right),
> jump over one neighboring piece to an empty field (up, down, left or right).
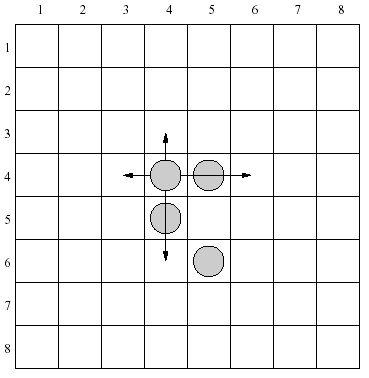
There are 4 moves allowed for each piece in the configuration shown above. As an example let's consider a piece placed in the row 4, column 4. It can be moved one row up, two rows down, one column left or two columns right.
Write a program that:
> reads two chessboard configurations from the standard input,
> verifies whether the second one is reachable from the first one in at most 8 moves,
> writes the result to the standard output.
Input
Each of two input lines contains 8 integers a1, a2, ..., a8 separated by single spaces and describes one configuration of pieces on the chessboard. Integers a2j-1 and a2j (1 <= j <= 4) describe the position of one piece - the row number and the column number respectively. Process to the end of file.
Output
The output should contain one word for each test case - YES if a configuration described in the second input line is reachable from the configuration described in the first input line in at most 8 moves, or one word NO otherwise.
Sample Input
4 4 4 5 5 4 6 5 2 4 3 3 3 6 4 6
Sample Output
YES
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define N 100005
#define P pair<int,int>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int M=1e9+7;
const int inf=1e9+7;
struct node{
int x[4],y[4],d,f;
void sort()
{
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
for(int j=i+1;j<4;j++){
if(x[i]>x[j]||(x[i]==x[j]&&y[i]>y[j])){
swap(x[i],x[j]);
swap(y[i],y[j]);
}
}
}
}
};
map<int,bool>mp[2];
int u[]={0,0,1,-1};
int v[]={1,-1,0,0};
bool juege(int x,int y){
if(x<1||y<1||x>8||y>8)return 1;
return 0;
}
int gethash(node p){
int k=0;
p.sort();
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
k*=64;
k+=p.x[i]*8+p.y[i]-9;
}
return k;
}
bool bfs(node s,node to)
{
mp[s.f][gethash(s)]=1;
mp[to.f][gethash(to)]=1;
queue<node>Q;
Q.push(s);Q.push(to);
int ji[9][9];
memset(ji,0,sizeof(ji));
while(!Q.empty())
{
node p=Q.front();
Q.pop();
if(mp[!p.f][gethash(p)])return 1;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
ji[p.x[i]][p.y[i]]=1;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
int x=p.x[i]+u[j],y=p.y[i]+v[j];
if(juege(x,y))continue;
if(ji[x][y]){
x+=u[j];
y+=v[j];
if(juege(x,y)||ji[x][y])continue;
}
node now=p;
now.d++;
now.x[i]=x;
now.y[i]=y;
int k=gethash(now);
if(mp[p.f][k])continue;
if(mp[!p.f][k])return 1;
mp[p.f][k]=1;
if(now.d<4)Q.push(now);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
ji[p.x[i]][p.y[i]]=0;
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
node s,to;
while(~scanf("%d%d",&s.x[0],&s.y[0]))
{
mp[0].clear();
mp[1].clear();
for(int i=1;i<4;i++)
scanf("%d%d",&s.x[i],&s.y[i]);
for(int i=0;i<4;i++)
scanf("%d%d",&to.x[i],&to.y[i]);
s.d=0;s.f=1;
to.d=0;to.f=0;
if(bfs(s,to))printf("YES\n");
else printf("NO\n");
}
return 0;
}
























 2531
2531

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








