InceptionV3代码解析
读了Google的GoogleNet以及InceptionV3的论文,决定把它实现一下,尽管很难,但是网上有不少资源,就一条一条的写完了,对于网络的解析都在代码里面了,是在原博主的基础上进行修改的,添加了更多的细节,以及自己的理解。总之,是更详细更啰嗦的一个版本,适合初学者。
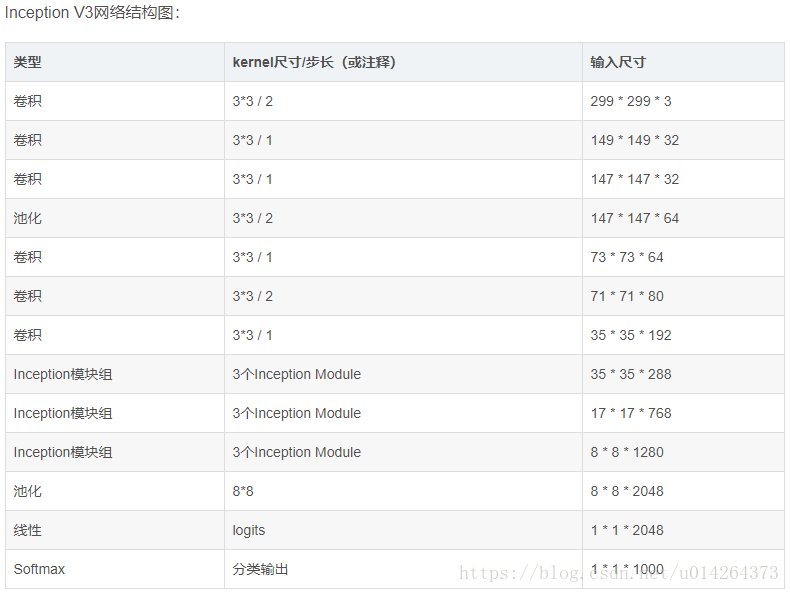
1 import tensorflow as tf 2 from datetime import datetime 3 import math 4 import time 5 6 ##参考tensorflow实战书籍+博客https://blog.csdn.net/superman_xxx/article/details/65451916,不过丰富了很多细节 7 ##适合像我一样的初学者 8 slim = tf.contrib.slim 9 #Slim is an interface to contrib functions, examples and models. 10 #只是一个接口作用 11 trunc_normal = lambda stddev: tf.truncated_normal_initializer(0.0, stddev) 12 #匿名函数 lambda x: x * x 实际上就是:返回x的平方 13 # tf.truncated_normal_initializer产生截断的正态分布 14 15 ########定义函数生成网络中经常用到的函数的默认参数######## 16 # 默认参数:卷积的激活函数、权重初始化方式、标准化器等 17 def inception_v3_arg_scope(weight_decay=0.00004, # 设置L2正则的weight_decay 18 stddev=0.1, # 标准差默认值0.1 19 batch_norm_var_collection='moving_vars'): 20 21 # 定义batch normalization(批量标准化/归一化)的参数字典 22 batch_norm_params = { 23 'decay': 0.9997, # 定义参数衰减系数 24 'epsilon': 0.001, 25 'updates_collections': tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS, 26 'variables_collections': { 27 'beta': None, 28 'gamma': None, 29 'moving_mean': [batch_norm_var_collection], 30 'moving_variance': [batch_norm_var_collection],#值就是前面设置的batch_norm_var_collection='moving_vars' 31 } 32 } 33 34 # 给函数的参数自动赋予某些默认值 35 # slim.arg_scope常用于为tensorflow里的layer函数提供默认值以使构建模型的代码更加紧凑苗条(slim): 36 with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.fully_connected], 37 weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay)): 38 # 对[slim.conv2d, slim.fully_connected]自动赋值,可以是列表或元组 39 # 使用slim.arg_scope后就不需要每次都重复设置参数了,只需要在有修改时设置 40 with slim.arg_scope( # 嵌套一个slim.arg_scope对卷积层生成函数slim.conv2d的几个参数赋予默认值 41 [slim.conv2d], 42 weights_initializer=trunc_normal(stddev), # 权重初始化器 43 activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, # 激活函数 44 normalizer_fn=slim.batch_norm, # 标准化器 45 normalizer_params=batch_norm_params) as sc: # 标准化器的参数设置为前面定义的batch_norm_params 46 return sc # 最后返回定义好的scope 47 48 ########定义函数可以生成Inception V3网络的卷积部分######## 49 #########Inception V3架构见TENSORFLOW实战书-黄文坚 p124-p125页 50 def inception_v3_base(inputs, scope=None): 51 ''' 52 Args: 53 inputs:输入的tensor 54 scope:包含了函数默认参数的环境 55 ''' 56 end_points = {} # 定义一个字典表保存某些关键节点供之后使用 57 58 with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'InceptionV3', [inputs]): 59 with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.max_pool2d, slim.avg_pool2d], # 对三个参数设置默认值 60 stride=1, padding='VALID'): 61 # 正式定义Inception V3的网络结构。首先是前面的非Inception Module的卷积层 62 #输入图像尺寸299 x 299 x 3 63 # slim.conv2d的第一个参数为输入的tensor,第二个是输出的通道数,卷积核尺寸,步长stride,padding模式 64 net = slim.conv2d(inputs, 32, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='Conv2d_1a_3x3') 65 # 输出尺寸149 x 149 x 32 66 ''' 67 因为使用了slim以及slim.arg_scope,我们一行代码就可以定义好一个卷积层 68 相比AlexNet使用好几行代码定义一个卷积层,或是VGGNet中专门写一个函数定义卷积层,都更加方便 69 ''' 70 net = slim.conv2d(net, 32, [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_2a_3x3') 71 # 输出尺寸147 x 147 x 32 72 net = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [3, 3], padding='SAME', scope='Conv2d_2b_3x3') 73 # 输出尺寸147 x 147 x 64 74 net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='MaxPool_3a_3x3') 75 # 输出尺寸73 x 73 x 64 76 net = slim.conv2d(net, 80, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_3b_1x1') 77 #输出尺寸 73 x 73 x 80. 78 net = slim.conv2d(net, 192, [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_4a_3x3') 79 #输出尺寸 71 x 71 x 192. 80 net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='MaxPool_5a_3x3') 81 # 输出尺寸35 x 35 x 192. 82 83 '''上面部分代码一共有5个卷积层,2个池化层,实现了对图片数据的尺寸压缩,并对图片特征进行了抽象 84 有个疑问是框架例里给出的表格中是6个卷积和一个池化,并没有1x1的卷积,为什么要这么做,以及scope后面的名字为什么要这样叫。 85 ''' 86 87 ''' 88 接下来就是三个连续的Inception模块组,三个Inception模块组中各自分别有多个Inception Module,这部分是Inception Module V3 89 的精华所在。每个Inception模块组内部的几个Inception Mdoule结构非常相似,但是存在一些细节的不同 90 ''' 91 # Inception blocks 92 with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.max_pool2d, slim.avg_pool2d], # 设置所有模块组的默认参数 93 stride=1, padding='SAME'): # 将所有卷积层、最大池化、平均池化层步长都设置为1 94 #注意这个模块已经统一指定了padding='SAME',后面不用再说明 95 # 第一个模块组包含了三个结构类似的Inception Module 96 # 第一个模块组第一个Inception Module,Mixed_5b 97 with tf.variable_scope('Mixed_5b'): # 第一个Inception Module名称。Inception Module有四个分支 98 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'): # 第一个分支64通道的1*1卷积 99 branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 100 #输出尺寸35*35*64 101 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'): # 第二个分支48通道1*1卷积后一层链接一个64通道的5*5卷积 102 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, 48, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 103 #输出尺寸35*35*48 104 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 64, [5, 5], scope='Conv2d_0b_5x5') 105 #输出尺寸35*35*64 106 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'): #第三个分支64通道1*1卷积后一层链接2个96通道的5*5卷积 107 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 108 #输出尺寸35*35*64 109 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 96, [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3') 110 #输出尺寸35*35*96 111 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 96, [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_0c_3x3') 112 # 输出尺寸35*35*96 113 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'): # 第四个分支为3*3的平均池化后一层连接32通道的1*1卷积 114 branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3') 115 # 输出尺寸35*35*192 116 branch_3 = slim.conv2d(branch_3, 32, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1') 117 # 输出尺寸35*35*32 118 net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 3) 119 # 将四个分支的输出合并在一起(第三个维度合并,即输出通道上合并)64+64+96+32=256个通道 120 # 输出尺寸35*35*256 121 122 # 第一个模块组第二个Inception Module 名称是:Mixed_5c 123 with tf.variable_scope('Mixed_5c'): #同样有4个分支,唯一不同的是第4个分支最后接的是64输出通道 124 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'): 125 branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 126 # 输出尺寸35*35*64 127 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'): 128 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, 48, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1') 129 # 输出尺寸35*35*48 130 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 64, [5, 5], scope='Conv_1_0c_5x5') 131 # 输出尺寸35*35*64 132 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'): 133 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 134 # 输出尺寸35*35*64 135 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 96, [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3') 136 # 输出尺寸35*35*96 137 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 96, [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_0c_3x3') 138 # 输出尺寸35*35*96 139 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'): 140 branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3') 141 # 输出尺寸35*35*192 142 branch_3 = slim.conv2d(branch_3, 64, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1') 143 # 输出尺寸35*35*64 144 net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 3) 145 # 将四个分支的输出合并在一起(第三个维度合并,即输出通道上合并)64+64+96+64=288个通道 146 # 输出尺寸35*35*288 147 148 # 第一个模块组第3个Inception Module 名称是:Mixed_5d 149 with tf.variable_scope('Mixed_5d'): 150 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'): 151 branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 152 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'): 153 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, 48, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 154 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 64, [5, 5], scope='Conv2d_0b_5x5') 155 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'): 156 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 157 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 96, [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3') 158 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 96, [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_0c_3x3') 159 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'): 160 branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3') 161 branch_3 = slim.conv2d(branch_3, 64, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1') 162 net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 3) 163 # 将四个分支的输出合并在一起(第三个维度合并,即输出通道上合并)64+64+96+64=288个通道 164 # 输出尺寸35*35*288 165 166 167 # 第二个Inception模块组是一个非常大的模块组,包含了5个Inception Mdoule,2-5个Inception Mdoule结构非常相似 168 #第二个模块组第一个Inception Module 名称是:Mixed_6a 169 #输入是35*35*288 170 with tf.variable_scope('Mixed_6a'): #包含3个分支 171 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'): 172 branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, 384, [3, 3], stride=2, 173 padding='VALID', scope='Conv2d_1a_1x1') 174 # padding='VALID'图片尺寸会被压缩,通道数增加 175 # 输出尺寸17*17*384 176 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'): #64通道的1*1加2个96通道的3*3卷积 177 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 178 #输出尺寸35 * 35 * 64 179 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 96, [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3') 180 #输出尺寸35*35*96 181 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 96, [3, 3], stride=2, 182 padding='VALID', scope='Conv2d_1a_1x1') 183 # 图片被压缩/输出尺寸17*17*96 184 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'): 185 branch_2 = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=2, padding='VALID', 186 scope='MaxPool_1a_3x3') 187 #输出尺寸17 * 17 * 288(这里大家注意,书上还有很多博客上都是384+96+256=736并不是768,所以最后应该加288) 188 net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2], 3) 189 # 输出尺寸定格在17 x 17 x 768 190 191 # 第二个模块组第二个Inception Module 名称是:Mixed_6b 192 with tf.variable_scope('Mixed_6b'): #4个分支 193 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'): 194 branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 195 # 输出尺寸17*17*192 196 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'): 197 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 198 # 输出尺寸17 * 17 * 128 199 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 128, [1, 7], 200 scope='Conv2d_0b_1x7') 201 # 输出尺寸17 * 17 * 128 202 # 串联1*7卷积和7*1卷积合成7*7卷积,减少了参数,减轻了过拟合 203 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 192, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0c_7x1') 204 # 输出尺寸17 * 17 * 192 205 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'): 206 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 207 # 输出尺寸17 * 17 * 128 208 # 反复将7*7卷积拆分 209 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 128, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_7x1') 210 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 128, [1, 7], scope='Conv2d_0c_1x7') 211 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 128, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0d_7x1') 212 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 192, [1, 7], scope='Conv2d_0e_1x7') 213 # 这种方法算是利用Factorization into small convolutions 的典范 214 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'): #3*3的平均池化 215 branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3') 216 # 输出尺寸17 * 17 * 768 217 branch_3 = slim.conv2d(branch_3, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1') 218 # 输出尺寸17 * 17 * 192 219 net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 3) 220 # 输出尺寸定格在17 x 17 x (192*4)=17*17*768 221 222 # 第二个模块组第三个Inception Module 名称是:Mixed_6c 223 # 同前面一个相似,第二个分支和第三个分支的前几层通道由120升为160 224 with tf.variable_scope('Mixed_6c'): 225 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'): 226 ''' 227 我们的网络每经过一个inception module,即使输出尺寸不变,但是特征都相当于被重新精炼了一遍, 228 其中丰富的卷积和非线性化对提升网络性能帮助很大。 229 ''' 230 branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 231 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'): 232 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, 160, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 233 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 160, [1, 7], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x7') 234 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 192, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0c_7x1') 235 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'): 236 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, 160, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 237 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 160, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_7x1') 238 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 160, [1, 7], scope='Conv2d_0c_1x7') 239 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 160, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0d_7x1') 240 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 192, [1, 7], scope='Conv2d_0e_1x7') 241 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'): 242 branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3') 243 branch_3 = slim.conv2d(branch_3, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1') 244 net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 3) 245 # 输出尺寸定格在17 x 17 x (192*4)=17*17*768 246 247 # 第二个模块组第四个Inception Module 名称是:Mixed_6d 248 # 和前面一个完全一样,增加卷积和非线性,提炼特征 249 with tf.variable_scope('Mixed_6d'): 250 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'): 251 branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 252 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'): 253 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, 160, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 254 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 160, [1, 7], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x7') 255 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 192, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0c_7x1') 256 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'): 257 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, 160, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 258 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 160, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_7x1') 259 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 160, [1, 7], scope='Conv2d_0c_1x7') 260 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 160, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0d_7x1') 261 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 192, [1, 7], scope='Conv2d_0e_1x7') 262 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'): 263 branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3') 264 branch_3 = slim.conv2d(branch_3, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1') 265 net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 3) 266 # 输出尺寸定格在17 x 17 x (192*4)=17*17*768 267 268 # 第二个模块组第五个Inception Module 名称是:Mixed_6e 269 # 也同前面一样,通道数变为192,但是要将Mixed_6e存储在end_points中 270 with tf.variable_scope('Mixed_6e'): 271 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'): 272 branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 273 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'): 274 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 275 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 192, [1, 7], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x7') 276 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 192, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0c_7x1') 277 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'): 278 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 279 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 192, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_7x1') 280 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 192, [1, 7], scope='Conv2d_0c_1x7') 281 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 192, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0d_7x1') 282 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(branch_2, 192, [1, 7], scope='Conv2d_0e_1x7') 283 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'): 284 branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3') 285 branch_3 = slim.conv2d(branch_3, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1') 286 net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 3) 287 # 输出尺寸定格在17 x 17 x (192*4)=17*17*768 288 end_points['Mixed_6e'] = net 289 # 将Mixed_6e存储于end_points中,作为Auxiliary Classifier辅助模型的分类 290 291 # 第三个Inception模块包含了3个Inception Mdoule,后两个个Inception Mdoule结构非常相似 292 # 第三个模块组第一个Inception Module 名称是:Mixed_7a 293 with tf.variable_scope('Mixed_7a'): # 3个分支 294 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'): 295 branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 296 # 输出尺寸17*17*192 297 branch_0 = slim.conv2d(branch_0, 320, [3, 3], stride=2, 298 padding='VALID', scope='Conv2d_1a_3x3') 299 # 压缩图片# 输出尺寸8*8*320 300 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'): 301 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 302 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 192, [1, 7], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x7') 303 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 192, [7, 1], scope='Conv2d_0c_7x1') 304 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(branch_1, 192, [3, 3], stride=2, 305 padding='VALID', scope='Conv2d_1a_3x3') 306 # 输出尺寸8*8*192 307 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'): # 池化层不会对输出通道数产生改变 308 branch_2 = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=2, padding='VALID', 309 scope='MaxPool_1a_3x3') 310 # 输出尺寸8*8*768 311 net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2], 3) 312 # 输出图片尺寸被缩小,通道数增加,tensor的总size在持续下降中 313 # 输出尺寸8*8*(320+192+768)=8*8*1280 314 315 # 第三个模块组第二个Inception Module 名称是:Mixed_7b 316 ''' 317 这个模块最大的区别是分支内又有分支,network in network in network 318 ''' 319 with tf.variable_scope('Mixed_7b'): # 4 个分支 320 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'): 321 branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, 320, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 322 # 输出尺寸8*8*320 323 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'): #第二个分支里还有分支 324 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, 384, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 325 # 输出尺寸8*8*384 326 branch_1 = tf.concat([ 327 slim.conv2d(branch_1, 384, [1, 3], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x3'), 328 slim.conv2d(branch_1, 384, [3, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_3x1')], 3) 329 # 输出尺寸8 * 8 * (384+384)=8*8*768 330 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'): #这个分支更复杂:1*1>3*3>1*3+3*1,总共有三层 331 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, 448, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 332 branch_2 = slim.conv2d( 333 branch_2, 384, [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3') 334 branch_2 = tf.concat([ 335 slim.conv2d(branch_2, 384, [1, 3], scope='Conv2d_0c_1x3'), 336 slim.conv2d(branch_2, 384, [3, 1], scope='Conv2d_0d_3x1')], 3) 337 # 输出尺寸8 * 8 * (384+384)=8*8*768 338 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'): 339 branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3') 340 branch_3 = slim.conv2d( 341 branch_3, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1') 342 # 输出尺寸8 * 8 * (384+384)=8*8*192 343 net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 3) 344 # 输出通道数增加到2048 # 输出尺寸8 * 8 * (320+768+768+192)=8*8*2048 345 346 # 第三个模块组第三个Inception Module 名称是:Mixed_7c 347 #同前一个一样 348 with tf.variable_scope('Mixed_7c'): 349 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'): 350 branch_0 = slim.conv2d(net, 320, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 351 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'): 352 branch_1 = slim.conv2d(net, 384, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 353 branch_1 = tf.concat([ 354 slim.conv2d(branch_1, 384, [1, 3], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x3'), 355 slim.conv2d(branch_1, 384, [3, 1], scope='Conv2d_0c_3x1')], 3) 356 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'): 357 branch_2 = slim.conv2d(net, 448, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0a_1x1') 358 branch_2 = slim.conv2d( 359 branch_2, 384, [3, 3], scope='Conv2d_0b_3x3') 360 branch_2 = tf.concat([ 361 slim.conv2d(branch_2, 384, [1, 3], scope='Conv2d_0c_1x3'), 362 slim.conv2d(branch_2, 384, [3, 1], scope='Conv2d_0d_3x1')], 3) 363 with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'): 364 branch_3 = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [3, 3], scope='AvgPool_0a_3x3') 365 branch_3 = slim.conv2d( 366 branch_3, 192, [1, 1], scope='Conv2d_0b_1x1') 367 net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 3) 368 # 输出尺寸8 * 8 * (320+768+768+192)=8*8*2048 369 370 return net, end_points 371 #Inception V3网络的核心部分,即卷积层部分就完成了 372 ''' 373 设计inception net的重要原则是图片尺寸不断缩小,inception模块组的目的都是将空间结构简化,同时将空间信息转化为 374 高阶抽象的特征信息,即将空间维度转为通道的维度。降低了计算量。Inception Module是通过组合比较简单的特征 375 抽象(分支1)、比较比较复杂的特征抽象(分支2和分支3)和一个简化结构的池化层(分支4),一共四种不同程度的 376 特征抽象和变换来有选择地保留不同层次的高阶特征,这样最大程度地丰富网络的表达能力。 377 ''' 378 379 ########全局平均池化、Softmax和Auxiliary Logits(之前6e模块的辅助分类节点)######## 380 def inception_v3(inputs, 381 num_classes=1000, # 最后需要分类的数量(比赛数据集的种类数) 382 is_training=True, # 标志是否为训练过程,只有在训练时Batch normalization和Dropout才会启用 383 dropout_keep_prob=0.8, # 节点保留比率 384 prediction_fn=slim.softmax, # 最后用来分类的函数 385 spatial_squeeze=True, # 参数标志是否对输出进行squeeze操作(去除维度数为1的维度,比如5*3*1转为5*3) 386 reuse=None, # 是否对网络和Variable进行重复使用 387 scope='InceptionV3'): # 包含函数默认参数的环境 388 389 with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'InceptionV3', [inputs, num_classes], # 定义参数默认值 390 reuse=reuse) as scope: 391 #'InceptionV3'是命名空间 392 with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm, slim.dropout], # 定义标志默认值 393 is_training=is_training): 394 # 拿到最后一层的输出net和重要节点的字典表end_points 395 net, end_points = inception_v3_base(inputs, scope=scope) # 用定义好的函数构筑整个网络的卷积部分 396 397 # Auxiliary Head logits作为辅助分类的节点,对分类结果预测有很大帮助, 398 # 对end_points的结界做平均池化、卷积最后通过1*1的卷积将通道变为1000 399 with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.max_pool2d, slim.avg_pool2d], 400 stride=1, padding='SAME'): # 将卷积、最大池化、平均池化步长设置为1 401 aux_logits = end_points['Mixed_6e'] # 通过end_points取到Mixed_6e 402 with tf.variable_scope('AuxLogits'): 403 aux_logits = slim.avg_pool2d( 404 aux_logits, [5, 5], stride=3, padding='VALID', # 在Mixed_6e之后接平均池化。压缩图像尺寸 405 scope='AvgPool_1a_5x5') 406 # 输入图像尺寸17*17*768,输出5*5*768 407 aux_logits = slim.conv2d(aux_logits, 128, [1, 1], # 卷积。压缩图像尺寸。 408 scope='Conv2d_1b_1x1') 409 # 输出图像尺寸5*5*128 410 # Shape of feature map before the final layer. 411 aux_logits = slim.conv2d( 412 aux_logits, 768, [5,5], 413 weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.01), # 权重初始化方式重设为标准差为0.01的正态分布 414 padding='VALID', scope='Conv2d_2a_5x5') 415 # 输出图像尺寸1*1*768 416 aux_logits = slim.conv2d( 417 aux_logits, num_classes, [1, 1], activation_fn=None, 418 normalizer_fn=None, weights_initializer=trunc_normal(0.001), 419 scope='Conv2d_2b_1x1') 420 # 输出变为1*1*1000,这里的num_classes表示输出通道数,不用激活和标准化,权重重设为0.001的正态分布 421 if spatial_squeeze: # tf.squeeze消除tensor中前两个为1的维度。 422 aux_logits = tf.squeeze(aux_logits, [1, 2], name='SpatialSqueeze') 423 424 # 这里非常值得注意,tf.squeeze(aux_logits, [1, 2])为什么是[1, 2]而不是[0,1],括号里表示为1的维度 425 #因为训练的时候是输入的批次,第一维不是1,[32,1,1,1000]. 426 end_points['AuxLogits'] = aux_logits 427 # 最后将辅助分类节点的输出aux_logits储存到字典表end_points中 428 429 # 处理正常的分类预测逻辑 430 # Final pooling and prediction 431 # 这一过程的主要步骤:对Mixed_7c的输出进行8*8的全局平均池化>Dropout>1*1*1000的卷积>除去维数为1>softmax分类 432 with tf.variable_scope('Logits'): 433 net = slim.avg_pool2d(net, [8, 8], padding='VALID', 434 scope='AvgPool_1a_8x8') 435 #输入为8*8*2048 输出为1 x 1 x 2048 436 net = slim.dropout(net, keep_prob=dropout_keep_prob, scope='Dropout_1b') 437 end_points['PreLogits'] = net 438 # 1*1*2048 439 logits = slim.conv2d(net, num_classes, [1, 1], activation_fn=None, 440 normalizer_fn=None, scope='Conv2d_1c_1x1') 441 # 激活函数和规范化函数设为空 # 输出通道数1*1*1000 442 if spatial_squeeze: # tf.squeeze去除输出tensor中维度为1的节点 443 logits = tf.squeeze(logits, [1, 2], name='SpatialSqueeze') 444 end_points['Logits'] = logits 445 end_points['Predictions'] = prediction_fn(logits, scope='Predictions') 446 # Softmax对结果进行分类预测 447 return logits, end_points # 最后返回logits和包含辅助节点的end_points 448 #end_points里面有'AuxLogits'、'Logits'、'Predictions'分别是辅助分类的输出,主线的输出以及经过softmax后的预测输出 449 450 ''' 451 到这里,前向传播已经写完,对其进行运算性能测试 452 ''' 453 ########评估网络每轮计算时间######## 454 def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string): 455 456 # Args: 457 # session:the TensorFlow session to run the computation under. 458 # target:需要评测的运算算子。 459 # info_string:测试名称。 460 461 num_steps_burn_in = 10 462 # 先定义预热轮数(头几轮跌代有显存加载、cache命中等问题因此可以跳过,只考量10轮迭代之后的计算时间) 463 total_duration = 0.0 # 记录总时间 464 total_duration_squared = 0.0 # 总时间平方和 -----用来后面计算方差 465 466 #迭代计算时间 467 for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in): # 迭代轮数 468 start_time = time.time() # 记录时间 469 _ = session.run(target) # 每次迭代通过session.run(target) 470 duration = time.time() - start_time 471 #每十轮输出一次 472 if i >= num_steps_burn_in: 473 if not i % 10: 474 print ('%s: step %d, duration = %.3f' % 475 (datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration)) 476 total_duration += duration # 累加便于后面计算每轮耗时的均值和标准差 477 total_duration_squared += duration * duration 478 mn = total_duration / num_batches # 每轮迭代的平均耗时 479 vr = total_duration_squared / num_batches - mn * mn 480 # 方差,是把一般的方差公式进行化解之后的结果,值得 借鉴 481 sd = math.sqrt(vr) # 标准差 482 print ('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' % 483 (datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd)) 484 #输出的时间是处理一批次的平均时间加减标准差 485 486 # 测试前向传播性能 487 batch_size = 32 # 因为网络结构较大依然设置为32,以免GPU显存不够 488 height, width = 299, 299 # 图片尺寸 489 # 随机生成图片数据作为input 490 inputs = tf.random_uniform((batch_size, height, width, 3)) 491 492 with slim.arg_scope(inception_v3_arg_scope()): 493 # scope中包含了batch normalization默认参数,激活函数和参数初始化方式的默认值 494 logits, end_points = inception_v3(inputs, is_training=False) 495 # inception_v3中传入inputs获取里logits和end_points 496 497 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() # 初始化全部模型参数 498 sess = tf.Session() # 创建session 499 sess.run(init) 500 num_batches=100 # 测试的batch数量 501 time_tensorflow_run(sess, logits, "Forward") 502 ''' 503 虽然输入图片比VGGNet的224*224大了78%,但是forward速度却比VGGNet更快。 504 这主要归功于其较小的参数量,inception V3参数量比inception V1的700万 505 多了很多,不过仍然不到AlexNet的6000万参数量的一半。相比VGGNet的1.4 506 亿参数量就更少了。整个网络的浮点计算量为50亿次,比inception V1的15亿 507 次大了不少,但是相比VGGNet来说不算大。因此较少的计算量让inception V3 508 网络变得非常实用,可以轻松地移植到普通服务器上提供快速响应服务,甚至 509 移植到手机上进行实时的图像识别。 510 ''' 511 #分析结果:前面的输出是当前时间下每10步的计算时间,最后输出的是当前时间下前向传播的总批次以及平均时间+-标准差





















 5005
5005











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








