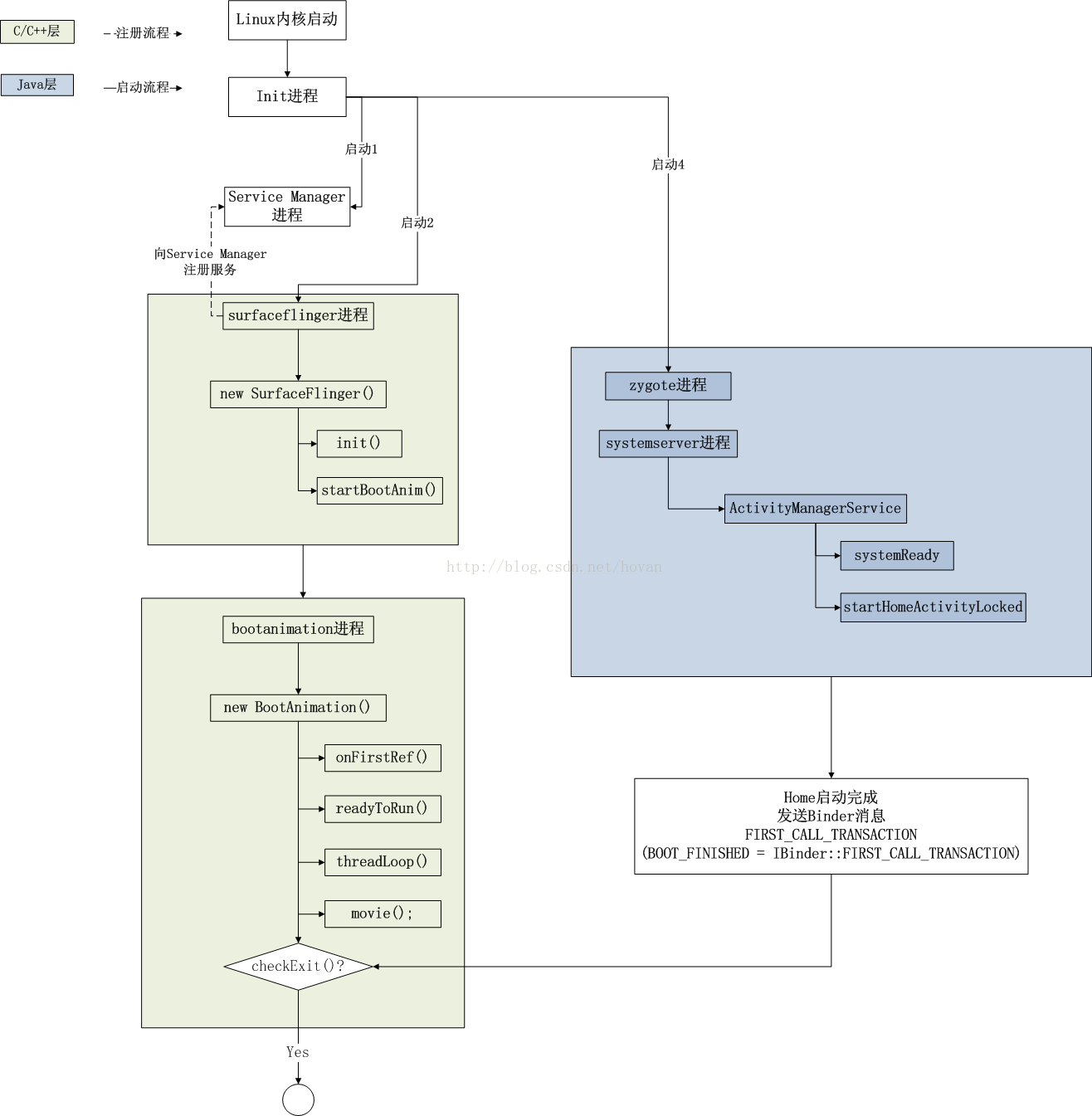
从android的Surface Flinger服务启动分析知道,开机动画是在SurfaceFlinger实例通过调用startBootAnim()启动的。
下面我们就一起学习BootAnim是如何启动和结束的,我精读代码前都喜欢先描出框架图,以此图为基础再去研读会达到事半功倍的效果。好吧,直接上图。
内核起来后会启动第一个进程,即init进程。
init进程会根据init.rc配置启动surfaceflinger进程。
service surfaceflinger /system/bin/surfaceflinger
class main
user system
group graphics drmrpc
onrestart restart zygotesurfaceflinger进程便启动了,跟着就会跑进程的main()函数。
frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/main_surfaceflinger.cpp
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
....
// instantiate surfaceflinger
sp<SurfaceFlinger> flinger = new SurfaceFlinger();//创建surfaceflinger服务实例
....
flinger->init();
// publish surface flinger
sp<IServiceManager> sm(defaultServiceManager());
sm->addService(String16(SurfaceFlinger::getServiceName()), flinger, false);//注册到service manager里
// run in this thread
flinger->run();//开跑
return 0;
}首先new一个SurfaceFlinger实例,然后init,然后run
frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
void SurfaceFlinger::init() {
ALOGI( "SurfaceFlinger's main thread ready to run. "
"Initializing graphics H/W...");
.....
// start boot animation
startBootAnim();//开始播放动画
}初始化graphics之后,就调用startBootAnim()播放开机动画。
void SurfaceFlinger::startBootAnim() {
// start boot animation
mBootFinished = false;
property_set("service.bootanim.exit", "0");//这个会有bootanimation进程周期检测,=1退出动画
property_set("ctl.start", "bootanim");//通过ctl.start命令启动bootanim
}把service.bootanim.exit属性设为0,这个属性bootanimation进程里会周期检查,=1时就退出动画,这里=0表示要播放动画。
后面通过ctl.start的命令启动bootanim进程,动画就开始播放了。
下面来到bootanimation的实现
frameworks/base/cmds/bootanimation/bootanimation_main.cpp
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
sp<ProcessState> proc(ProcessState::self());
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
// create the boot animation object
sp<BootAnimation> boot = new BootAnimation();//创建BootAnimation实例
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();//binder线程池,与surfaceflinger通信用的。
}
return 0;
}new一个BootAnimation实例,然后建个binder线程池,因为BootAnimation在显示动画时要与SurfaceFlinger服务进程通信,所以要启个binder线程池。
frameworks/base/cmds/bootanimation/BootAnimation.cpp
BootAnimation::BootAnimation() : Thread(false)
{
mSession = new SurfaceComposerClient();//创建一个对象
}创建实例时,构造函数就会被调用,new一个SurfaceComposerClient实例,他是用来与surfaceflinger通信的
void BootAnimation::onFirstRef() {
status_t err = mSession->linkToComposerDeath(this);//注册surfaceflinger死亡消息的通知书
ALOGE_IF(err, "linkToComposerDeath failed (%s) ", strerror(-err));
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
run("BootAnimation", PRIORITY_DISPLAY);//开跑
}
}
如下,收到通知后就退出动画了,因为surfaceflinger都挂掉了,播放不了了。
void BootAnimation::binderDied(const wp<IBinder>& who)
{
// woah, surfaceflinger died!
ALOGD("SurfaceFlinger died, exiting...");
// calling requestExit() is not enough here because the Surface code
// might be blocked on a condition variable that will never be updated.
kill( getpid(), SIGKILL );//收到surfaceflinger死亡的消息,好吧自己也跟着去了。
requestExit();
}另一个函数run()在BootAnimation的父类Thead里,用来创建一个线程并跑起来。
父类
system/core/libutils/Threads.cpp
status_t Thread::run(const char* name, int32_t priority, size_t stack)
{
...
if (mCanCallJava) {
res = createThreadEtc(_threadLoop,//创建线程
this, name, priority, stack, &mThread);
} else {
res = androidCreateRawThreadEtc(_threadLoop,
this, name, priority, stack, &mThread);
}
....
}创建_threadLoop线程
int Thread::_threadLoop(void* user)
{
....
do {
bool result;
if (first) {
first = false;
self->mStatus = self->readyToRun();//这个函数被bootanimation重写了
result = (self->mStatus == NO_ERROR);
if (result && !self->exitPending()) {
...
result = self->threadLoop();//这个函数被bootanimation重写了
}
} else {
result = self->threadLoop();
}
...
return 0;
}
readyToRun函数实现
status_t BootAnimation::readyToRun() {
mAssets.addDefaultAssets();
sp<IBinder> dtoken(SurfaceComposerClient::getBuiltInDisplay(
ISurfaceComposer::eDisplayIdMain));
DisplayInfo dinfo;
status_t status = SurfaceComposerClient::getDisplayInfo(dtoken, &dinfo);
if (status)
return -1;
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("persist.panel.orientation", value, "0");
int orient = atoi(value) / 90;
if(orient == eOrientation90 || orient == eOrientation270) {
int temp = dinfo.h;
dinfo.h = dinfo.w;
dinfo.w = temp;
}
Rect destRect(dinfo.w, dinfo.h);
mSession->setDisplayProjection(dtoken, orient, destRect, destRect);
// create the native surface
sp<SurfaceControl> control = session()->createSurface(String8("BootAnimation"),
dinfo.w, dinfo.h, PIXEL_FORMAT_RGB_565);
SurfaceComposerClient::openGlobalTransaction();
control->setLayer(0x40000000);
SurfaceComposerClient::closeGlobalTransaction();
sp<Surface> s = control->getSurface();
// initialize opengl and egl
const EGLint attribs[] = {
EGL_RED_SIZE, 8,
EGL_GREEN_SIZE, 8,
EGL_BLUE_SIZE, 8,
EGL_DEPTH_SIZE, 0,
EGL_NONE
};
EGLint w, h, dummy;
EGLint numConfigs;
EGLConfig config;
EGLSurface surface;
EGLContext context;
EGLDisplay display = eglGetDisplay(EGL_DEFAULT_DISPLAY);
eglInitialize(display, 0, 0);
eglChooseConfig(display, attribs, &config, 1, &numConfigs);
surface = eglCreateWindowSurface(display, config, s.get(), NULL);
context = eglCreateContext(display, config, NULL, NULL);
eglQuerySurface(display, surface, EGL_WIDTH, &w);
eglQuerySurface(display, surface, EGL_HEIGHT, &h);
if (eglMakeCurrent(display, surface, surface, context) == EGL_FALSE)
return NO_INIT;
mDisplay = display;
mContext = context;
mSurface = surface;
mWidth = w;
mHeight = h;
mFlingerSurfaceControl = control;
mFlingerSurface = s;
mAndroidAnimation = true;
// If the device has encryption turned on or is in process
// of being encrypted we show the encrypted boot animation.
char decrypt[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get("vold.decrypt", decrypt, "");
bool encryptedAnimation = atoi(decrypt) != 0 || !strcmp("trigger_restart_min_framework", decrypt);
if ((encryptedAnimation &&
(access(SYSTEM_ENCRYPTED_BOOTANIMATION_FILE, R_OK) == 0) &&
(mZip.open(SYSTEM_ENCRYPTED_BOOTANIMATION_FILE) == NO_ERROR)) ||
((access(USER_BOOTANIMATION_FILE, R_OK) == 0) &&
(mZip.open(USER_BOOTANIMATION_FILE) == NO_ERROR)) ||
((access(SYSTEM_BOOTANIMATION_FILE, R_OK) == 0) &&
(mZip.open(SYSTEM_BOOTANIMATION_FILE) == NO_ERROR))) {
mAndroidAnimation = false;
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
threadloop实现
bool BootAnimation::threadLoop()
{
bool r;
if (mAndroidAnimation) {
r = android();//显示android默认动画
} else {
r = movie();//显示自定义的动画
}
// No need to force exit anymore
property_set(EXIT_PROP_NAME, "0");
eglMakeCurrent(mDisplay, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_SURFACE, EGL_NO_CONTEXT);
eglDestroyContext(mDisplay, mContext);
eglDestroySurface(mDisplay, mSurface);
mFlingerSurface.clear();
mFlingerSurfaceControl.clear();
eglTerminate(mDisplay);
IPCThreadState::self()->stopProcess();
return r;
}movie()的实现
bool BootAnimation::movie()
{
//读取bootanimation.zip文件并解释
// clear screen
//下面是循环显示
for (int i=0 ; i<pcount ; i++) {
const Animation::Part& part(animation.parts[i]);
const size_t fcount = part.frames.size();
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0);
for (int r=0 ; !part.count || r<part.count ; r++) {
// Exit any non playuntil complete parts immediately
if(exitPending() && !part.playUntilComplete)
break;
for (int j=0 ; j<fcount && (!exitPending() || part.playUntilComplete) ; j++) {
const Animation::Frame& frame(part.frames[j]);
nsecs_t lastFrame = systemTime();
if (r > 0) {
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, frame.tid);
} else {
if (part.count != 1) {
glGenTextures(1, &frame.tid);
glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, frame.tid);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
glTexParameterx(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_LINEAR);
}
initTexture(
frame.map->getDataPtr(),
frame.map->getDataLength());
}
if (!clearReg.isEmpty()) {
Region::const_iterator head(clearReg.begin());
Region::const_iterator tail(clearReg.end());
glEnable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
while (head != tail) {
const Rect& r(*head++);
glScissor(r.left, mHeight - r.bottom,
r.width(), r.height());
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
}
glDisable(GL_SCISSOR_TEST);
}
glDrawTexiOES(xc, yc, 0, animation.width, animation.height);
eglSwapBuffers(mDisplay, mSurface);
nsecs_t now = systemTime();
nsecs_t delay = frameDuration - (now - lastFrame);
//ALOGD("%lld, %lld", ns2ms(now - lastFrame), ns2ms(delay));
lastFrame = now;
if (delay > 0) {
struct timespec spec;
spec.tv_sec = (now + delay) / 1000000000;
spec.tv_nsec = (now + delay) % 1000000000;
int err;
do {
err = clock_nanosleep(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, TIMER_ABSTIME, &spec, NULL);
} while (err<0 && errno == EINTR);
}
checkExit();//检测是否退出动画
}
usleep(part.pause * ns2us(frameDuration));
// For infinite parts, we've now played them at least once, so perhaps exit
if(exitPending() && !part.count)
break;
}
// free the textures for this part
if (part.count != 1) {
for (int j=0 ; j<fcount ; j++) {
const Animation::Frame& frame(part.frames[j]);
glDeleteTextures(1, &frame.tid);
}
}
}
return false;
}那么到movie为止,动画是在播放了,而且还在循环检测是否退出,即checkExit()
checkExit()的实现
void BootAnimation::checkExit() {
// Allow surface flinger to gracefully request shutdown
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
property_get(EXIT_PROP_NAME, value, "0");//属性为1,说明要退出了
int exitnow = atoi(value);
if (exitnow) {
requestExit();
}
}property_get(EXIT_PROP_NAME, value, "0");检测这个属性,=1就退出动画#define EXIT_PROP_NAME "service.bootanim.exit"
那动画是什么时候退出的?
当launcher应用程序主线程跑起来后,如果主线程处于空闲,就会向ActivityManagerService发送一个activityIdle的消息。
应用程序主线程是ActivityThread.java来描述的,activityIdle是这个类来实现的
private class Idler implements MessageQueue.IdleHandler {
...
IActivityManager am = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault();
...
try {
am.activityIdle(a.token, a.createdConfig, stopProfiling);
a.createdConfig = null;
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
// Ignore
}
....
}
上面的ActivityManagerNavtive.getDefault()得到am
来到frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityManagerNative.java
static public IActivityManager getDefault() {
return gDefault.get();//getDefault的实现
}private static final Singleton<IActivityManager> gDefault = new Singleton<IActivityManager>() {
protected IActivityManager create() {
IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService("activity");
if (false) {
Log.v("ActivityManager", "default service binder = " + b);
}
IActivityManager am = asInterface(b);
if (false) {
Log.v("ActivityManager", "default service = " + am);
}
return am;
}
};gDefault实际上是IActivityManager,往下看
class ActivityManagerProxy implements IActivityManager
{
那么am.activityIdle()就是ActivityManagerProxy里的函数,如下
public void activityIdle(IBinder token, Configuration config, boolean stopProfiling)
throws RemoteException
{
...
mRemote.transact(ACTIVITY_IDLE_TRANSACTION, data, reply, IBinder.FLAG_ONEWAY);//发送ACTIVITY_IDLE_TRANSACTION
....
}发送了ACTIVITY_IDLE_TRANSACTION的进程间通信,这个消息被 ActivityManagerNative 接收处理了。
case ACTIVITY_IDLE_TRANSACTION: {//收到消息
data.enforceInterface(IActivityManager.descriptor);
IBinder token = data.readStrongBinder();
Configuration config = null;
if (data.readInt() != 0) {
config = Configuration.CREATOR.createFromParcel(data);
}
boolean stopProfiling = data.readInt() != 0;
if (token != null) {
activityIdle(token, config, stopProfiling);//这个函数在ActivityManagerService被重写
}
reply.writeNoException();
return true;
}收到消息后就调用了activityIdle函数,这个函数被ActivityManagerService重写了,如下
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
@Override
public final void activityIdle(IBinder token, Configuration config, boolean stopProfiling) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
synchronized (this) {
ActivityStack stack = ActivityRecord.getStackLocked(token);
if (stack != null) {
ActivityRecord r =
mStackSupervisor.activityIdleInternalLocked(token, false, config);
if (stopProfiling) {
if ((mProfileProc == r.app) && (mProfileFd != null)) {
try {
mProfileFd.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
}
clearProfilerLocked();
}
}
}
}
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}调用activityIdleInternalLocked函数,在下面实现
frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityStackSupervisor.java
final ActivityRecord activityIdleInternalLocked(final IBinder token, boolean fromTimeout,
Configuration config) {
....
if (enableScreen) {
mService.enableScreenAfterBoot();//调ActivityManagerService类的enableScreenAfterBoot()函数
}
....
if (activityRemoved) {
resumeTopActivitiesLocked();
}
return r;
}来到frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
void enableScreenAfterBoot() {
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_ENABLE_SCREEN,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
mWindowManager.enableScreenAfterBoot();//调WindowManagerService类里的enableScreenAfterBoot()函数
synchronized (this) {
updateEventDispatchingLocked();
}
}来到frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
public void enableScreenAfterBoot() {
....
performEnableScreen();
}performEnableScreen()实现
public void performEnableScreen() {
.....
surfaceFlinger.transact(IBinder.FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION, // BOOT_FINISHED
data, null, 0);
....
}发送了FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION的请求
因为从下面知道FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION = BOOT_FINISHED
所以BnSurfaceComposer收到消息
frameworks/native/include/gui/ISurfaceComposer.h
class BnSurfaceComposer: public BnInterface<ISurfaceComposer> {
public:
enum {
// Note: BOOT_FINISHED must remain this value, it is called from
// Java by ActivityManagerService.
BOOT_FINISHED = IBinder::FIRST_CALL_TRANSACTION,
...
};
virtual status_t onTransact(uint32_t code, const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags = 0);
};
</pre></p><p><span style="color:#333333;">frameworks/native/libs/gui/ISurfaceComposer.cpp</span></p><p><span style="color:#333333;"></span><pre name="code" class="cpp">status_t BnSurfaceComposer::onTransact(
uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
{
switch(code) {
....
case BOOT_FINISHED: {
CHECK_INTERFACE(ISurfaceComposer, data, reply);
bootFinished();//调用 bootFinished()
return NO_ERROR;
}
....
}
// should be unreachable
return NO_ERROR;
}bootFinished()函数BpSurfaceComposer里实现,但发现没有,他又发了一个BOOT_FINISHED,死循环了,其实没有。bootFinished()被 SurfaceFlinger类重写了
class BpSurfaceComposer : public BpInterface<ISurfaceComposer>
{
virtual void bootFinished()
{
Parcel data, reply;
data.writeInterfaceToken(ISurfaceComposer::getInterfaceDescriptor());
remote()->transact(BnSurfaceComposer::BOOT_FINISHED, data, &reply);
}
重写
frameworks/native/services/surfaceflinger/SurfaceFlinger.cpp
void SurfaceFlinger::bootFinished()
{
...
property_set("service.bootanim.exit", "1");
}把service.bootanim.exit写成1,然后bootanimation进程的checkExit()检测到就退出进程,停止播放。
1、制作开关机动画
1.1 开机动画的位置
system/media/bootanimation.zip,要修改开机动画就是修改bootanimation这个压缩文件。如果不存在该压缩包,使用原生自带的资源,其路径在system/framework/framework-res.apk/assets/images(Android-logo-mask.png,android-logo-shine.png),但是比较难看,比较常见的就是“android”。所以要定制自己的开关机动画一般都是在system/media/目录下放置bootanimation.zip和shutanimation.zip.这里以开机动画为例,关机动画和开机动画其原理一样。
1.2 bootanimation.zip文件结构
bootanimation里面主要包含一个desc.txt以及N个文件夹。而文件夹里面放着的就是开机动画的图片资源。decs.txt的作用就是指导系统如何去执行开机动画。
desc.txt编写规范,例如开机动画需要用到2个文件夹,分别是folder1和folder2,开机的时候,先把folder1里面的图片都播放一遍,然后再循环播放folder2里面的文件,直到进入系统,decs.txt文档的内容如下:
320 480是代表屏幕的分辨率,12表示12帧每秒,简单地说12代表一秒钟播放12张图片;
p 1 0 part1:p就是play。1是播放一次,0是无限次。0代表阶段间隔帧数为0。folder1就是说,这条指令是针对folder1这个文件夹的;
p 0 0 part2:第一个0这里是代表循环播放,第二个0和上面第二条指令一样。folder2就是第二个文件夹。
总结规则如下:
第一条指令:[屏幕的分辨率] [播放频率]
第二条指令:[p] [播放次数] [间隔帧数] [文件夹]
第N条指令: 同上
1.3 压缩包
把需要用到的folder文件夹跟decs.txt打包成zip格式,必须是zip,不能是rar,且打包的时压缩方式选择“存储”模式。然后改名成为bootanimation.zip,最后将制作好的zip包push到/system/media目录下。
注意:bootanimation不能太大,一般最好不要超过3M。
1.4 查看动画
在终端中输入命令:
adb shell---> cd /system/bin--->bootanimation 或者bootanimation shut
这样不用重启即可查看定制的动画,方便。
1.5 硬性条件
2、播放原理
通过上面的准备开机资源已经制作好了,那android是怎么来实现播放的。首先对于开关机动画的播放,android专门使用了一个 native service来实现播放(/system/bin/bootanimation),包括开机铃声的实现也是用该service来实现的。
2.1 bootanimation的启动
Android系统在init.rc中定义了很多Service,具体定义格式可以参考《Android Platform Developer’s Guide》中的“Android Init Language”。Init.rc中定义的Service将会被Init进程创建,其中已经定义的服务就包含bootanimation。
每一项服务必须在/init.rc中定义.Android系统启动时,init守护进程将解析init.rc和启动属性服务,属性“ ctl.start ”和“ctl.stop ”是用来启动和停止服务的。一旦收到设置“ ctrl.start ”属性的请求,属性服务将使用该属性值作为服务名找到该服务,启动该服务。这项服务的启动结果将会放入“ init.svc.<服务名>“属性中 。
定义了一个bootanim的服务,对应执行/system/bin/bootanimation
disabled 表示init进程创建只是创建它,但不立刻执行;
oneshot 表示该服务只执行一次;
2.2 开机动画调用
通过上面可知,bootanimation的调用同故宫clt.start 和ctl.stop来实现的,当我们开机启动时,系统内核起来后,启动android,这时就会启动开机动画具体是在
SurfaceFlinger.cpp的readyToRun方法中调用,为什么会在这调用,请回顾一下开机流程。
当android启动完成后,关闭掉开机动画
2.3 bootanimation 源码分析
2.3.1 Bootanimation_main.cpp
该文件是主入口文件;
其主要的功能是根据传进来的参数决定是是要播放开机还是关机动画/铃音,并且启动BootAnimation;2.3.2 BootAnimation.cpp
BootAnimation.cpp集成自Thread,在创建时会调用readyToRun()->threadLoop()。
readyToRun() 方法判断/system/media/bootanimation.zip(shutanimaion.zip)是否存在,如果存在,则将 mAndroidAnimation 设置false,这个变量决定threadLoop中调用android()还是movie()来具体实现动画的播放。
threadLoop()方法根据 mAndroidAnimation 变量调用android()/movie(). 如果system/media/shutanimation.zip/bootanimation.zip存在的话,调用movie(),该接口会解析zip文件中的desc.txt文件,根据txt文件中的配置来播放动画。否则就调用android来播放原生自带的资源。






















 1224
1224

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








