数组是一组相关数据的集合,一个数组实际上是一连串的变量,数组按照使用可以分为一维数组,二维数组和多维数组。
一. 一维数组
一维数组可以存放上千万个数据,并且这些数据的类型是完全相同的。
要使用Java中的数组,必须经过声明数组和分配内给数组两个步骤。
一般步骤:
数据类型 数组名[]=null;
数组名=new 数据类型[长度];也可简化为:
数据类型[] 数组名=null;数组声明格式中,“数据类型”指的是声明数组元素的数据类型,“数组名”是用来统一这一组相同数据类型的元素的名称,其命名规则和变量命名规则相同,建议用有意义的名字来命名。 数组声明后实际上是在栈内存中保存了此数组的名称(实际上是保存了对堆内存的引用地址),接下来就要在堆内存中配置数组所需的内存。“长度”是告诉编译器所声明的数组要存放多少个数据,而关键字new则是命令编译器根据括号里的长度在堆内存中开辟一块堆内存供该数组使用。
【例】
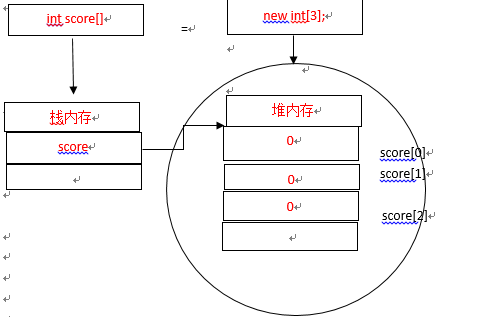
int score[]=null;//null表示引用数据类型的默认值。
score=new int[3];内存分配的过程:
过程分析:一个数组开辟了堆内存之后,将在堆内存中存储保存数据,并将堆内存的操作地址给了数组的名称score。因为数组是引用数据类型,所以数组变量score所保存的不是数组的实体,而是数组堆内存的参考地址。
二. 数组中元素的表示方法
要访问数组中的元素,必须利用索引来完成。Java中的数组索引编号是从0开始的。以score[10],为例,score[0]代表第一个元素,score[1]是第二个元素、、、score[9]是第十个元素。
【数组的声明及输出】
public class ArrayDemo01{
public static void main(String args[]){
int score[] = null ; // 声明数组
score = new int[3] ; // 为数组开辟空间,大小为3
System.out.println("score[0] = " + score[0]) ;
System.out.println("score[1] = " + score[1]) ;
System.out.println("score[2] = " + score[2]) ;
for(int x=0;x<3;x++){
System.out.println("score["+x+"] = " + score[x]) ;
}
System.out.println("score[3] = " + score[3]) ;
}
};运行结果:
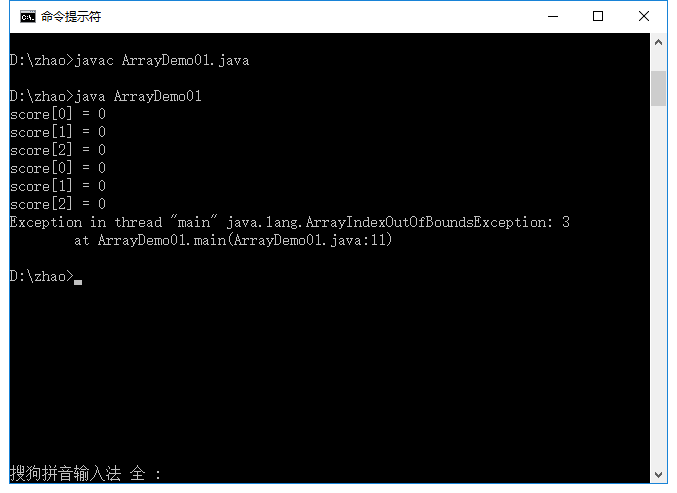
前面运行正常的结果。假设程序中取出的内容超过了这个下标,如score[3],则程序壶提示错误数组下标越界异常(图中):
java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 3
这在编写程序时要注意。
三. 数组的静态初始化
数组的内容分为动态初始化和静态初始化。前面所提为动态初始化。也可以通过数组静态初始化,在数组声明时就指定其内容。
【数组的静态初始化】
public class ArrayDemo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score[]={69,65,87,99};
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
System.out.println("score["+i+"]="+score[i]);
}
}
}运行结果:
score[0]=69
score[1]=65
score[2]=87
score[3]=99四. 数组应用范例
【求数组中的最大值与最小值】
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score[]={67,89,87,69,70,100,75,90};
int max=0;
int min=0;
max=min=score[0];
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
if (score[i]>max) {
max=score[i];
}
if (score[i]<min) {
min=score[i];
}
}
System.out.println("最大值为:"+max);
System.out.println("最小值为:"+min);
}
}运行结果:
最大值为:100
最小值为:67【将元素从小到大排序】(经典冒泡排序)
public class ArrayDemo06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score[]={67,89,87,69,90,100,75,90};
for (int i = 1; i < score.length; i++) {//循环判断
for (int j = 0; j < score.length; j++) {
if (score[i]<score[j]) {//交换位置
int temp=score[i];
score[i]=score[j];
score[j]=temp;
}
}
System.out.print("第"+i+"次排序的结果:\t");
for (int j = 0; j < score.length; j++) {
System.out.print(score[j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println("");
}
System.out.print("最终结果为:\t");
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) {
System.out.print(score[i]+"\t");
}
}
}运行结果:
第1次排序的结果: 67 100 87 69 89 90 75 90
第2次排序的结果: 67 87 100 69 89 90 75 90
第3次排序的结果: 67 69 87 100 89 90 75 90
第4次排序的结果: 67 69 87 89 100 90 75 90
第5次排序的结果: 67 69 87 89 90 100 75 90
第6次排序的结果: 67 69 75 87 89 90 100 90
第7次排序的结果: 67 69 75 87 89 90 90 100
最终结果为: 67 69 75 87 89 90 90 100 五. 二维数组
如果把一维数组比作线性图形,那么二维数组就相当于一个表格。
二维数组的声明格式:
数据类型 数组名[][];
数组名=new 数据类型[行的个数][列的个数];
二维数组在分配内存时,必须告诉编译器二维数组行与列的个数。例:
int score[][];
score=new int[4][3];等价于:
int score[][]=new int[4][3];上述语句score可以保存元素为4*3=12个,而在Java中,int数据类型为4个字节,因此,score所占内存为4*12=48个字节。
【二维数组的定义及使用】
public class ArrayDemo08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int score[][]={{55,56},{32,45,89},{98,45,53,78}};
for (int i = 0; i < score.length; i++) { //循环输出行
for (int j = 0; j < score[i].length; j++) {//循环输出列
System.out.print(score[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
}运行结果:
55 56
32 45 89
98 45 53 78 六. 多维数组
通过一维、二维数组可以发现,多维数组可以理解为多层循环的嵌套。
【定义和使用三维数组】
public class ArrayDemo10{
public static void main(String args[]){
int score[][][] = {
{
{5,1} ,{6,7}
},
{
{9,4},{8,3}
}
} ; // 静态初始化完成,每行的数组元素个数不一样1
for(int i=0;i<score.length;i++){
for(int j=0;j<score[i].length;j++){
for(int k=0;k<score[i][j].length;k++)
{
System.out.println("score["+i+"]["+j+"]["+k+"] = "+score[i][j][k] + "\t") ;
}
}
}
}
};运行结果为:
score[0][0][0] = 5
score[0][0][1] = 1
score[0][1][0] = 6
score[0][1][1] = 7
score[1][0][0] = 9
score[1][0][1] = 4
score[1][1][0] = 8
score[1][1][1] = 3如果是四维数组,则可以使用四层嵌套结构,以此类推。
























 1433
1433

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










